UNIT 1 BM VOCAB
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BUSINESS ORGANISATION AND ENVIRONMENT
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
A good is a physical product and a service is an intangible product.
* Land: physical space and resources
* Labour: worforce
* Capital: finance and capital goods
* Enterprise: driving force of business (management, decision making and coordinating role)
* Finance and accounts
* Marketing
* Operations management
Public sector
Part of the economy that is owned and controlled by the government
Usually aimed at entrepreneurs of small businesses, especially at females and those on low incomes.
Non-governamental organizations (NGO)
A legally constituted body with no participation or representation of any government which has a specific aim and purpose. These are usually international organisations to tackle issues that support the public good
Types of PPPs:
* Government funded but privately managed
* Private sector-funded but government managed (also know as Private finance initiative (PFI): investemnt by private sector organisations in public sector projects)
* Goverment-directed but private-sector finance and management
* Economic: to make a profit to reinvest back into the business and provide some return to the owners
* Environmental: to protect the environment and to manage the business in an environmentally sustainable way
* Specific
* Measurable
* Attainable
* Realistic
* Time-specific
Ethical code (code of conduct)
a document detailing a company's rules and guidelines on staff behavior that must be followed by all employees
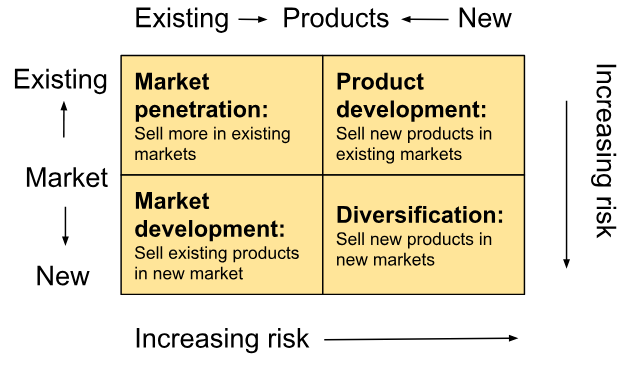
Ansoff’s Matrix
Model used to show the degree of risk associated with the 4 growth strategies of:
Market penetration: achieving higher market shares in existing markets with existing products
Market development: strategy of selling existing products in new markets
Product development: development and sale of new products or new developments of existing products in existing markets
Diversification: Process of selling different, unrelated goods or services in new markets
* Mission
* Corporate objectives
* Divisional objectives
* Departamental objectives
* Individual targets
These can be:
* Profit maximization
* Profit satisficing
* Increase market share
* Survival
* Growth
* Maximizing short-term sales revenue
* Maximizing shareholder value
\
Workers participation: Negotiating with the workers, listening to their opinions, having employees in charge of identifying the workers needs
\
Profit-sharing schemes: making the workers take part in the profits to reduce conflict between workers and shareholders over the allocation of profits and to share the benefits of the business
\
Share-ownership schemes: giving workers bonifications in shares instead of money
* Cost-push inflation: caused by rising costs forcing businesses to increase prices
* Demand-pull inflation: caused by excess demand in an economy (e.g. economic boom → allowing businesses to raise their prices)
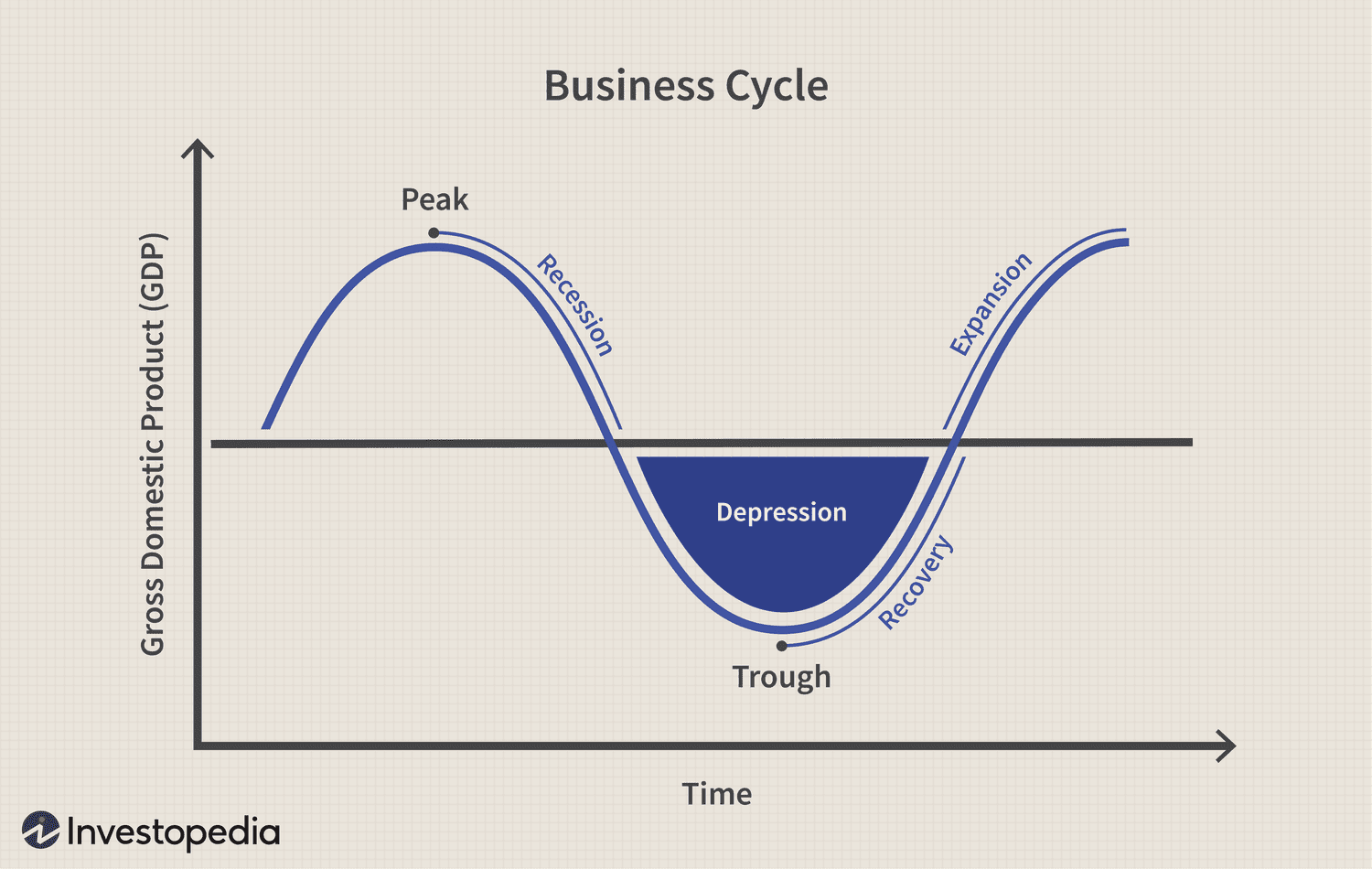
Business cycle
Fluctuation in the level of business activity over time.
4 stages: peak, trough, contraction/recession and expansion
Scale of operations
The maximum output that can be achieved using the available inputs (resources) This scale can only be increased in the long term by employing more of all inputs
* Purchasing economies (bulk-buying bring discounts)
* Technical economies (able to buy machinery)
* Financial economies (need more financing)
* Marketing economies (marketing costs rise with business size, but not at the same rate)
* Managerial economies (more staff)
* Communication problems
* Alienation of the workforce
* Poor coordination and slow decision making
* Forward vertical integration: same industry, but a customer of the existing business (towards customer)
* Backward vertical integration: same industry but a supplier of the existing business (towards supplier)
* Conglomerate integration: merger with or takeover of a business in a different industry
* Franchiser (owner of the brand) and franchisee (the one with some money decides to open a store)
* Franchise agreement: contract between franchisee and franchisor which provides all the terms and conditions
Tariffs (transportation tax) affect the price of the product, so that the price is not as cheap, so it won’t damage the county’s industry
Quotas (cupos): limit of the supply that a country can receive during one year
\
Shows all the tasks taken in a particular project against a timescale.