Skeleton
1/7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What are the six functions of the endoskeleton?
supports our body
site for muscle attachment allows movement
protects organs
makes blood cells
stores fats and minerals
endocrine organ; produces a hormone called osteoclacin which is involved in the metabolism and fight or flight
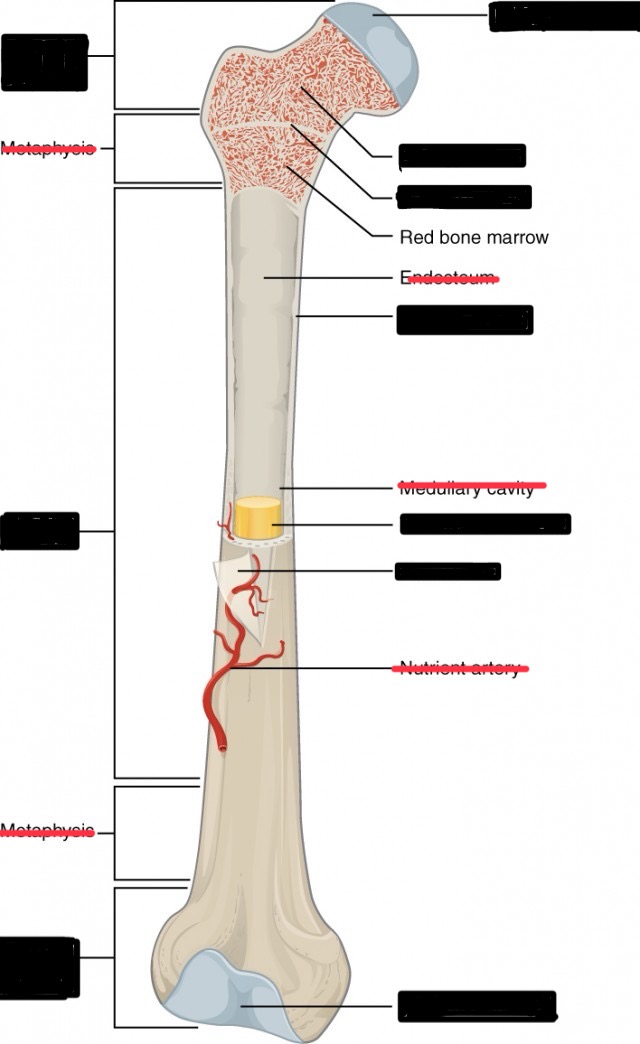
Describe the parts of a long bone (femur or humerus)
Diaphysis
Distal and proximal epiphysis
articulate cartilage
periosteum
compact bone
spongy bone
marrow cavity
epiphyseal line plate
What are the two types of bone growth?
ossification of fibrous membranes form skull bones and clavicles
Endochondral ossification of hyaline cartilage forms all other bones
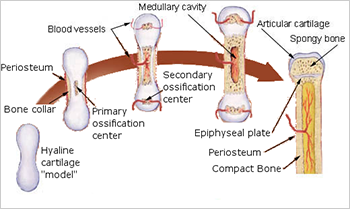
Describe the process of endochondral ossification
As a fetus you have cartilage bone → osteoblasts enter perichondrium and starts mineralization, which kill cartilage cells, creates a bone collar that stabilizes the growing bone. At the same time hypertrophic cartilage cells secrete an enzyme to break-up cartilage matrix in preparation for osteoblasts→Primary ossification center forms as periosteal bud moves in delivering an artery, neuron, nerves, osteogenic cells, bone marrow elements starts ossification, killing cartilage cells, replacing them with osteoblasts. → secondary ossification center happens in the epiphysis, same process as before, occurring at the same time. Osteoclasts will break down bone forming a medullary marrow cavity, spongy bone is formed. → bone continues to grow length by replacing cartilage at the epiphyseal plate and articular cartilage. It grows in width by ossification at periosteum and osteoclasts continue to make spongy bone from compact bone
Osteogenic cells make…
Osteoblasts
Osteoblasts
do active mitosis, secrete bone matrix called the osteoid and deposit minerals into osteoid to harden bone. they can become osteocytes
Osteocytes
monitor and maintain bone health, communicate with osteoblasts to make more bone with osteoclasts
Osteoclasts
break down and recycle bone, release calcium to blood stream when needed, and maintain bone thickness