chapter 12 final flashcards
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What are the four main types of intermolecular forces?
Dispersion, dipole–dipole, hydrogen bonding, ion–dipole.
Order IMFs by strength (weakest → strongest).
Dispersion < dipole–dipole < hydrogen bonding < ion–dipole.
How does IMF strength affect boiling point, melting point, viscosity, and vapor pressure?
↑ IMF → ↑ BP, ↑ MP, ↑ viscosity, ↓ vapor pressure.
What formula is used for heating/cooling within a phase?
q=mcΔT
What formula is used during a phase change?
q=nΔHfus/vap.
What is the triple point on a phase diagram?
The condition where solid, liquid, and gas coexist in equilibrium.
What is the critical point on a phase diagram?
The end of the liquid–gas line; beyond it is a supercritical fluid.
Why does water’s solid–liquid line slope negatively?
Ice is less dense than liquid water, so pressure favors melting.
What equation relates vapor pressure and temperature?
Clausius–Clapeyron
ln(P2/P1) = - ΔHvap/R (1/T2 - 1/T1)
Atoms per unit cell, coordination number (CN), and packing efficiency for simple cubic unit cell
sc = 1 atom
CN=6
packing efficiency: 52%
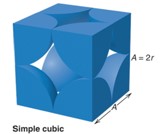
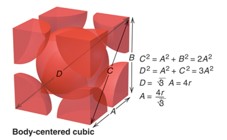
Atoms per unit cell, coordination number (CN), and packing efficiency values for body centered cubic unit cell?
bcc = 2 atoms,
CN=8
packing efficiency: 68%
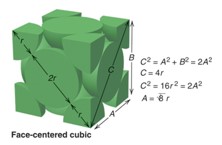
Atoms per unit cell, coordination number (CN), and packing efficiency for face centered cubic unit cell
fcc = 4 atoms
CN=12
packing efficiency: 74%
Relationship between edge length and radius for simple cubic unit cell
sc: a=2r
Relationship between edge length and radius for body centered cubic unit cell
bcc: a = 4r / √3
Relationship between edge length and radius for face centered cubic unit cell
a = 4r / √2
What is the difference between crystalline and amorphous solids?
Crystalline = ordered repeating structure; amorphous = no long-range order.
Compare ΔHfus vs ΔHvap.
ΔHvap > ΔHfus (takes more energy to separate molecules fully).
What is the critical temperature?
The highest temperature at which a substance can exist as a liquid (above this, it becomes a gas no matter how much pressure you apply).
What conditions are required for hydrogen bonding?
H covalently bonded to N, O, or F + lone pair on N/O/F.
Why is ice less dense than liquid water?
Open hydrogen-bonded lattice structure.
What is the coordination number?
The number of nearest-neighbor atoms surrounding one atom.
What distinguishes metallic, ionic, covalent, and molecular solids?
Metallic → conductive, malleable.
Ionic → brittle, high MP, conduct only molten/solution.
Covalent network → hard, high MP (diamond, SiO₂).
Molecular → weak IMFs, low MP (ice, CO₂).
Which unit cell structure has the highest packing efficiency?
Face-centered cubic (FCC, 74%).
Why do metals conduct electricity?
They have a “sea of delocalized electrons” that move freely throughout the metallic lattice.
Why are metals malleable and ductile?
In metals, atoms are held together by a sea of electrons, so the atoms can slide past each other without the metal breaking. (non directional metallic bonding)
Why are ionic solids poor conductors as solids but good conductors when molten or in solution?
In solid form, ions are fixed in the lattice. In liquid/solution, ions are mobile and carry charge.
Why are covalent network solids (like diamond or quartz) non-conductive?
All electrons are localized in strong directional bonds (no free electrons).
What exception in covalent network solids is conductive? Why?
Graphite — has delocalized electrons between layers, so it conducts electricity.
Why is ice less dense than liquid water?
Ice forms an open hydrogen-bonded lattice with lots of empty space; liquid water packs more closely.
What is a lattice?
A 3D repeating arrangement of particles (atoms, ions, or molecules) that defines the structure of a solid.
What holds ionic lattices together?
Strong electrostatic forces between cations and anions.
Why are ionic solids brittle?
If the layers in an ionic solid move, like-charged ions are brought into close proximity, they repel each other, and the solid breaks (directional bonding)
Which types of solids are best electrical conductors, poor conductors, and insulators?
Metals (metallic solids) = best conductors
Ionic solids = conduct only when molten/aqueous
Molecular & covalent network (except graphite) = insulators
How do you convert picometers (pm) to centimeters (cm)?
1pm=1×10^−10 cm.
What happens to a in the density formula?
It must be cubed: a³ gives the volume of the unit cell in cm³.
Formula for density from a unit cell? What does each unit mean? What is the final unit?
Z: number of atoms per unit cell
M: molar mass in (g/mol)
NA = Avogadro’s number 6.022 × 10²³ particles/mol
a = edge length (cm)
What is the final unit: g/cm³
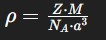
What is Avogadro’s number? And what does it tell us?
6.022 × 10²³ particles/mol
It tells how many atoms, molecules, or formula units are in exactly 1 mole of a substance.