Human Bio Test 1: Organization of Human Body and Homeostasis, Chemistry of Life, Anatomy of the Cell, Plasma Membrane Transport, Cell Cycle, Protien Synthesis
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
Homeostasis
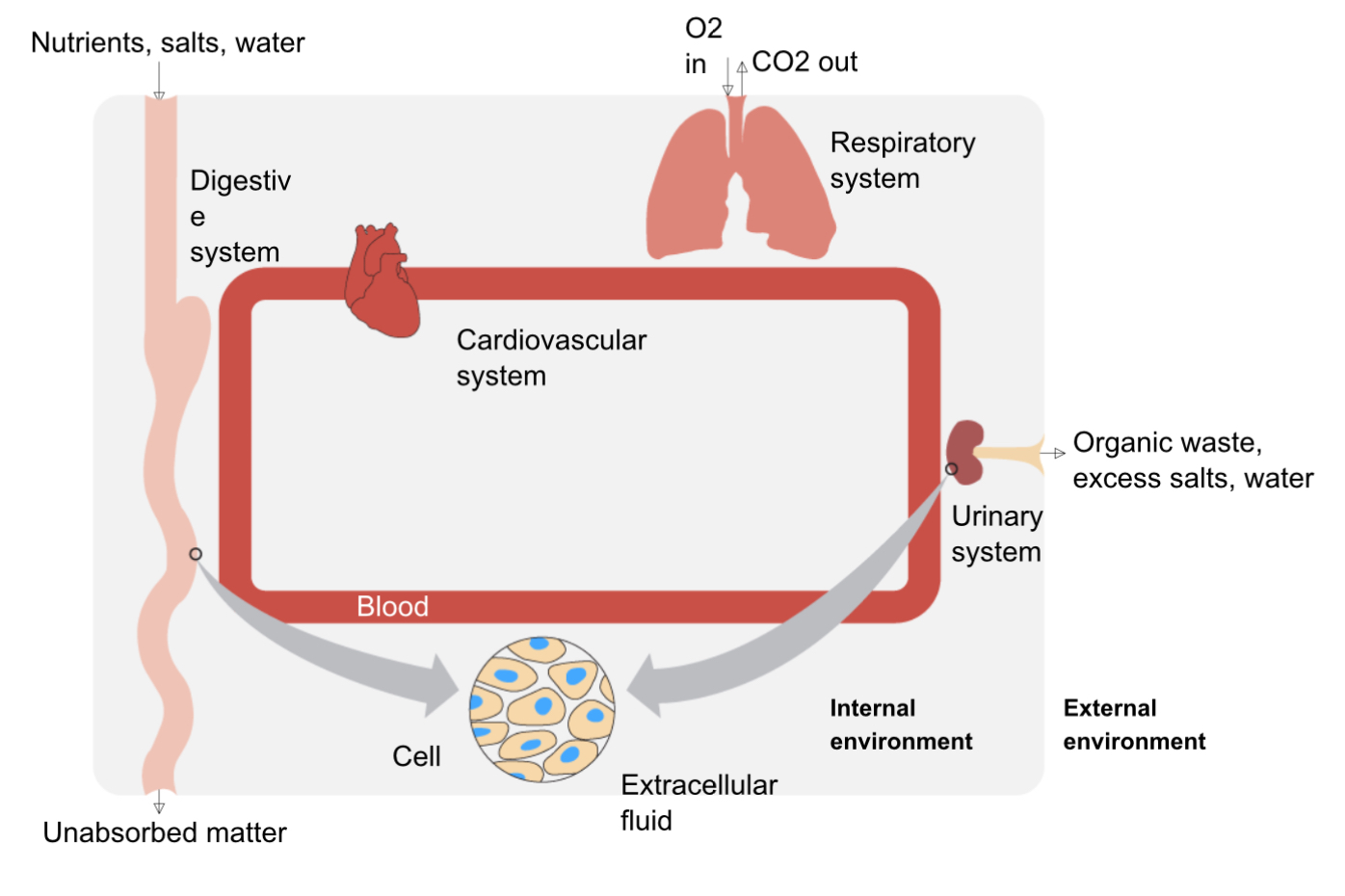
Maintenance of constant internal environment
blood delivers nutrients to cells and removes waste
main sources of intake: respiratory system (take in O2) and digestive system (absorb nutrients)
main systems of waste removal: respiratory system (remove CO2) and urinary system (removes excess water, salts, and organic waste
Regulation of Homeostasis
Receptor —> Control Center —> Effector
Receptor detects change
Control Center processes information and reports to effector
Effector creates needed change
Feedback
How a process is regulated by the products of the process
2 types: Negative and positive feedback
Negative Feedback
Inhibition of a process by the products of the same process
stops the process once the products accumulate
most common form of regulation
ex: shivering warms you up so you stop shivering
Positive Feedback
Enhancement of a process from the products of the process
good for creating quick response/exponential production of product
must have a turn off method
ex: blood vessel is cut, chemicals trigger clotting which produces more chemicals, accelerating the process, once the blood clot is formed, clotting stops
Elements
Substances made of one type of atom
building blocks of all molecules
each has unique chemical properties
13 bulk elements in the body: (top 3: Oxygen, Carbon, and Hydrogen)
14 trace elements
top 3 bulk elements in the body
Oxygen, Carbon, Hydrogen
Atoms
Smallest unit of matter
made of protons (+), electrons (-) and neutrons (0)
Electron Shell Rules
Lower shells are filled first (Aufbau Principle)
2 electrons per orbital (Pauli Exclusion Principle)
2 e- in first shell, 8 e- in 2nd and 3rd shell
if valence shell is filled, the atom is inert
# of valence electrons determines behavior/reactivity
Atomic number
number of protons, determines element
Atomic Mass
number of protons and neutrons
Ions
charged atoms that gained or lost e-
atoms gain or lose e- to fill valence shell
Cations = positively charged
Anions = negatively charged
Molecules
Particle formed when atoms chemically bond
Electronegativity
How well an atom attracts electrons
EN increases across a period as the protons increase, increasing attraction
decreases down a group as # of shells increase, more shells= more repulsion from internal e- —> less attraction
Ionic Bonds
Chemical Bonds formed by attraction of anions and cations
an atom with high electronegativity steals the electrons of a an atom with lower electronegativity
the resulting ions attract
usually metals and nonmetals
strongest bond but dissociates in water
Covalent Bonds
Chemical Bonds formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms to fill valence shells
2 types:
non-polar (uneven charge)
polar (even charge)
Non-polar Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds that equally share electrons
no partial charges
atoms have equal electronegativity
Polar Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds that unequally share electrons
Molecule has partial negatively charged end (towards most electronegative atom) and partial positively charged end (towards least electronegative atom)
An atom has a higher electronegativity than the other(s)
Hydrogen bonds
Attraction between the partial positive hydrogen end of a polar molecule and the partial negative end (Fluorine, Oxygen, Nitrogen) of a different polar molecule
SUM EFFECT is biologically significant
Solution
a homogenous mixture
Solvent
Dissolves solute
Solute
Dissolves into solvent
Ionic Compounds Dissociate in water
Ionic compounds are broken into their ionic components in water as the polar charges of water surround the oppositely charged ions of the ionic compound, creating a hydration sphere, seperating the compound
Polar Covalent Compounds Dissolve into water
A compound/matrix of polar covalent bonds do not dissociate, but instead are separated into individual molecules as water’s partial positive and negative charges surround the partial positively charged and negative ends of the molecules, separating the compound
Solute Concentrations Expressions
Molarity (Mole/Liter): moles of molecule per liter
Osmolarity (Osmoles/Liter): number of particles a solute dissolves into per liter
Percentage % (Weight/Volume): grams of solute per 100 mL of solvent
Equivalents (Equivalents/Liter): number of moles ionized times valence/charge of ions
Molarity M (moles/liter)
moles of molecule per liter of substance
Osmolarity Osm/L (osmoles/liter)
number of particles a solute dissolves into per liter of solution
mOsmole/L =mOsm
cell osmolarity is 300 mOSM
colligative property: osmolarity dependent on number of particles, not size or charge
isosmotic = 2 solutions with same molarity
hyperosmotic = solution has higher osmolarity
hypoosmotic = solution has lower osmolarity
hydrostatic pressure:
fluid pressure of vessel (osmolarities unequal between 2 solutions)
can oppose osmotic pressure
can limit movement of water
Percent % (weight/volume)
grams of solute per 100 mL of solvent
Equivalents (equivalents/ liter)
number of moles ionized times the valence/charge of ion
for electrolytes
Electrolyte
ionized solute that can conduct electrical currents
normal blood values of electrolytes are heavily regulated for homeostasis
Proportion of % of body weight
60% of body weight is Total Body Water (TBW)
40% of body weight is Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
20% of body weight is Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
fluid found inside the cell
40% of body weight
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
fluid found outside the cell
20% of body weight
5% plasma (fluid in blood)
15% interstitial fluid (fluid surrounding cells)
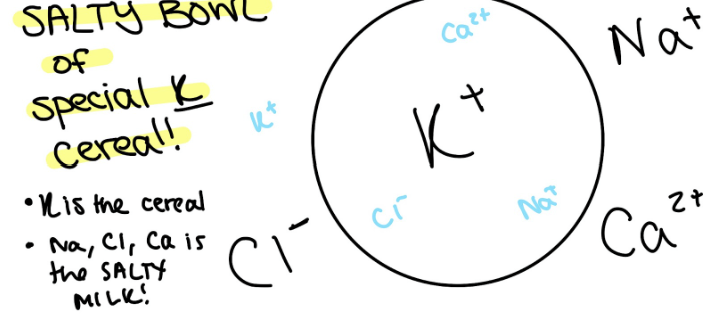
Composition of ICF and ECF
Intracellular Fluid: has most K+ (special K cereal)
Extracellular Fluid: has most Ca²+, Na+, Cl- (salty milk)
Acid
solute that releases H+ when dissociating into solution
Base
solute that removes H+ ions from solutions
pH
measure of H+ ions in solution
more H+ = more acidic (<7)
less H+ = less acidic (>7)
Normal pH of blood
pH = 7.35-7.45
Acidosis in blood (too acidic)
pH < 7.35
Alkalosis in blood (too basic)
pH > 7.45
Biomolecules
Carbon is the most abundant element in organic molecules
4 major classes of biomolecules that are macromolecules:
Protein (made of amino acids)
Lipid
Nucleic Acid (made of nucleotides)
Carbs (polysaccharides are made of monosaccharides)
Organic molecules are mostly made of:
Carbon
because it has 4/8 valence electrons it has a middling electronegativity, meaning it is more likely to form covalent bonds
because of its tetrahedron structure, it has higher mobility, and makes versatile bonds
Functional Groups
Common chemical structures that influence bonding properties and can be used to predict chemical properties
Ex:
Hydroxyl group (OH)
Carbonyl group (CO)
Carboxyl group (COOH)
Amino group (NH2)
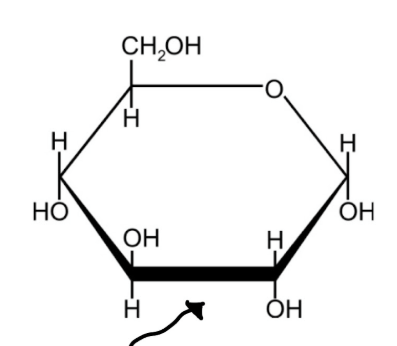
Carbohydrates
1:2:1 carbon, hydrogen, oxygen ratio
3 major classifications
monosaccharides (1 monomer)
disaccharides (2 monomers)
polysaccharides (3+ monomers)
Carbohydrate Function
important source of calories
energy storage
component of nucleic acids
structure of cell wall in plants and bacteria
modifying protein to alter function
mediate recognition events at cell surface (acts as molecular marker)
Monosaccharide (simple sugars)
building blocks to construct larger carbohydrates
di= 2 monosaccharides
oligo 3-10 monosaccharides
poly = 10+ monosaccharides
classified by number of carbon atoms
5C = pentose
6C = hexose
GLUCOSE IS MOST COMMON MONOSACCHARIDE IN DIET
Glycosidic Bonds
monosaccharides link to form disaccharides
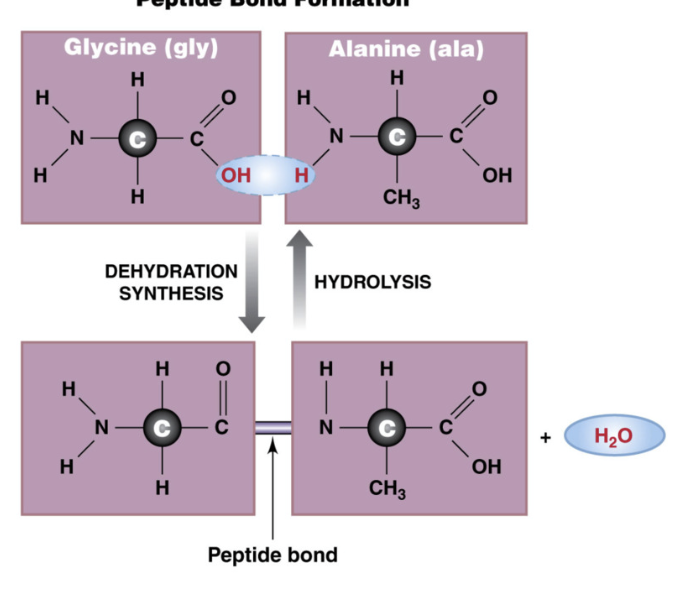
formed by dehydration synthesis reaction: removal of one water molecule to form a glycosidic bond
broken apart by hydrolysis reaction (addition of one water molecule to break glycosidic bond
REMEMBER
sucrose = glucose + fructose (table sugar)
lactose = glucose + galactose (milk sugar)
maltose = glucose + glucose (malt sugar)
Dehydration Synthesis Reaction
Removal of a water molecule to form a bond
Hydrolysis reaction
Addition of a water molecule to break a bond
Sucrose (table sugar)
glucose + fructose
Lactose (milk sugar)
glucose + galactose
Maltose (malt sugar)
glucose + glucose
Polysaccharides
monosaccharides —> monomer (repeating subunit of larger molecule)
polysaccharides —> polymer (>10 monosaccharides)
types of polysaccharides:
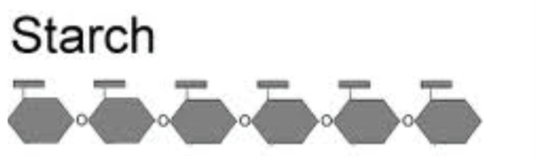
Starch: glucose storage in plants
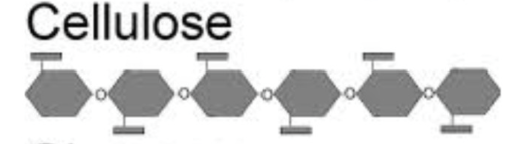
Cellulose: structure component of plant cell walls
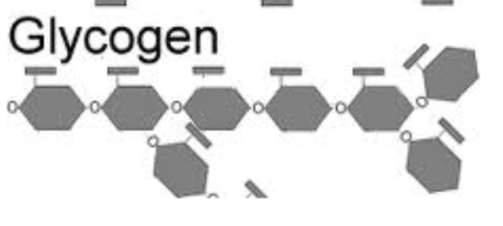
Glycogen: glucose storage in animals
branched polymer of glucose
found in liver and skeletal muscle
Starch
Storage form of glucose in plants
polysaccharide
Cellulose
Structural component of plant cell walls
polysaccharide
Glycogen
storage form of glucose in animals
branched polymer of glucose
found in liver and skeletal muscle
polysaccharide
Lipids
water insoluble group of organic molecules
1:2 carbon to hydrogen ratio (very little oxygen)
include
fatty acids, glycerides, phospholipids and glycolipids, steroids, and eicosanoids
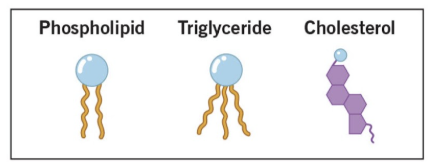
types of lipids
fatty acids
glycerides
phospholipids and glycolipids
steroids
eicosanoids
Lipid functions
energy
energy storage
structure (ex phospholipid bilayer)
signaling molecules
Fatty Acids
type of lipid that is incorporated into larger lipid molecules
used for energy storage to convert to energy
Long chain (up to 24 Carbons attached to hydrogens)
carboxyl group (COOH) on one end and methyl group (CH3) on other
include saturated and unsaturated fats
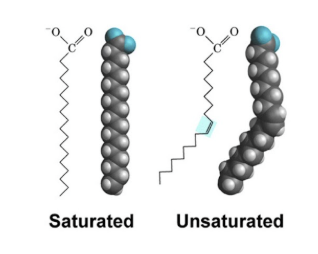
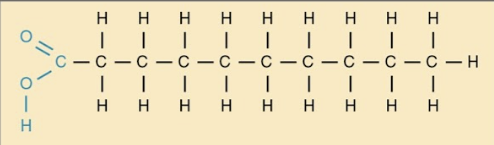
Saturated fatty acids
Fatty acids that have no double bonds and are saturated with hydrogen
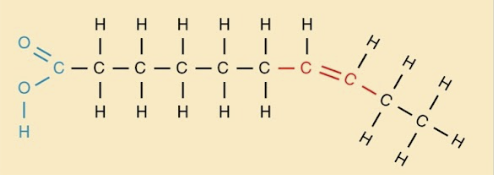
Unsaturated fatty acids
Fatty acids with at least 1 double bond.
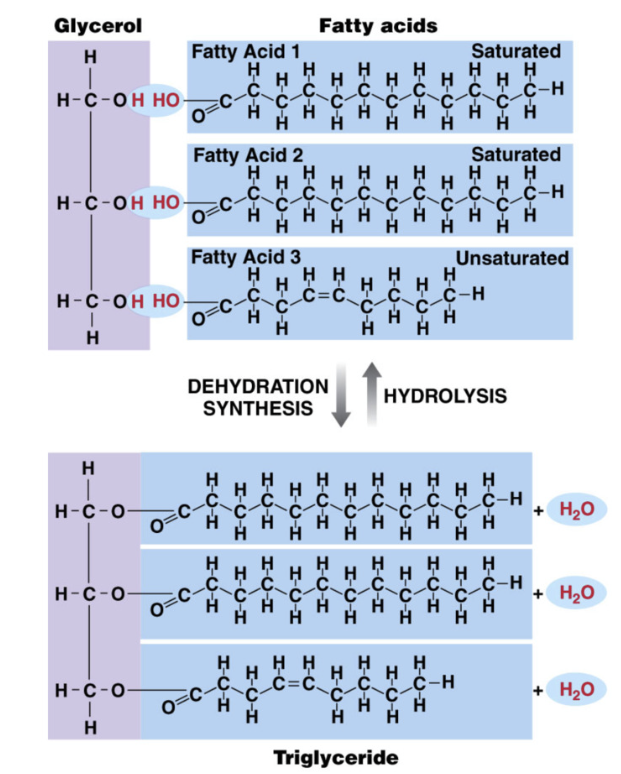
Glycerides
Key functions of triglycerides (glycerol + 3 fatty acids)
energy storage
insulation
shock absorber
glycerol + fatty acids
glycerol = 3 carbon sugar
formed by dehydration synthesis
triglycerides stored as lipid droplets in cells of body (adipocytes)
human body good at making and storing triglycerides
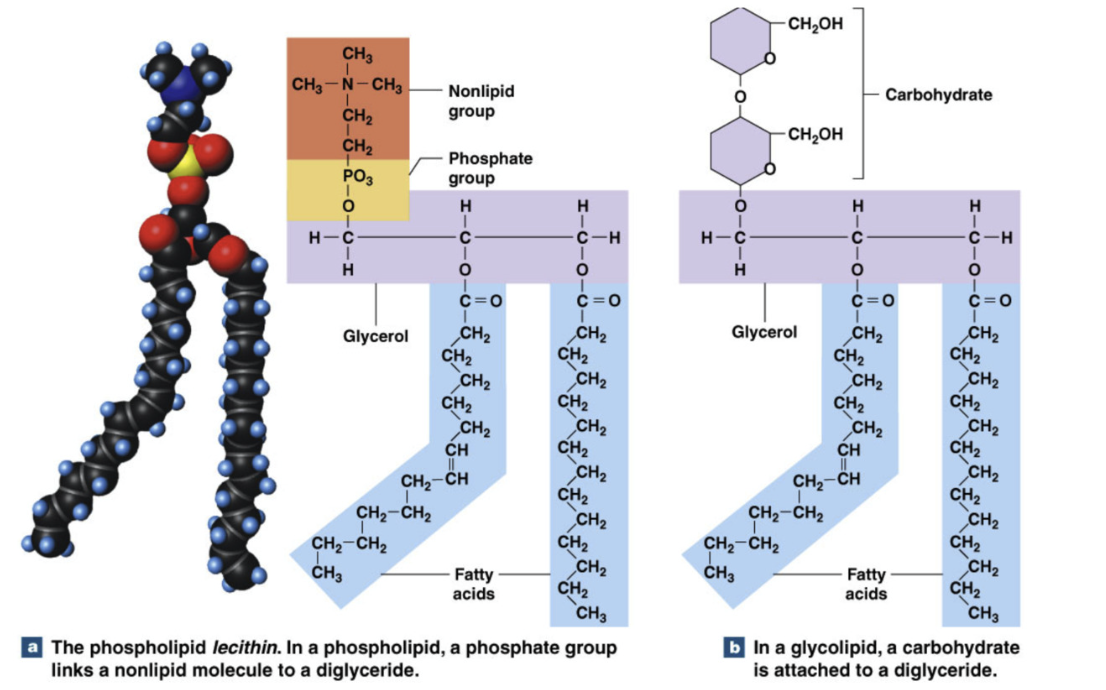
Phospholipids and Glycolipids
Key functions:
Cell membrane structure/ function (phospholipid bilayer)
transport of other lipids
both have glycerol with 2 fatty acids (unsaturated and saturated): diglyceride
Phospholipids = diglyceride, phosphate group, and nonlipid group
Glycolipids = diglyceride, carbohydrate (sugar)
Amphipathic: partially hydrophobic and hydrophilic
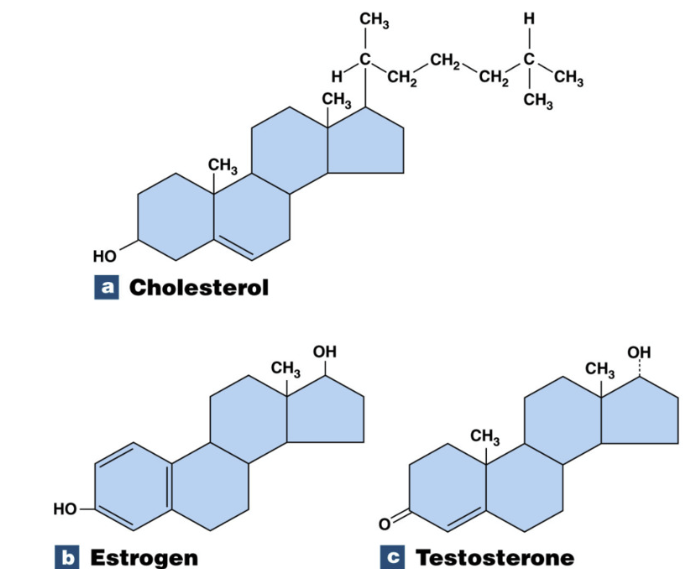
Steroid
Key functions:
chemical messengers, cell membrane structure, can span full body
lipid with many carbons arranged in 4 ring structure
Cholesterol make steroid hormones
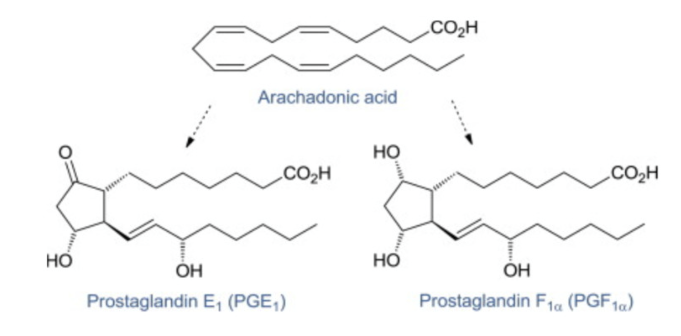
Eicosanoids
Key function
local chemical signaling
20 carbon compounds derived from arachidonic acid
produced in small amounts in tissues
act locally
Proteins
Polymers of amino acids connected by peptide bonds
Protein functions
Catalysts (enzymes)
Immune function (antibodies)
movement (contractile proteins)
signaling (receptor proteins)
Structural support (connective tissues)
oxygen delivery (hemoglobin/myoglobin)
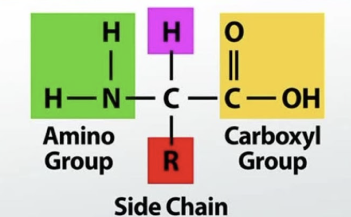
Amino Acids
components of proteins
made of carboxyl group (COOH), amino group (NH3), H, and variable R group (differentiates amino acids), attached to central C
R groups can be hydrophilic, hydrophobic, acidic, basic
20 amino acids in humans
Peptide Bonds
connect amino acids to form proteins
formed by dehydration synthesis
Peptides have directionality (OH of COOH terminal binds to H of NH3 terminal)
amino terminal (NH3)
carboxyl terminal (COOH
Dipeptide = 2 amino acids
oligopeptide (short chain) = 3-20 amino acids
polypeptide = more than 20 amino acids
>20 amino acid = protein
Protein (polypeptide) structure
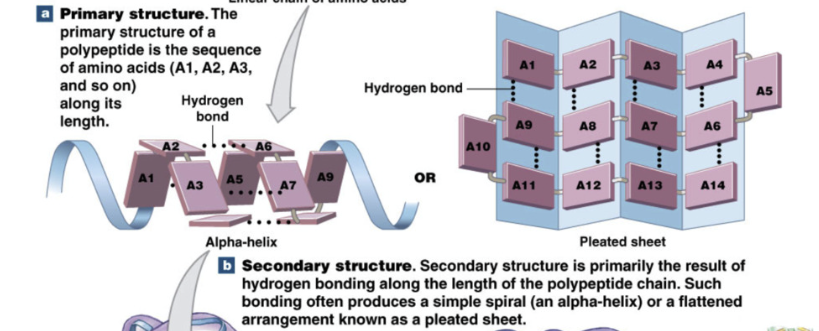
Primary: sequence of amino acids
Secondary: alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
Tertiary: coiling or folding of one polypeptide (can exist without second secondary structure)
Quaternary: interaction between multiple peptide chains
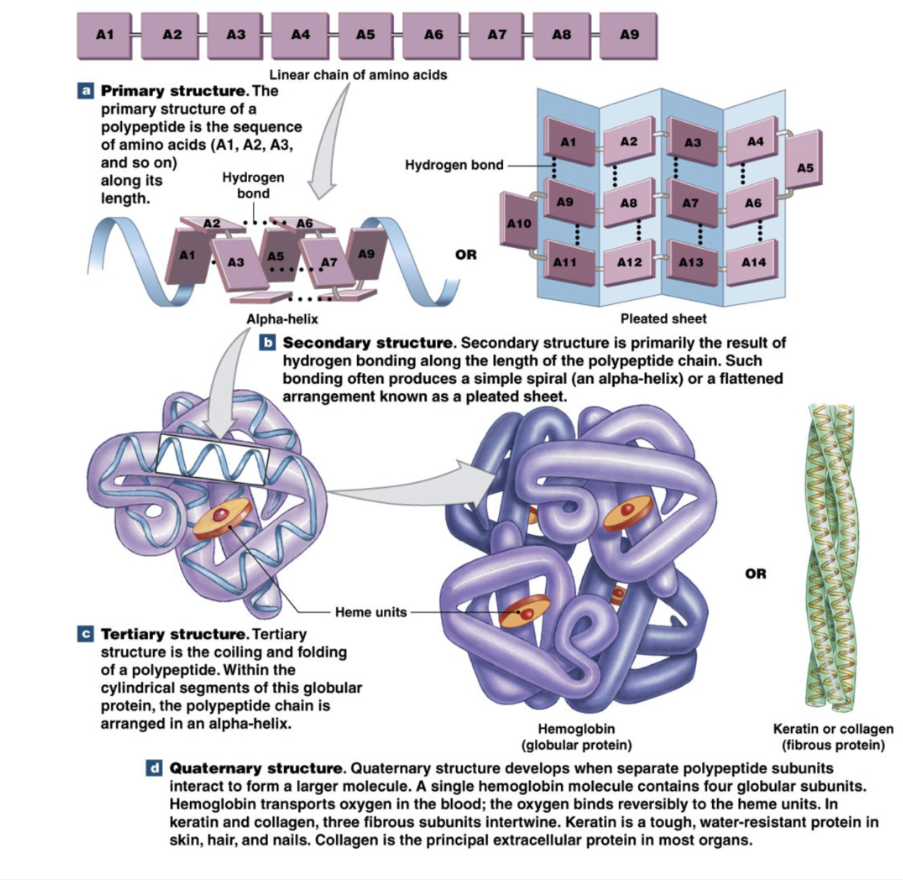
Protein primary structure
sequence of amino acids
Protein secondary structure
Alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
proteins can be produced without secondary structure
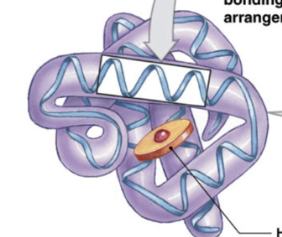
Protein tertiary structure
coiling and folding of 1 polypeptide
all proteins have tertiary structures but don’t need secondary structure
Protein quaternary structure
interactions between multiple polypeptides
Nucleic acids
polymers of nucleotides
bound by sugar phosphate backbone = phosphate bound to free carbon of sugar
hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotides of DNA
5’ - 3’
Functions
storage and transfer of genetic material
instructions for protein production
energy
types: DNA deoxyribonucleic acid, RNA ribonucleic acid
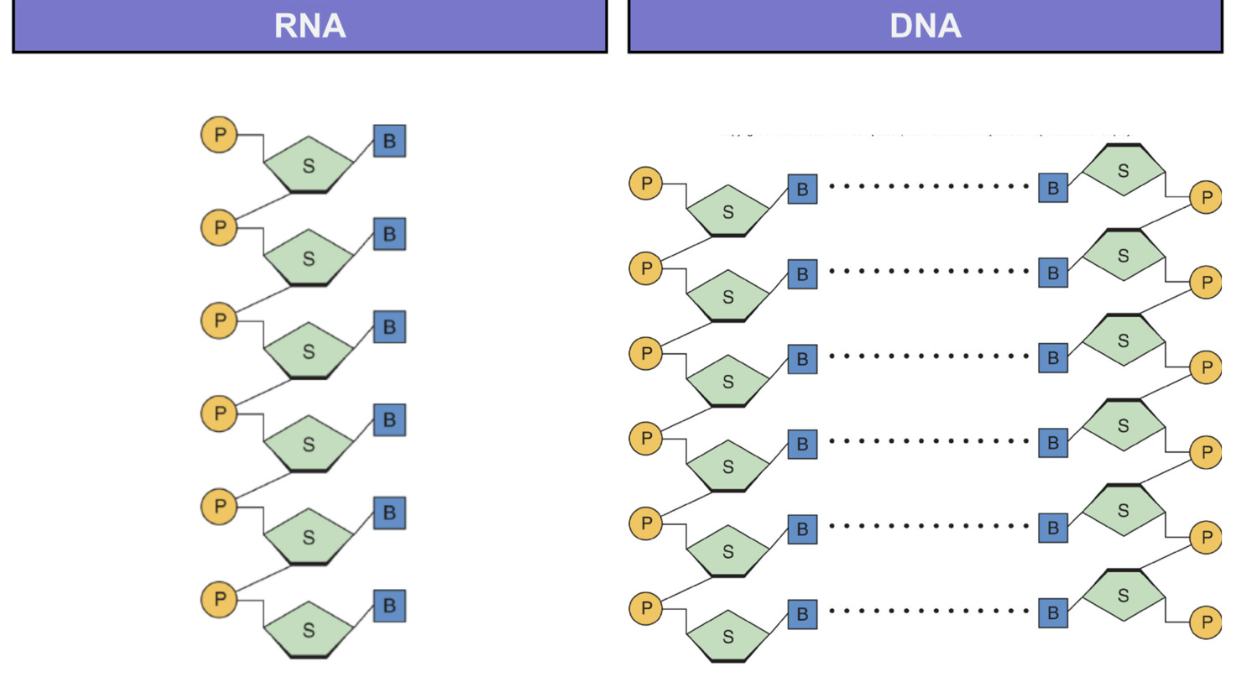
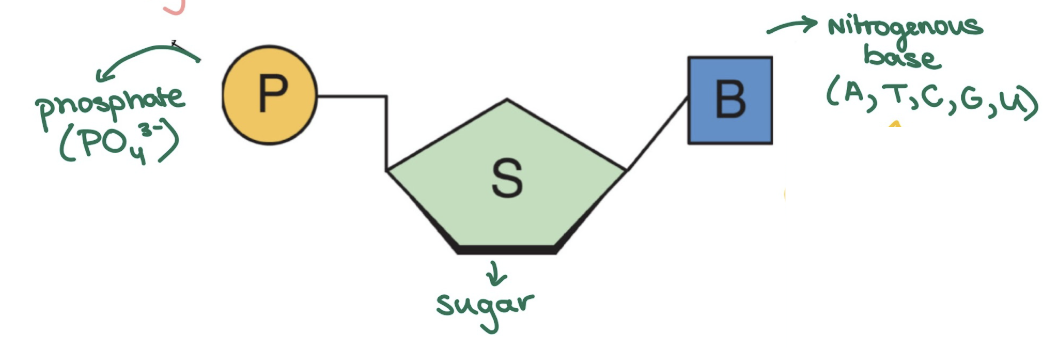
Nucleotide structure
made of phosphate, sugar, nitrogenous base
DNA has H in sugar (deoxi = without O)
bp: AT, GC
RNA has OH in sugar
bp: AU, GC
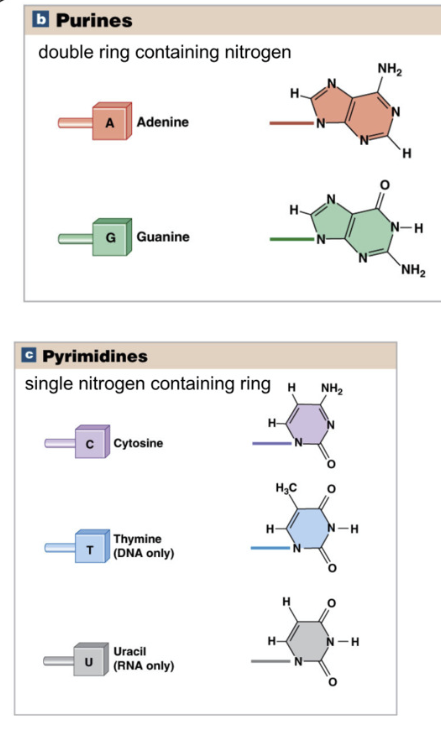
Types of Nucleotides
Purines: double nitrogen ring
Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidines: single nitrogen ring
Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil
Purines always pair with pyrimidines
A - T/U
G - C
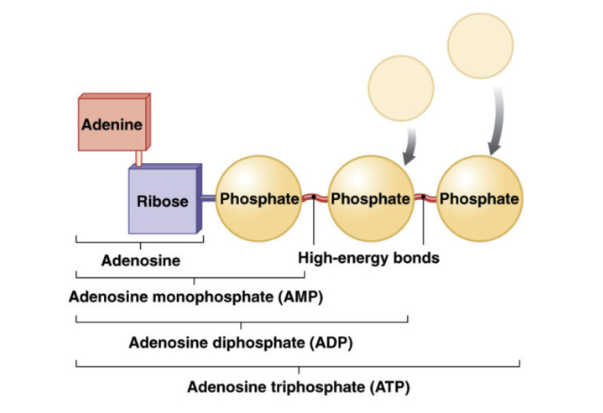
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
currency of energy
formed by attaching/ phosphate groups to adenosine (adenine + ribose)
phosphorylation = adding phosphate group
tri = 3 phosphate groups
release energy when ATP (tri) is broken to generate ADP (di)
relies on ATPase enzyme
Cell size
10-15um (micrometers)
biggest cell 140 um = oocyte
cell size is limited due to surface area (r²) volume ratio (r³)
Mammalian Cells
Eukaryotic cell = have nucleus
cell membrane forms selectively-permeable barrier
Membrane bound organelles in Mammalian cells
nucleus
mitochondria
golgi apparatus
endoplasmic reticulum
lysosomes
peroxisomes
Nonmembrane bound structures in mammalian cell
ribosomes
proteasomes
cytoskeleton
centrosome and centrioles
cilia
Plasma Membrane fluid mosaic model
fluid: membrane moves
mosaic: phospholipids, protein, sugar
Glycocalyx = sugar coat on extracellular surface of membrane (glycolipid, glycoproteins, carbs for cell recognition)
Composition of phospholipid bilayer
mostly phospholipids
phosphate head is hydrophilic and fatty acid tails → hydrophobic
have at least 1 saturated fatty acid of phospholipid
2nd fatty acid = unsaturated, kink → fluid part of membrane
in water, phospholipids naturally form leaflet (sphere shape) to avoid water touching the inner fatty acid tails
amphipathic: both hydrophilic + hydrophobic region
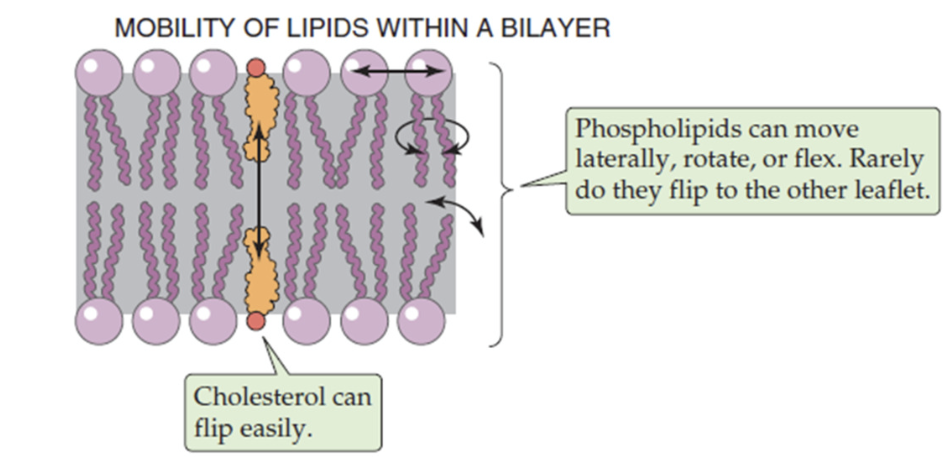
Fluidity of phospholipid bilayer
determined by phospholipids and cholesterol
because of kinked unsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids are mobile, move laterally, rotate and flex
cholesterol embedded in bilayer adds to membrane rigidity
balance maintains fluidity
Proteins in Plasma Membrane
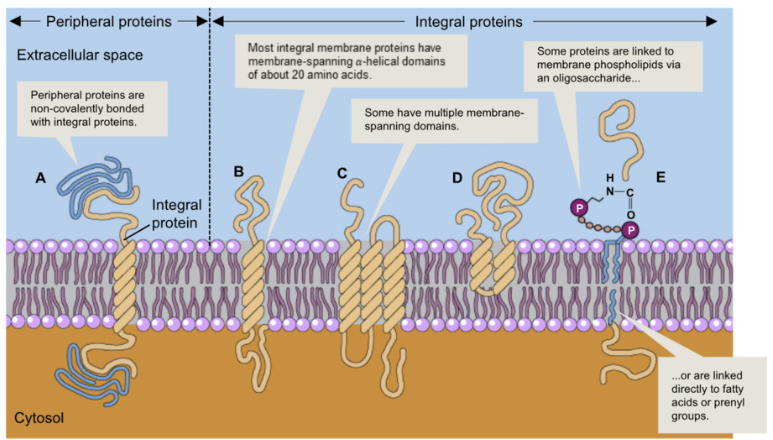
Integral Proteins:
embedded in plasma membrane or attached via covalent bonds
transmembrane proteins span the plasma membrane
embedded proteins within the membrane
proteins anchored to membrane by covalent bonds
Peripheral Proteins:
located at extracellular or intracellular surface of membrane
bound to surface or non-covalently bonded to integral proteins
Plasma membrane protein function
carrier
channel
receptor
recognition
enzymes
cell-cell interactions
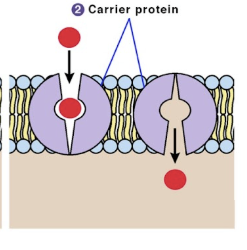
Carrier proteins (plasma membrane)
integral proteins that transport chemicals across the plasma membrane to both up or down concentration gradient via active transport
bind on end, conformational (shape) change, and release
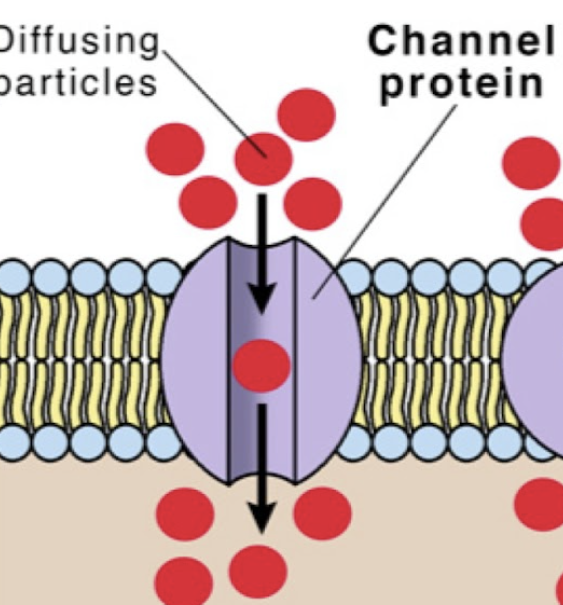
ion channel protein (plasma membrane)
integral protein that is constantly open to allow ions to pass in and out of the cell down their concentration gradient via passive transport
pore
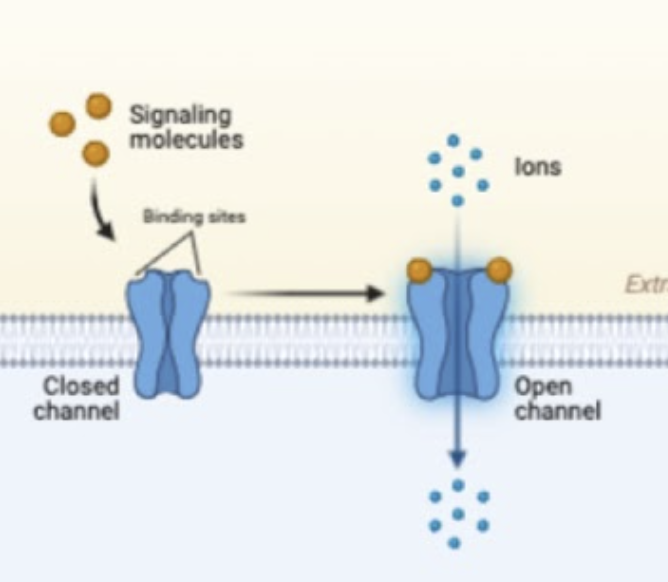
Gated ion channel (plasma membrane)
integral protein that allows the movement of ions in and out of the cell down their concentration gradient that open and close
Cytoskeleton
made of
microtubles 25μm
intermediate filaments 8-10 μm
microfilaments 5-8 μm
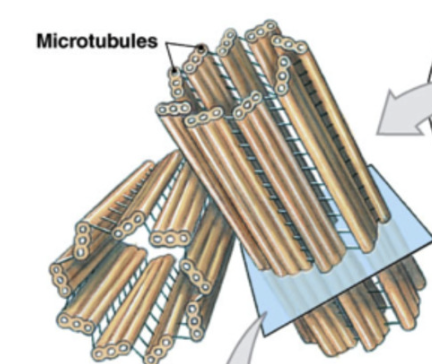
Microtuble
largest and main component of cytoskeleton
made of tubulin
create highways across cell (moved by motor protein dyenin and kinesin)
25 um
more rigid than microfilaments
component of spindle fibers, cilia, flagella
important for fast axon transport of substances in nerve cells
Microfilaments
smallest component of cytoskeleton
found just under cell membrane for structure (periphery)
2 helix polymers of actin
help anchor integral plasma membrane proteins to cytoskeleton
aid in cytokinesis
myosin + actin filaments → contraction (ex in muscles)
track for cargo → myosin motor
make microvilli
5-8 um
Intermediate Filaments
middle sized filaments
protein composition varies (eg keratin (epithelial), desmin (muscle))
rope like
provides structure/ mechanical strength to cell
8-10um
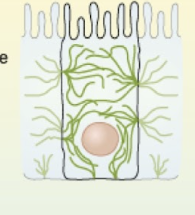
Cilia
generates movement to mix substances at cell surface
composed of microtubules
wave-like movement
basal body = where microtubules grow from
short
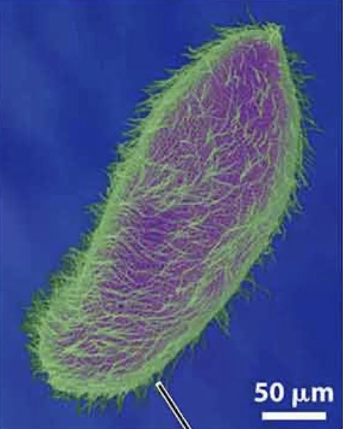
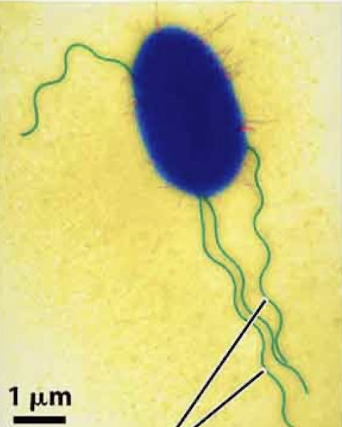
Flagella
propel cell
comprised of microtubules
whip-like movement
basal body = where microtubules grow from
eg sperm
long
microvilli
made of microfilaments actin
don’t move
Centriole
component of centrosomes
1 microtubule organization center
single cylinder of 9 groups of microtubule triplets

Centrosome
microtubule organizing center of the cell
made of two perpendicular centrioles
specialized region of cytoplasm by nucleus
form spindle apparatus during cell division