Aromatic chemistry
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Describe the bonding in benzene
Each C has 3 covalent bonds
Spare electrons in p orbital overlap causing delocalisation
Describe the shape of benzene
Planar molecule, 6-carbon ring, C-C bonds equal in length (intermediate between C-C and C=C)
Describe the stability of benzene
The expected enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexatriene is -360 kJ mol^-1, but the actual value for benzene is less exothermic by 152 kJ mol^-1, so benzene is more stable
Why do substitution reactions occur in benzene in preference to addition reactions?
Addition reactions would involve breaking up the delocalised system
Which form of substitution reactions does benzene undergo and why?
Electrophilic, because benzene has a high electron density and so attracts electrophiles
Give the change in functional group during the nitration of benzene
Benzene to nitrobenzene
Give the reagents needed for the nitration of benzene
Conc. nitric acid in the presence of conc. Sulfuric acid catalyst
State the name of the mechanism of the nitration of benzene
Electrophilic substitution
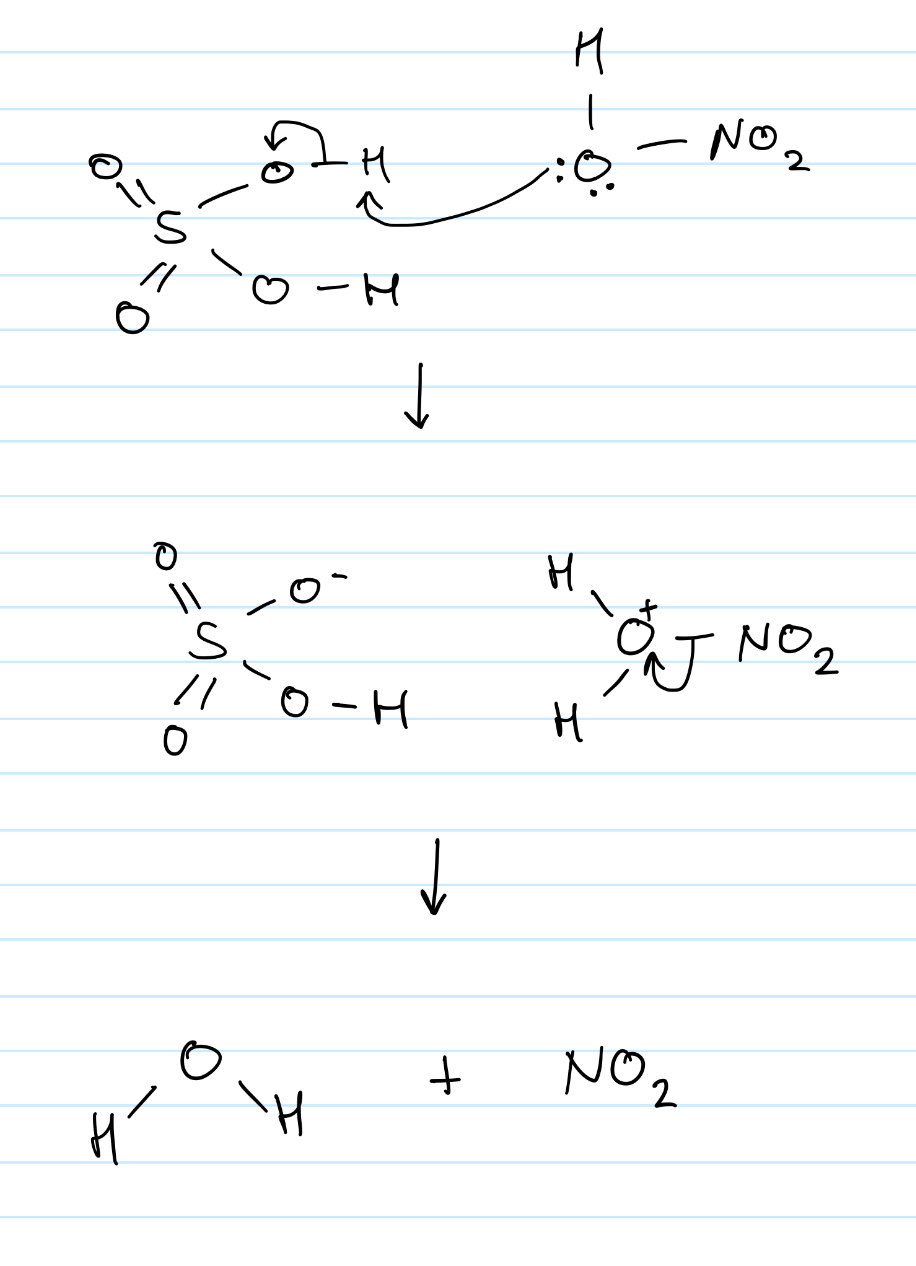
Give the formula of the electrophile used in the nitration of benzene
+NO2
Give the overall equation for the formation of the electrophile in nitration of benzene
HNO3 + 2H2SO4 —> +NO2 + 2HSO4- + H2O
Draw the 2-step mechanism for the formation of the electrophile in nitration of benzene
What temperature is the nitration of benzene carried out at?
60 °C
Why aren’t temperatures higher than 60°C used during nitration of benzene for production of aromatic amines?
At higher temperatures, multiple substitutions can occur and it is vital only one occurs for production of aromatic amines
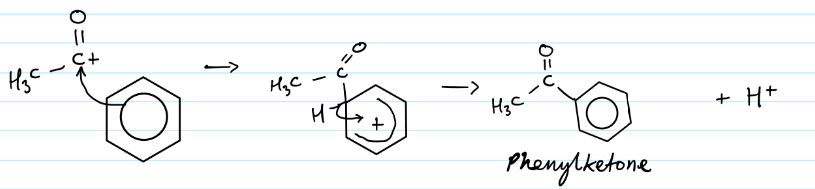
Give the change in functional group during friedel crafts acylation of benzene
Benzene to phenyl ketone
Give the equation for the formation of the electrophile used in acylation of benzene
AlCl3 + R-COCl —> R-CO+ + AlCl4 -
Draw the mechanism for the acylation of benzene using
State the type of mechanism for acylation of benzene
Electrophilic substitution
Give the reagents and conditions needed for acylation of benzene
acyl chloride in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride catalyst, heat under reflux
Give the equation for the reform of AlCl3 catalyst in acylation
H+ + AlCl4 - —> AlCl3 + HCl
Give the reagents and conditions for the reduction of nitroarenes to aromatic amines
Sn/HCl OR H2/Ni, heating
Give the full equation for the reduction of nitrobenzene
C6H5(NO2) + 6 [H] —> C6H5(NH2) + 2H2O
How does the delocalisation affect the C-Cl bond in chlorobenzene?
Made stronger, so typical haloalkanes substitution and elimination reactions don’t occur, the electron rich benzene ring will repel nucleophiles
How does delocalisation affect the C-O and O-H bonds in phenol?
Makes C-O stronger and O-H weaker
How does delocalisation affect the base strength of phenylamine?
Less basic than aliphatic amines as lone pair is delocalised and less available for accepting a proton
Give a use of phenyl ketones
Pharmaceuticals