Self-report techniques
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Questionnaires
participants provide information relating to their thoughts, feelings and behaviour. Can comprise of open questions, closed questions or a mix of both
self-report techniques
questionnaires and interviews
Open questions
allows participants to answer how they wish, generating qualitative data as there is no fixed number of responses to select from. Provides rich data that provides insight
Strength of open question questionnaires
Less chance of researcher bias, especially if it is anonymous, where participant can answer questions in their own words, without input from the researcher.
Limitation of open question questionnaires
Social desirability bias, so lacks validity
Closed questions
restricts the participant to a predetermined set of responses, generating quantitative data. There are different types: checklist, Likert response scale and ranking scale
checklist
participants tick the answer(s) that apply to them
e.g. What is the highest academic qualification you hold?
GCSEs
A-Levels
Bachelor’s degree
Postgraduate degree
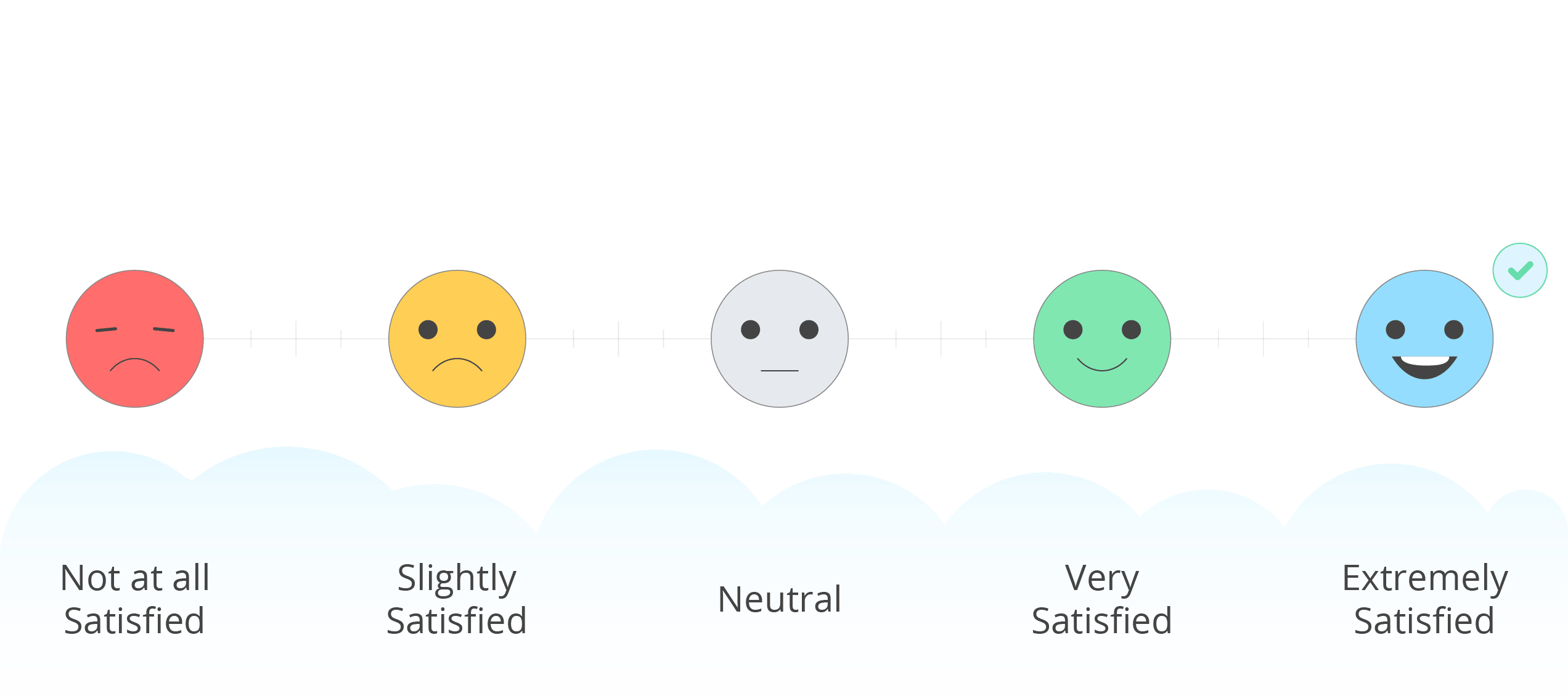
Likert response scale
participants rate on a scale their views/opinions on a question
e.g. Psychology is the most interesting A-Level subject (Circle the number that applies)
ranking scale
participants place a list of items in their preferred order
e.g. rank the following activities according to how much time you spend on them each day (1 = most time, 4 = least time)
Talking face-to-face
Talking on the phone
Text messaging
Other
strength of closed question questionnaire
Collects quantitative data which makes it easy to analyse the results statistically or in a graphical format. This means direct comparisons can be made between groups so trends can be found and more research can be conducted
limitation of closed question questionnaires
less detailed responses
response bias which could be due to participants not fully reading the questions, so the data may lack internal validity
Factors that should be considered when making a questionnaire
simple and clear terminology
short
avoid personal questions
no leading questions
no questions that make assumptions
use a pilot study and modify the questionnaire
Interviews
usually face-to-face but can happen over the phone. There are 3 different interview designs: participants answering a predetermined list of questions (structured interview), relaxed conversation (unstructured interview), or a mix of the two (semi-structured interview). Responses are usually recorded, using an interview schedule that the interviewer completes and/or audio or video recording, with the informed consent of the interviewee(s)
structured interview
predetermined list of questions, in which participants are asked in the exact same order for each interviewee taking part. Interviewer uses an interview schedule and will sometimes record the answers to each question by taking notes or ticking boxes on their schedule
strength of structured interviews
Collects quantitative data which is easy to statistically analyse, leading to comparisons being made between groups so the researcher can look for trends in the data. Easy to replicate due to the standardised procedures
limitation of structured interviews
Investigator effects. Body language etc may give accidental bias. Can also occur between researchers when there is more than one researcher conducting the interviews
Interviewers cannot elaborate - limits richness of data
unstructured interviews
conducted like a conversation, in which the interviewer facilitates a discussion rather than asking set questions. Very little is decided in advance, so this type of interview produces lots of qualitative data. Answers will usually be audio or video recorded as writing would be very difficult for the interviewer and it would also spoil the relaxed environment
strength of unstructured interview
increases validity of findings by reducing investigator effects
Reduces demand characteristics due to open questions being used
Greater flexibility
limitation of unstructured interviews
generates lots of qualitative data that is hard to be statistically analysed - need to use content analysis to find trends in data
time consuming and expensive - requires a trained psychologist
semi-structured interviews
mostly prepared questions that can be supplemented with additional questions as seen fit by the interviewer. Usually produces rich qualitative data
strengths of semi-structured interviews
Increases validity of findings. Reduces social desirability bias because of the use of open questions
Rich qualitative data
limitation of semi-structured interviews
uses qualitative data so is harder to analyse
time consuming and expensive
higher chance of demand characteristics
Criteria for a good questionnaire
avoid jargon
Avoid double-barrelled questions
Avoid leading questions
Criteria for a good interview
interview schedule - standardised list of questions to reduce bias
Quiet room - more likely interviewee opens up
Rapport - start with neutral questions to make participant feel relaxed
Ethics - remind them answers will be treated in confidence