Physics: Magnetism & Electromagnetism
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is a permanent magnet?
Produces its own magnetic field
They repel when like poles are together
Attract when different poles are together
What is an induced magnet?
A temporary magnet
When put near a permanent magnet, the material becomes magnet due to the surrounding magnetic field.
Always cause a force of attraction
Lose magnetism quickly when not in a magnetic field
What are the 4 magnetic materials?
Iron
Steel (alloy of iron, not an element)
CobaltNickel
Can be made into a permanent or induced magnet
What is a magnetic field?
Strength of magnetic field depends on the distance between magnet and material. Strongest at the poles.
The area around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet or magnetic material
How to find the magnetic field RP
Draw around the bar magnet
Place compass at north pole of magnet
Draw a cross where the N arrow points
Place the S arrow on the N cross
Keep plotting until you reach the other pole.
Draw a line through the crosses
Add arrows (N to S) to show which direction a North pole would travel.
Why does a compass work?
Compass always points towards North because of the earths natural magnetic field.
Needle (iron)
Floats in water
North side is attracted to South pole
What is a solenoid?
Coil of wire
How can you prove there is a magnetic field around a wire?
When current is turned on
There is a magnetic field around wire
Which causes the needle in a compas to deflect
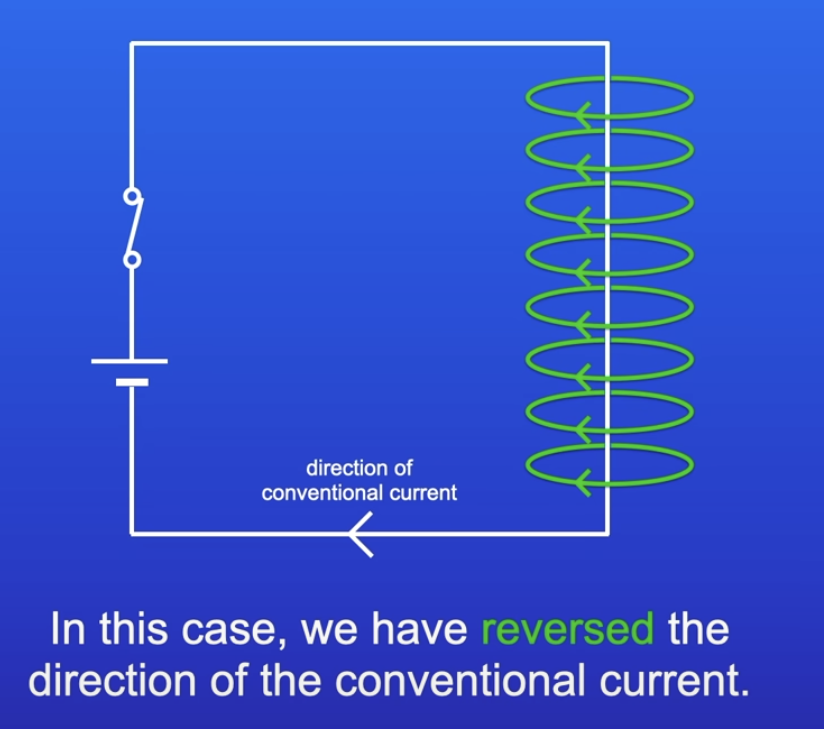
WHat happens when you change the direction of the current in a circuit?
The direction of the magnetic field changes / reverses
What is Flemings left hand rule?
FBI
Thumb - F - Force
Index finger - B - Magnetic field (N to S)
Middle finger - I - current (Positive to negative)
How can you make the magnetic field stronger?
Coil the wire / more turns in the coil
Stronger current
Place iron core inside solenoid (electromagnet)
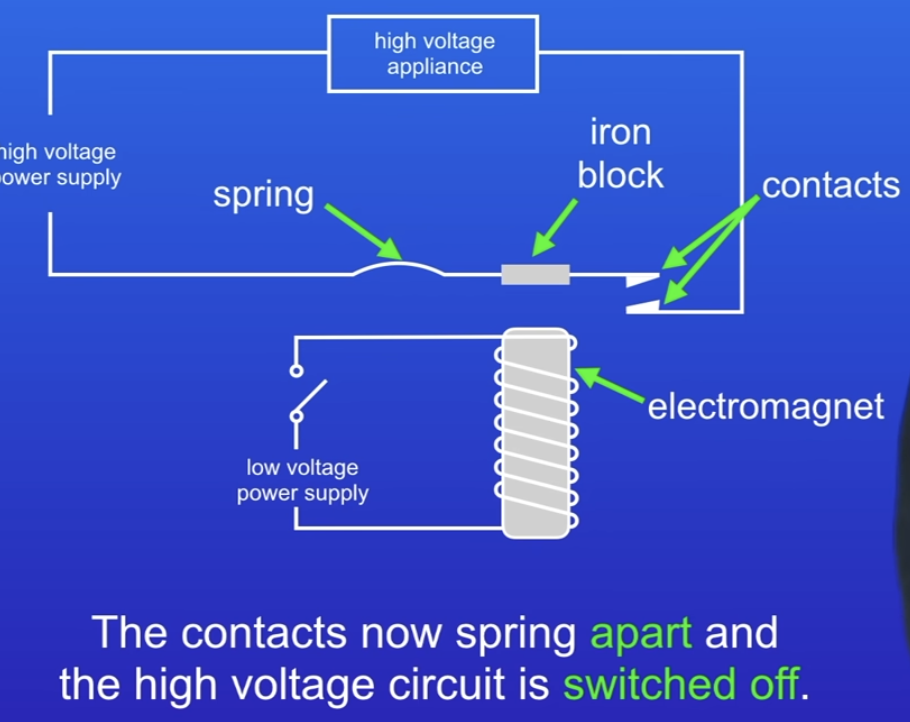
How does a relay work?
Using a switch in a high voltage circuit is dangerous (sparks)
Use relay instead
Two separate circuit
One low voltage with electromagnet
other high voltage, replace switch with 2 metal contacts, one contact connected to spring keeping contact s apart & iron block next to spring
When low voltage circuit is switched on the current produces a magnetic field around the electromagnet. This attracts the iron block and makes the contacts touch.
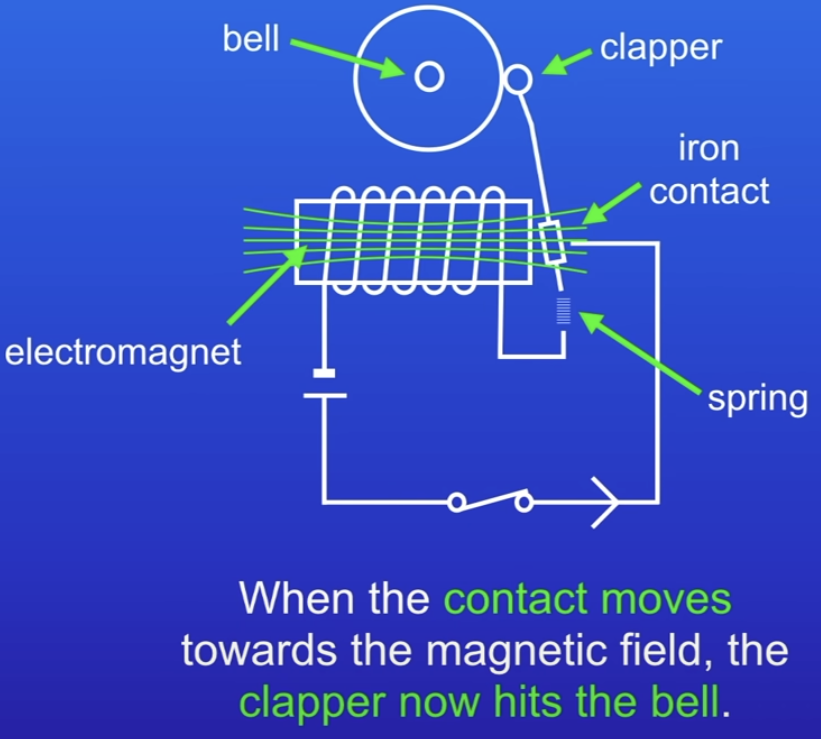
How does a doorbell work?
Switch is closed when buzzer is pressed
Current flows through
Makes magnetic field around electromagnet
Attracts the iron contact
Clapper hits the bell
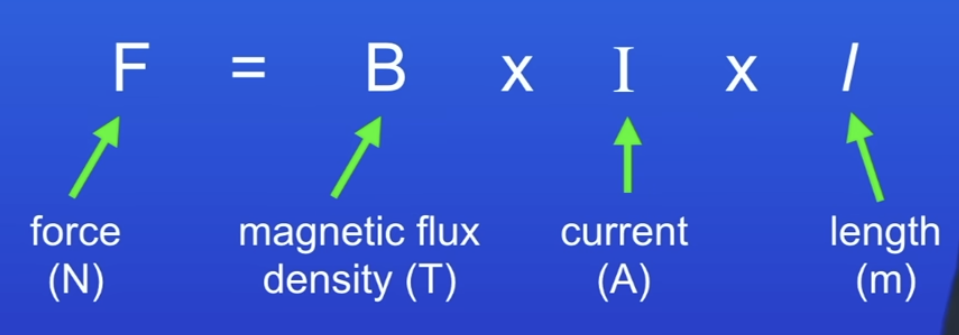
What is the motor effect?
A current carrying wire experiences a force when in a magnetic field.
Only experiences force when current flows
Can reverse direction of force by switching poles of magnet o r changing the direction of the current.
Force, Magnetic flux density & current are all at right angles to each other.
If the magnets are parallel to the conductor, no force
How does an Electric motor work?
Loop of wire carrying a current
The current is back → front on the left, front → back on right side
This means the force is up on the left and down on the right (Moment)
Causing the loop to rotate.
At 90º the loop stops rotating.
If it goes over 90º, The current makes left side force down and right side force up which pushes it back to 90º
The current can be switched direction at 90º so it rotates all the way.
Use a split-ring commutator → connected to brushes (allow electric current to pass onto ring) so the motor can keep rotating in same direction
How do speakers and headphones work?
Coil of wire around one end of cone
Connected to AC
Permanent magnet in solenoid
Current through coil, generates Magnetic field
MF of solenoid and magnet interact (attract or repel)
Resultant force. Cone moves in and out when current reverses → sound waves
Changing freq of AC supply, change freq that the cone vibrates.
Higher freq = higher pitched sound vice versa.
Increase size of current, increase amplitude of vibration → increases volume
What is the generator effect?
Opposite of motor effect
Kinetic energy → electrical energy
Wire below magnetic field → moved up through magnetic field, induces PD across ends of wire
When wire stops moving PD is lost
When moved down, induce PD again but reversed
This is called induced potential
If it is a complete circuit, we induce current - the generator effect
Works the same is the wire is still and the magnetic field moves through.
How can we increase the induced PD and current?
Use stronger magnetic field
Move wire more rapidly
Shape wire into coils & add more turns
What happens when you move a magnet in and out a coil of wire?
Magnet moving in and out coil of wire
Direction of current changes when direction of magnet changes
Magnet in wire induces current which always makes its own magnetic field which opposes the movement of the magnet.
When N side is in the coil, the coil becomes N. Repelling the magnet
When N is coming out of coil, coil becomes S. Attracting the magnet
This struggle to move the magnet is doing work
Transfers energy from movement of magnet into movement of the current.
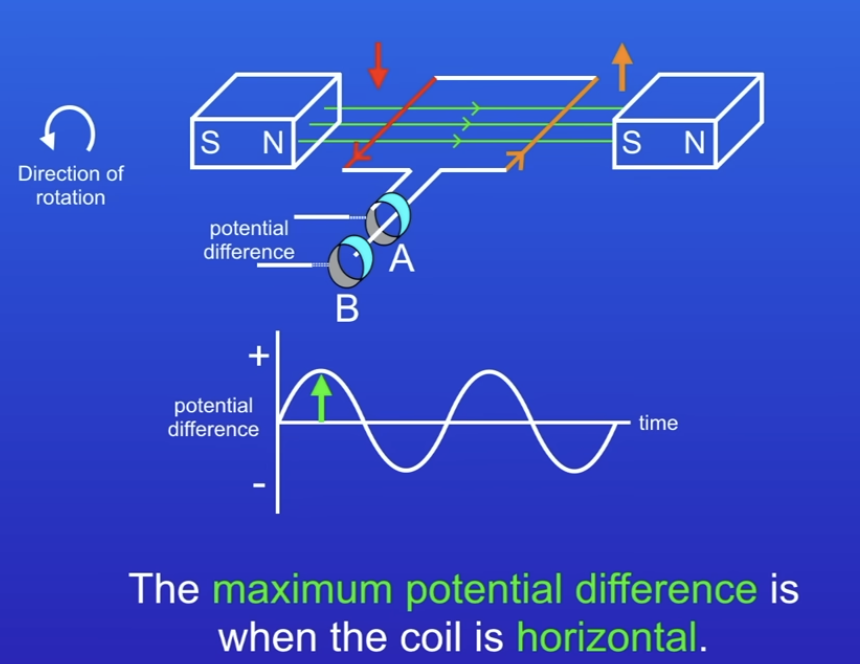
What is the alternator effect?
Wire rotating in magnetic field, inducing PD
Coil connected to two metal rings (commutators)
Red - ring A (down), Orange - ring B (up)
Horizontal - max PD, Vertical - no PD
When 2 sides of coil changes direction, PD reverses
Produces AC
How can you increase the size of the alternating current?
Increase number of turns in the coil / area of coil
Increase strength of magnetic field
Increase rotation speed - increases size and freq of AC
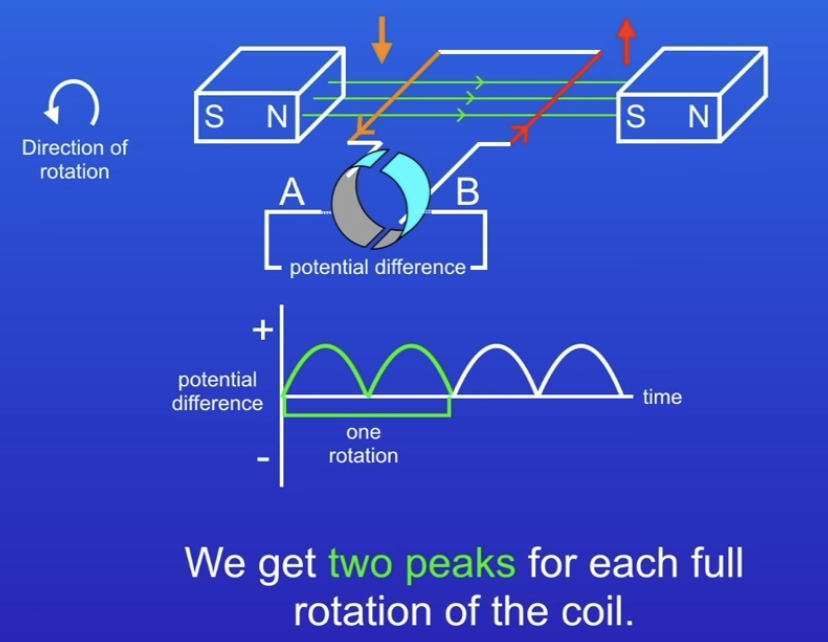
What is a dynamo?
DC, coil rotates in magnetic field, direction of coil never changes
Split-ring commutator (2 sides separated by gap)
A - down, B - up
Vertical - no PD
Induces PD and current
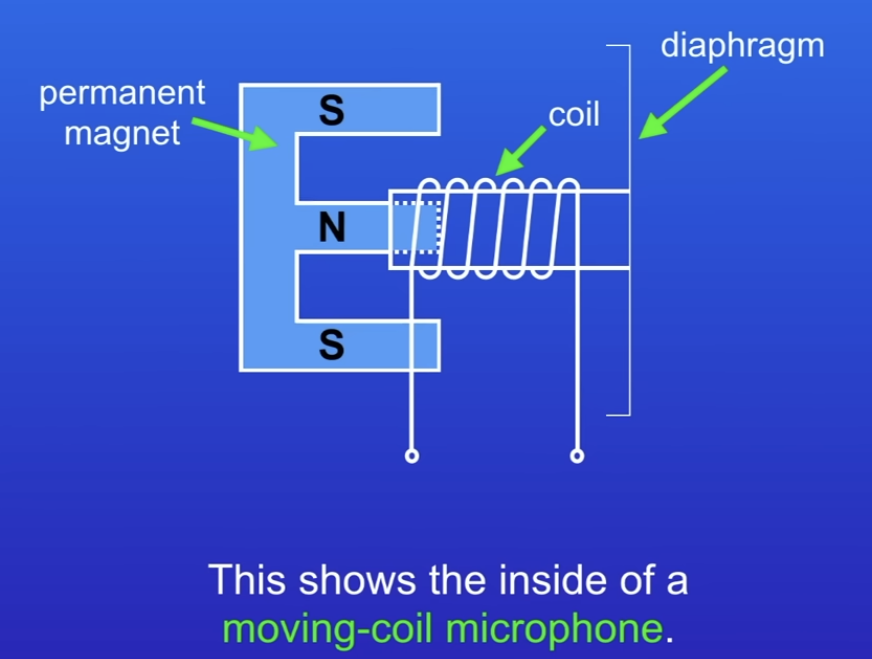
How does a microphone work?
Diaphragm attached to solenoid, on permanent magnet
Diaphragm vibrates when sound waves hit
Wire moves in and out through MF
Induces PD across ends of wire
Freq of PD = Freq of sound waves, passed through an amplifier → speaker (increase volume)
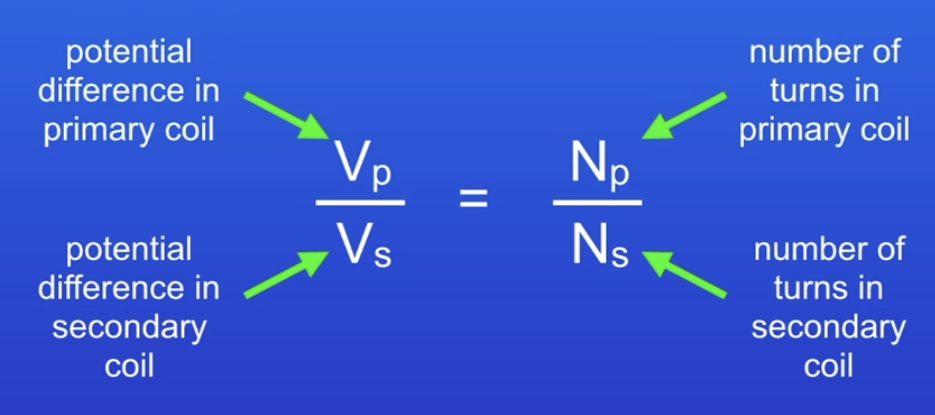
What is a transformer?
2 Separate coils (current can’t pass between them) with equal amount of turns
Coils wrapped around an iron core
Primary → AC, current flows, generates changing magnetic field
Magnetic field is transmitted along the iron core & passes through secondary coil, induce PD
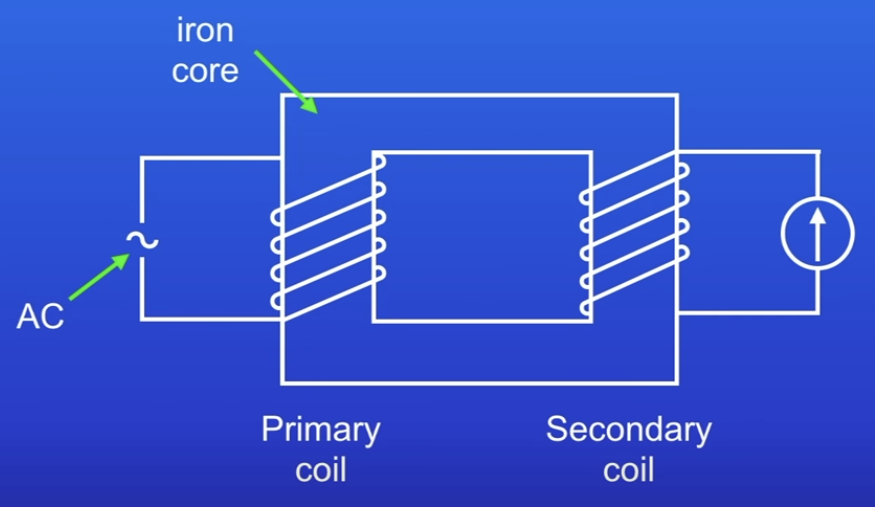
Why is an iron core used in a transformer?
Iron is easily magnetised
It increases the strength of the magnetic field
Transformers only work with AC (need a changing magnetic field to induce PD)
DC produces constant magnetic field so wouldn’t work
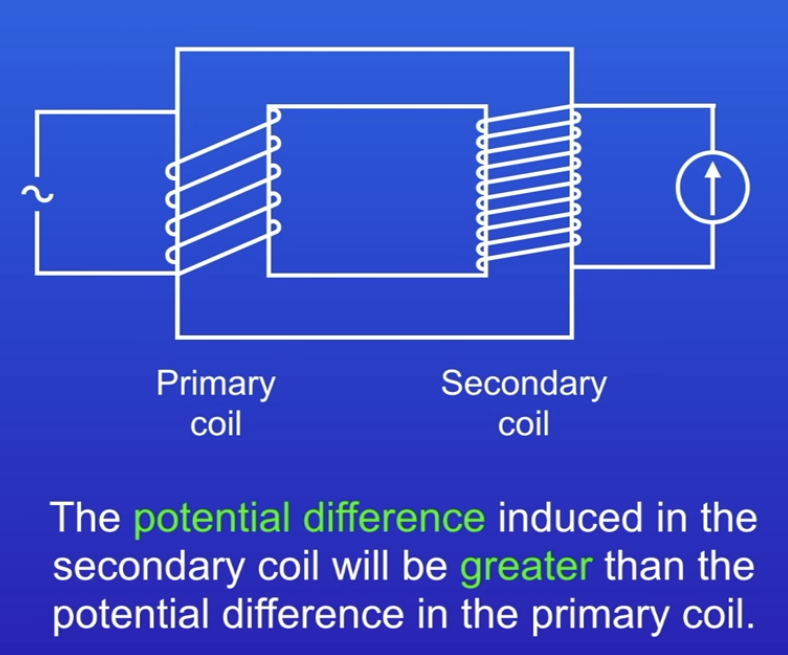
What is a step-up / step-down transformer?
The coils of wire have a different number of turns. This changes the PD along the transformer
Twice the tuns in secondary coil = Twice the PD in secondary coil
Step-down transformer has less turns in the secondary coil which decreases the PD.
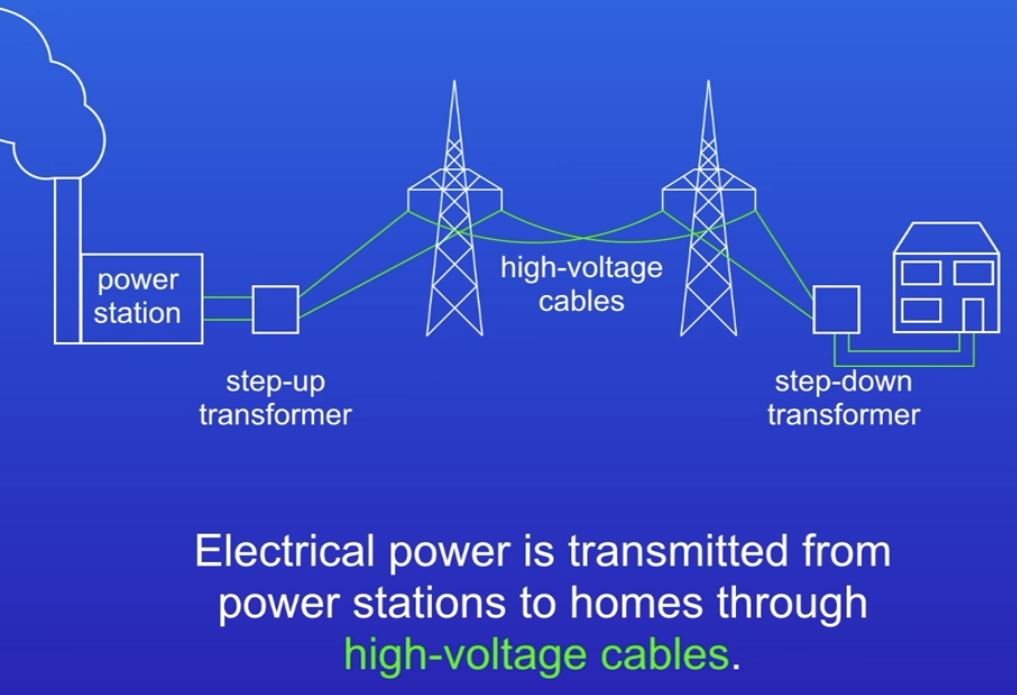
How are transformers used in power transmission?
High current in transmission cables waste lots of energy as heat. We use high PD instead.
Step up transformers increase PD
Step down transformers decrease PD to go into homes.
Transformer calculations (equation given)
Power of primary coil = Power of secondary coil