REVERSIBLE REACTIONS AND EQULIBRIUM:
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
WHAT IS A REVERSIBLE REACTION AND HOW CAN THE DIRECTIONS BE CHANGED? GIVE AN EXAMPLE.
In some chemical reactions, the products of the reaction can react to produce the original reactants.
The direction of reversible reactions can be changed by changing the conditions.
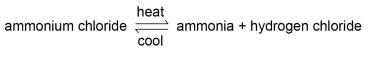
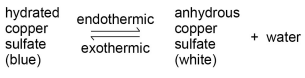
HOW DO ENERGY CHANGES OCCUR IN REVERSIBLE REACTIONS?
If a reversible reaction is exothermic in one direction, it is endothermic in the opposite direction. The same amount of energy is transferred in each case. For example:
WHAT HAPPENS IN REVERSIBLE REACTIONS IN TERMS OF CONCENTRATION? HOW DOES EQUILIBRIUM TIE INTO THIS?
As the reactants react, the concentrations decrease - so the forward reaction will slow down.
But as more and more products are made and their concentrations increase, the backward reaction will speed up.
After a while, the forward reaction will be going at exactly the same rate as the backward one - the system is at equilibrium.
At equilibrium both reactions are still happening, but there’s no overall effect (it’s a dynamic equilibrium). This means the concentrations of reactants and products have reached a balance and won’t change.
WHAT IS EQUILIBRIUM AND HOW CAN IT BE REACHED?
When a reversible reaction occurs in apparatus which prevents the escape of reactants and products, equilibrium is reached when the forward and reverse reactions occur at exactly the same rate.
WHAT IS DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM?
At equilibrium both reactions are still happening, but there’s no overall effect (it’s a dynamic equilibrium). This means the concentrations of reactants and products have reached a balance and won’t change.
WHAT DOES THE POSITION OF EQUILIBRIUM DEPEND ON?
When a reaction is at equilibrium, it doesn’t mean that the amount of products and reactants are equal.
If equilibrium lies to the right, the concentration of products is greater than that of the reactants.
If equilibrium lies to the left, the concentration of products is lesser than that of the reactants.
WHAT IS THE EFFECT OF CHANGING CONDITIONS ON EQUILIBRIUM AND WHICH PRINCIPLE CAN BE USED TO PREDICT THEM?
The relative amounts of all the reactants and products at equilibrium depend on the conditions of the reaction.
If a system is at equilibrium and a change is made to any of the conditions, then the system responds to counteract the change.
The effects of changing conditions on a system at equilibrium can be predicted using Le Chatelier’s Principle.
WHAT IS THE EFFECT OF CHANGING CONCENTRATION ON EQUILIBRIUM?
If the concentration of a reactant is increased, more products will be formed until equilibrium is reached again.
If the concentration of a product is decreased, more reactants will react until equilibrium is reached again.
If the concentration of a product is increased, more reactants will react.
If the concentration of a reactant (on the left) is increased, the equilibrium position moves in the direction away from this reactant, and so more of the products are produced (on the right). If one of the products is removed from a reaction (on the right), then the position of equilibrium moves to the right to make more of that product.
For example, bismuth chloride reacts with water in a reversible reaction:
BiCl3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ BiOCl(s) + 2HCl(aq)
The concentration of hydrochloric acid can be increased by adding more hydrochloric acid. When this happens, the equilibrium position moves to the left, away from HCl(aq) in the equation.
WHAT IS THE EFFECT OF CHANGING TEMPERATURE ON EQUILIBRIUM?
If the temperature of a system at equilibrium is increased the relative amount of products at equilibrium:
Increases for an endothermic reaction.
Decreases for an exothermic reaction.
This is because if you increase the temperature, the equilibrium will move in the endothermic direction to try and reduce the amount of heat.
Exact opposite if temperature is decreased. E.g If the temperature is decreased, equilibrium shifts to the right (for a forward exothermic reaction) to increase the temperature. The amount of N2O4 (substance on the right of arrows) increases and the other substance on the left decreases.
If the temperature is increased, the equilibrium position moves in the direction of the endothermic process.
WHAT IS THE EFFECT OF CHANGING PRESSURE ON EQUILIBRIUM?
For gaseous reactions at equilibrium:
Increase in pressure causes the equilibrium position to shift towards the side with the smaller number of molecules to reduce the pressure.
Exact opposite for decrease.
WHAT IS THE EFFECT OF ADDING A CATALYST ON EQUILIBRIUM?
There is no effect, the equilibrium position stays the same.
This is because the catalyst increases the forward reaction and backwards reaction by the same amount.
WHAT US THE EFFECT ON EQUILIBRIUM OF REMOVING SOME OF THE REACTANTS FROM A REACTION?
Equilibrium will move towards the reactants and the amount of reactants would increase.