Chapter 18 - soft tissue injuries + bleeding
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
blunt trauma
an injury to the body caused by forceful impact with a dull object or surface, without the skin being pierced
care for external bleeding
BSI and PPE
direct pressure w/ sterile dressing
apply pressure bandage (once blood isn’t soaking through dressing)
elevate wound (if no fractures)
if bleeding doesn’t stop, apply tourniquet
care for shock
oxygen
blanket
lay supine
how to apply pressure bandage
place a few layers of clean dressing over wound (maintain pressure)
use roller bandage or cravat
tightly wrap around dressing and wound (above and below wound as well)
check distal CSM (re-tie if no pulse)
applying touriquet
place pressure bandage over wound
put on tourniquet
check distal pulse (there SHOULD be NO pulse)
write time of application
care for shock, dont cover tourniquet
hemostatic dresssing function
helps promote blood to clot
recognizing internal bleeding
most often caused by blunt trauma (or penetrating wound)
bruises
vomiting or coughing up blood
rigidity or distension (swelling)
vaginal or rectum bleeding
signs of shock
Care for Internal Bleeding
BSI
primary assessment (ABC’s)
likely high concentration oxygen
secondary assessment (look for evidence of trauma)
care for shock
reassure patient - keep them calm
rapid transport to trauma center
what does multisystem trauma lead to?
it leads to to quicker death because the body can’t compensate as well
what is as soft tissue injury
damage to the skin, muscles, nerves, blood vessels, or any of the connective tissues that hold these structures together
care for open wounds
PPE
primary assessment (care for breathing and airway first)
expose wound
wipe wound with sterile gauze pad
control bleeding
administer oxygen (if needed)
keep patient lying still - care for shock
transport and comfort patient
penetrating wound care
same as open wounds but DO NOT remove object AND stabilize object w/ bulky dressing
how to preserve amputated body parts
wrap in sterile gauze
put in plastic bag or plastic wrap
if possible, keep it cool (NOT cold)
what is an evisceration?
protruding organ. Place moist, sterile dressings over it and cover dressing with plastic covering
care for any head/face injuries
be careful of neck injuries and skull fractures (apply pressure on edges of wound if fracture).
Care is same as any other open wound
implaled object through cheek care
If there’s an impaled object through the cheek into the mouth, it' may need to be removed
place dressing between wound and patient’s teeth. Leave some dressing outside of mouth, so patient doesnt swollow it
position patient so blood flows out mouth - not back into throat
pack against inside wound
dress + bandage outside wound
care for shock
care for light burns to eyes
apply dark patches over both eyes
chemical burns eye care
flush eye for 20 minutes (clean water - does not have to be sterile)
after, cover eyes with loose moist dressings
care for ear injuries
Cuts. Apply dressings and bandage in place.
Tears. Apply bulky dressings, beginning with several layers behind the torn tissue.
Avulsions. Use bulky dressings bandaged into place. Save the avulsed part in a plastic bag or plastic wrap. Keep the part dry and cool. If no plastic is available, then wrap in dressing material. Be certain to label the bag, wrap, or dressing with the patient’s name.
recognizing neck injuries
Difficulty speaking, loss of voice
Difficulty swallowing
Obvious swelling or bruising of the neck
Pain on swallowing or speaking
Obvious cuts or puncture wounds
care for neck injuries
direct pressure to wound (using palm)
apply occulsive dressing or plastic cover to wound.
tape to seal the dressing down
care for shock
minor vs significant SUPERFICIAL (2nd degree) burn
minor burn if: covers less than 9 percent of BSA (body surface area)
significant: more than 9%, OR less than 9% if burns on face, hands, feet, major joints, groin, or involved respiratory system
rule of 9s
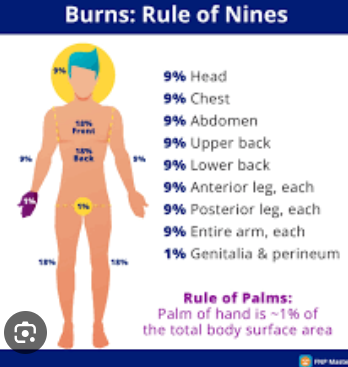
care for burns
Stop the burning process immediately. This may require the patient to stop, drop, and roll to extinguish the flames. You might also have to smother the flames and wet down or remove smoldering clothing.
Flush superficial burns with water (or saline) for several minutes. For partial- or full-thickness burns, do not flush with water unless they involve an area of less than 15% of the total BSA. Flushing large burn areas may cause the patient to become chilled. Follow local protocols.
Remove smoldering clothing and jewelry. Do not remove any clothing that is melted onto the skin.
Continually monitor the airway. Any burns to the face or exposure to smoke may cause airway problems. Administer oxygen per local protocols.
Prevent further contamination. Keep the burned area clean by covering it with a dressing. Infection is common with burns.
Cover partial- and full-thickness burns with dry, sterile dressings if available. In some EMS systems, you may be instructed to moisten dressings before placing them on the patient. Otherwise, place dry, sterile dressings onto the burned area. Follow local protocols.
If the eyes or eyelids have been burned, place clean dressings or pads over them. Moisten these pads with sterile water if possible.
If a serious burn involves the hands or feet, always place a clean pad between toes or fingers before completing the dressing.
Provide oxygen and care for shock.
card for electrical burns
Perform a scene size-up and take appropriate BSI precautions.
Perform a primary assessment and ensure an open airway and adequate breathing.
Evaluate the burn. Look for two burn sites: an entrance and an exit wound. The entrance wound (often the hand) is where the electricity entered the body. The exit wound is where the electricity came into contact with a ground (often a foot). The entrance wound may be small, and you may need to look very carefully for it. The exit wound may be large and obvious.
Apply dry, clean dressings to the burn sites. You may apply moistened dressings if transport is delayed, the burn involves less than 9% of the body surface area, and the patient will not be in a cold environment.
Provide oxygen and care for shock.