Biotechnology: Molecular Cloning and GMOs Overview Cartes | Quizlet
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Cell Cultures
Cells grown under controlled conditions for research.
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells with a nucleus, like human cells.
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells without a nucleus, like bacteria.
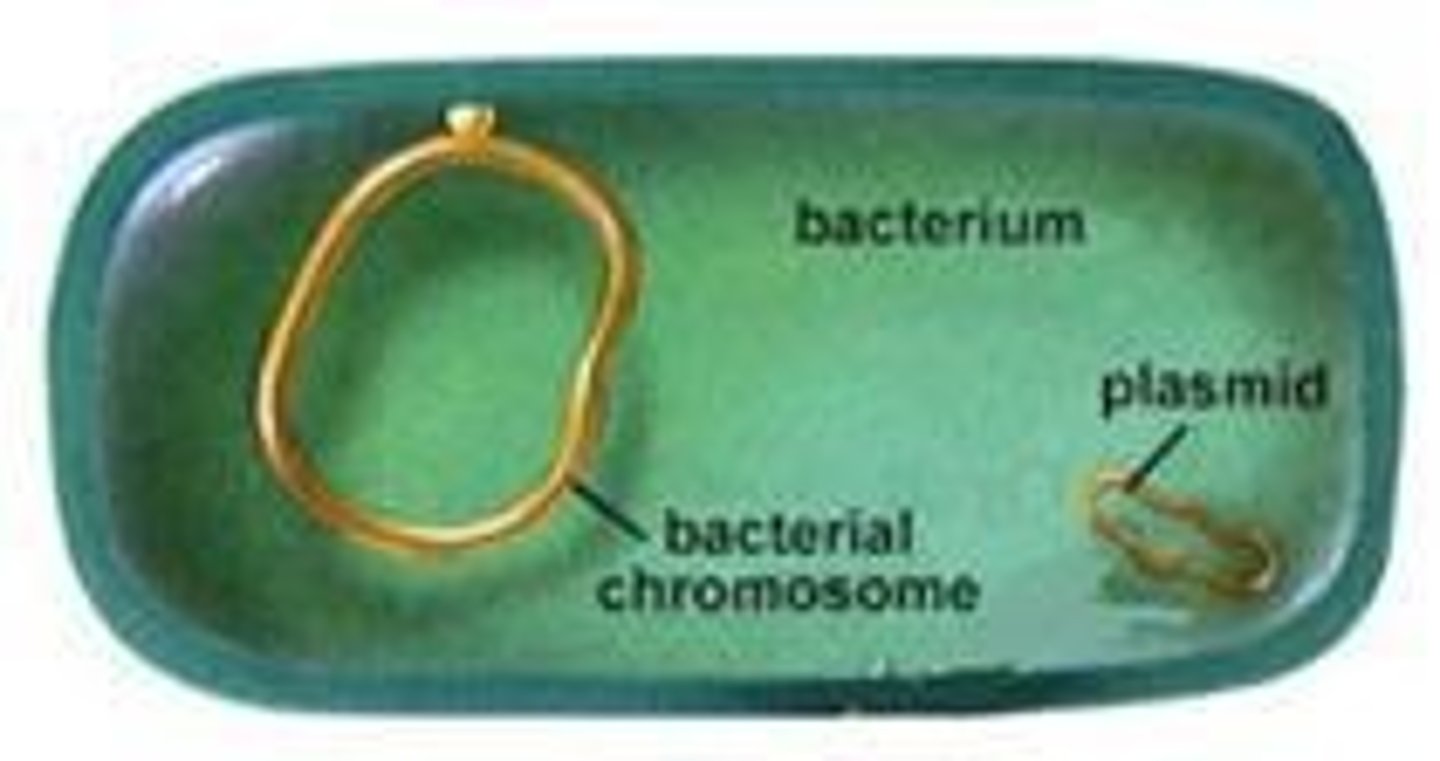
Plasmids
Independent DNA molecules used in genetic engineering.
Recombinant DNA (rDNA)
DNA formed by combining DNA from different sources.
Bacterial Transformation
Genetic alteration via uptake of external DNA.
DNA Extraction
Process of isolating DNA from cells.
RNA Extraction
Isolating RNA from cells for analysis.
Protein Extraction
Isolating proteins from cells for study.
Viral Vectors
Viruses used to deliver genetic material into cells.
Electrophoresis
Technique for separating DNA, RNA, or proteins.
Transfection
Introducing nucleic acids into cells artificially.
PCR
Polymerase Chain Reaction, amplifies DNA sequences.
DNA Sequencing
Determining the nucleotide order in DNA.
Scientific Articles
Published research findings in scientific journals.
Web Links
Online resources for additional information.
HEK 293 Cells
Human embryonic kidney cells used in research.
Vero Cells
Kidney epithelial cells from an African green monkey.
HuH-7 Cells
Hepatocyte cell line from a liver tumor.
HeLa Cells
Cervical cancer cells from Henrietta Lacks.
Multicloning Site (MCS)
Region in plasmids for inserting DNA sequences.
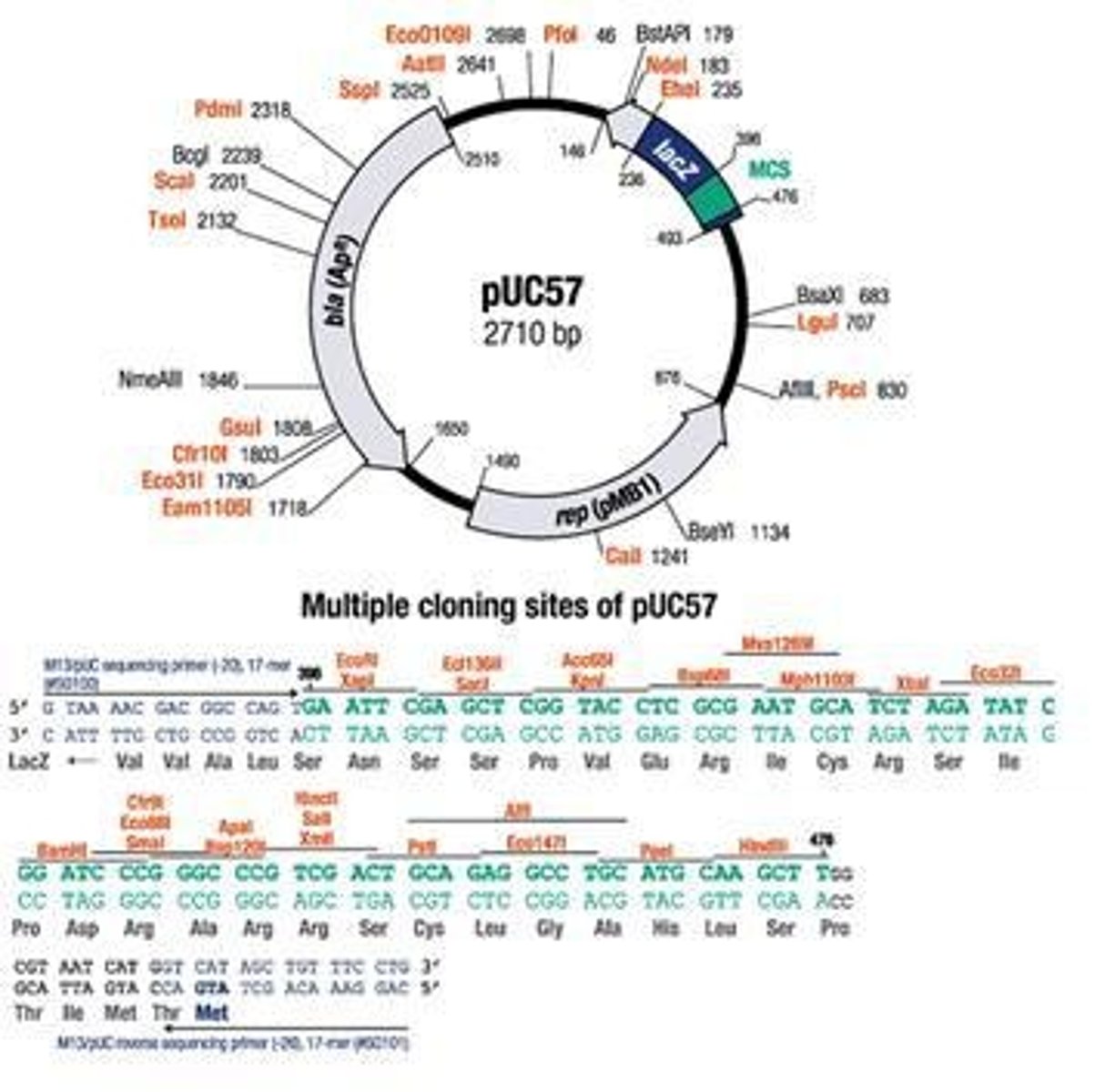
Antibiotic Resistance
Gene allowing selection of transformed bacteria.
MAX Efficiency® DH5α™ Competent Cells
Bacterial cells optimized for DNA uptake.
Bacterial Transformation
Process of introducing plasmid into bacteria.
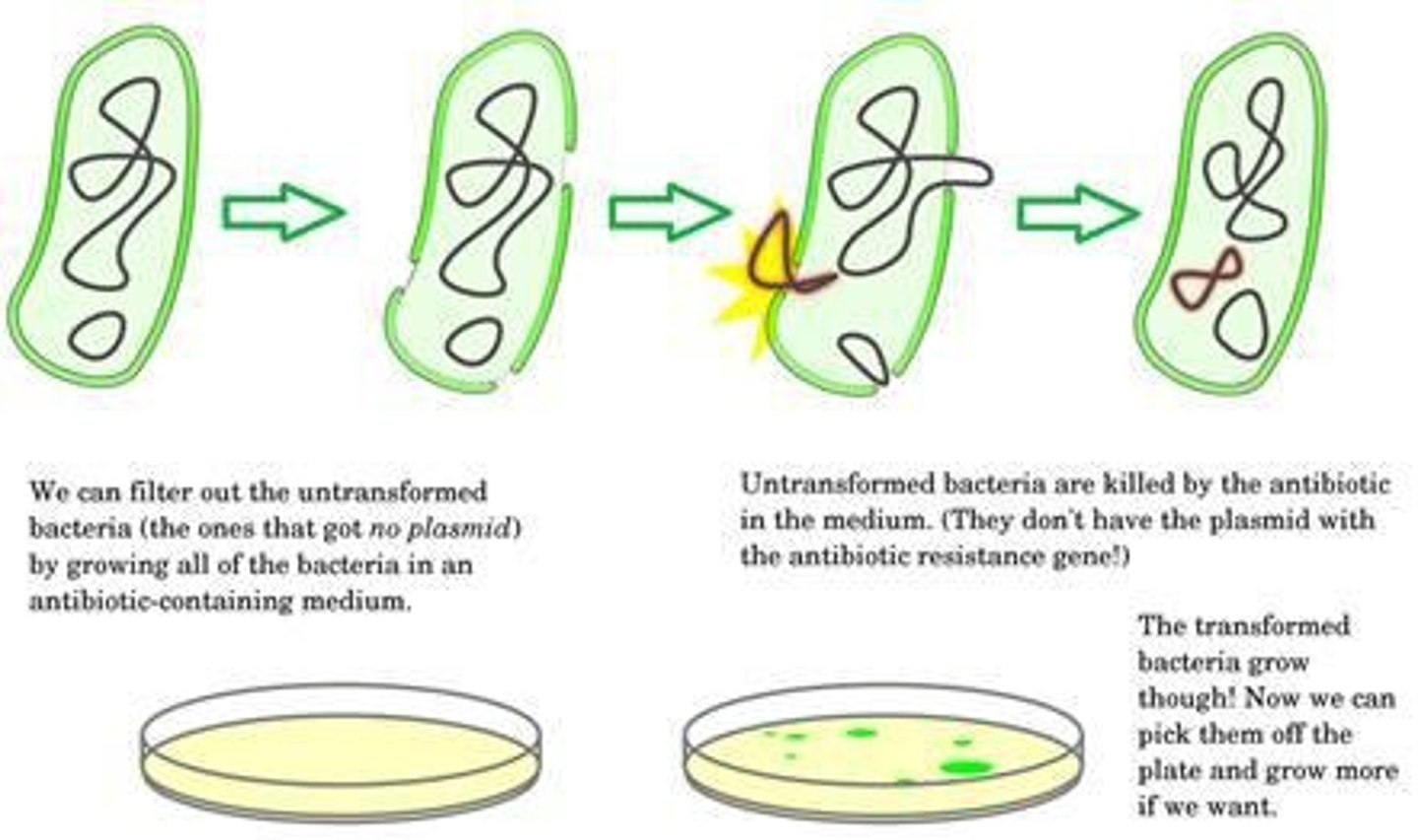
Competent Bacteria
Bacteria that can accept foreign DNA.
Heat Shock Method
Technique for transforming bacteria using temperature.
Plasmid
Circular DNA used for genetic engineering.
Growth Medium
Nutrient solution for bacterial growth.
Petri Dish
A flat dish for culturing bacteria.
DNA Purification
Isolating DNA from other cellular components.
Electrophoresis
Technique to separate DNA/RNA by size.
Mini-Prep
Small-scale plasmid extraction from bacteria.
Midi-Prep
Medium-scale plasmid extraction from bacteria.
Maxi-Prep
Large-scale plasmid extraction from bacteria.
Viral Vectors
DNA molecules for gene delivery into cells.
Gene Therapy
Using genes to treat or prevent diseases.
Adeno-X
Adenovirus vector commonly used in research.
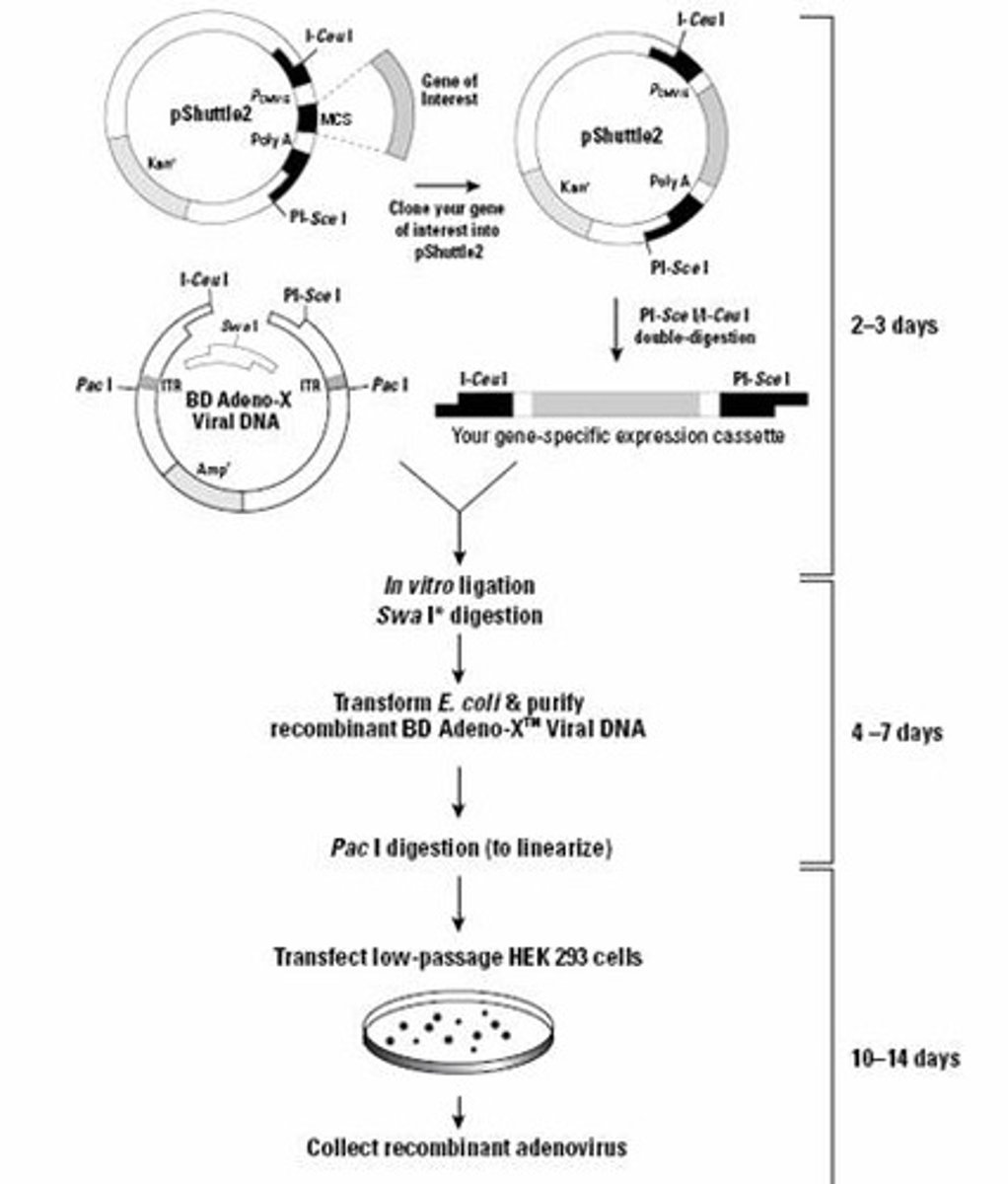
Lentiviral Vectors
Retroviruses for stable gene insertion.
Vaccinia Vector
Viral vector used in vaccine development.
Nucleic Acid Transfection
Introducing nucleic acids into cells intentionally.
PCR
Technique to amplify DNA segments.
Ethidium Bromide
Staining agent for visualizing DNA in gels.
Agarose Gel
Medium for electrophoresis of nucleic acids.
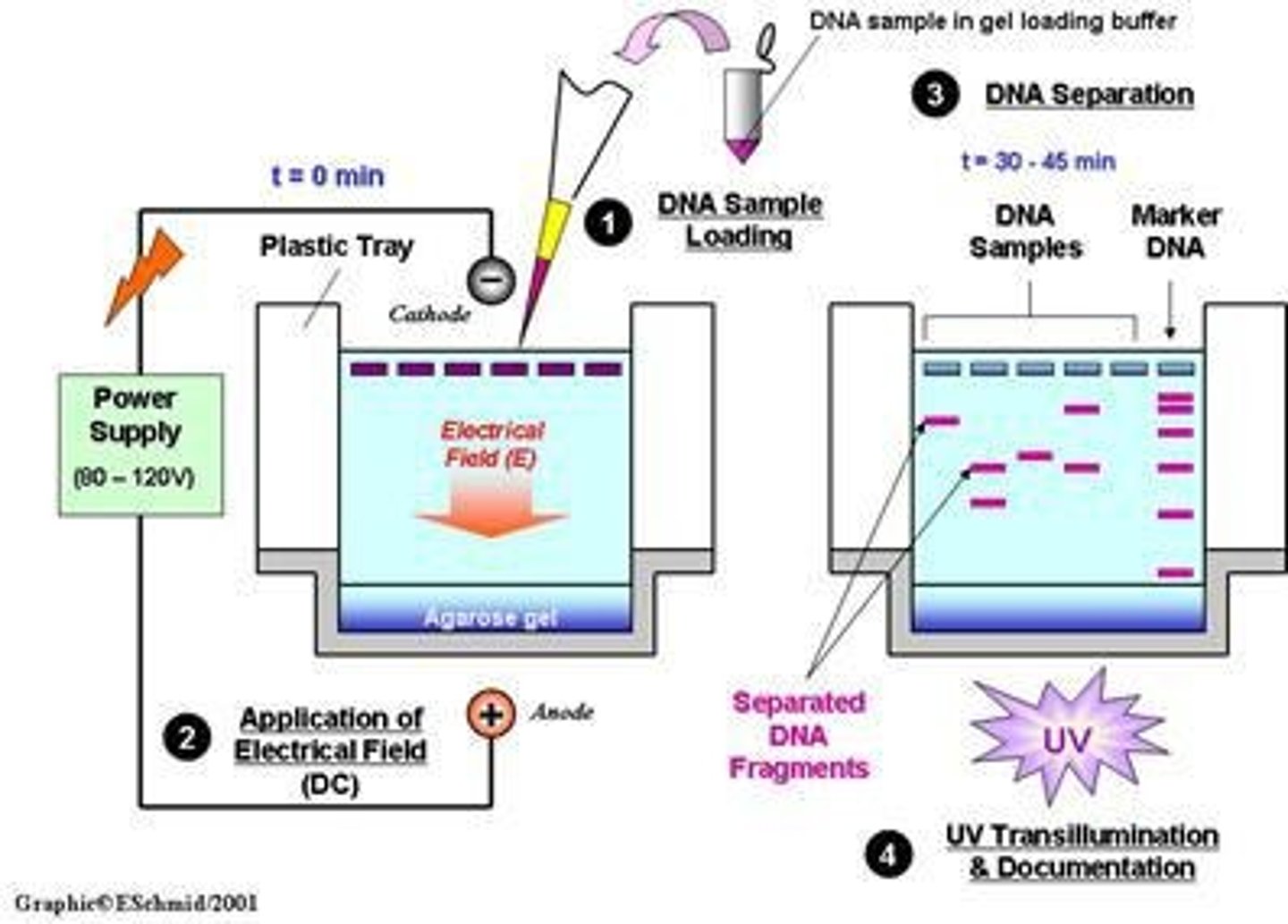
Ladder Sample
DNA size marker used in electrophoresis.
Transduction
Inserting plasmid/viral vector into a cell.
Transfection
Introducing foreign DNA into eukaryotic cells.
Lipofectamine® 2000
Reagent for transfecting cells with DNA.
Calcium Phosphate
Method for DNA transfection into cells.
PCR
Technique to amplify specific DNA sequences.
Amplification
Generating thousands to millions of DNA copies.
Electrophoresis
Visualizing DNA amplification results.
Denaturation Step
Heating to 94-98 °C to separate DNA strands.
Annealing Step
Lowering temperature to bind primers to DNA.
Extension Step
DNA synthesis by Taq polymerase at 75-80 °C.
Taq Polymerase
Enzyme used for DNA synthesis in PCR.
dNTP
Nucleotide building blocks for DNA synthesis.
Buffer with MgCl2
Provides optimal conditions for PCR reactions.
DNA Sequencing
Determining the order of nucleotides in DNA.
Mutation Verification
Confirming no mutations in inserted DNA sequences.
Purified DNA
Isolated DNA for sequencing or amplification.
DNA Primer
Short DNA sequence used to initiate synthesis.
Primer Length
Optimal length for primers is 20-25 nucleotides.
G-C Content
Desirable G-C content for primers is 40-60%.
Tm
Melting temperature for primers, ideally 55-75 °C.
Cell Culture
Growing cells in a controlled environment.
Petri Dish
Container used for culturing cells.
Tm
Melting temperature for DNA strand separation.
Chromatogram
File format displaying DNA sequencing data.
Abstract
Overview of objectives and findings in articles.
Introduction
Review of existing knowledge on the subject.
Methods
Details on experimental procedures and reagents used.
Results
Findings presented in graphs, tables, and images.
Discussion
Interpretation and implications of the results.
References
Citations for facts and sources used.
DNA Extraction
Isolating gene from the organism.
Gene Cloning
Replicating gene sequence for experimentation.
Gene Design
Modifying gene for functionality in new organism.
Transformation
Inserting new DNA into plant cell callus.
Backcross Breeding
Combining traits of transgenic plants with elite lines.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Bacterium causing crown gall disease in plants.
T-DNA
Transfer DNA segment inserted into plant cells.
Ti Plasmid
Plasmid containing genes for tumor production.
Cytokinin
Plant hormone promoting cell division.
Auxin
Plant hormone promoting DNA synthesis.
Virulence Genes
Genes mediating T-DNA transfer to plant cells.
Bacillus thuringiensis
Bacterium used as a biological pesticide.
δ-endotoxins
Crystal proteins with insecticidal properties from Bt.
Bt Corn
Genetically engineered corn containing Bacillus thuringiensis.
Refuge Planting
Planting non-Bt corn to prevent pest resistance.
Buffer requirement
Records must be maintained for two years post-planting.
BPC
Bureau of Pesticide Control overseeing agricultural practices.
PIPs
Planting information protocols for genetically modified crops.
Bacillus subtilis
Bacteria providing cold shock protein for survival.
CspB
Cold shock protein aiding Bacillus subtilis in cold conditions.
mRNA secondary structures
Formed during cold shock, hindering translation initiation.
RNA helicases
Proteins that unwind mRNA secondary structures.
CSPs
Cold shock proteins preventing mRNA refolding.
MON 87460
Drought-tolerant corn hybrid developed by Monsanto.
GMO advantages
Benefits of genetically modified organisms in agriculture.
Pest resistance
Genetic modification reducing crop losses from pests.