Skeletal and Appendicular Muscles
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
4 categories that skeletal muscles are classified by
Action, origin, insertion, function
When muscle the contracts the insertion is brought closer to the ___
origin
Insertion
the end of the muscle that attaches to the bone that it moves
Origin
The starting end of the muscle
Agonist
Muscle that is the primary mover/causes main action in a muscle group
Synergist
Muscles that works to support the main movement
Antagonist
Makes the opposite movement as the agonist
Muscle group
group of muscles that works to achieve the same movement
Superior limbs
Anterior group: flexion, posterior group: extension
Inferior Limbs
Anterior group: extension, Posterior group: flexion
Maximus
largest
Minimus
Smallest
Longus
Longest
Brevis
Shortest
Deltoid
Triangle (delta)
Recuts
Straight fibers (orientation)
Oblique
Diagonal muscle fibers
teres
round or cylinder shaped muscle
adduction
adding it back to the body
abductor
taking away form the midline
masseter
muscle in jaw, agonist in mastication
Oblique
diagonal or slanted, muscles in the abdomen
Fusiform
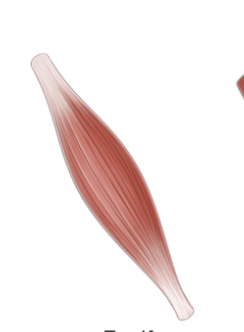
Parallel
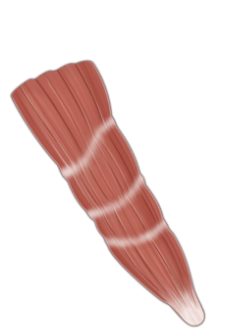
Bipennate
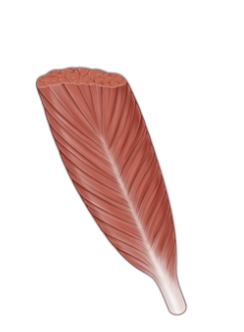
Unipennate
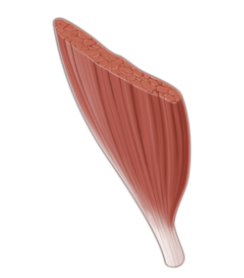
Circular

Convergant
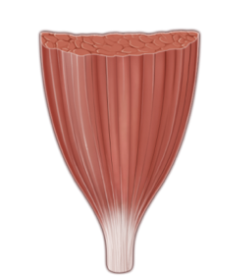
Multipennate

Fixator
Stabilizes the joints crossed by the prime mover, prevent movement of the origin by the prime mover
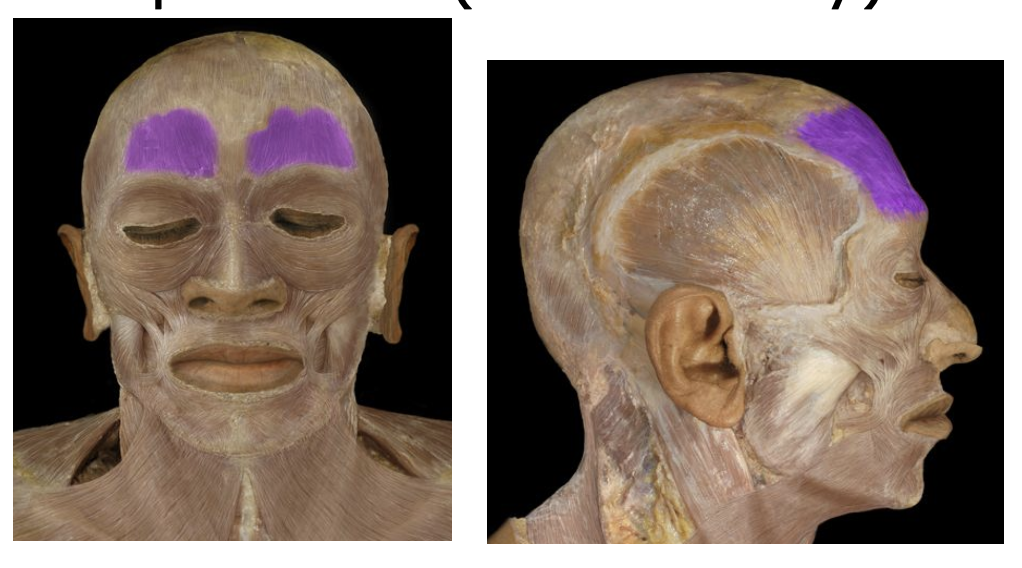
Epicranius Frontalis
Raises the eyebrows
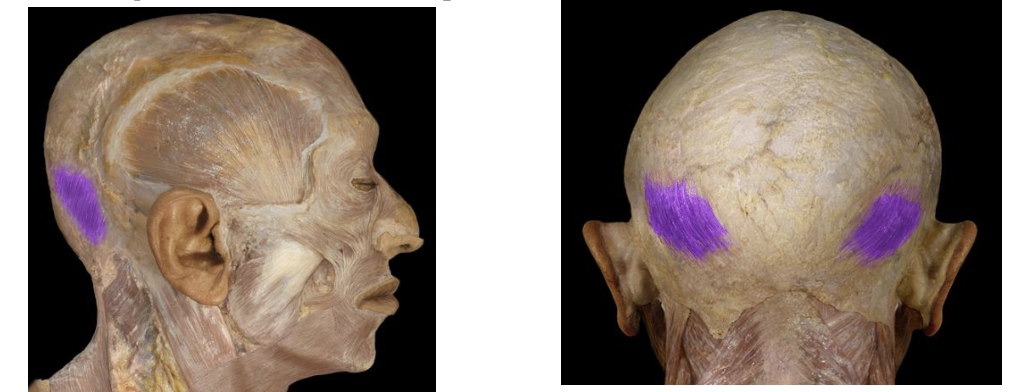
Epicranius Occipitalis
Fixes the connective tissue and pulled the scalp backwards
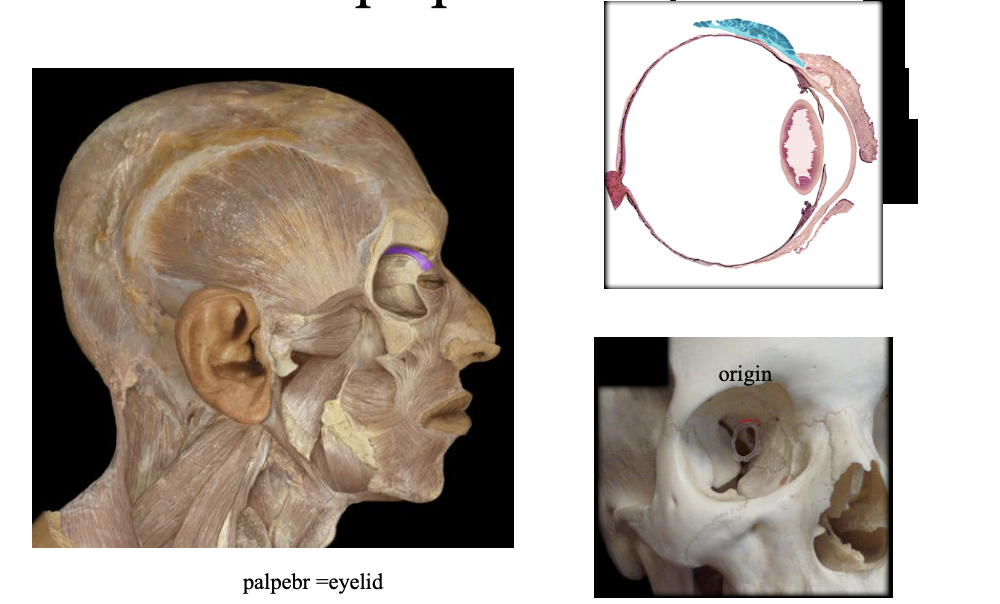
Levator Palpebrae Superioris- 2
Above the eye, attaches to the inside of the skin of the upper eyelid. Opens the eye
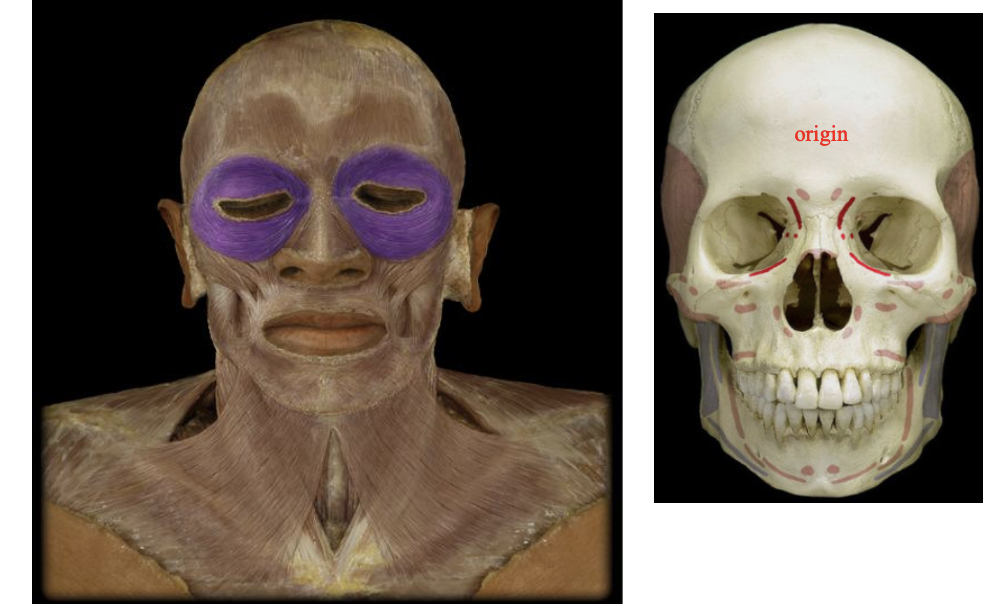
Orbicularis Occuli - 2
circular muscle around the eye., Shuts the eye
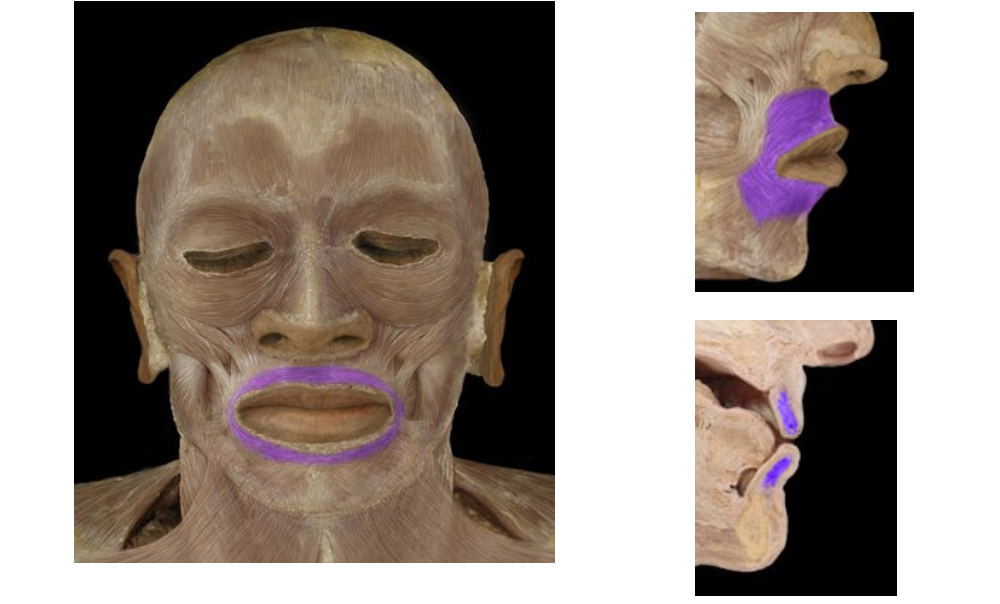
Orbicularis Oris
Circular Muscle around the mouth. Forces the lips closed and puckers the lips
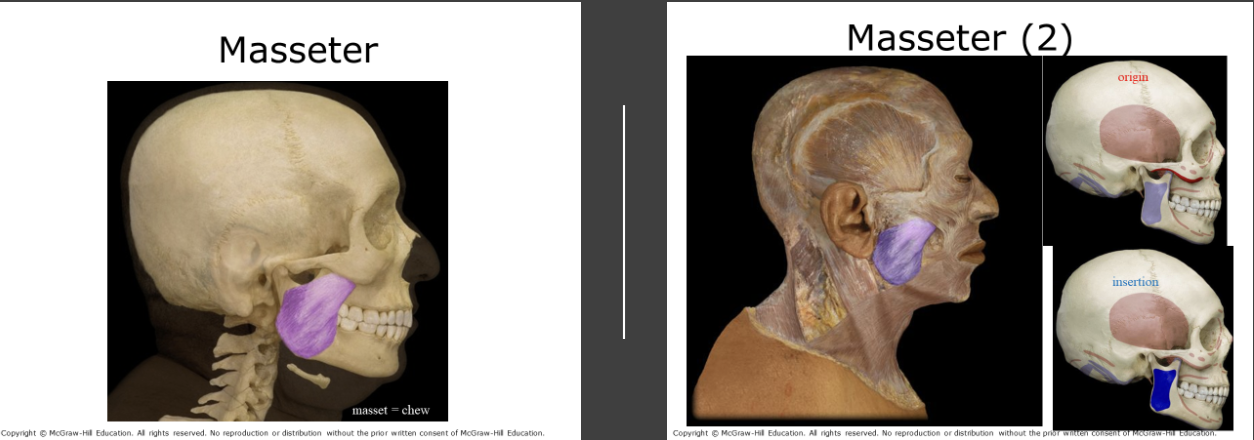
Masseter
On the surface of the mandible, aids in mastication
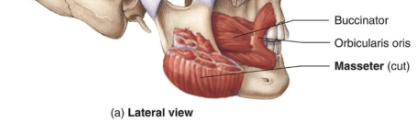
Buccinator
Thin, flat muscle in the cheek area, compresses puffed out cheeks
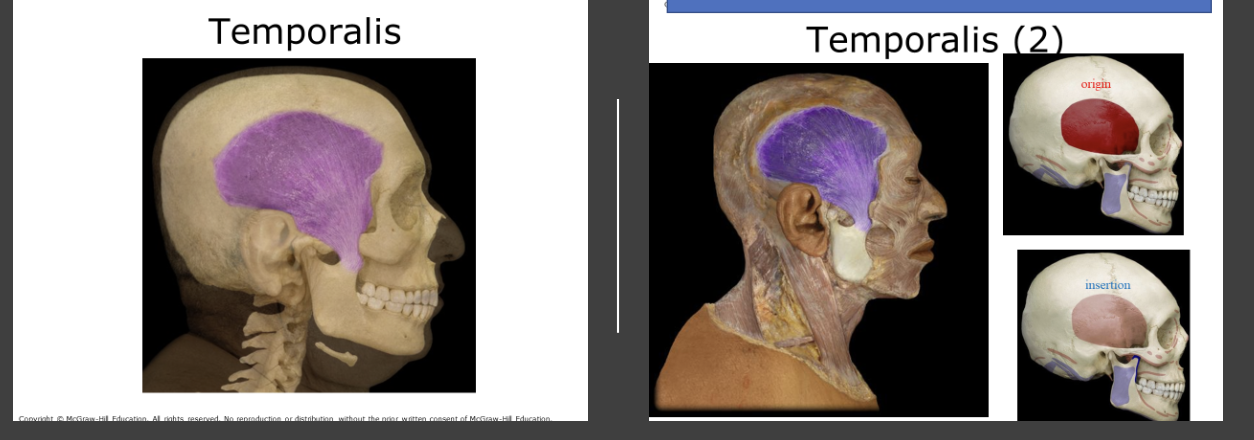
Temporalis
fan shaped muscle over the temporal bone. Raises the mandible for chewing, like the masseter
Zygomatic major and minor
thin muscles that run from zygomatic bone to side of the mouth. raises the corner of the mouth, the smiling muscles
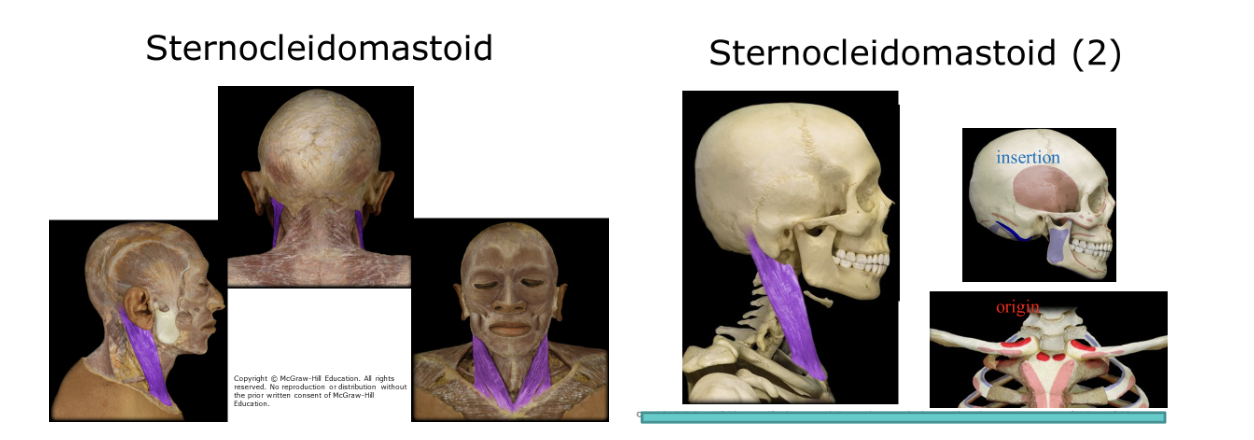
Sternocleidomastoid
Paired thin, belt-shaped muscles from mastoid process to top of sternum. Flex the head forward, each rotates the head to opposite side. Shake head no
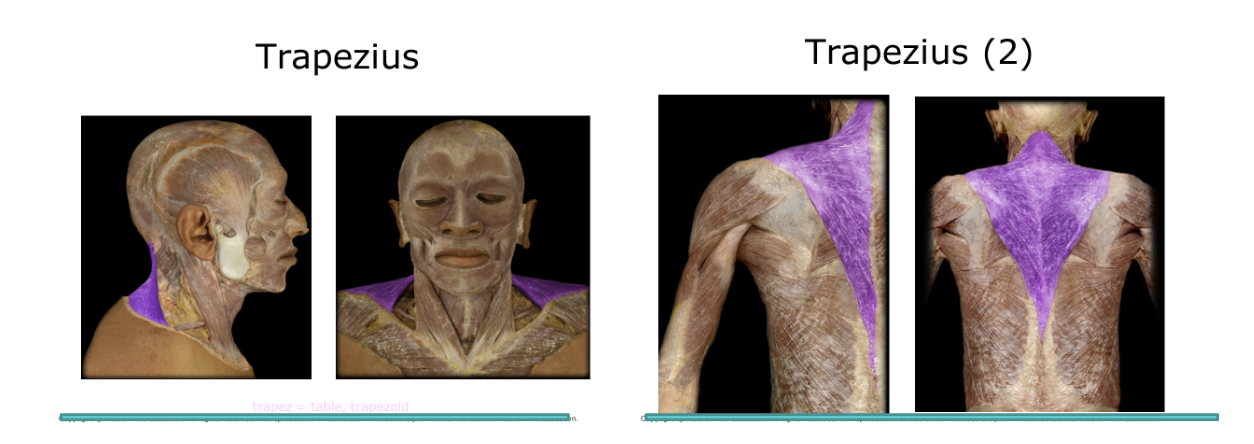
Trapezius
SeLarge diamond shaped muscle on the back, the triangular top flexes the head, also hold scapula and connects to other arm movements
Serratus Anterior
Serrated tooth-like muscle on some of the lateral portions of the ribs and the scapula. Fixes the shoulder/scapula, but also moves the scapula in relation to other arm movements
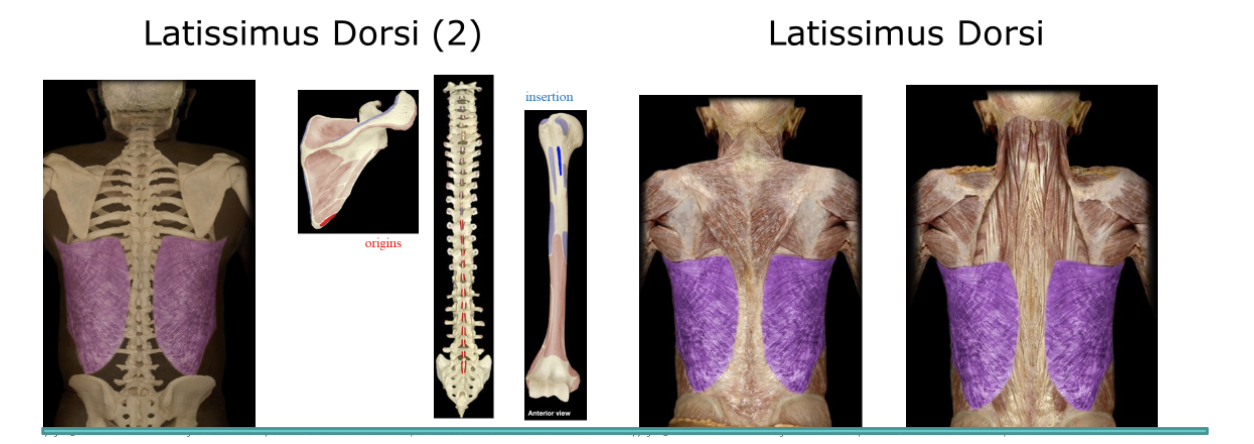
Latissimus Dorsi
The 2 large muscles on the posterior of the back, the wings. Attached to the humorous and backbone, contraction mainly extends the arm, but also adducts the upper arm.
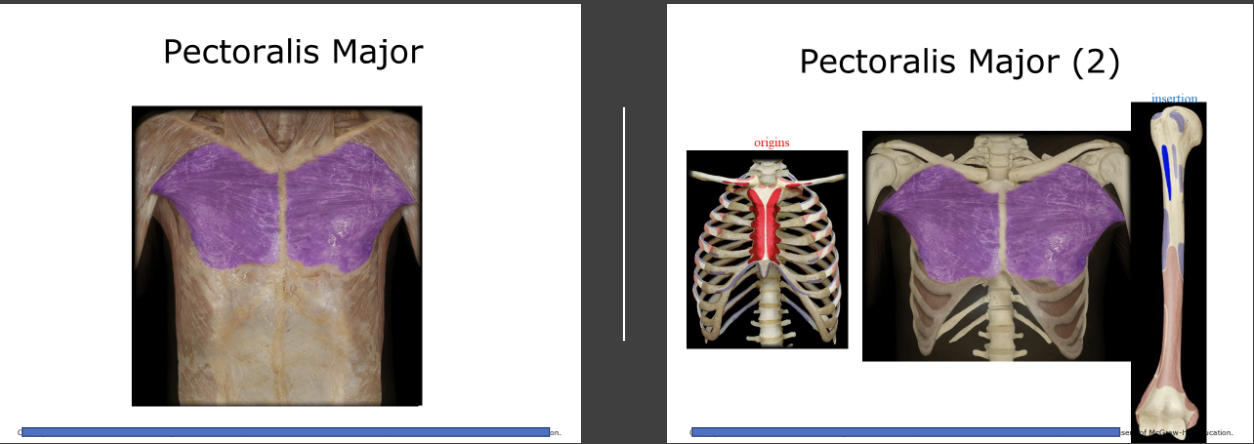
Pectoralis major
The large muscles on each side of the chest that tapers laterally to insert on the humorous. Contracts the upper arm, also adducts them.
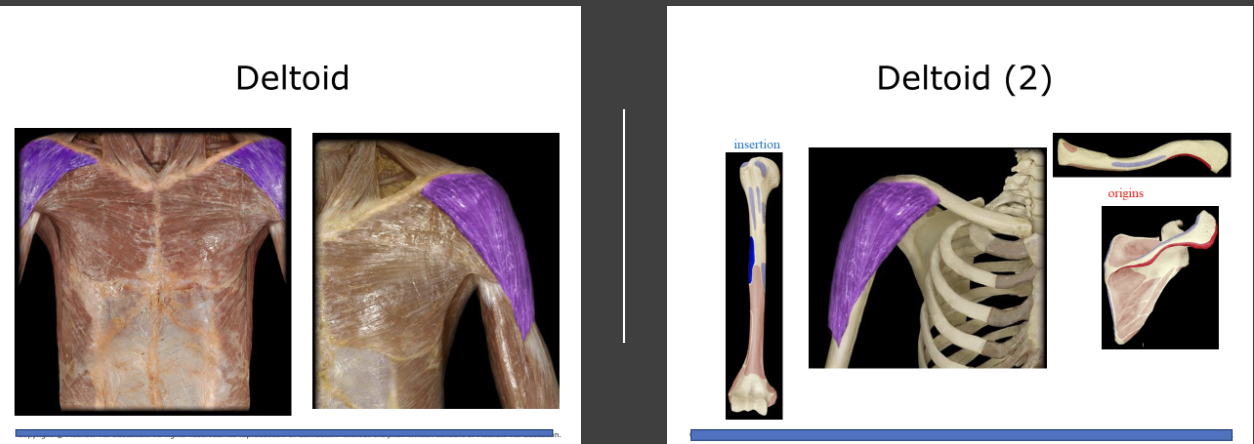
Deltoid
Makes up the flesh of the shoulder abducts the upper arm, an important synergist in flexion and extension of the upper arm
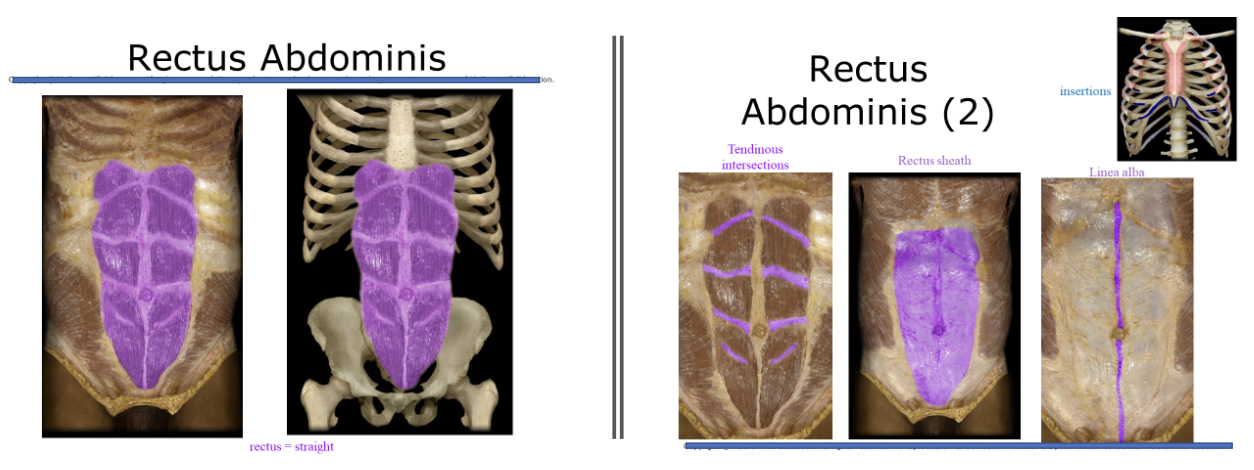
Rectus Abdominus
The abs. fibers run in superior inferior direction
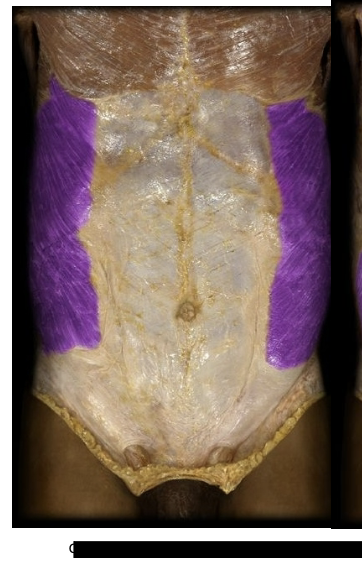
External Oblique
Major Muscle in the abdominal area located laterally to the abs, fibers running 45 degrees. Together they assist with forward flexion of torso, separately bend to eh torso laterally as in doing sit ups.
Internal Oblique
Same as external, but fibers run oppositely. assets with flexion and lateral movement of torso
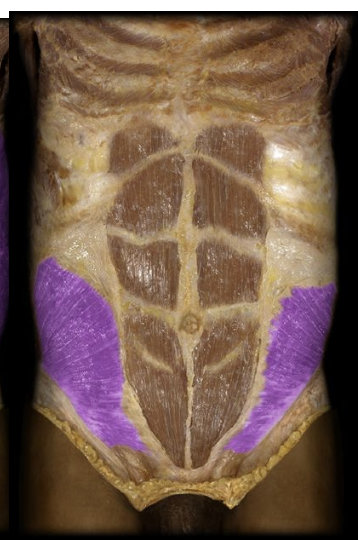
Transverse Abdominis
Under the rectus and obliques, fibers run transversely. doens’t move torso but can compress the abdominal area in forced exileration
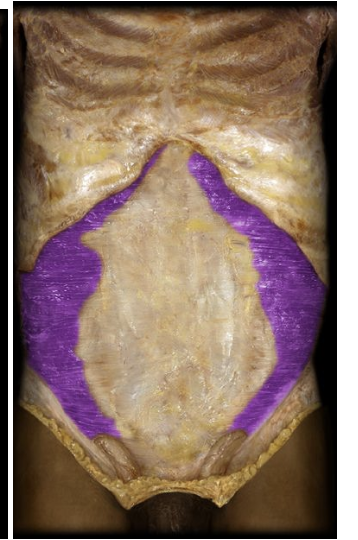
Internal and external Intercostals
superficial and deep muscles between the ribs. Moves the ribcage, internals assist exhilation, externals assist inhilationScales
Scalenes
Muscle group attached to the upper ribcage. elevates the ribcage during forced inhilationGlu
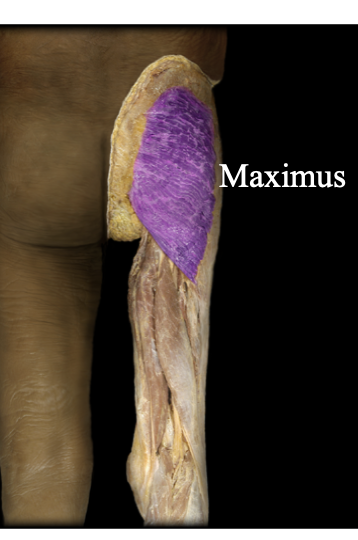
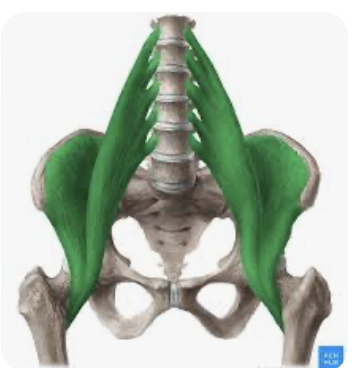
Gluteus Maximus
The butt muscle, inserts into the thigh. Extends the thigh and rotates the thigh sideways and back
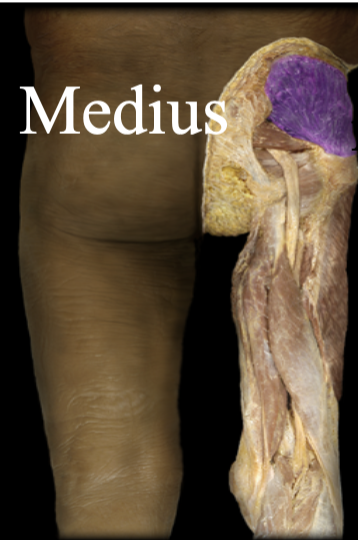
Gluteus Medius
Fibers run mostly up and down, along the side of the pelvis (allium) to the femur, tucks under the gluteus Maximus. Abducts thigh
Illiopsoas
Really 2 muscles, the iliac and the poses major. fibers run from lumbar vertebrae and upper pelvis to femur. Flex thigh or flex trunk laterally.
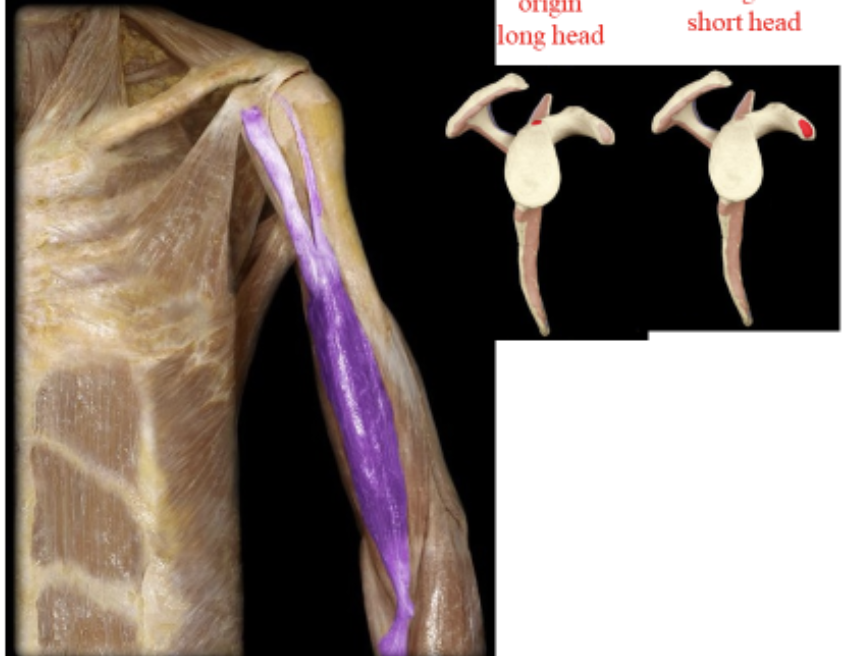
Biceps brachii
large bi headed muscle on anterior surface of arm. Flexes the forearm, also supinates the hand.
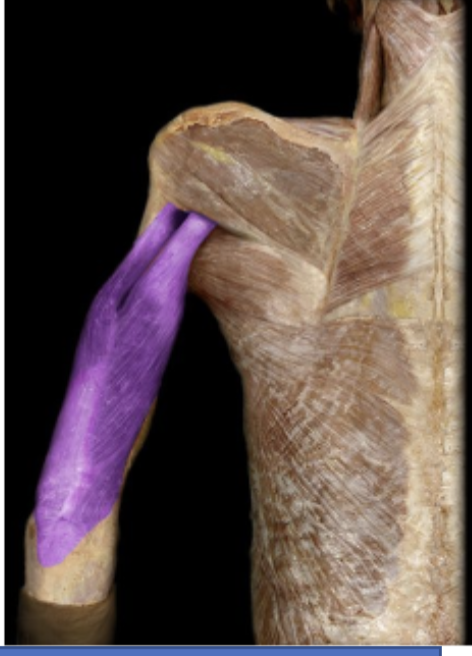
Triceps brachii
Large tri headed muscle on the posterior surface of the upper arm. mainly extends the forearm.
Flexor Digitorum
on the anterior