Early Animal Evolution and Biomes Overview
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Mesozoic
Era of complex vascular and respiratory systems.
Dinosaurs
Dominant land vertebrates during the Mesozoic.
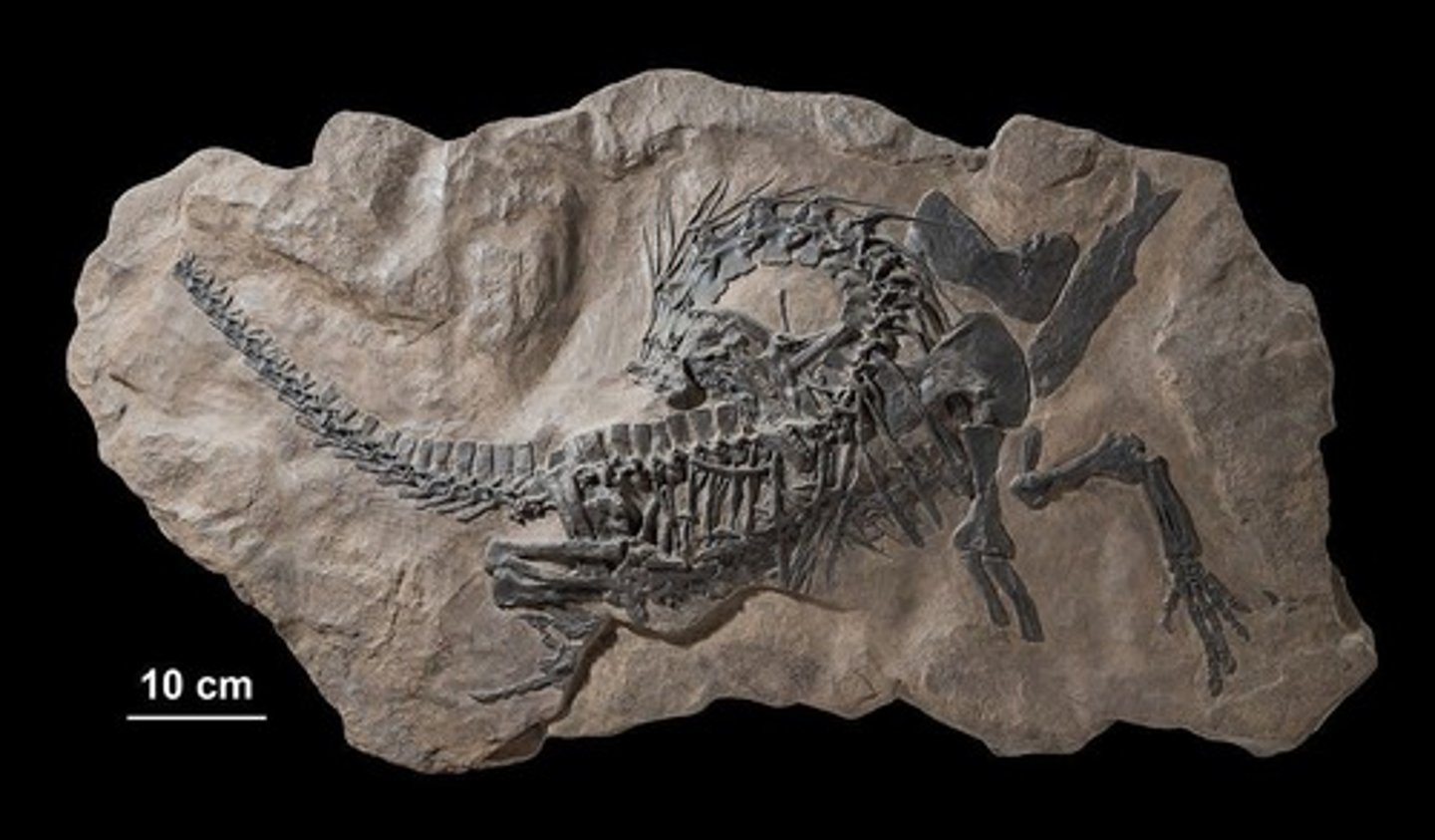

Triassic-Jurassic extinction event
Fourth mass extinction, affecting large amphibians.
K-Pg extinction
Fifth mass extinction; non-avian dinosaurs extinct.
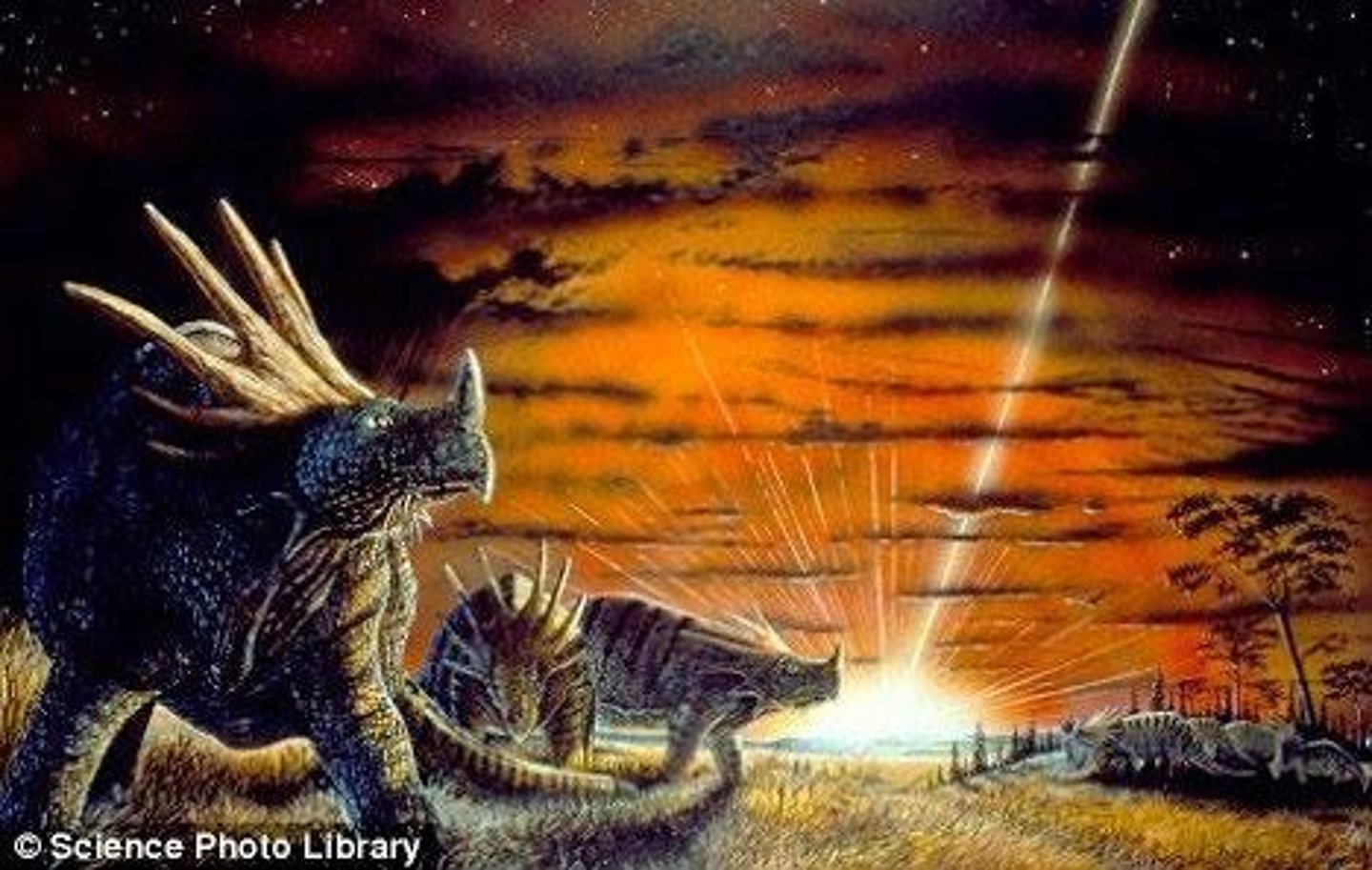

Asteroid impact
Event causing K-Pg extinction in Yucatan.
Great Mammalian Radiation
Rapid increase in mammal size and behavior.
Taxonomic richness
Doubled in 100k years post-K-Pg impact.
Mammal size increase
From 0.5 kg to 50 kg over 700k years.
Coevolution
Reciprocal evolutionary changes between interacting taxa.
Plesiadapiforms
Ancestral primates diversifying after K-Pg boundary.
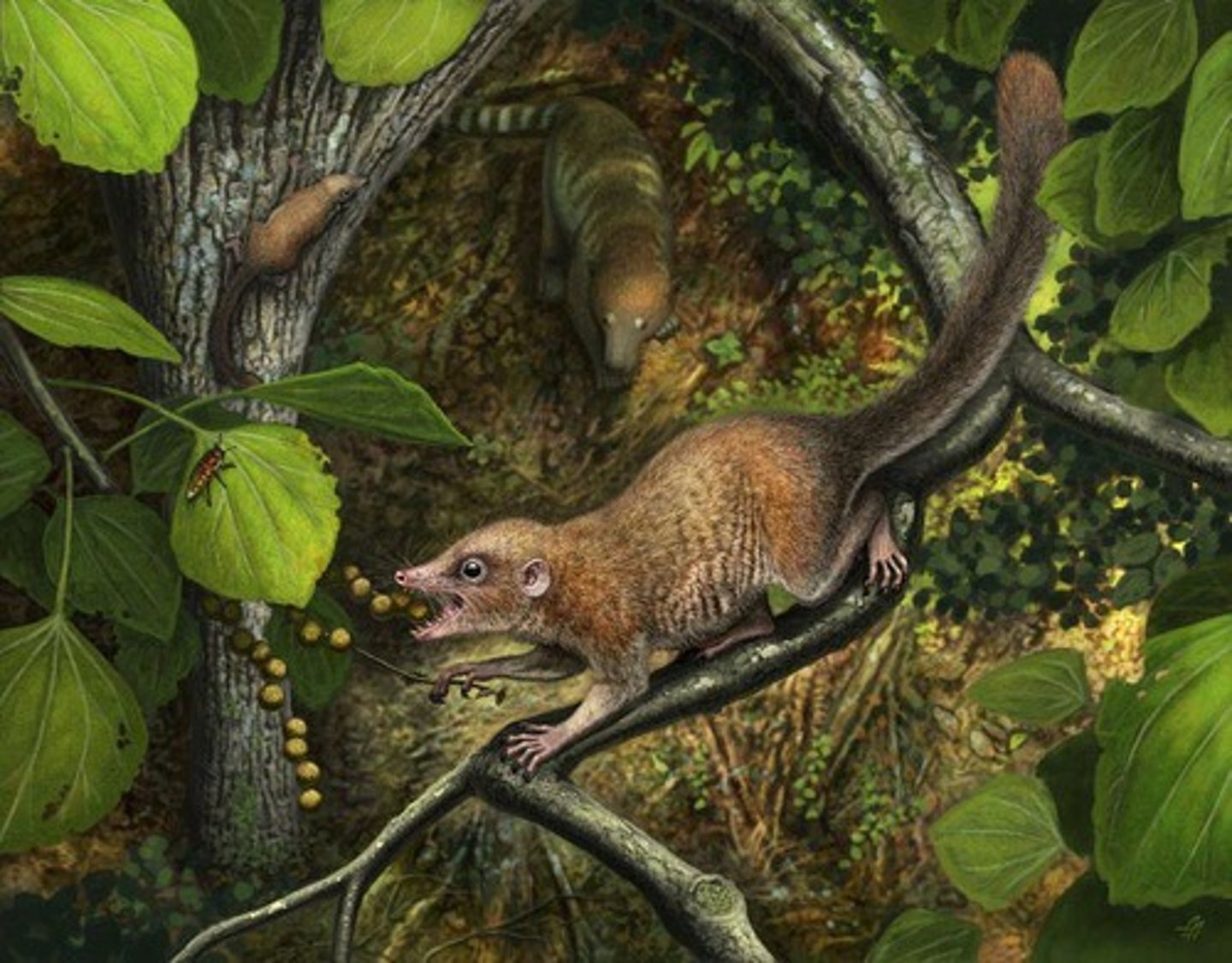

Purgatorious mckeeveri
Oldest genus of plesiadapiforms.
Megafauna
Large animals that existed during Pleistocene.
Glaciations
Periods of extensive ice coverage on Earth.
Wisconsinan Glaciation
Last glacial maximum in North America, ~21,000 ybp.
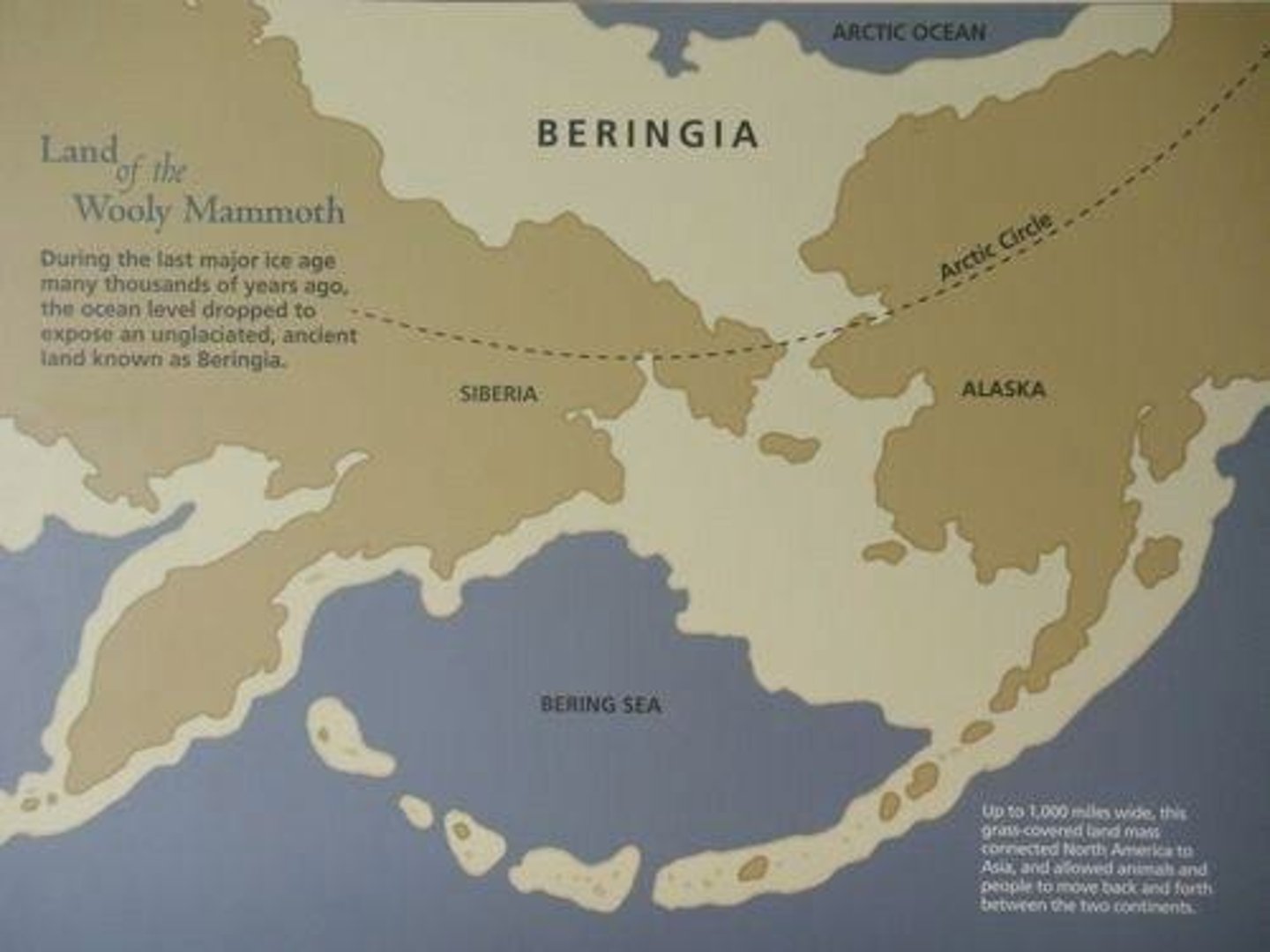
Beringia
Land bridge facilitating migration during glaciations.
Overkill hypothesis
Humans caused megafauna extinction via hunting.
Climate change
Altered ecosystems leading to megafauna extinction.
Glacial drift
Soil and sediments deposited by glacial movement.
Biotic communities
Organisms interacting within a specific environment.
Canadian ecosystems
Ecosystems shaped by glaciation and climate.
Climate variation
Differences in climate due to latitude and altitude.
Solar radiation
Energy from the sun affecting climate patterns.
Air pressure
Decreases with altitude, influencing climate.
Plant community
Dominant vegetation type in a biome.
Terrestrial systems
Land-based ecosystems influenced by climate.
Heat Capacity
Water cools and warms slower than land.
Climate Patterns
Influenced by oceans, wind, and topography.
Rain Shadow Effect
Mountain ranges create precipitation extremes.
Air Rising
Air cools and causes rainfall over mountains.
Desert Conditions
Dry air on the leeward side of mountains.
Moisture-laden Air
Air from Pacific Ocean brings precipitation.
Cascade Mountains
Region affected by rain shadow effects.
Rocky Mountains
Mountain range influencing regional climate.
Tundra
Treeless land located above the treeline.
Tundra Origin
Derived from Finnish and Russian languages.
Climate of Tundra
Very cold, below freezing most of the year.
Seasonal Temperature Variation
Temperature changes significantly throughout the year.
Proximity to Arctic Ocean
Moderates tundra temperatures compared to inland.
Desert-like Conditions
Tundra experiences low rainfall variability.
Sunlight Variation
Day length changes seasonally in tundra.
Permafrost
Soil remains frozen most of the year.
Short Growing Season
Limited time for plant growth in tundra.
Nutrient Poor Soil
Soil lacks nutrients, limiting productivity.
Low Productivity
Tundra supports few primary producers.
Active Layer
Top soil layer thaws during summer.
Deep Permafrost Layer
Slows biological activity and root development.
Freeze-Thaw Cycle
Creates unique growing conditions and landforms.
Polygons
Landforms resulting from freeze-thaw cycles.
Solifluction
Slow movement of water-saturated soil.
Polar grassland
Tundra ecosystem with up to 100% plant cover.
Polar desert
Tundra ecosystem with < 250 mm precipitation/year.
Active layer
Top soil layer that thaws in summer.
Musk ox
Example of tundra animal with thick fur.
Arctic hare
Example of tundra animal with reduced surface area.
Caribou
Herbivorous tundra animal consuming plants and lichen.
Polar bear
Carnivorous tundra animal consuming terrestrial animals.
Arctic fox
Cold-adapted specialist with seasonal camouflage.
Arctic woolly bear moth
Hibernates to reduce metabolism when food is scarce.
Eider ducks
Tundra animals that migrate seasonally.
Alpine tundra
High-elevation biome unable to support trees.
Treeline
Elevation beyond which trees cannot grow.
Transition Zone
Area with smaller, sparsely growing trees.
Timberline
Elevation where trees form a closed canopy.
Alpine climate
Cold, windy, and dry with snow precipitation.
Growing season
Duration of 45-90 days for alpine producers.
Soil erosion
Caused by high winds in alpine regions.
Species diversity
Higher in alpine tundra than Arctic tundra.
Endemism
High rate of species found in one location.
Alpine ecosystems
Cover ~3.5% of global land area.
Flowering plant species
Alpine ecosystems host ~4% of all species.
Alpine Habitat
Cold, dry, windy environment with limited resources.
Bighorn Sheep
Ovis canadensis, adapted for mountainous terrains.
Boreal Region
Largest terrestrial biome, covers ~14% of Earth.
Taiga
Russian term for 'untraversable forest' in boreal regions.
Boreal
Derived from Boreas, god of the north wind.
Canadian Boreal
60% of Canada's land area, 75% forests.
Boreal Climate
Cold temperatures with significant seasonal changes.
Winter Temperature
Average -20°C in winter months.
Summer Temperature
Average 18°C during summer months.
Precipitation
Average 38-50 cm/year, mostly summer rain.
Continental Climate
Wide temperature range, low humidity, low precipitation.
Primary Producers
Low productivity, high standing biomass in boreal forests.
Growth Season
50-150 days above 5°C with long sunlight.
Natural Disturbances
Fire and insect outbreaks create species diversity.
Fire Adaptations
Resin sealed cones and vegetative growth in trees.
Spruce Budworm
Insect feeding on spruce tree needles.
Black-backed Woodpecker
Prefers burnt forests for foraging insects.
Wood Bison
Bison bison athabascae, adapted to cold climates.
Spruce Grouse
Falcipennis canadensis, herbivore in boreal forests.
Ermine
Mustela erminea, has seasonal camouflage adaptations.
Canada Lynx
Lynx canadensis, has snowshoe adaptations for movement.
Wood Frog
Lithobates sylvaticus, hibernates during food scarcity.
Dark-eyed Junco
Junco hyemalis, migrates to higher latitudes seasonally.