(a) introduction
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
hydrocarbon (4.1)
compound of hydrogen and carbon
how to represent organic molecules using empirical formulae (4.2)
the empirical formula shows the simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in a compound e.g. for butane it is C2H5 and for ethene it is CH2
how to represent organic molecules using molecular formulae (4.2)
the molecular forumla shows the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule e.g. for butane it is C4H10 and for ethene it is C2H4
how to represent organic molecules using general formulae (4.2)
the general formula shows the relationship between the number of atoms of one element to another within a molecule. members of a homologous series share the same general formula. e.g. for alkanes it is CnH2n+2 and for alkenes is CnH2n
how to represent organic molecules using structural formulae (4.2 / 4.5)
a structural formula shows how the atoms in a molecule are joined together e.g. for butane it is CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH3 and for ethene it is CH2 = CH2
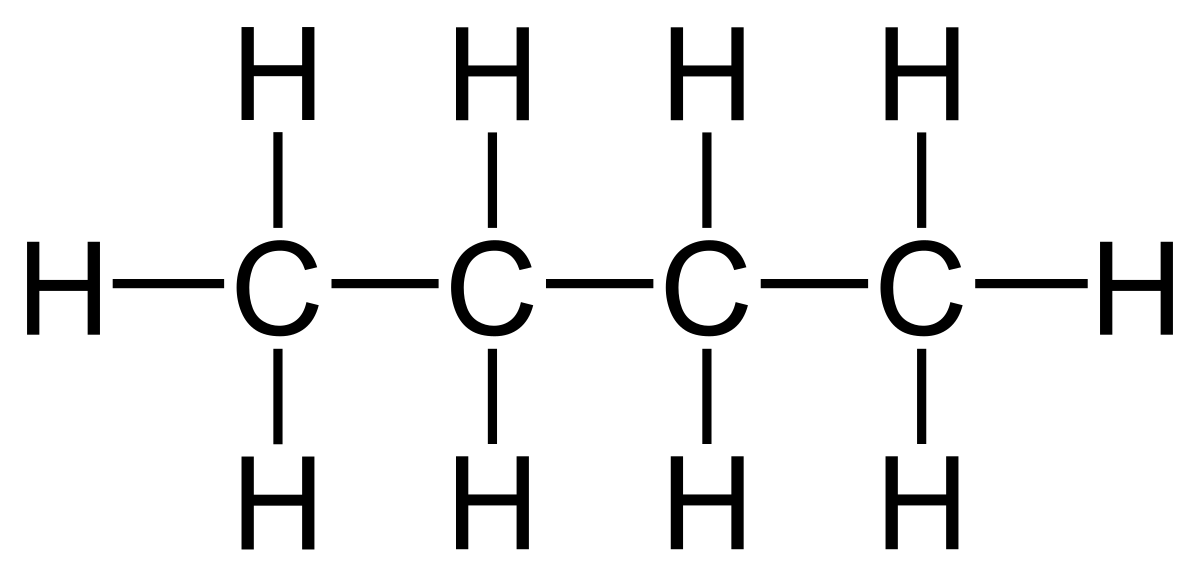
how to represent organic molecules using displayed formulae (4.2 / 4.5)
the displayed formula is a full structural formula which shows all the bonds in a molecule as individual lines e.g. this is the displayed formula for butane
homologous series (4.3)
a homologous series is a group of substances with the same general formula (e.g. for alkanes it is CnH2n+2 and for alkenes is CnH2n)
functional group (4.3)
an atom or group of atoms that determine the chemical properties of a compound
isomerism (4.3)
isomers are molecule with the same molecular formula but with a different structure
how to name compounds (4.4)
using the rules of international union of pure and applied chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature, the names of organic molecules are based on the number of carbon atoms in the longest chain.
1: meth-
2: eth-
3: prop-
4: but-
5: pent-
6: hex-
substitution (4.6)
in a substitution reaction, an atom or group of atoms is replaced by a different atom or group of atoms. e.g. when ethane reacts with bromine gas, one of the hydrogen atoms in ethane is substituted by one of the atoms of bromine from within the bromine molecule
ethane + bromine → bromoethane + hydrogen bromide
CH3-CH3 + Br-Br → CH3-CH2Br + H-Br
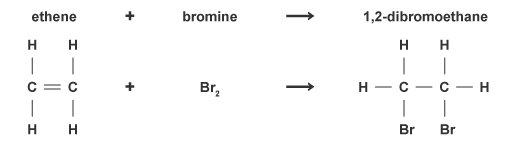
addition (4.6)
an addition reaction occurs when an atom or group of atoms is added to a molecule without taking anything away. e.g. when ethene reacts with bromine gas, the product is simply the addition of the two molecules
combustion (4.6)
a combustion reaction is another way to say ‘burning’ and is a reaction with oxygen. combustion of hydrocarbons with excess oxygen gives the products water and carbon dioxide, and also releases heat energy (exothermic reaction). e.g.
combustion of propane: C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
combustion of butene: C4H8 + 6O2 → 4CO2 + 4H2O