El Nino and La Nina + Coral Bleaching
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
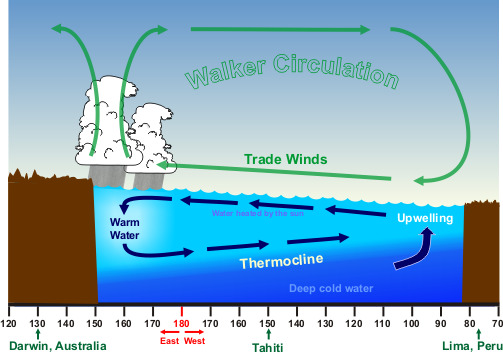
what happens to water In normal conditions
the wind moves water towards the west, convection current, upwelling (deep water reaches the surface + brings cold/nutrient rich water to the east)
What happens during El nino
(the opposite)
westerlies either stop blowing or are reversed to blow towards the east, there is no upwelling, water gets hot because there is no wind to cool it down
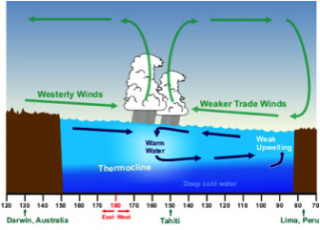
What are negative impacts of El nino
lower biological productivity off south america
coral bleaching due to warmer seawater
What happens during la nina
(normal conditions with so much more energy)
stronger upwelling, strengthening of the westerlies
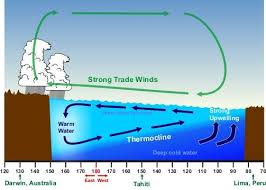
What are the effects of la nina
dry, mild conditions off south America, really cold water in the east (better for fishing), west has too much rain (monsoons in Indonesia)
Why do corals matter
Biodiversity/ habitats, add protection to coastlines (shoreline buffers), fishing
What creates the color of the coral
a symbiont located inside the corals cells
where is the symbiont and what is its signifiance
located in the Coral cell
responsible for capturing light energy and creating chemical energy
how much of the corals energy is from the symbiont
75-80%
what happens when a Coral is damaged
The damage occurs in the cytoplasm, the symbiont gets spit out ( gives the bleached appearance)
what does the symbiont not like
heat
Does bleached coral mean the Coral is dead
no it is just getting less energy
can a bleached coral go back to being healthy
yes if the water temperature increases
if there is prolonged temperature stress the Coral will die