HAP Connective tissues
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
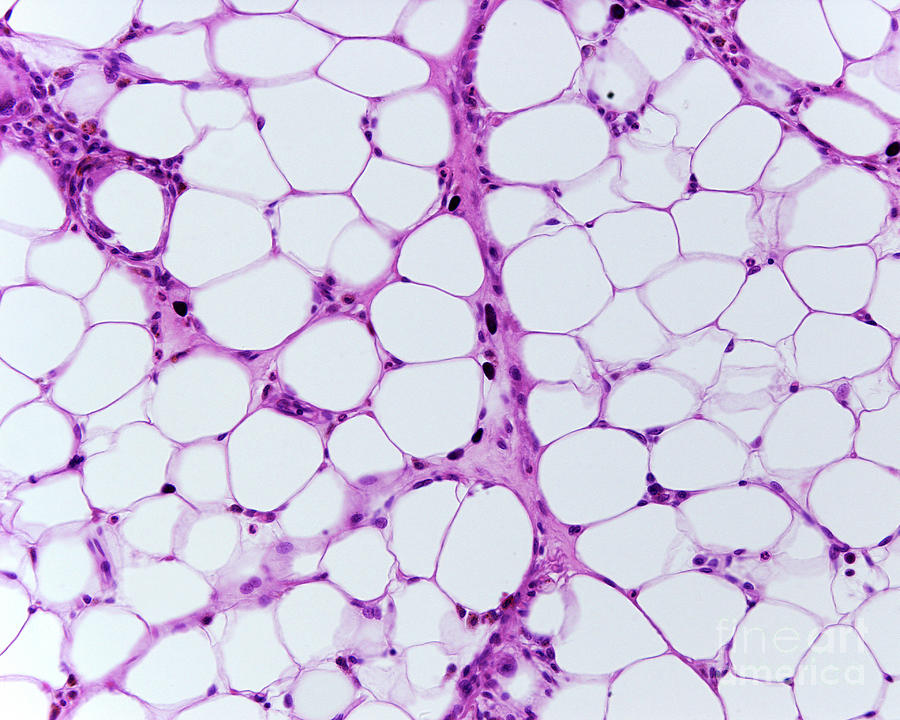
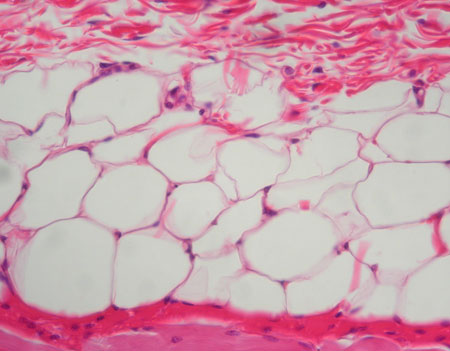
Adipose
A tissue that surrounds organs, protect and insulate organs, and has an intracellular matrix of lipids
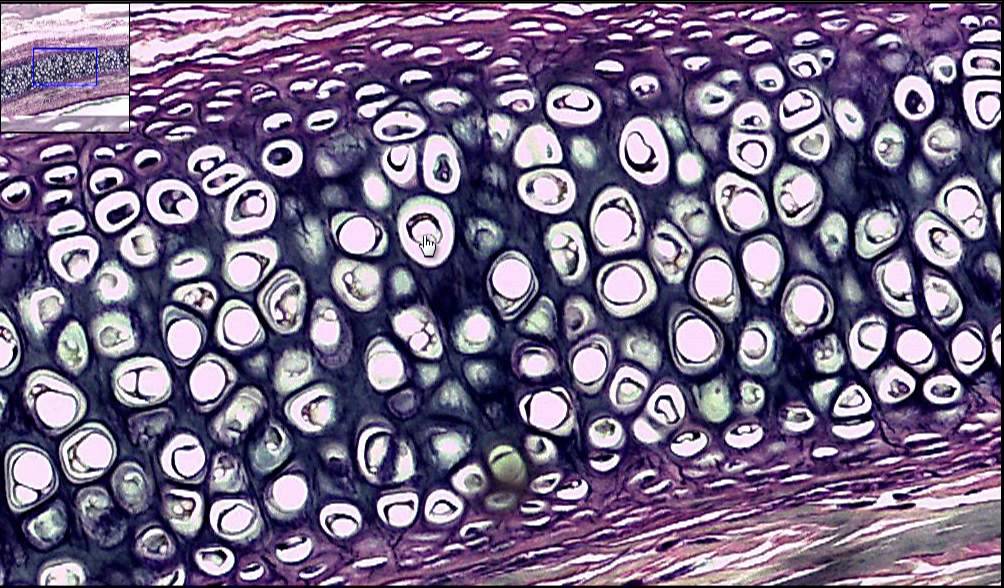
Elastic cartilage
Tissue that contains loosely held collagen and elastic fibers, makes up epiglottis of the larynx
areolar
Tissue that contains loosely held collagen and elastic fibers, makes up connective tissue of mucous membranes and around nearly every body structure
Dense Fibrous
contains fibroblasts and regularly arranged fibers
Fibrocartilage
Tissue that is found in the pubic system, contains chondrocytes with a lot of thick bundles of collagen fibers
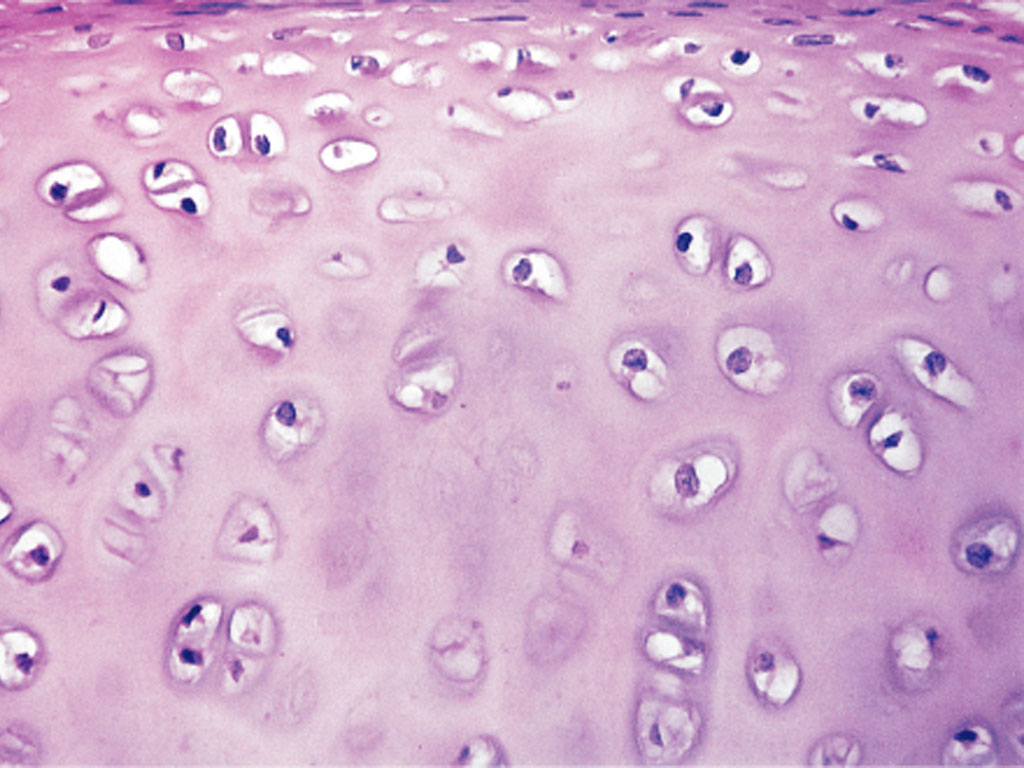
Hyaline cartilage
Tissue that is smooth and rubbery, withstanding pressure and reducing friction in certain places
Bone and cartilage
Found in supported connective tissues
Osteoblast
builds up bone tissue
Connective tissue
Tissue type that secretes a matrix, are vascular and have interspersed cells
Chondrocyte
A cartilage cell
Ostecyte
a bone cell
Mast cells
involved in inflammation
Hyaline cartilage
Adipose
Elastic Cartilage
Adipose
Dense Fibrous
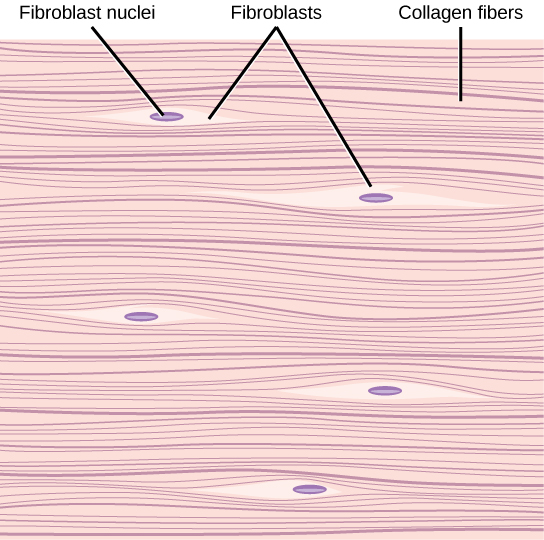
Dense Fibrous
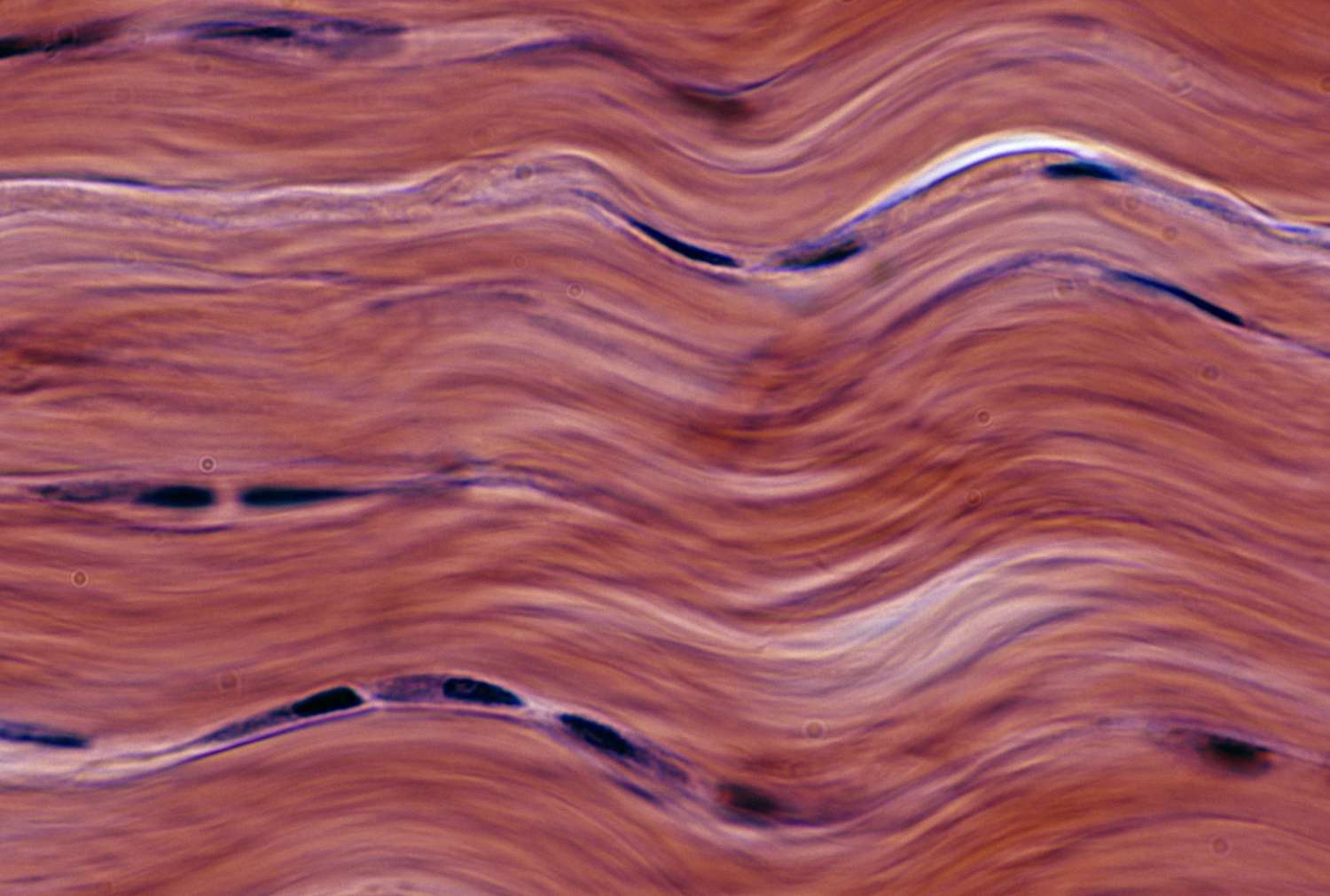
Hyaline Cartilage
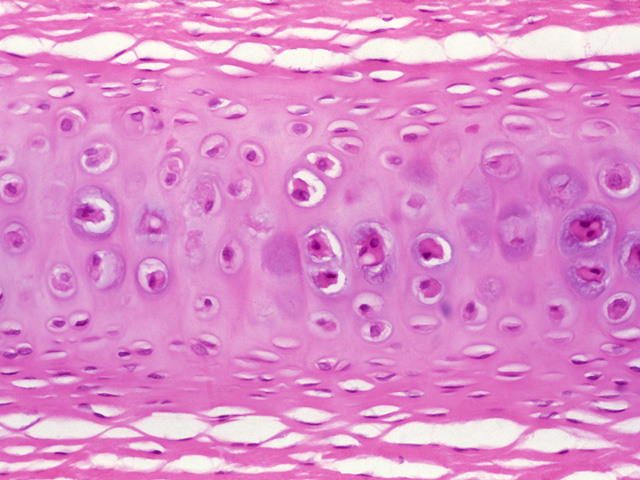
Fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage
Tissue
a group of cells that are grouped by function and structure
Connective, Epithelial, muscle, and nevous
Four types of tissue
cellularity, polarity, attachment, vascularity, and regeneration
Characteristics of Epithelial tissues
secretion, protection, absorption, transportation, and special sensory receptive
Functions of Epithelial tissue
Cilliated columnar
found in the respiratory tract, helps move/clear substances
Stratified squamous
protects underlying tissue by protecting against microorganisms and protects form water loss
Connective tissue membranes
encapsulates organs and moves joints
epithelial membranes
also known as mucous membranes
Visceral membranes
inner membranes that lines body cavities
parietal membranes
outer lining of body cavities
matrix and cells
General structural characteristics of connective tissues
supporting organs, transporting nutrients/waste, protection, and storing fat
Connective tissue main functions
Matrix
extracellular substance secreted in connective tissues
Loose connective tissues
holds organs in place
dense connective tissues
connects muscles to bones
Specialized connective tissues
stores and regulates energy and temperature
Made of cells, has a matrix, takes up large amounts of ground surface, contains protein fiber
Characteristics of connective tissues
Supporting, connecting, protecting, storing, transporting
Functions of Conective tissues
They are avascular, meaning there isn’t much blood flow
why does it take longer for tendons and ligaments longer to heal than bones?
Hyaline, Fibro, Elastic
Three types of cartilage
Blood
transports oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and waste through the body
regular
type of dense connective tissue that connects muscles to bones and bone to bone
bone
type of connective tissue with one of the hardest extracellular matrices that forms a protective structure used for muscle attachment, also called osteocyte
areolar
type of loose connective tissue that separates the cells of the body from the bloodstream
adipose
type of connective tissue also known as fat. Stores excess nutrients and fats as energy, it also insulates the body
cartilage
Semi solid connective tissue that is used both as a protective and supportive structure within the body, can be found in the nose, ears, ribs, and vertebral disks
Fibrous
type of dense connective tissue with irregularly arranged fibers that provides strength where tension is exerted in various directions such as in the dermis
osteoblast
specialized connective tissue responsible for synthesis/mineralization of bone
Chondrocyte
Cells found in cartilage of connective tissue
Erythrocyte
Red blood cells containing a matrix
Osteoclast
a type of cell found in bone
Hyaluronic acid
lubricates, cell growth, found in manny connective tissues
bone and cartilage
Supportive connective tissue include
secretes a matrix, has interspersed cells and are vascular
Three characteristics of the connective tissue
Mast cells
involved in inflammation