(c) gases in the atmosphere
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
four most abundant gases in dry air (2.9)
nitrogen (N2) - 78.1%
oxygen (O2) - 21.0%
argon (Ar) - 0.9%
carbon dioxide (CO2) - 0.04%
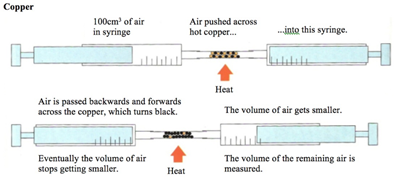
how to determine the percentage by volume of oxygen in the air using experiments involving the reactions of copper (2.10)
the copper is in excess and uses up the oxygen to form copper oxide (CuO)
copper + oxygen → copper oxide
2Cu + O2 → 2CuO
all the oxygen in the air is therefore used up, so the volume of the air decreases by about 20%
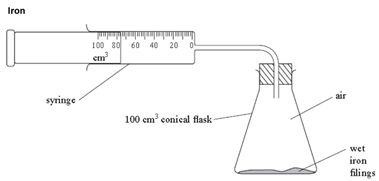
how to determine the percentage by volume of oxygen in the air using experiments involving the reactions of iron (2.10)
the iron reacts with the oxygen in the air (rusting). as long as both the iron and water are in excess, the total volume of air enclosed by the apparatus decreases by around 20% over several days.
iron + oxygen + water → hydrated iron(III) oxide (aka rust)
4Fe + 3O2 + nH2O → 2Fe2O3.nH2O
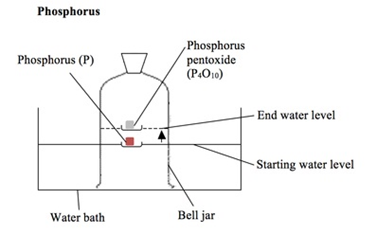
how to determine the percentage by volume of oxygen in the air using experiments involving the reactions of phosphorus (2.10)
the phosphorus is lit with a hot wire, reacting with the oxygen in the air and causing the water level in the bell jar to rise by about 20%
phosphorus + oxygen → phosphorus oxide
4P + 5O2 → 1P4O10
combustion of magnesium in oxygen (2.11)
when magnesium reacts with oxygen, a bright white flame is produce, leaving behind a white ash of magnesium oxide
magnesium + oxygen → magnesium oxide
2Mg (s) + O2 → 2MgO
combustion of hydrogen in oxygen (2.11)
hydrogen reacts with oxygen explosively. this is the basis of the ‘squeaky pop’ test (where a lit split is held into a test tube. if a ‘squeaky pop’ sound is heard, hydrogen is present in the test tube) this can be dangerous when larger quantities of hydrogen are present
hydrogen + oxygen → water
2H2 (s) + O2 → 2H2O (l)
combustion of sulfur in oxygen (2.11)
when sulfur reacts with oxygen, it produces a blue flame.
sulfur + oxygen → sulfur dioxide
S (s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
when sulfur dioxide dissolves in water, it forms an acidic solution of sulfurous acid
sulfur dioxide + water → sulfurous acid
SO2 (g) + H2O (l) → H2SO3 (aq)
describe the formation of carbon dioxide from the thermal decomposition of metal carbonates (2.12)
thermal decomposition is the process of breaking something down by heating it
upon heating, metal carbonates thermally decompose into metal oxides and carbon dioxide
e.g.
copper carbonate → copper oxide + carbon dioxide
CuCO3 → CuO + CO2
carbon dioxide is..? (2.13)
a greenhouse gas. increasing amounts of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere may contribute to a climate change due to their ability to absorb infrared radiation, therefore warming the atmosphere
determine the approximate percentage by volume of oxygen in air using a metal or a non-metal (2.14)
see point 2.10