The senses
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Information Input
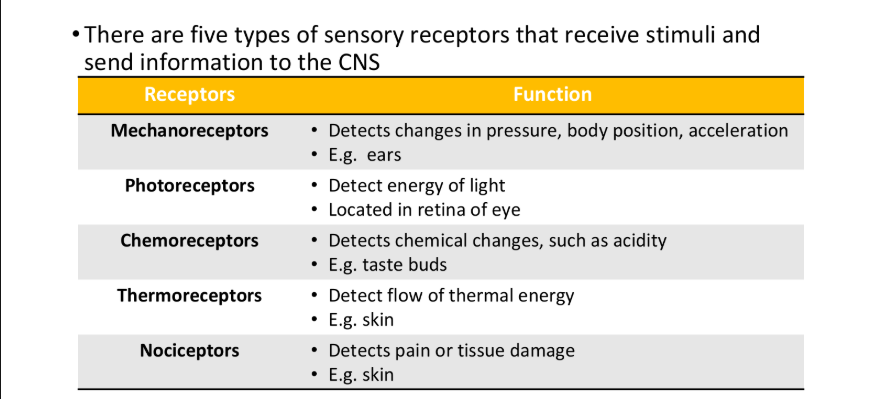
Sensory Adaptation
Sensory receptors are not evenly distributed across the body
E.g. fingers and lips have more receptors
For many sensory systems, the effect of a stimulus is reduced if it continues at a constant level
This is called sensory adaptation
E.g. when getting into bed, you feel the touch and pressure of the sheets. Over time, this feeling goes away
Traditional Senses
There are five traditional
senses
Vision
Hearing
Taste
Smell
Touch
Vision
Vision is the most complex of all senses
Photoreceptors in the retina detect light at particular wavelengths
It converts light stimuli to nerve impulses
There are two types of photoreceptors
Cones: specialized to detect different wavelengths
Rods: specialized to detect light at low intensities
Hearing
The auditory organ for humans is the ear
The pinna (outer war) focuses on soundwaves
The soundwaves travel inside the ear, where it hits the ear drum
This causes sound vibrations
These vibrations then hit a chain of tiny bones in the middle ear
Malleus (hammer)
Incus (anvil)
Stapes (stirrup)
Hearing Con’t
The inner ear contains several fluid-filled compartments
Semicircular canals
Cochlea
The vibrations reach the cochlea, which causes hair cells to bend
In turn, a neurotransmitter is released
Taste
A tastebud is a receptor that forms a small, pear-shaped capsule with a pore that opens to the exterior at the top
They are scattered over the roof of mouth, tongue, and throat
The tastebuds on the tongue are embedded in outgrowths called papillae
We can experience 5 basic tastes
Sweet, bitter, sour, salty and umami
Taste Con’t
Signals from taste receptors are sent to the thalamus
Some signals can trigger emotional responses
A pleasant taste can cause salivation
An unpleasant taste may produce vomiting and nausea
Smell
Olfactory receptors are found in the nose
Each receptor projects into a layer of mucus in the nose
To be detected, airborne molecules must dissolve into the watery mucus
Like taste, smell can also trigger emotional responses
Touch
Mechanoreceptors are embedded in the skin and other surface tissues
A stimulus can distort proteins in the plasma membrane, which alters the flow of ions
In turn, an action potential can occur
Most touch receptors are located in the fingers, lips, and top of the tongue
These areas have the greatest sensitivity to touch
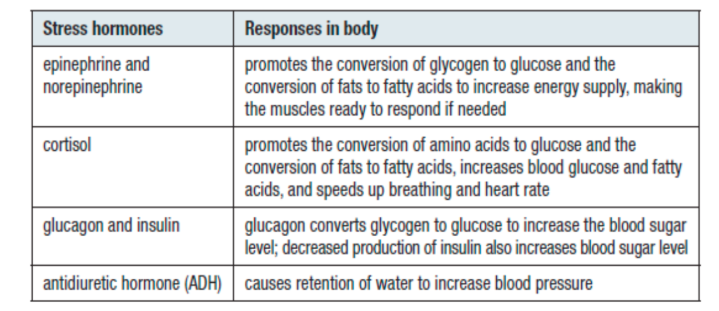
Stress
Stress is the body’s response to a stimulus that triggers a move away from homeostasis
Short-term stress is not bad for the body
It can cause the body to adapt to changing situations
Chronic stress, on the other hand, can be dangerous
Symptoms of Stress
Increase in respiration and heart rate
Muscle tension
Frequent urination
Irritability
Tiredness
Trouble sleeping
Hormones Involved in Stress Responses
Pain
Pain is a protective mechanism that prompts animals to do something to remove or reduce the stimulus immediately
Pain initiates a reflex response
E.g. removing a hand from a hot stove
Pain receptors (nociceptors) are the most concentrated sensory receptors
For every square centimeter of skin, there are around 200 pain receptors
For protection, pain receptors do not adapt to the environment