MMI 188a: ch. 13-16
1/790
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
791 Terms
Pathogen
An agent that can cause disease in healthy individuals.

Opportunistic Pathogen
An agent that causes disease only when host defenses are weak.
Obligatory Steps for Pathogens
Attachment and entry into host cell, multiplication, local or systemic spread in the body, evasion of host defense mechanisms, transmission.
Stages of an Infection
Infectious microorganism enters through epithelial tissues, adheres to epithelial cells, crosses the epithelium, and may trigger local innate immune response.
Local Innate Immune Response
May prevent an infection from being established.
Adaptive Immune Response
Initiated by the innate response to help clear the infection.
Survival Strategies of Pathogens
Rapid replication, evasion of host response, inducing a minimal response, antigenic variation, suppression of host response.

Macrophages
Found in healthy tissues, long-lived, survive after phagocytosis of pathogen.
Neutrophils
Found only in inflamed tissues, short-lived, die after phagocytosis of pathogen.
Genetic Variation of Pathogens
Prevents effective long-term immunity.
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Causes bacterial pneumonia, otitis media, meningitis.

Serotypes of S. pneumoniae
Different strains have antigenically different capsular polysaccharides.
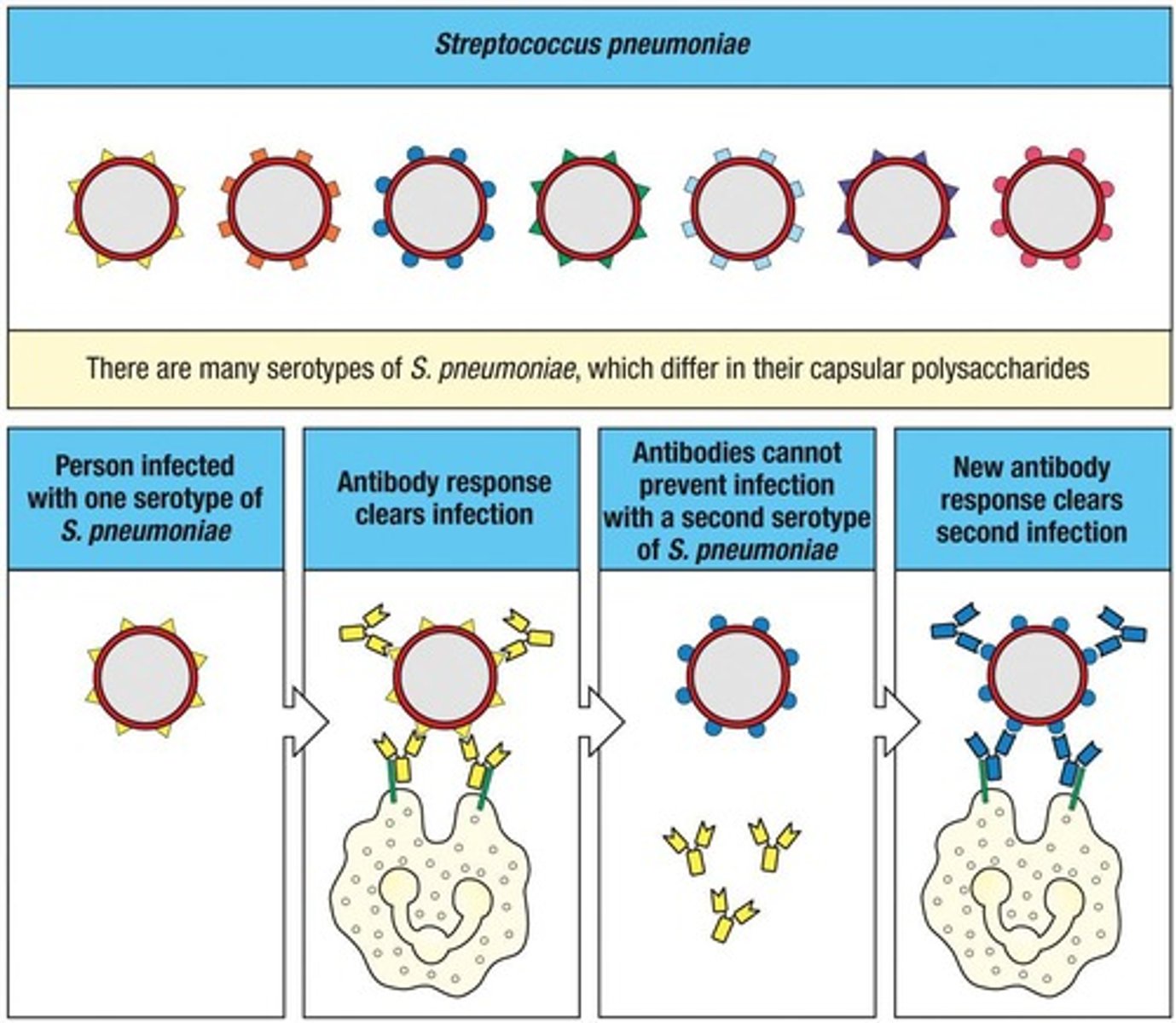
Opsonization
Antibodies against capsular polysaccharides bind to the pathogen to facilitate phagocytosis.
Type-Specific Antibody
Clears the infection with one serotype of S. pneumoniae but provides no protection against a different serotype.
Primary Immune Response
Required to clear a second infection with a different serotype of S. pneumoniae.
Inflammation Phase Response
Rapid increase in neutrophils during acute inflammation.
Phagocytosis
The process by which pathogens are engulfed and destroyed by immune cells.
Epithelial Tissues
The entry point for infectious microorganisms.
Innate Immune Response
Helps to contain the infection and delivers the infectious agent to local lymph nodes.
Dendritic Cells
Carry the infectious agent to local lymph nodes.
Antigenic Variation
A strategy used by pathogens to evade the immune system.
Suppression of Host Response
A survival strategy employed by pathogens.
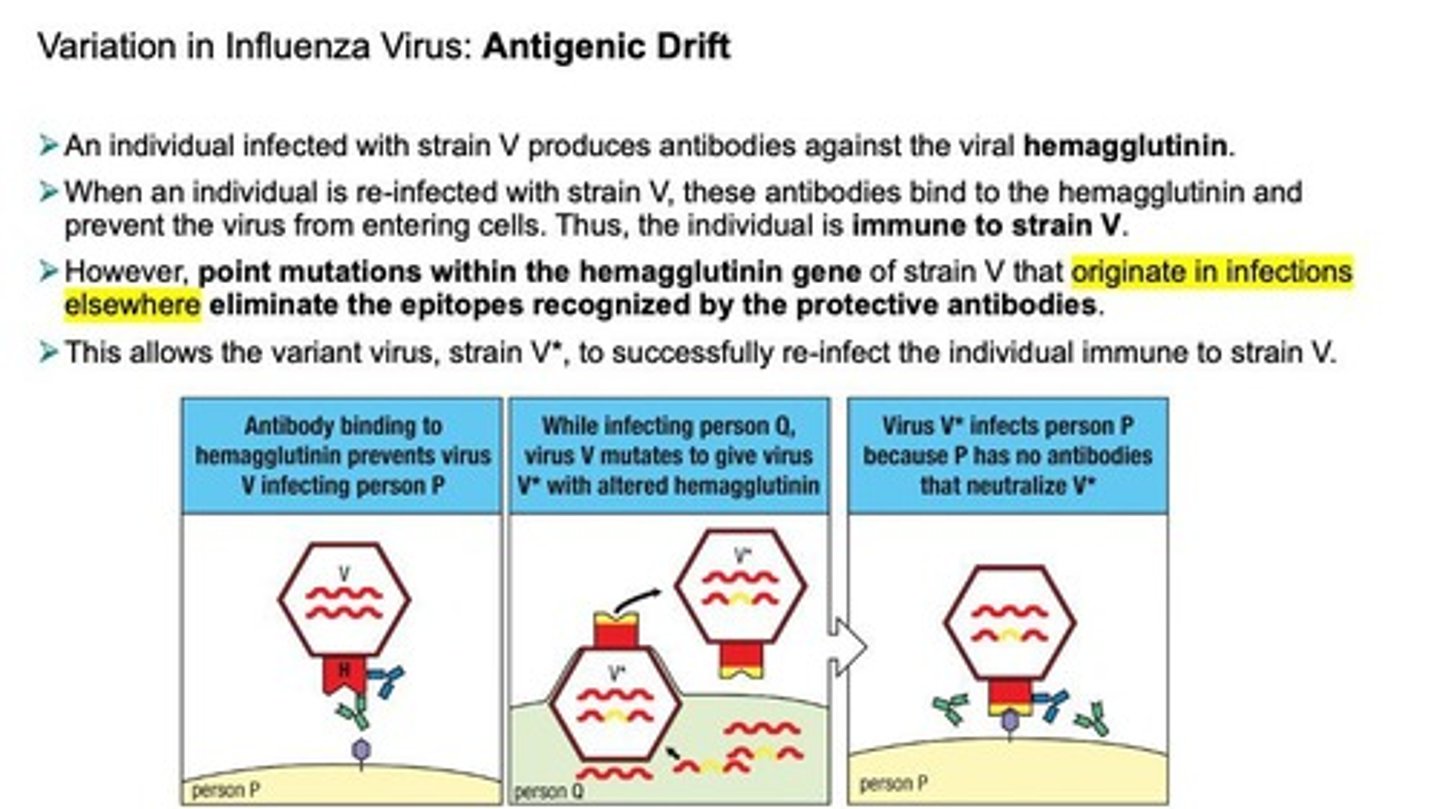
Antigenic Drift
Antigenic variation in Influenza due to accumulation of point mutations.
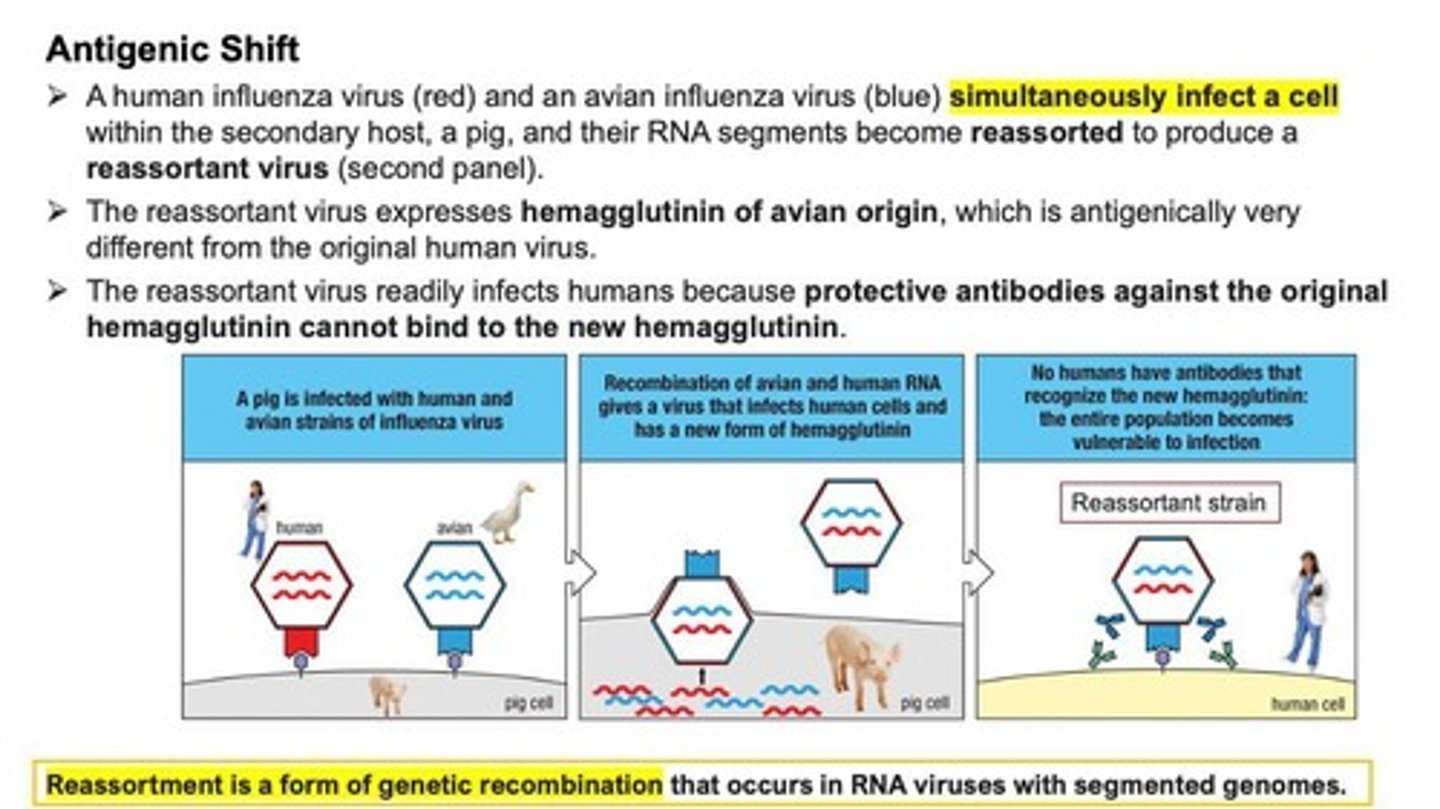
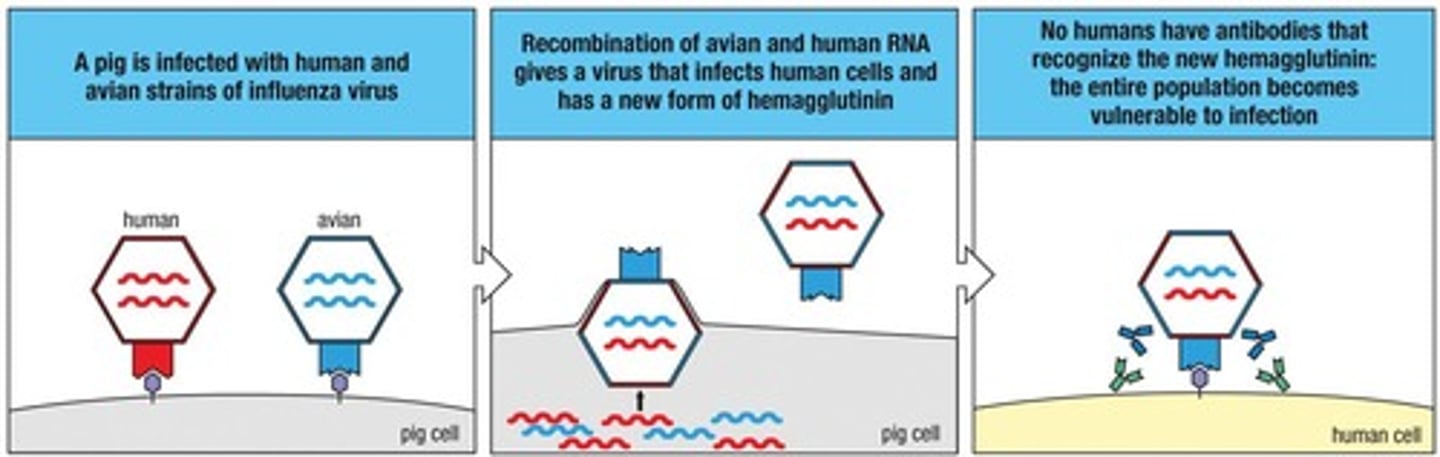
Antigenic Shift
A process where a human influenza virus and an avian influenza virus simultaneously infect a cell and their RNA segments become reassorted to produce a reassortant virus.
Influenza Virus
RNA virus whose genome has 8 RNA segments, causes rapidly spreading, but short-lived epidemics of respiratory tract infections, and every 10-50 years causes a worldwide pandemic.
Mutation
A change in the viral genome that leads to Antigenic Drift.
Reassortment
A form of genetic recombination that occurs in RNA viruses with segmented genomes.
Hemagglutinin
A viral protein that is targeted by antibodies produced during an infection.
Neuraminidase
Another viral protein subject to antigenic drift, similar to hemagglutinin.
Strain V
An influenza virus strain that can elicit an immune response in an infected individual.
Strain V*
A variant of strain V that can re-infect individuals immune to strain V due to point mutations.
Epitopes
Specific parts of the viral hemagglutinin recognized by protective antibodies.
Reassortant Virus
A virus produced from the reassortment of RNA segments from different influenza virus strains.
Secondary Host
An organism, such as a pig, that can be infected by both human and avian influenza viruses, facilitating reassortment.
Protective Antibodies
Antibodies that bind to hemagglutinin and prevent the virus from entering cells.
Pandemic
A worldwide outbreak of a disease, such as influenza, that can occur every 10-50 years.
Point Mutations
Small changes in the viral genome that can lead to antigenic drift.
Viral Infection
The process by which a virus enters cells and replicates, leading to disease.
Epidemic
A rapid spread of a disease within a specific population or area.
Infectious Cells
Cells that can be infected by a virus, leading to further spread of the virus.
Neutralizing Antibodies
Antibodies that effectively prevent viral infection by binding to specific epitopes.
Gene Reassortment
A process in which genes are rearranged to create new combinations, often seen in viruses like influenza.
Trypanosomes
A genus of parasitic protozoa that can change surface antigens through gene rearrangements.
Trypanosoma brucei
A species of Trypanosome that causes African trypanosomiasis, leading to sleeping sickness.
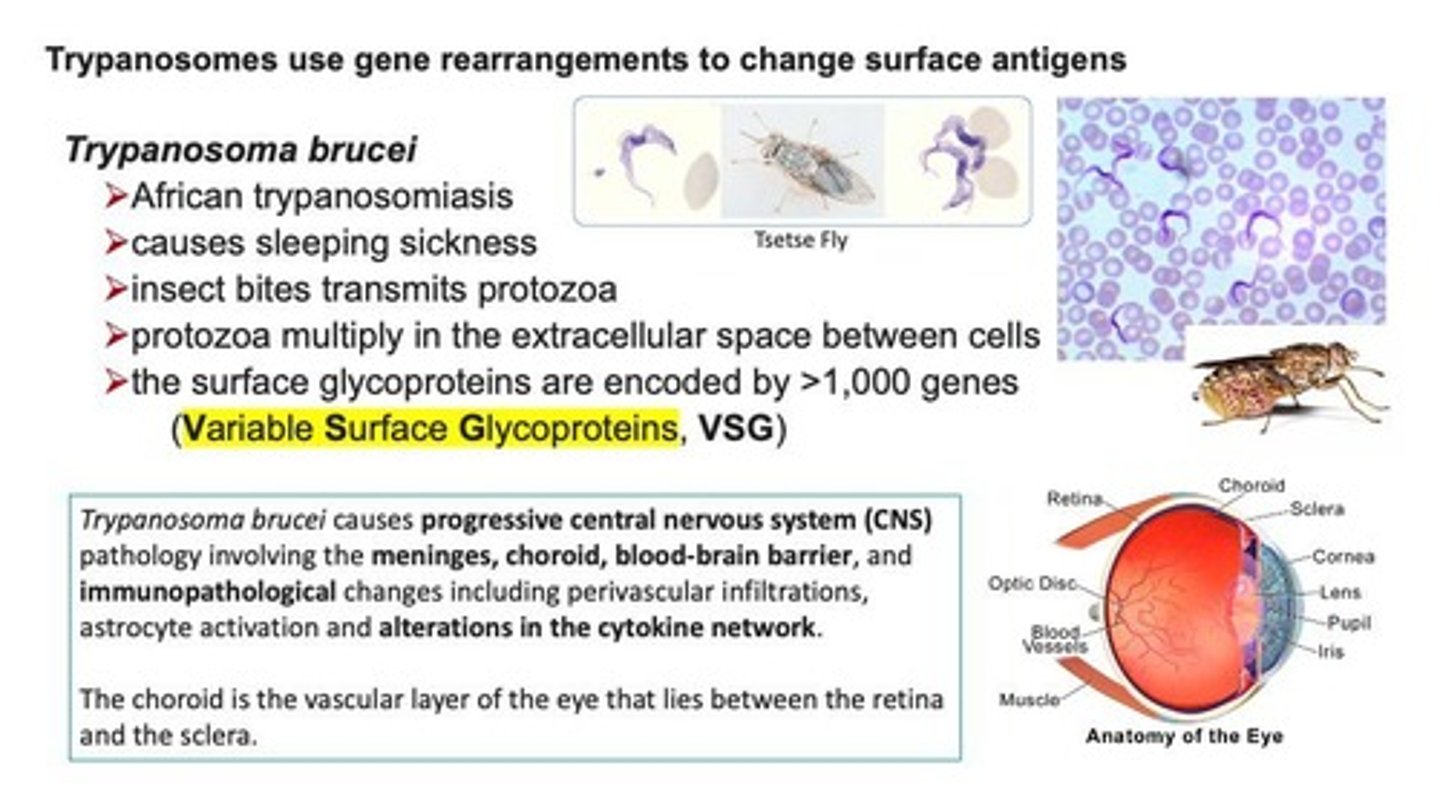
Tsetse Fly
An insect that transmits Trypanosoma brucei to humans.
African trypanosomiasis
A disease caused by Trypanosoma brucei, characterized by symptoms such as sleeping sickness.
Sleeping Sickness
A disease caused by the bite of the tsetse fly infected with Trypanosoma brucei.
Protozoa
Single-celled organisms that can multiply in the extracellular space between cells.
Variable Surface Glycoproteins (VSG)
Surface glycoproteins encoded by more than 1,000 genes in Trypanosoma brucei.
Progressive CNS Pathology
A condition caused by Trypanosoma brucei infections that affects the central nervous system.
Meninges
The protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
Choroid
The vascular layer of the eye that lies between the retina and the sclera.
Blood-brain barrier
A selective permeability barrier that protects the brain from pathogens and toxins.
Immunopathological changes
Alterations in immune response due to infections, including perivascular infiltrations and cytokine network changes.
Gene Conversion
A process where one gene replaces another at the expression site, as seen in VSG genes.
Chagas Disease
A disease caused by Trypanosoma cruzi, characterized by its ability to hide from the immune system.
Trypanosoma cruzi
A species of Trypanosome that causes Chagas disease and does not have VSGs.
Lysozyme
An enzyme that breaks down bacterial cell walls, which T. cruzi escapes from.
California Chagas Disease Statistics
California has up to 100,000 people infected with Chagas disease, primarily from Latin America.
Kissing Bugs
Insects capable of transmitting Chagas disease, with Triatoma protracta being the most common in California.
Latino Population Infection Rate
1% of the Latino population in Los Angeles is infected with Chagas disease.
Antiparasitic Medications
Medications used to treat parasitic infections that may have serious side effects.
Herpes simplex viruses
Cause cold sores (HSV-1) and genital herpes (HSV-2).
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
Causes chickenpox and shingles.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
Causes mononucleosis and cancer.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Causes birth defects and disease in newborns and immunosuppressed patients (retinitis, hepatitis, colitis, pneumonia, encephalitis).
HHV-8
Causes Kaposi's Sarcoma (KS) in immunosuppressed patients.
Acute infection
A type of infection caused by herpes viruses.
Reactivated Infections
Include recurrent herpes and zoster (shingles).
Certain cancers
Include lymphoma, KS, and nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV)
Interferes with MHC Class I function in many ways.
CMV immune response blocking
Involves 10 different proteins produced by CMV.
Persistence of HSV
The virus enters sensory neurons and persists in a latent state.
Cold sores
Manifestation of tissue damage after the immune response clears the initial HSV infection.
Transmission of HSV
Easier during the active phase of infection.
Bacterial superantigens
Bind α:β T cell receptors and MHC class II in a non-specific manner.
Cytokine storm
A massive but inappropriate response caused by superantigens leading to high levels of proinflammatory cytokines.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin (TSST-1)
An example of a superantigen.
Staphylococcal Superantigen-Like Protein 7 (SSLP7)
Evasion of IgA-mediated defense by blocking IgA from binding to FcαR1 receptor.
IgA
A type of antibody that plays a crucial role in mucosal immunity.
FcαR1
Receptor on phagocytes that interacts with IgA.
Complement-mediated killing
A mechanism for disposing of bacteria that SSLP7 prevents.
SSLP7
Staphylococcal superantigen-like protein 7 that binds to both C5 and the Fc region of IgA, preventing IgA from binding to FcαRI or activating complement-mediated killing of bacteria.
Primary immunodeficiency syndromes
Comprise eight functional groups that affect the immune system.
X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia (XLA)
A condition where B cells do not develop beyond the pre-B cell stage due to a defective Bruton's kinase (BTK), leading to recurrent bacterial infections.
Bruton's kinase (BTK)
A protein that is defective in XLA, preventing the pre-B-cell receptor from generating intracellular signals.
Pre-B-cell stage
The developmental stage of B cells that is not progressed beyond in XLA due to the inability to generate intracellular signals.
Heterozygous females in XLA
Carriers of the XLA trait who are healthy because one X chromosome is randomly inactivated.
C1INH
A protease inhibitor that permanently inhibits C1r and C1s, preventing their activation.
Hereditary angioedema
A syndrome associated with C1INH deficiency.
Granuloma
An aggregation of macrophages that forms in response to chronic inflammation to isolate foreign substances that the immune system cannot eliminate.
Complement deficiency diseases
Diseases caused by deficiencies in the pathways of complement activation, leading to immune complex diseases characterized by antigen-antibody deposition.
Immune complex diseases
Inflammatory conditions characterized by antigen-antibody deposition and activation of complement, with common manifestations including glomerulonephritis, synovitis, and dermal vasculitis.
Defects on phagocytic cells
Genetic defects affecting phagocytes that cause persistent bacterial infections.
C1r and C1s
Enzymes that are inactivated by C1INH, preventing complement activation.
Protease inhibitors
A class of proteins, including C1INH, that act as pseudosubstrates and form permanent covalent linkages with proteases.
Chronic inflammation
A prolonged inflammatory response that can lead to the formation of granulomas.
Antigen-antibody deposition
The accumulation of immune complexes that can lead to immune complex diseases.
Glomerulonephritis
A common manifestation of immune complex diseases characterized by inflammation of the kidney's filtering units.
Synovitis
Inflammation of the synovial membrane, often associated with immune complex diseases.