shapes
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
simple squamous
main function is for diffusion
you can find in lungs, blood, arteries, etc.
one layer of flat cells
squished together
simple cuboidal
single layer of cells as tall as they are wided
allows for absorption, secretion
ex. kidney tubules, ducts of exocrine glands
simple columnar
single layer of tall, narrow cells
allows for absorption and secretion
ciliated and nonciliated forms
nonciliated form may have microvilli (brush b order) and goblet cells (secrete mucin)
conciliated ex. most of digestive tract, from stomach to anal canal
ciliated ex. uterine tube
ciliated can be found in respiratory
pseudostratified columnar
looks like it has multiple layers but it’s not
can be skinny, fat, etc.
single layer of narrow cells with varying heights
all cells touch basement membrane, but not all reach the apical surface
ciliated and nonciliated forms
functions in protection; ciliated form secretes mucin; moves mucus
ex. respiratory tract lining
stratified squamous
functions in protection
keratinized and nonkeratinized
apical cells
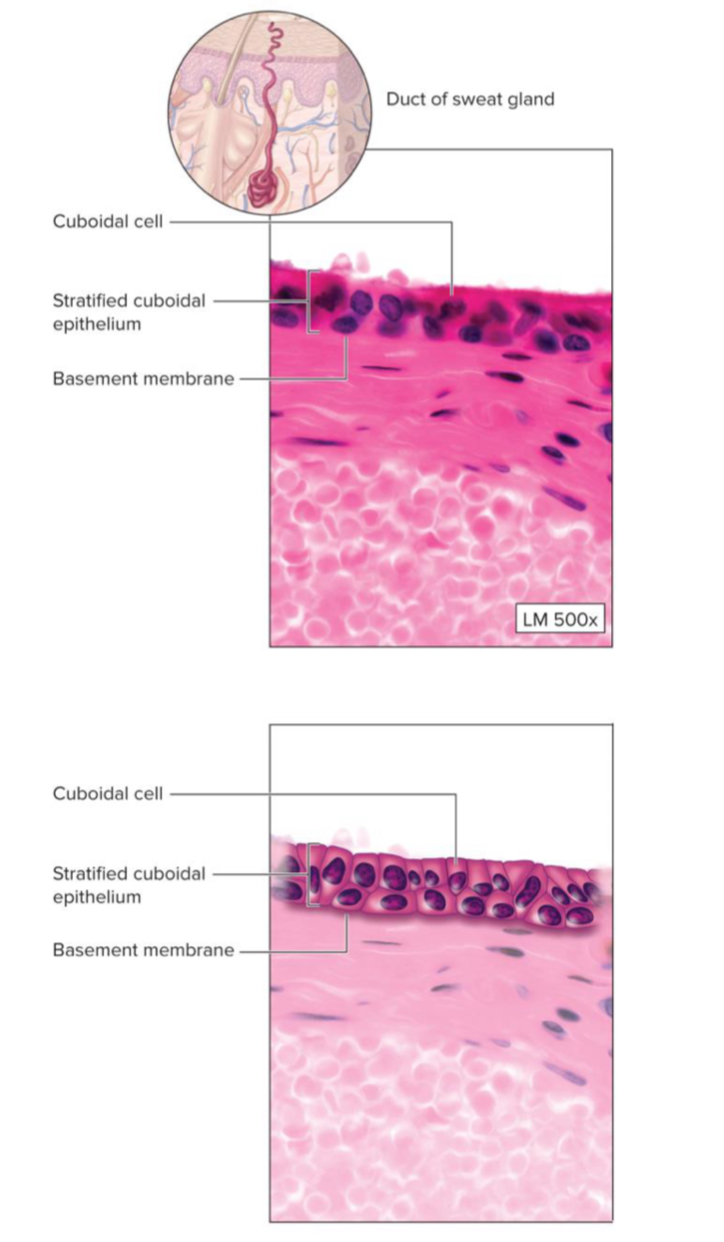
stratified cuboidal
very rare
ex. lining of sweat gland duct
stratified columnar
multiple layer of cells, elongated apical cells
protection, support, and secretion
ex. part of male urethra, ducts of some salivary glands
transitional ET
multiple layers, apical cell shape varies depending on degree of stretch
polyhedral when resting, squamous when stretched
some binucleated cells (sometimes has 2 nuclei)
ex. lining of urinary tract