Organization and Cells of the Nervous System
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What are the main functions of the nervous system?
Communication through electrical and chemical signals, sensory input, integration of information, and motor output.
What are the two main divisions of the nervous system?
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
What does the Central Nervous System consist of?
The brain and spinal cord.
What is the role of the Peripheral Nervous System?
It carries messages to and from the brain and spinal cord via spinal and cranial nerves.
What are the two functional subdivisions of the Peripheral Nervous System?
Sensory (afferent) and Motor (efferent) divisions.
What is the function of sensory afferent fibers?
They carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscle, and joints to the brain.
What is the role of motor efferent fibers?
They carry impulses from the CNS to effector organs.
What are effector organs?
an organ, such as a muscle or a gland, that responds to neural stimulation by producing a particular physical response or initiating a specific physiological event.
What are the two main parts of the Motor Division of the PNS?
Somatic Nervous System (voluntary control of skeletal muscle) and Autonomic Nervous System (involuntary control of smooth and cardiac muscle).
What is a neuron?
Excitable cells that transmit electrochemical signals and release neurotransmitters
What are components of a neuron?
the cell body (soma), dendrites, and axon
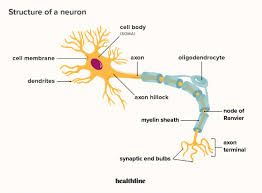
What do the dendrites of a neuron do?
transmit electrical impulses to perikaryon & Provide a high surface area to receive signals from other neurons
What do axons do?
Transmit nerve impulses & secrete neurotransmitters from the axonal terminals (terminal bouton)
What are the different types of neurons?
sensory, motor, and interneurons
What is a supporting cell (neuroglia)?
Surround, wrap neurons, and provide nourishment
What are the supporting cells of the CNS?
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells
What are the supporting cells of the PNS?
Schwann cells and satellite cells
What are astrocytes and their functions?
most abundant supporting cells that anchor neurons to nutrient supplies, metabolize glucose for ATP, and regulate neuronal function.
What is the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)?
A protective barrier that separates blood-borne substances from neurons, composed of continuous endothelium with tight junctions.
What substances can diffuse through the Blood-Brain Barrier?
Extremely lipophilic substances, gases (O2 and CO2), and ethanol.
What are ependymal cells?
Epithelial cells that line the brain cavities and spinal canal, forming a semipermeable barrier between cerebrospinal fluid and nervous tissue.
What is the role of microglia?
They act as immune cells in the brain, monitoring neuron health and phagocytizing pathogens and debris.
What do oligodendrocytes do?
They wrap multiple axons in the CNS to form myelin sheaths, which speed up nerve conduction.
What is the myelin sheath?
A whitish, fatty segmented covering around larger axons that provides protection and electrical insulation.
How is the myelin sheath generated in the central nervous system?
formed by the oligodendroglial cell
How is the myelin sheath generated in the peripheral nervous system?
Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
What are Satellite cells?
(ganglionic gliocytes) “Astrocytes of the PNS”
What are Schwann cells?
Supporting cells in the PNS that form myelin sheaths around peripheral axons.
What are the two types of motor neurons?
Somatic motor neurons (control voluntary movements) and autonomic motor neurons (control involuntary functions).
What are Nodes of Ranvier?
Gaps in the myelin sheath that contain voltage-regulated Na+ channels, allowing for faster nerve conduction.
What is saltatory conduction?
The process by which nerve impulses jump from one Node of Ranvier to another, increasing conduction speed.
What is the neurilemma?
The outermost layer of the Schwann cell that surrounds the myelinated axon in the PNS.
What is the perikaryon?
The major biosynthetic center of a neuron that contains the cell nucleus and organelles.
What are dendrites?
Arm-like extensions from the perikaryon that receive signals from other neurons.
What are axons?
Extensions that transmit nerve impulses away from the neuron and secrete neurotransmitters at the terminal boutons.
What is the difference between nuclei and ganglia?
Nuclei are collections of nerve cell bodies in the CNS, while ganglia are collections in the PNS.
What are the main types of neurons based on function?
Sensory (afferent), Interneurons (association), and Motor (efferent) neurons.
What is the significance of neurotrophic factors in nerve regeneration?
They guide axons to re-establish proper connections after injury.
Collections of nerve cell bodies located within the central nervous system are called:
Nuclei
Collections of nerve cell bodies located within the peripheral nervous system are called:
Ganglia
All of the following are functions of astrocytes EXCEPT:
Defending against invading microorganisms, releasing inflammatory mediators, and phagocytizing dying cell debris
What are interneurons?
neuron which transmits impulses between other neurons, especially as part of a reflex arc.