2: GENERAL CHEMISTRY: BMP/CMP
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
BMP includes ___ to ___ tests
7 to 8
Eighth test in BMP is
calcium
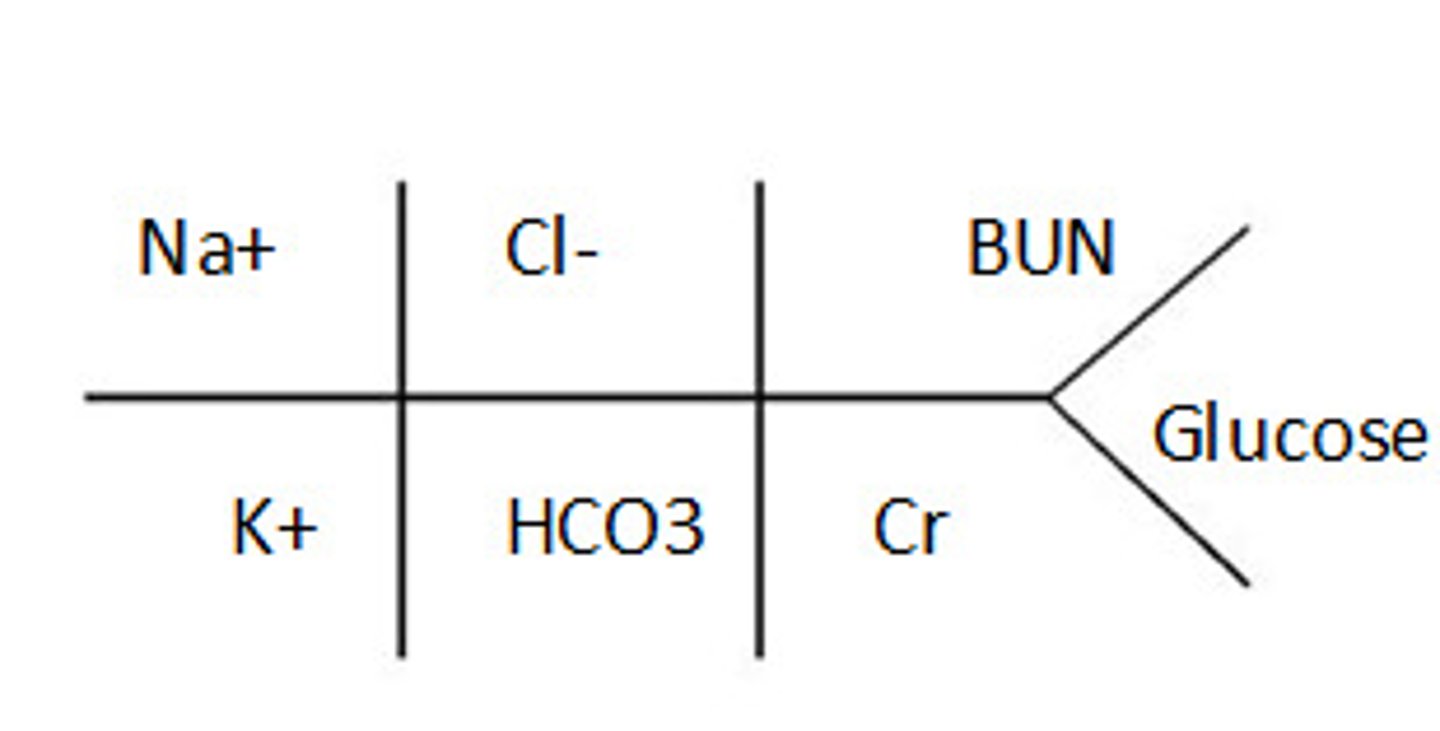
what is included in a BMP
Sodium
Potassium
BUN
Creatinine
Glucose
Calcium
Chloride
Bicarb
BMP fishbone
CMP includes what
Basic panel PLUS
albumin, alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST, bilirubin, and total protein
Function of Na
Evaluation and monitoring of fluid and electrolyte balance; indicator of solutes in extracellular space
What causes hypernatremia and what is the clinical presentation?
Cause: due to water loss or sodium overload
Clinical presentation: Dry mucous membranes, thirst, agitation, convulsions
What causes hyponatremia and what is the clinical presentation?
Cause: due to hypo/eu/hypervolemia or water excess
Clinical presentation: lethargy, confusion, coma
What is the function of K
major electrolyte for cardiac function; intracellular
What causes hyperkalemia and what is the clinical presentation?
Causes: excess ingestion, chronic renal failure
Clinical presentation: Irritability, nausea/vomiting, arrhythmias, Peaked T-waves on ECG
What causes hypokalemia and what is the clinical presentation?
Causes: diarrhea, poor intake
Clinical presentation: Decreased muscular contractility, Arrhythmias , Flat T-waves on ECG
what is the function of Cl-
determining acid/base status and hydration
Cl- is partnered with _____ in movement of water
sodium
hyperchloremia is due to
dehydration
hyperchloremia results in
lethargy, weakness, deep breathing
hypochloremia is usually due to
vomiting, gastric suctioning, burns
hypochloremia results in
NS and muscular excitability, tetany, hypotension, shallow breathing
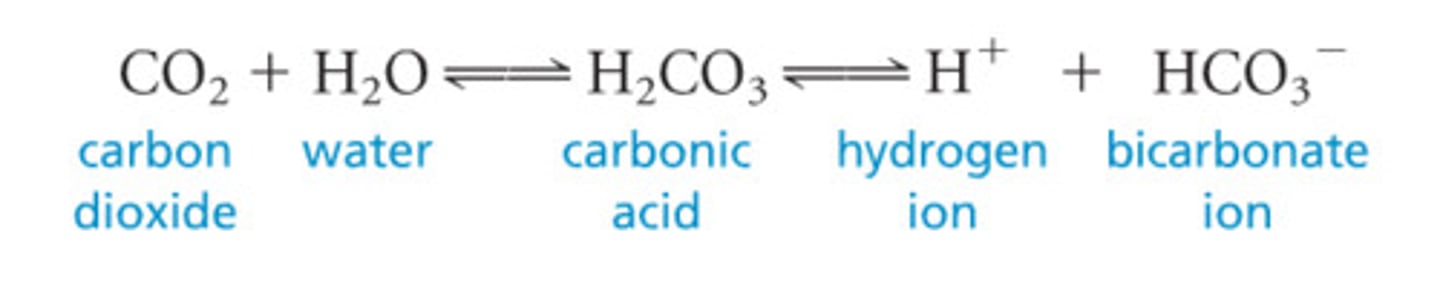
function of CO2/HCO3-
•buffering to maintain appropriate pH values
CO2/HCO3- is excreted from the
kidneys
____ is the best indicator of CO2
arterial blood, but venous blood provides an estimate of pH
Carbonic acid
anion gap
The calculated difference between the cations (positive) and anions (negative)
anion gap is used for
•evaluation of acid-base disorders
•Identify underlying cause
•Monitor therapy
how to calculate anion gap
(Na + K) - (Cl + HCO3)
the more acid you have, the ____ the anion gap
bigger
what causes increased leveled anion gap
•Lactic acidosis
•Diabetic ketoacidosis
•Alcohol intoxication
•Renal failure
•Starvation
what causes decreased levels of anion gap
•Ingestion of alkali (antacids)
•Chronic emesis/GI suctioning (removing acid)
•Multiple myeloma
mneumonic for high anion gap acidosis
Methanol
Uremia
DKA
Prophylene glycol
Isoniazid, iron
Lactic acidosis
Ethylene glycol
Salicylates

What is the function of BUN
estimate of renal function and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) if liver is functioning properly
____ is a nitrogen containing waste product produced in the liver and excreted by kidneys
urea
NH3 is ____ and Urea is ____
toxic
neutral non toxic
BUN is directly related to metabolic function of the ____ and excretory function of the ____
liver
kidneys
if BUN is low, it means
liver dysfunction (not making Urea)
if BUN is high, it means
kidneys are dysfunctioning (urea is building up and the kidneys aren't getting rid of it)
Creatinine is an indicator of
indicator of renal function (measured in serum)
creatinine depends on
muscle mass
creatinine is filtered through ____ and excreted in ____
glomeruli
urine
creatinine is increased in
•Kidney dz - glomerulonephritis, CRF pyelonephritis, acute tubular necrosis
•Dehydration
•Shock
•Rhabdomyolysis (breakdown of skeletal muscle) - damages glomeruli
creatinine is decreased in
•Diseases that decrease muscle mass
•Muscular dystrophy
•Myasthenia gravis
Creatine is a
compound produced by pancreas, kidneys, or by eating meat (ends up turning into creatinine)
Ratio of _____ is indicative of renal function
BUN/Creatinine
function of glucose
Indicative of pancreatic endocrine function and general metabolic state
glucose levels are controlled by
insulin and glucagon produced in pancreatic islets of Langerhans
hyperglycemia is caused by
•Diabetes mellitus
•Medications (steroids)
•Sepsis
•Obesity
hypoglycemia is caused by
•Inadvertent insulin dosing
•Insulinoma
•Severe liver disease
•Hypothyroidism
•Malnutrition
ALP function
Indicates liver injury or obstruction
you can get ____ to distinguish source of ALP
fractionated (ALP 1-liver, ALP-2 bone)
which ALP fractionation is used the most
ALP-1
what causes increased ALP
intrahepatic: hepatitis, cirrhosis
extrahepatic: Choledocholithiasis, Bile duct strictures, tumor metastases to liver
ALT function
Indicates liver injury or obstruction
transaminase is the most abundant in the
liver
increased ALT is due to
•Alcoholic liver disease
•Hepatitis B or C
•Hemochromatosis (excess iron storage)
•Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
AST indicates
Indicates liver injury or obstruction
AST is a _____ present in tissues/organs with high ____ rates
transaminase
metabolic (liver, heart, skeletal muscle)
is ALT or AST more specific to liver disease
ALT (L- liver)
there are increased AST in
•Cirrhosis, gallstones, hepatitis
•Pancreatitis, diabetic ketoacidosis
•Numerous medications
albumin function
Indicates hepatocellular function to synthesize proteins
albumin is a protein formed in the
liver
albumin makes up ____ % of total protein in body
60
albumin is important for
Important for maintaining osmotic pressure – keep fluid within vessels
half life of albumin
21 days
decreased albumin in
*** anything that causes depletion of AA to make albumin
•Malnutrition
•Hepatic failure
•Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, celiac dz
•Nephrotic syndrome (losing lots of protein)
•Pregnancy
•Severe burns
What causes increased albumin?
dehydration (decreased intravascular volume)
what is the name for pre-albumin
transthyretin
what is the function of pre-albumin
hepatocellular function
what is the half life of pre-albumin
2 days
pre-albumin fluctuates in response to
nutritional status
pre-albumin is a better indicator of liver function and nutrition than ______ due to _____
albumin
rapid turnover
decreased pre-albumin is from
•Malnutrition
•Liver damage
•Inflammation - negative acute phase protein
•Severe burns
increased pre-albumin is from
•Pregnancy
•Nephrotic syndrome
what is the function of bilirubin
•Indicates hepatocellular function
increased unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin is always due to
breakdown of RBCs
•Hemolysis (hemolytic anemia)
•Hepatocellular dysfunction
•Neonatal jaundice (no maturity of enzymes)
increased in conjugated (direct) bilirubin is due to
•Cholelithiasis
•Extrahepatic obstruction
•Tumor/metastasis
•Congenital defects
function of Ca
evaluation of parathyroid function and calcium metabolism
Ca is useful in monitoring pts for what conditions
•Renal failure, renal transplant
•Hyperparathyroidism
•Malignancies
•Massive blood transfusions
PTH increases _____ levels
calcium
what are the components of total serum Ca
1/2 free (ionized) form/nonbound
1/2 protein bound form (albumin and globulin)
if serum albumin is low, calcium will be ____
low
causes of hypercalcemia
•Hyperparathyroidism – most common cause
•Malignancy – paraneoplastic PTHrP (parathyroid hormone-related protein)
signs and symptoms of hypercalcemia
•Anorexia, nausea & vomiting; constipation
•Lethargy; cognitive dysfunction, psychosis
patient with normal calcium may actually be _____ if their serum albumin is _____
hypercalcemia
low
what is the main cause of hypocalcemia
hypoalbuminemia due to malnutrition in alcoholics
***also hypoparathyroidism
what are the signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia
generally asymptomatic
severe cases: muscle spasms, cramps, numbness in hands and feet
function of Mg
Regulation of nerve & muscle function, blood sugar & blood pressure, bone, DNA & protein metabolism
2/3 of Mg is in ___, 1/3 of Mg is in____
bone
cells
Mg is mostly ______ (intracellular/extracellular)
intracellular
Mg is bound to
ATP for phosphorylation
Mg is linked to ___ and ____ levels
K and Ca
hypermagnesemia is caused by
•Ingestion of antacids – common
•Renal insufficiency
signs and symptoms of hypermagnesemia
•Nausea & vomiting
•Headache; neurologic changes
•Flushing of skin
causes of hypomagnesemia
•Malnutrition
•Malabsorption
•Alcoholism with increased urinary excretion secondary to ethanol
signs and symptoms of hypomagnesemia
•Nausea & vomiting
•Weakness; muscle spasms
•Seizures
•Cardiovascular disease
function of phosphate
assist in evaluation of parathyroid and calcium abnormalities
what are the two forms of phosphate
•Organic
•Part of another compound
•Not measured
•Inorganic
•15% of total
•Unbound
•Measured in serum phosphate test
•Electrical and acid-base homeostasis
levels of phosphate are determined by
Ca metabolism
PTH
Small bowel absorption
renal excretion
hyperphosphatemia caused by
Caused by renal insufficiency where
Ca++ and PO4--- exist in an inverse
relationship
signs and symptoms of hyperphosphatemia
•Muscle cramps and spasms
•Bone/joint pain
•Pruritis
hypophosphatemia caused by
Long-term malnutrition, anorexia or starvation due to chronic infection, disease or long hospital admission
signs and symptoms of hypophosphatemia
•Muscle weakness; loss of muscle mass
•Numbness; seizures