Anatomy 2 Ch 21
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:07 PM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
1
New cards
arteries
always carry blood away from heart
2
New cards
arterioles
smaller branches from arteries
3
New cards
capillaries
smallest vessels; where exchange of materials takes place
4
New cards
venules
smaller branches that merge into veins; carry blood to veins
5
New cards
veinss
always return blood to the heart
6
New cards
tunica interna
aka tunica intima
innermost layer
simple squamous epithelium
direct contact with lumen (interior opening)
innermost layer
simple squamous epithelium
direct contact with lumen (interior opening)
7
New cards
tunica media
middle layer
smooth muscle and elastic fibers
smooth muscle allows vasoconstriction and vasodilation (controls diameter of vessels)
smooth muscle and elastic fibers
smooth muscle allows vasoconstriction and vasodilation (controls diameter of vessels)
8
New cards
tunica externa
outermost layer
elastic and collagen fibers
adjacent to surrounding tissue
elastic and collagen fibers
adjacent to surrounding tissue
9
New cards
layers
tunics
10
New cards
artery tunica media
thick, muscle allows diameter control, elastic fibers allow high compliance (walls stretch and expand in response to small increase in pressure)
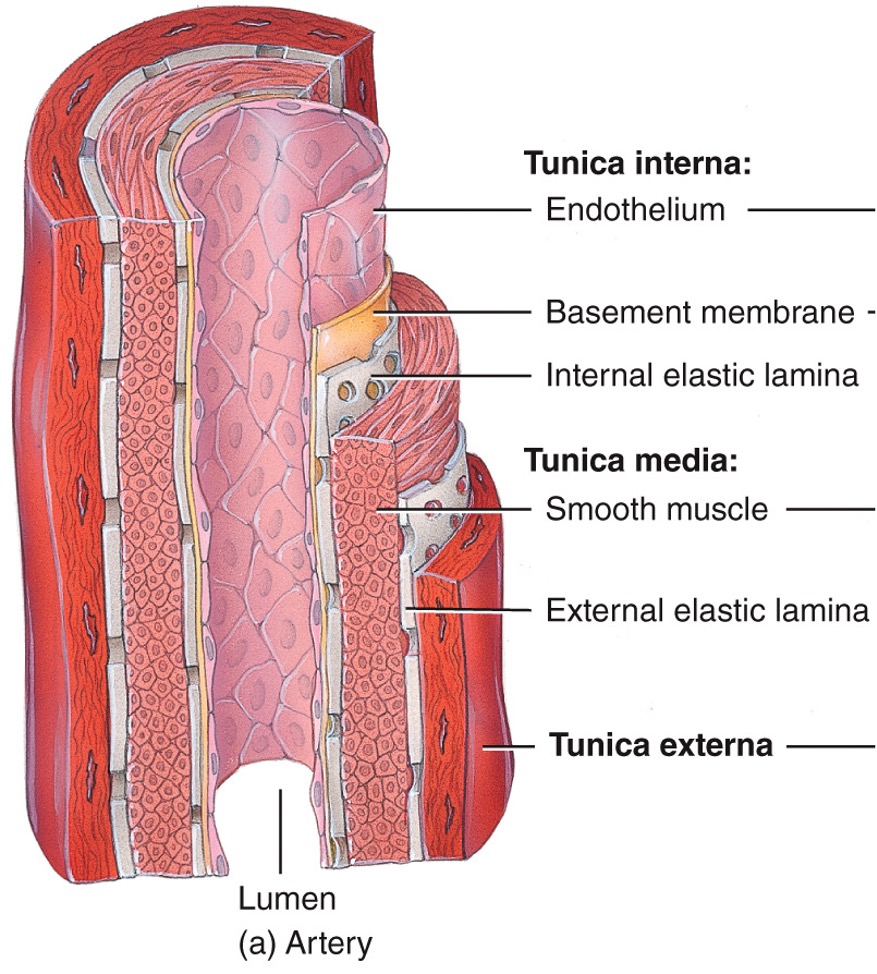
11
New cards
compliance
ability for tissue to stretch to accommodate pressure and go back to its original shape
12
New cards
elastic arteries
* conducting arteries
* large diameter
* more elastic fibers, less smooth muscle (more compliance closer to heart)
* function as pressure reservoirs
* ex aorta and pulmonary trunk
* large diameter
* more elastic fibers, less smooth muscle (more compliance closer to heart)
* function as pressure reservoirs
* ex aorta and pulmonary trunk
13
New cards
muscular arteries
* distributing arteries
* medium diameter
* more smooth muscle, fewer elastic fibers
* distribute blood to various parts of the body (instrumental in controlling blood flow to body and adjusting blood pressure)
* ex radial artery
* medium diameter
* more smooth muscle, fewer elastic fibers
* distribute blood to various parts of the body (instrumental in controlling blood flow to body and adjusting blood pressure)
* ex radial artery
14
New cards
pressure reservoir
blood ejected from the heart enters elastic arteries, their walls stretch to accommodate the surge of blood. As this occurs and the elastic fibers stretch, they store mechanical energy and function as a pressure reservoir. When they recoil and their stored energy propels the blood forward even though the ventricles are relaxed
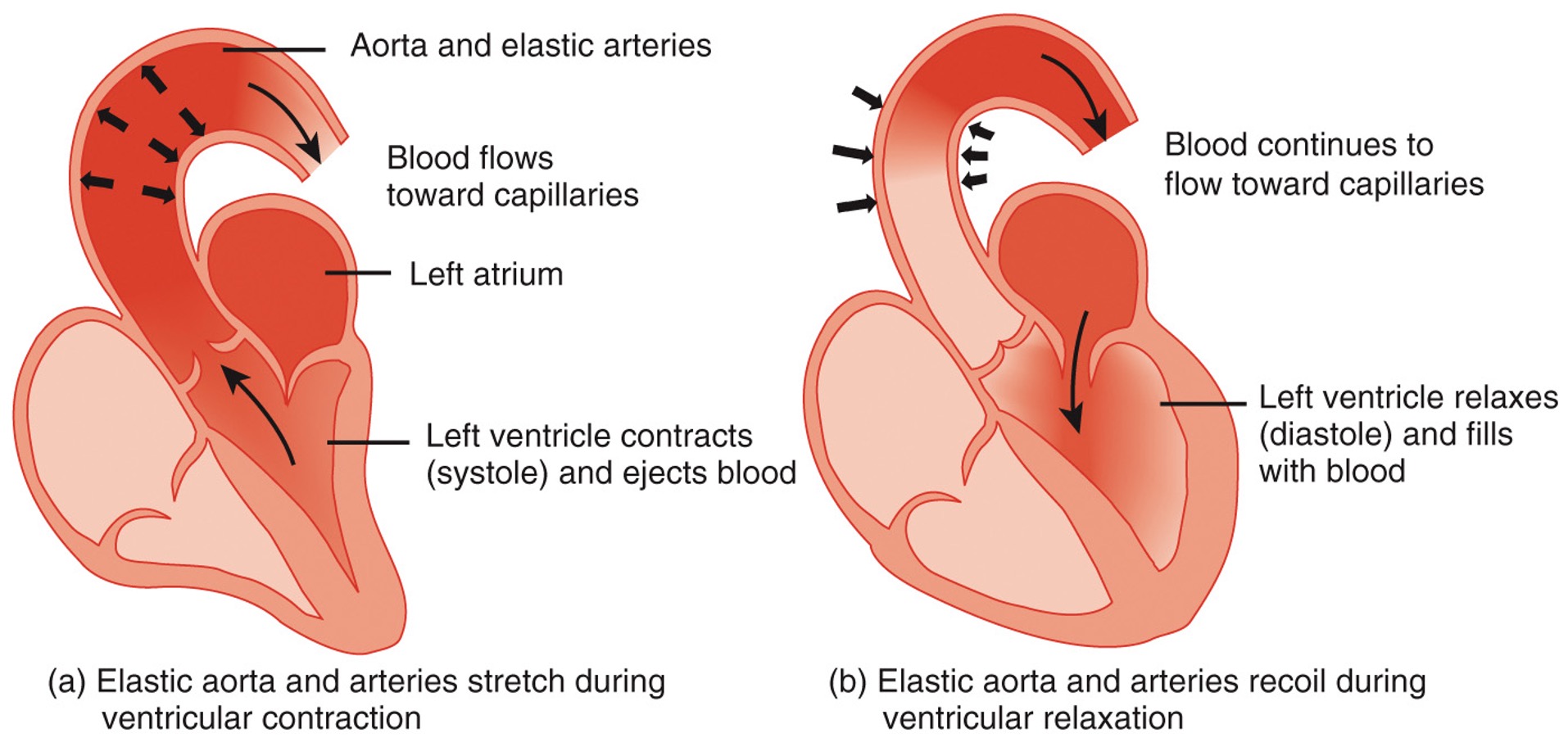
15
New cards
anastomosis
* when the branches of 2 or more arteries supplying the same area unite (may also occur between veins, arterioles and venules aka net arteriole)
* provides alternative routes if there is a blockage (collateral circulation)
* provides alternative routes if there is a blockage (collateral circulation)
16
New cards
end arteries
do not anastomose
no alternative route for circulation → obstruction leads to necrosis
happens a lot with coronary arteries so if a vessel gets blocked heart suffers ischemia and eventually infarction and dies
no alternative route for circulation → obstruction leads to necrosis
happens a lot with coronary arteries so if a vessel gets blocked heart suffers ischemia and eventually infarction and dies
17
New cards
necrosis
tissue death
18
New cards
arterioles
* microscopic arteries that lead to capillaries
19
New cards
metarteriole
end of artery that tapers toward capillary junction
20
New cards
precapillary sphincter
distal-most muscle cell at capillary junction (found between net arteriole and capillary bed to control blood flow)
regulates blood flow
regulates blood flow
21
New cards
thoroughfare channel
distal end of metarteriole with no precapillary sphincter
allows circulation from arteriole directly to venule; bypasses capillaries
allows circulation from arteriole directly to venule; bypasses capillaries
22
New cards
capillaries
* microscopic, thin-walled vessels
* tunica interna is simple squamous epithelium
* lack tunica media and tunica externa
* flow is controlled by precapillary sphincters and is intermittent (vasomotion)
* where most exchange of materials takes place
* permeability varies from one tissue to the next
* the pattern of capillary density also varies from one body part to the next
* high count in kidney and liver
* tunica interna is simple squamous epithelium
* lack tunica media and tunica externa
* flow is controlled by precapillary sphincters and is intermittent (vasomotion)
* where most exchange of materials takes place
* permeability varies from one tissue to the next
* the pattern of capillary density also varies from one body part to the next
* high count in kidney and liver
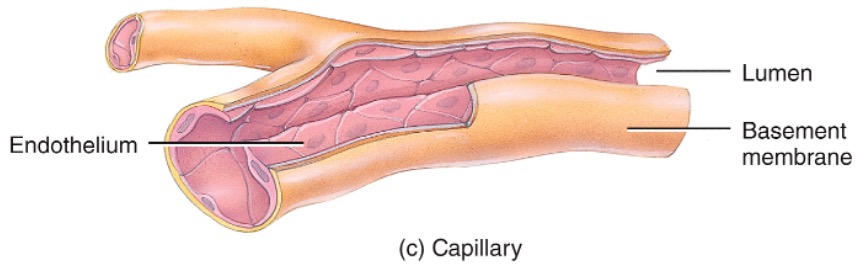
23
New cards
continuous capillary
* most capillaries are tis
* found in CNS, lungs, muscle tissue, skin
* found in CNS, lungs, muscle tissue, skin
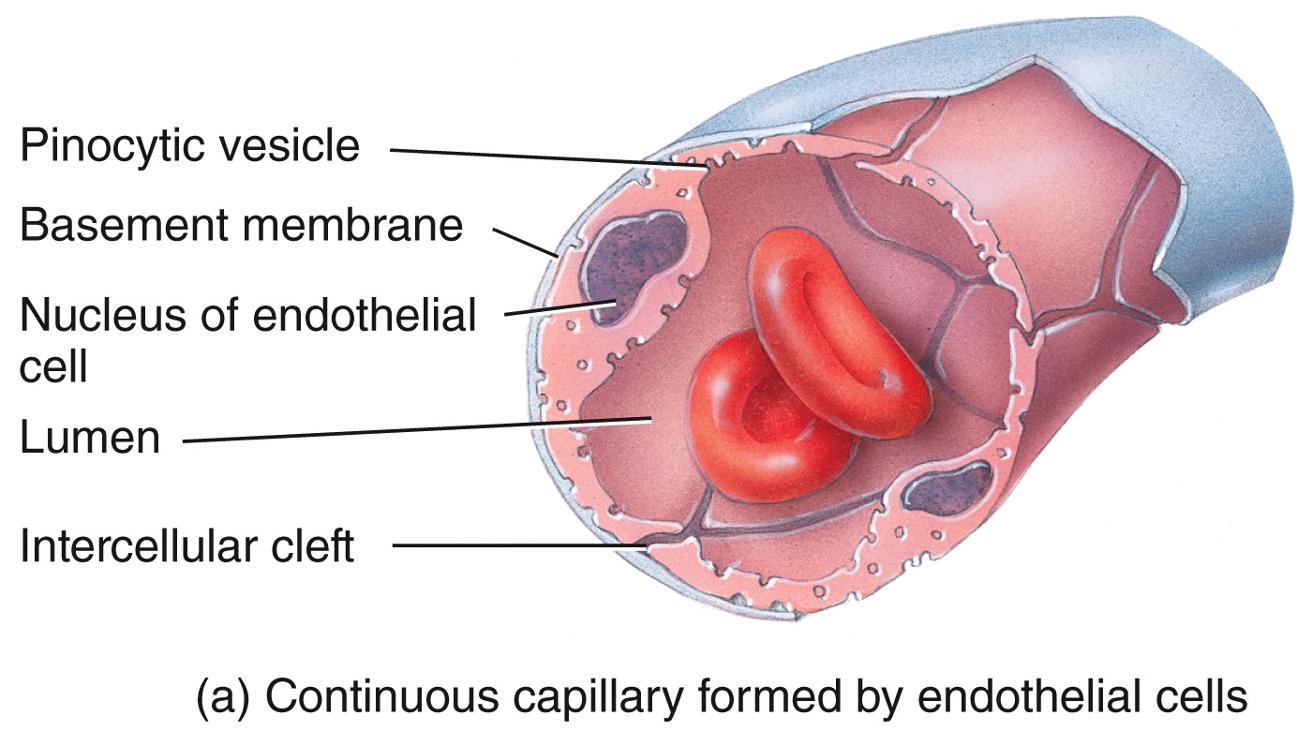
24
New cards
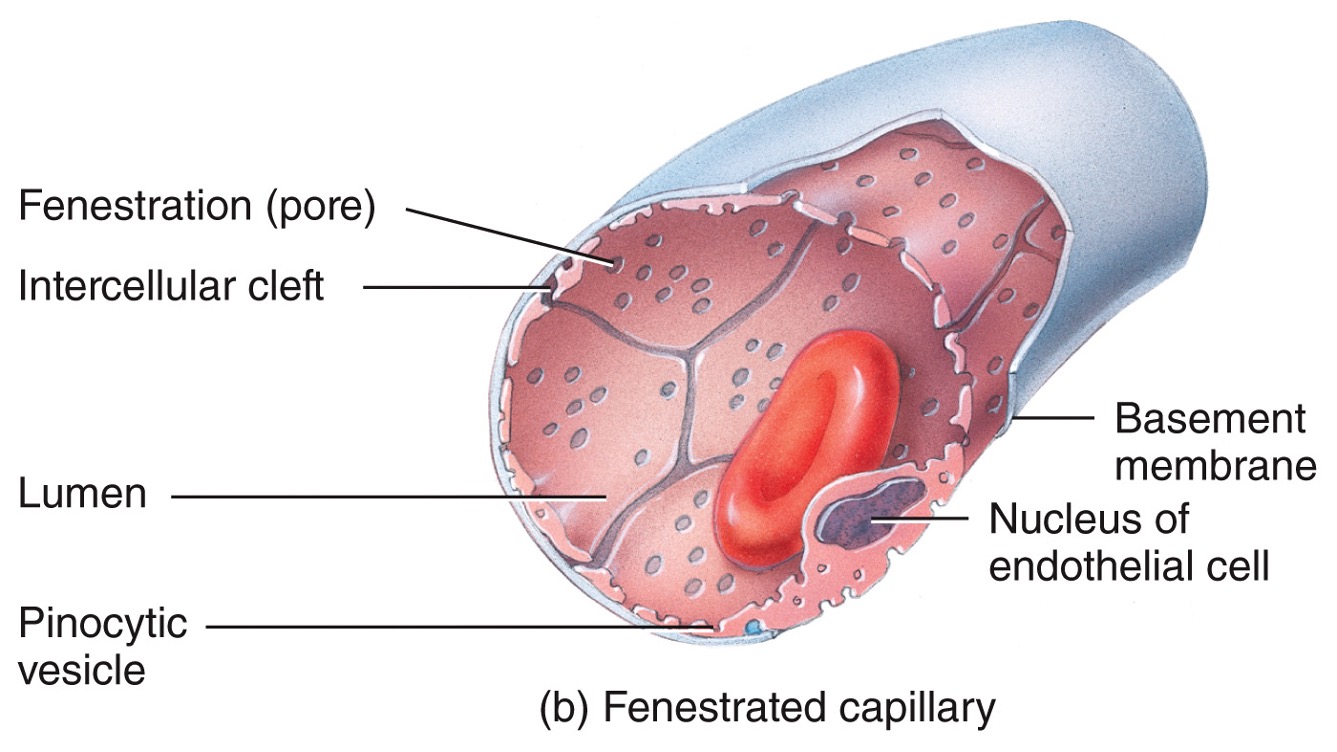
fenestrated capillaries
* pores allow some smaller proteins such as hormones to enter circulation
* found in kidneys, villi of small intestines, choroid plexuses in brain ventricles, most endocrine glands
* found in kidneys, villi of small intestines, choroid plexuses in brain ventricles, most endocrine glands
25
New cards
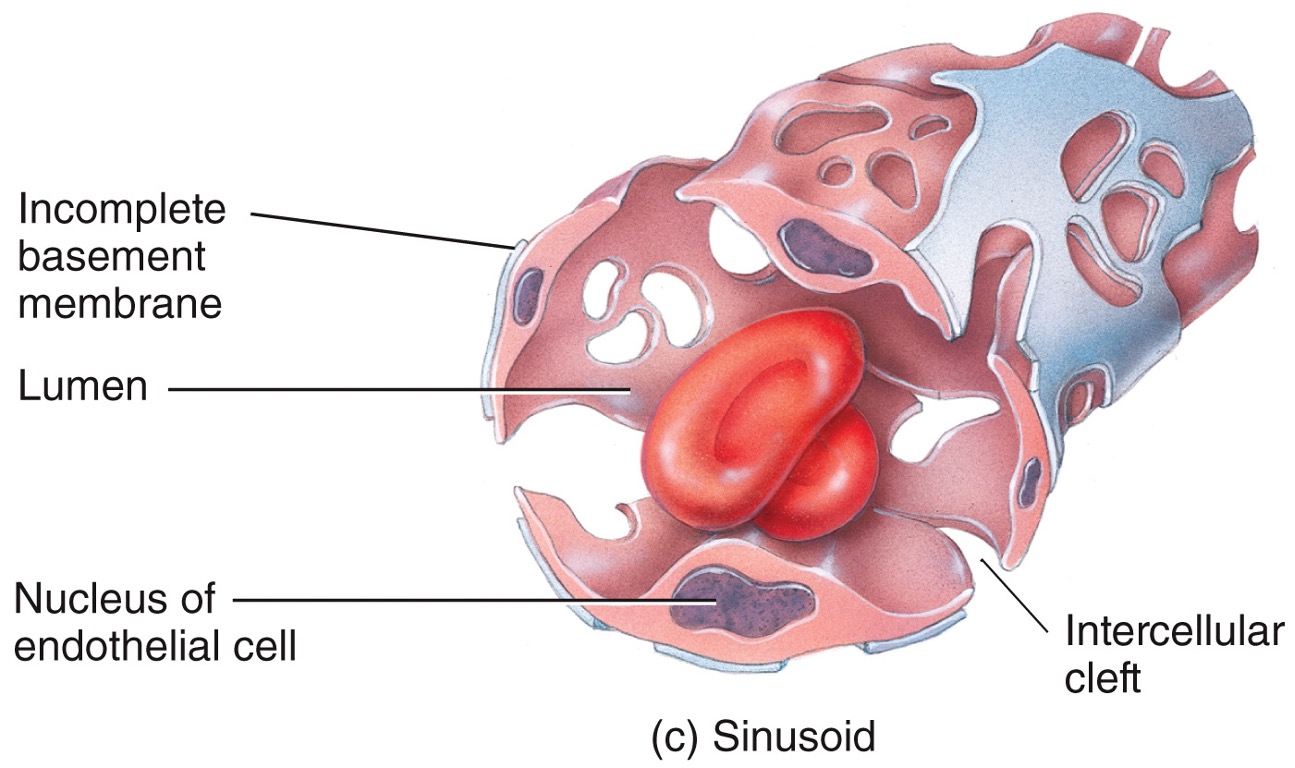
Sinusoid capillaries
* wider and more winding than other capillaries
* can allow proteins or even blood cells to enter bloodstream from tissues (this is how RBCs enter bloodstream in red bone marrow)
* contain special lining cells adapted to function of the tissue
* found in liver, spleen, anterior pituitary, parathyroids, adrenals
* can allow proteins or even blood cells to enter bloodstream from tissues (this is how RBCs enter bloodstream in red bone marrow)
* contain special lining cells adapted to function of the tissue
* found in liver, spleen, anterior pituitary, parathyroids, adrenals
26
New cards
venules
* thin-walled
* formed by merging capillaries
* drain blood from capillaries into veins
* distensible walls and act as blood reservoirs
* formed by merging capillaries
* drain blood from capillaries into veins
* distensible walls and act as blood reservoirs
27
New cards
postcapillary venules
* nutrient/waste exchange
* WBC diapedesis
* lead to muscular venules
* WBC diapedesis
* lead to muscular venules
28
New cards
muscular venules
have smooth muscle
29
New cards
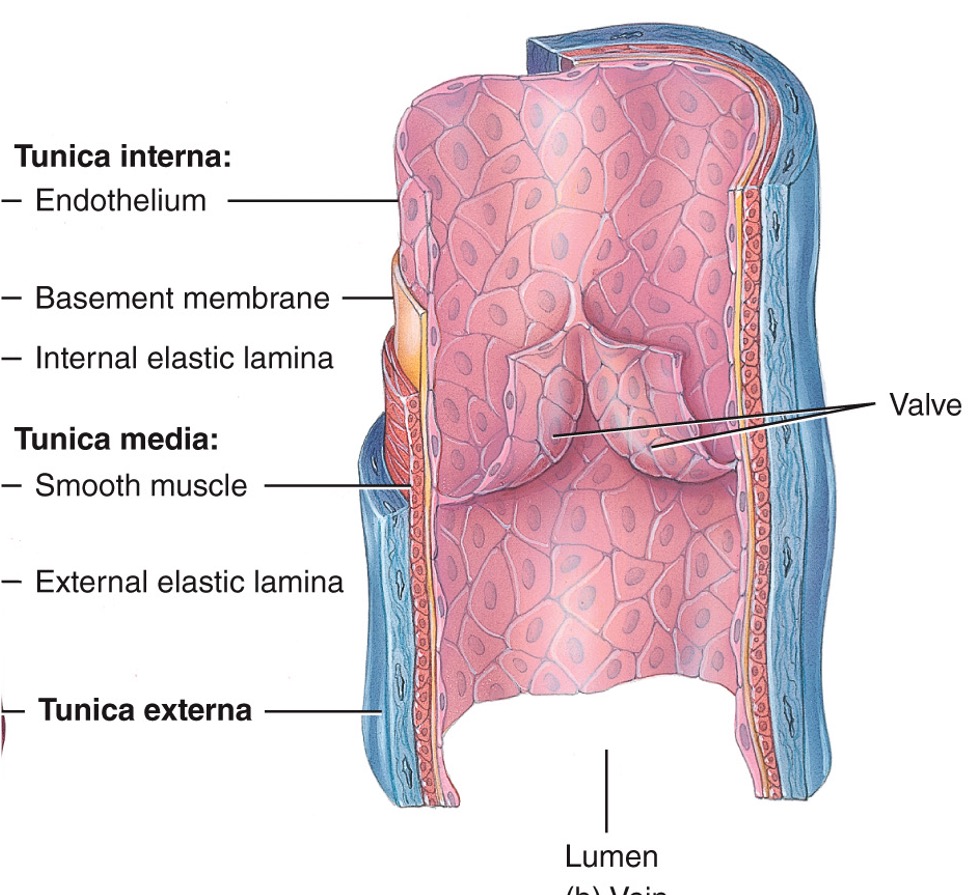
veins
* always return blood to heart
* increase in size as move further from venules
* thinner walls and larger lumen than arteries (tunica media is thin and tunica externa is thick)
* one-way valves to prevent backflow (always point toward heart and found in limbs)
* not designed to withstand high pressure
* situated between skeletal muscles so that movement aids circulation
* increase in size as move further from venules
* thinner walls and larger lumen than arteries (tunica media is thin and tunica externa is thick)
* one-way valves to prevent backflow (always point toward heart and found in limbs)
* not designed to withstand high pressure
* situated between skeletal muscles so that movement aids circulation
30
New cards
blood distribution at rest
31
New cards
elastic artery size
largest arteries in the body
32
New cards
artery tunica interna
well-defined internal elastic lamina
33
New cards
muscular artery size
medium-sized arteries
34
New cards
elastic artery tunica media
thick and dominated by elastic fibers; well-defined external elastic lamina
35
New cards
elastic artery tunica externa
thinner than tunica media
36
New cards
elastic artery function
conduct blood from heart to muscular arteries
37
New cards
muscular artery tunica media
thick and dominated by smooth muscle; thin external elastic lamina
38
New cards
muscular artery tunica externa
thicker than tunica media
39
New cards
muscular artery function
distribute blood to arterioles
40
New cards
arteriole size
microscopic (15-300 um in diameter)
41
New cards
arteriole tunica interna
thin with a fenestrated internal elastic lamina that disappears distally
42
New cards
arteriole tunica media
one or two layers of circularly oriented smooth muscle; distalmost smooth muscle cell forms a precapillary sphincter
43
New cards
arteriole tunica externa
loose collagenous connective tissue and sympathetic nerves
44
New cards
arteriole function
deliver blood to capillaries and help regulate blood flow from arteries to capillaries
45
New cards
capillary size
miscroscopic; smallest blood vessels (5-10 um in diameter)
46
New cards
capillary and venules tunica interna
endothelium and basement membrane
47
New cards
capillary and postcapillary venule tunica media
none
48
New cards
capillary tunica externa
n/a
49
New cards
capillary function
permit exchange of nutrients and wastes between blood and interstitial fluid; distribute blood to postcapillary venules
50
New cards
postcapillary venule size
microscopic (10-50 um in dimater)
51
New cards
venule tunica externa
sparse
52
New cards
postcapillary venule function
pass blood into muscular venules; permit exchange of nutrients and wastes between blood and interstitial fluid and function in white blood cell emigration
53
New cards
muscular venules size
micrscopic (50-200 um in diamter)
54
New cards
muscular venule tunica media
one or two layers of circulary oriented smooth muscle
55
New cards
muscular venule function
pass blood into vein; act as reservoirs for accumulating large volumes of blood (along with postcapillary venules)
56
New cards
veins size
range from .5mm to 3 cm in diamter
57
New cards
vein tunica interna
endothelium and basement membrane; no internal elastic lamina, contain valves; lumen much larger than in accompanying arteryc
58
New cards
vein tunica media
much thinner than in arteries; no external elastic lamina
59
New cards
vein tunica externa
thickest of the three layers
60
New cards
vein function
return blood to heart, facilitated by valves in limb veins
61
New cards
diffusion
* movement of substances from areas to greater to lower concentration
* important for solute exchange between blood and ISG
* lipid soluble substances: O2, CO2, and steroid hormones - simple diffusion through endothelium of capillary wall
* fenestrations allow larger, water soluble molecules such as NaCl and other nutrients
* sinusoids allow large proteins, such as fibrinogen, and RBCs to cross membrane
* important for solute exchange between blood and ISG
* lipid soluble substances: O2, CO2, and steroid hormones - simple diffusion through endothelium of capillary wall
* fenestrations allow larger, water soluble molecules such as NaCl and other nutrients
* sinusoids allow large proteins, such as fibrinogen, and RBCs to cross membrane
62
New cards
Transcytosis
* endocytosis on one side - moves across endothelium of capillary wall - exocytosis to other side
* large lipid-insoluble molecules
* how insulin (small protein) enters blood
* how certain antibodies pass from maternal circulation to fetal circulation
* large lipid-insoluble molecules
* how insulin (small protein) enters blood
* how certain antibodies pass from maternal circulation to fetal circulation
63
New cards
Bulk Flow
* large numbers of particles or ions in a fluid move together in the same direction
* occurs from an area of higher pressure to an area of lower pressure, and it continues as long as a pressure difference exists
* important for regulating relative volumes of blood and ISF
* occurs from an area of higher pressure to an area of lower pressure, and it continues as long as a pressure difference exists
* important for regulating relative volumes of blood and ISF
64
New cards
filtration
* how materials move from capillary to interstitial space
* pressure (hydrostatic) driven movement of fluids and solutes from blood to ISF
* occurs more at arterial end than venous end of capillaries
* blood hydrostatic pressure and interstitial fluid osmotic pressure promote filtration
* pressure (hydrostatic) driven movement of fluids and solutes from blood to ISF
* occurs more at arterial end than venous end of capillaries
* blood hydrostatic pressure and interstitial fluid osmotic pressure promote filtration
65
New cards
interstitial fluid
ISF
tissue fluid
tissue fluid
66
New cards
hydrostatic pressure
BHP
force exerted by the blood confined within blood vessels or heart chambers
higher at the arterial end of the capillary than it is at the venous end
force exerted by the blood confined within blood vessels or heart chambers
higher at the arterial end of the capillary than it is at the venous end
67
New cards
interstitial osmotic pressure
IFOP
form of osmotic pressure exerted by proteins in the blood plasma or interstitial fluid
form of osmotic pressure exerted by proteins in the blood plasma or interstitial fluid
68
New cards
blood colloid osmotic pressure
BCOP
pressure created by the concentration of colloidal proteins in the blood; mostly albumins
pressure created by the concentration of colloidal proteins in the blood; mostly albumins
69
New cards
Reabsorption
* how fluid returns to capillaries from ISF
* pressure (osmotic) driven movement of fluids and solutes from ISF back t blood
* IFHP and BCOP promote reabsorption
* pressure (osmotic) driven movement of fluids and solutes from ISF back t blood
* IFHP and BCOP promote reabsorption
70
New cards
Starling’s Law of the Capillaries
under normal conditions, the volume of fluid and solutes reabsorbed is almost as large as the volume filtered
NFP=(BHP+IFOP)-(BCOP+IFHP)
NFP=(BHP+IFOP)-(BCOP+IFHP)
71
New cards
hemodynamics
forces involved in blood circulation
72
New cards
blood flow
volume of blood flowing through a tissue at any given time period
73
New cards
factors affecting blood flow
Cardiac output
pressure difference: greater difference = greater blood flow
resistance: higher resistance = lower blood flow
pressure difference: greater difference = greater blood flow
resistance: higher resistance = lower blood flow
74
New cards
Cardiac output
CO = HR x SV
CO = MAP / R
CO = MAP / R
75
New cards
Blood Pressure
* hydrostatic pressure exerted on vessel walls
* highest in aorta and large systemic arteries, gets lower further away from heart
* the higher the BP, the higher the blood flow
* changes in blood volume affect BP
* created by ventricular contraction and ejection
* measured as systolic/diastolic
* higher the BP the greater the blood flow (highest in arteries closest to heart and lowest in veins closest to heart)
* highest in aorta and large systemic arteries, gets lower further away from heart
* the higher the BP, the higher the blood flow
* changes in blood volume affect BP
* created by ventricular contraction and ejection
* measured as systolic/diastolic
* higher the BP the greater the blood flow (highest in arteries closest to heart and lowest in veins closest to heart)
76
New cards
MAP
diastolic BP + 1/3(systolic BP - diastolic BP)
the average pressure in the arteries during 1 cardiac cycle (considered a better indicator of perfusion to vital organs than systemic BP is)
>60mmHg is enough to sustain organs in average person
the average pressure in the arteries during 1 cardiac cycle (considered a better indicator of perfusion to vital organs than systemic BP is)
>60mmHg is enough to sustain organs in average person
77
New cards
Vascular Resistance
R
opposition of blood flow due to friction of blood against walls of vessels
1. size of lumen - smaller diameter = greater resistance, and vice versa
2. blood viscosity - higher viscosity (thickness) = greater resistance, and vice versa
1. total blood vessel length - resistance is directly proportional to the length of the vessel
opposition of blood flow due to friction of blood against walls of vessels
1. size of lumen - smaller diameter = greater resistance, and vice versa
2. blood viscosity - higher viscosity (thickness) = greater resistance, and vice versa
1. total blood vessel length - resistance is directly proportional to the length of the vessel
78
New cards
SVR or TPR
total vascular resistance by all systemic blood vessels
* smallest vessels contribute most resistance
* controlled by arterioles
* smallest vessels contribute most resistance
* controlled by arterioles
79
New cards
systemic vascular resistance
SVR
80
New cards
total peripheral resistance
TPR
81
New cards
venous return
* occurs due to pressure of left ventricular contraction
* valves
* skeletal muscle pump
* respiratory pump
* valves
* skeletal muscle pump
* respiratory pump
82
New cards
skeletal muscle pump and respiratory pump
aid venous return due to compressing larger veins and aiding blood flow
leaky tricuspid valve hinders return due to blood regurgitation as ventricles contract
leads to systemic return backup
leaky tricuspid valve hinders return due to blood regurgitation as ventricles contract
leads to systemic return backup
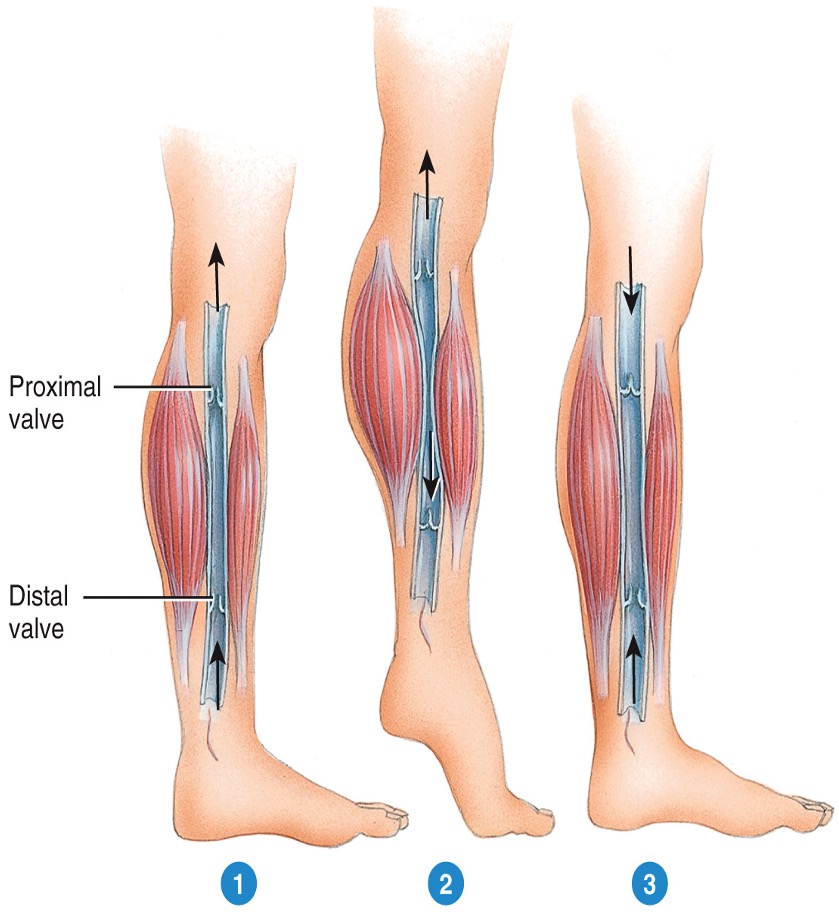
83
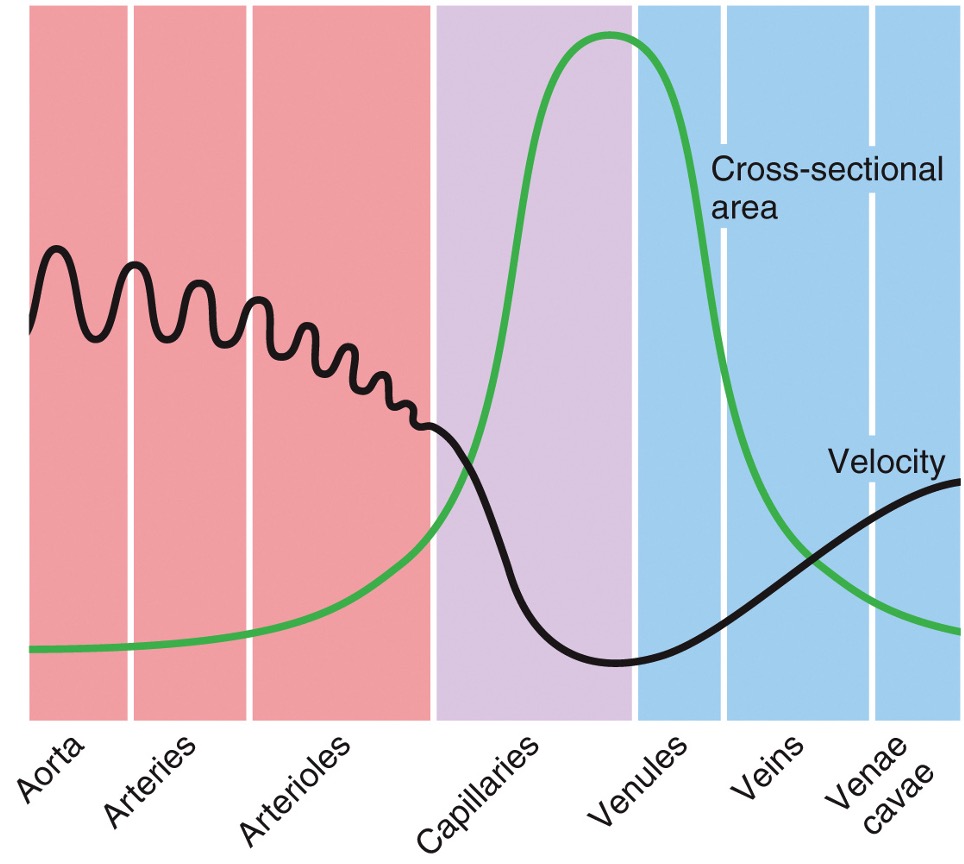
New cards
velocity of blood flow
* inversely related to the total cross-sectional area
* there are many more capillaries, therefore much more cross-sectional area, this means much lower velocity of blood flow
* velocity is highest in arteries close to heart, lowest in capillary beds
* there are many more capillaries, therefore much more cross-sectional area, this means much lower velocity of blood flow
* velocity is highest in arteries close to heart, lowest in capillary beds
84
New cards
systolic pressure
highest arterial pressure measured during ventricular systoled
85
New cards
diastolic pressure
lowerst arterial pressure measured during ventricular diastole
86
New cards
resting BP
110/70 mmHg
87
New cards
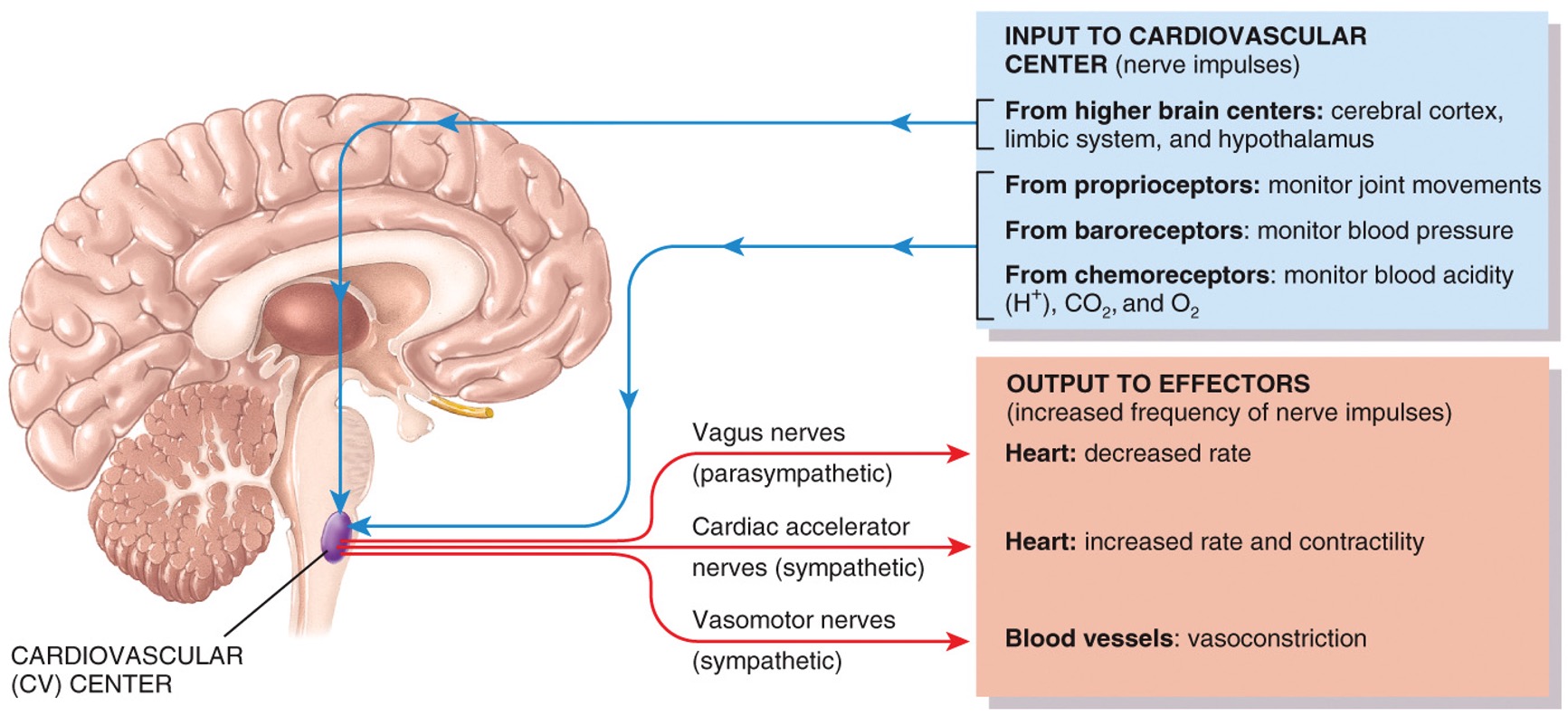
Neural regulation
* baroreceptor reflexes
* chemoreceptor reflexes
* hypoxia, hypercapnia, acidosis
* hormonal reflexes
* autoregulation
* found in aorta and large arteries in chest and neck
* chemoreceptor reflexes
* hypoxia, hypercapnia, acidosis
* hormonal reflexes
* autoregulation
* found in aorta and large arteries in chest and neck
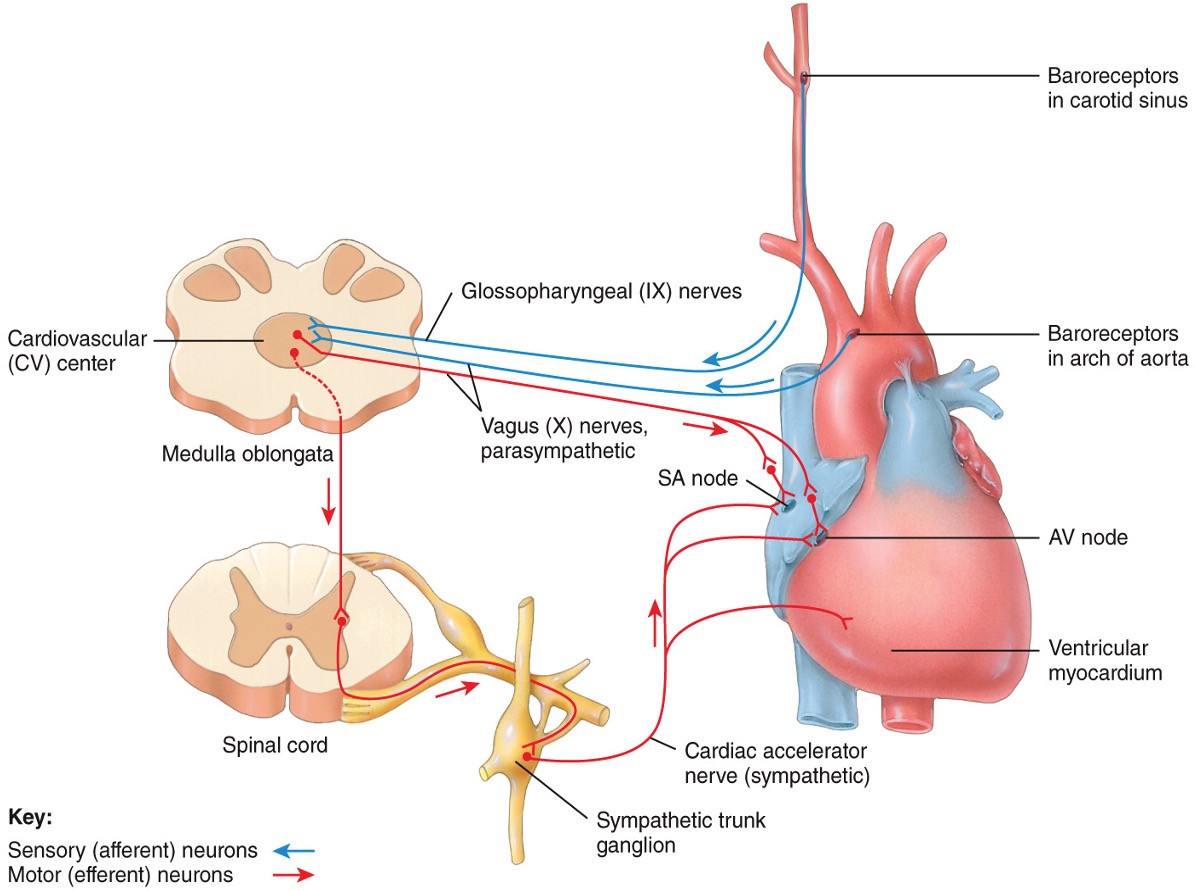
88
New cards
CV center
group of neurons that regulate heart rate, contractility and blood vessel diameter
89
New cards
baroreceptor reflexes
pressure sensitive
monitor stretching of walls in blood vessels and atria
monitor stretching of walls in blood vessels and atria
90
New cards
chemoreceptor reflexes
chemical sensitive
carotid bodies
aortic bodies
O2, CO2, H+
carotid bodies
aortic bodies
O2, CO2, H+
91
New cards
hypoxia, hypercapnia, acidosis
CV center increases sympathetic stimulation → vasoconstriction arterioles and veins
increases BP
increases BP
92
New cards
Hormonal regulation
* RAA system
* renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
* increases BP
* Epinephrine/norepinephrine
* increases BP
* ADH
* Increases BP
* ANP
* decreases BP
* renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
* increases BP
* Epinephrine/norepinephrine
* increases BP
* ADH
* Increases BP
* ANP
* decreases BP
93
New cards
autoregulation
* ability of a tissue to automatically adjust its own blood flow to match its metabolic demand for delivery of oxygen and nutrients and removal wastes
* physical and chemical stimuli can lead to autoregulation
* physical and chemical stimuli can lead to autoregulation
94
New cards
duration of blood travel
one minute to travel throughout body and back to your heart; shorter time for heart to brain
95
New cards
varicose veins
* formed when venous valves become weak or damaged
* veins are dilated and twisted in appearance
* dark blue or purple color
* veins protrude above the surface of the skin and can lead to pain, burning and spasms
* veins are dilated and twisted in appearance
* dark blue or purple color
* veins protrude above the surface of the skin and can lead to pain, burning and spasms
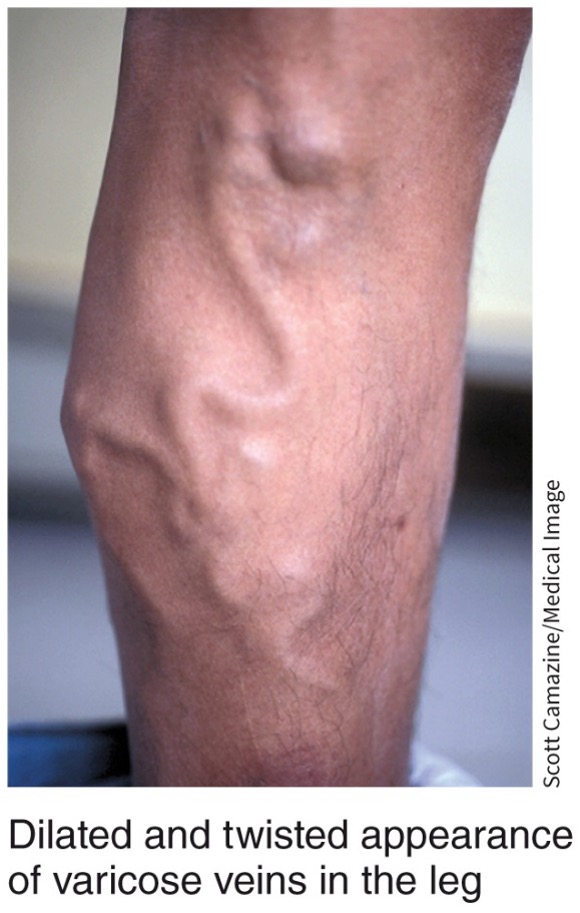
96
New cards
spider veins
* dilated venules close to the skin, especially in the lower limb and face
* appear red, blue or purple, resembling a spider web
* accompanied by pain and discomfort in the affected area
* appear red, blue or purple, resembling a spider web
* accompanied by pain and discomfort in the affected area
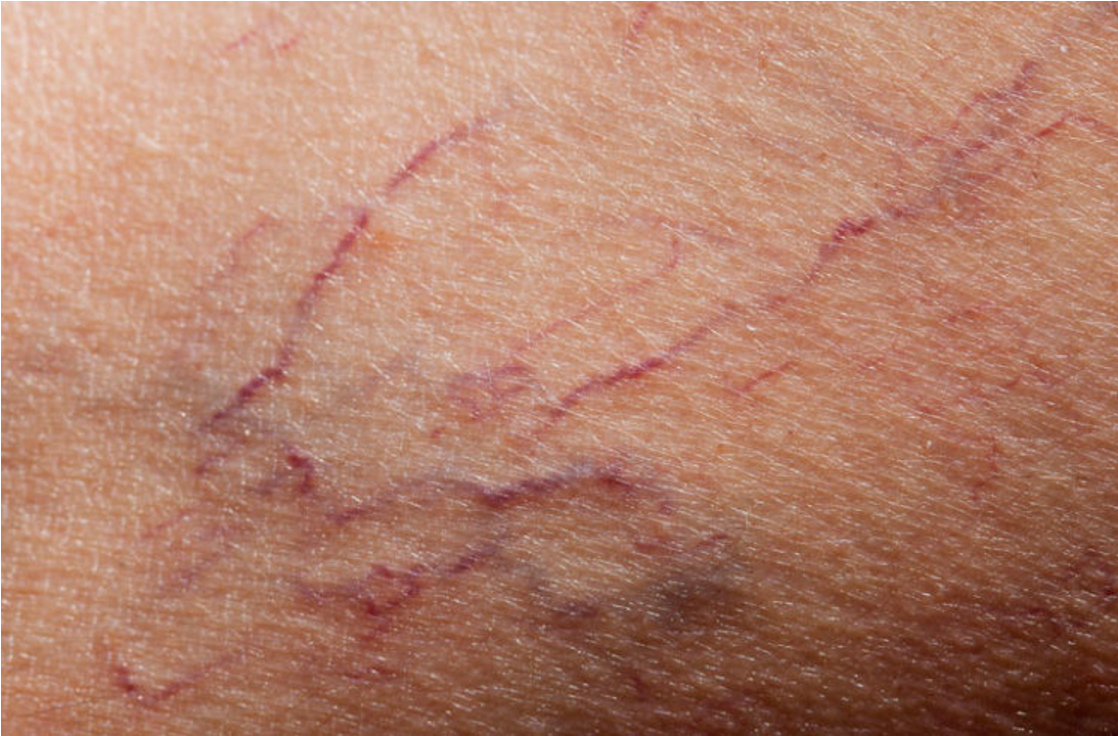
97
New cards
Shock
failure of cardiovascular to deliver enough Os and nutrients to meet cellular metabolic needs
98
New cards
hypovolemic shock
* low blood volume
* hemorrhage, loss of fluids, diabetes mellitus
* hemorrhage, loss of fluids, diabetes mellitus
99
New cards
100
New cards
cardiogenic shock
* poor heart function