SOCI 1510: Exam 1 Review
5.0(7)Studied by 368 people
Card Sorting
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:51 PM on 9/25/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
1
New cards
Sociology
A social science that examines the human or social world
Study of people doing things together
Study of people doing things together
2
New cards
Society
Group of people who shape their lives in patterned ways that distinguish their groups from others
3
New cards
Sociological perspective
Taking a sociological approach or thinking sociologically
Lense- how we view and understand the world
Lense- how we view and understand the world
4
New cards
Beginner’s Mind
Approach to the world without knowing in advance: open and receptive to experience
5
New cards
Culture Shock
Understand other cultures without personal perspective
6
New cards
Sociological Imagination
C. Wright Mills: “To understand social life, we must understand the intersection between biography and history”.
A way to step aside ourselves to understand
A way to step aside ourselves to understand
7
New cards
Micro sociology
Small group interactions
Concentrated on the interactions between individuals and the ways in which those interactions construct the larger patterns, processes, and institutions of society
Concentrated on the interactions between individuals and the ways in which those interactions construct the larger patterns, processes, and institutions of society
8
New cards
Macrosociology
Large-scale social structures and how they impact groups and individuals
9
New cards
The micro-macro continuum
Sociology covers a wide range of topics at different levels of analysis
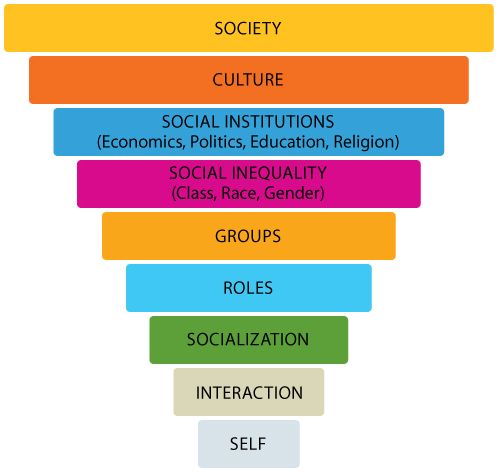
10
New cards
Sociological Theories
Propositions that explain the social world and help make predictions about the future
Sometimes referred to as:
Approach, schools of thoughts , paradigms, perspectives
Sometimes referred to as:
Approach, schools of thoughts , paradigms, perspectives
11
New cards
Auguste Comte
Founder of sociology: the most significant and complex
Sociology as a social discipline
Laid the groundwork & helped build discipline
Sociology as a social discipline
Laid the groundwork & helped build discipline
12
New cards
Herbert Spencer
Coined phrase “survival of the fittest” : social Darwinism
Societies evolve by adapting to their changing environment
Societies evolve by adapting to their changing environment
13
New cards
Emile Durkheim
3 contributions:
Mechanical & organic solidarity
Sociological explanations for individual actions
-anomie
Religion
-sacred
-profane
Structural functionalist
Mechanical & organic solidarity
Sociological explanations for individual actions
-anomie
Religion
-sacred
-profane
Structural functionalist
14
New cards
Structural Functionalism
Society is a unified whole
-family, education, politics, economy, etc.
each structure meets the needs of society
-dysfunction
Manifest vs. latent functions
-family, education, politics, economy, etc.
each structure meets the needs of society
-dysfunction
Manifest vs. latent functions
15
New cards
Karl Marx
Conflict theory: means of production
-central: understanding group dynamics
-change
Capitalism
-central: understanding group dynamics
-change
Capitalism
16
New cards
George Herbert Mead
Symbolic interactionism
-connection between thought and action
-between the individual and society
-meaning derived from social processes
Society is produced and reproduced through interaction
-language
-face-to-face interaction
-connection between thought and action
-between the individual and society
-meaning derived from social processes
Society is produced and reproduced through interaction
-language
-face-to-face interaction
17
New cards
Culture
The entire way of life of a group of people
It is hard to see own culture
Shapes and defines who we are
Culture is learned
It is hard to see own culture
Shapes and defines who we are
Culture is learned
18
New cards
Ethnocentrism
One’s own culture as a standard to evaluate another group or individual
Leads to the view that cultures other than one’s own is abnormal
Leads to the view that cultures other than one’s own is abnormal
19
New cards
Cultural Relativism
Process of understanding other cultures on their own terms
20
New cards
Components of culture
Material culture
-objects associated with a cultural group
Symbolic culture
-ways of thinking (beliefs, values, assumptions)
-Ways of behaving (norms, interactions, and communication)
Communication through signs, gestures and language
-objects associated with a cultural group
Symbolic culture
-ways of thinking (beliefs, values, assumptions)
-Ways of behaving (norms, interactions, and communication)
Communication through signs, gestures and language
21
New cards
Language
System of communication usual vocal sounds, gestures and written symbols
Most significant component of culture
Shapes perceptions
Most significant component of culture
Shapes perceptions
22
New cards
Values and Norms
Values: shared beliefs about what is worthwhile or desirable
-guide the creation of norms
Norms: formal and informal rules for acceptable and appropriate behavior within culture
-guide the creation of norms
Norms: formal and informal rules for acceptable and appropriate behavior within culture
23
New cards
Types of Norms
Folkways: loosely enforced norm, helps ensure smooth social interaction
Mores: carries greater moral significance, closely related to core values of a group
Taboos: deeply engrained norm
-violations evoke strong feelings of disgust, horror or revulsion
Mores: carries greater moral significance, closely related to core values of a group
Taboos: deeply engrained norm
-violations evoke strong feelings of disgust, horror or revulsion
24
New cards
Norm Enforcement
Sanctions: positive- rewards. Negative- punishments
Social control: formal and informal mechanisms used to:
-increase conformity to values and norms
-increase social cohesion
Social control: formal and informal mechanisms used to:
-increase conformity to values and norms
-increase social cohesion
25
New cards
Multiculturalism
Values diverse racial, ethnic, national and linguistic backgrounds
Encourages the retention of cultural differences within a society, rather than assimilation
Encourages the retention of cultural differences within a society, rather than assimilation
26
New cards
Dominant culture
Values, norms, perspectives of the group within society that is most powerful in terms of wealth, prestige, status and influence
27
New cards
Subcultures
Group within society that is differentiated by its distinctive values, norms, and lifestyle
28
New cards
Counterculture
Openly rejects and/or actively opposes society’s values and norms
29
New cards
Socialization
Values, beliefs, and norms of social groups:
-society teaches
-individuals learn and internalize
-society teaches
-individuals learn and internalize
30
New cards
Self
Personal identity
Created and modified through social interaction
Created and modified through social interaction
31
New cards
Sigmund Freud
Subconscious and unconscious mind
32
New cards
Charles Cooley
Looking-glass self
-the self develops through our:
-perceptions of others evaluations
-appraisals of (interactions with) us
We experience a feeling about ourselves based on our perception of other peoples judgment
-the self develops through our:
-perceptions of others evaluations
-appraisals of (interactions with) us
We experience a feeling about ourselves based on our perception of other peoples judgment
33
New cards
Erving Goffman
Meaning is constructed through interaction and the self
Dramaturgy
-compares social interactions to the theater
-individuals take on roles and act them out
Dramaturgy
-compares social interactions to the theater
-individuals take on roles and act them out
34
New cards
The Thomas Theorem
“If people define situations as real, they are real in their consequences.”
Ambiguous situations allow for many possible meanings
-the way we define each situation, then, becomes it’s reality
Ambiguous situations allow for many possible meanings
-the way we define each situation, then, becomes it’s reality
35
New cards
Impression Management
Social life as a game
-we work to control the impressions others have of use
-front
-personal front
-region
-backstage
-front stage
-we work to control the impressions others have of use
-front
-personal front
-region
-backstage
-front stage
36
New cards
Agents of Socialization
Social groups, institutions, and individuals that provide structured situations where socialization occurs
-family
-schools
-peers
-mass media
-family
-schools
-peers
-mass media
37
New cards
Resocialization
Process of replacing previously learned norms and values with new ones as a part of a transition in life
38
New cards
Total Institution
Cuts individuals off from the rest of society so that their lives can be controlled and regulated
-dramatic form of resocialization
-prison, military, mental health unit
-dramatic form of resocialization
-prison, military, mental health unit
39
New cards
Status
A position in a social hierarchy that Carrie’s a particular set of expectations
40
New cards
Ascribed Status
A status we are born with that is unlikely to change
41
New cards
Achieved status
One that we earned through individual effort or that is imposed by others
42
New cards
Master Status
Status that seems to override all others and affects all other statuses that we possess
43
New cards
Roles
Behaviors expected from a particular status
44
New cards
Role Conflict
Roles associated with one status with the role’s associated with a different status
45
New cards
Role Strain
Roses associated with a single status clash
46
New cards
Role Exit
Process of leaving a role that we will no longer occupy
47
New cards
Deviance
Departs from the norm
Generates a negative reaction
Necessary in society
Generates a negative reaction
Necessary in society
48
New cards
Cultural Relativism vs Ethnocentrism
What is deviant in one culture may not be deviant in another culture
49
New cards
Functionalism
Deviance serves a positive social function in society
-norms and values
-moral boundaries
-social cohesion
-social change
-norms and values
-moral boundaries
-social cohesion
-social change
50
New cards
Structural Strain Theory
There are goals in our society that people want to achieve
-but they can not always reach these goals
Created stress/strain because people are aware of these goals but do not have the means to achieve them
-fertility, money, love, fame, etc.
-but they can not always reach these goals
Created stress/strain because people are aware of these goals but do not have the means to achieve them
-fertility, money, love, fame, etc.
51
New cards
Merton’s Typology
Conformity, innovators, ritualists, retreatists, rebels
52
New cards
Conflict Theory
Means of production
-bourgeoise/owners/capitalists
Proletariat/works
-bourgeoise/owners/capitalists
Proletariat/works
53
New cards
Differential Association
Symbolic interactionism
Learn deviance from deviant peers
Learn deviance from deviant peers
54
New cards
Labeling Theory
Deviance is caused by external judgments- labels
-change a persons self concept and the way that others respond
Self-fulfilling prophecy
-a prediction that causes itself to come true
-change a persons self concept and the way that others respond
Self-fulfilling prophecy
-a prediction that causes itself to come true
55
New cards
Deviant Identities- Stigma
Physical or social attribute
Devalues identity
Excludes the devalued/stigmatized
3 types: physical, moral, tribal
Devalues identity
Excludes the devalued/stigmatized
3 types: physical, moral, tribal
56
New cards
Physical Stigma
Physical or mental impairments
57
New cards
Moral stigma
Signs of flawed character
Ex: cheating
Ex: cheating
58
New cards
Tribal Stigma
Membership in a discredited or oppressed group
Ex: gang members
Ex: gang members
59
New cards
Deviant Identities- Passing
Stigmatized individuals may try to pass as if they are part of the mainstream
60
New cards
In-group Orientation
Stigmatized individuals
-reject judgement and prejudice
-Develop new standards
-value their group identity
-reject judgement and prejudice
-Develop new standards
-value their group identity
61
New cards
Crime
Violation of a norm that has been confined into law
Punishable by:
-fine
-community service
-imprisonment
Punishable by:
-fine
-community service
-imprisonment
62
New cards
Cross-Cultural Crime
Punishment in other countries:
-shunning
-banishment
-corporal punishment
-shunning
-banishment
-corporal punishment
63
New cards
Deterrence
An approach to punishment that relies on the threat of harsh penalties to discourage people from committing crimes
64
New cards
Retribution
Emphasizes retaliation or revenge for the crime as the appropriate goal
65
New cards
Incapacitation
Seeks to protect society from criminals by imprisoning or executing them
66
New cards
Rehabilitation
Attempts to reform criminals as part of their penalty
67
New cards
Manifest function
Intended purpose
Ex: a car is intended to get you around
Ex: a car is intended to get you around
68
New cards
Latent function
Unintended purpose
Ex: a cars unintended purpose is causing pollution
Ex: a cars unintended purpose is causing pollution