TROPICAL DESIGN
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/175
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AQE 1
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms
1
New cards
from Greek klima; in Oxford dictionary as ‘region with certain conditions of temperature, dryness, wind, light, etc
CLIMATE
2
New cards
momentary state of the atmospheric environment at a certain location, could define as “the integration in time of weather conditions”.
weather
3
New cards
– Latin word “tropicus” meaning to turn; Greek word “tropikos” meaning to turn or change
tropical
4
New cards
types of louvers
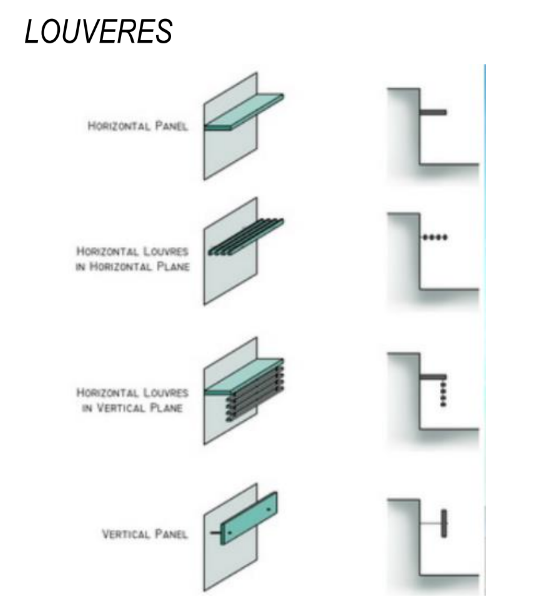
5
New cards
types of atrium (or open spaces)
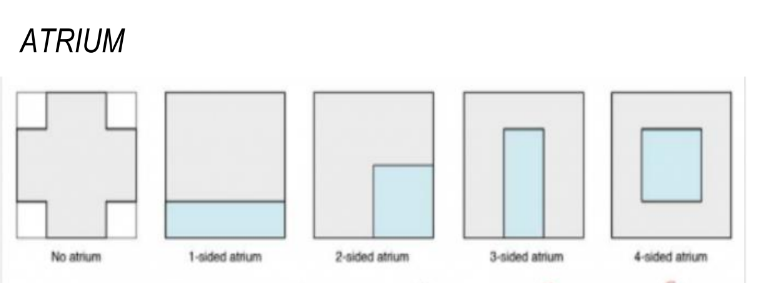
6
New cards
famous dictum- Architecture or Revolution; architecture is the skillful, accurate and magnificent play of masses seen in light
Le Corbusier
7
New cards
fixed or movable device, such as fins or louvres, designed to block the direct entrance of sun rays into a building
Brise Soleil
8
New cards
horizontal distance measured 90dg from outermost surface of the building/structure to the property lines
Setback
9
New cards
vacant space left between the outermost face of the building/structure and the property lines
Yard
10
New cards
– permitted minimal opening along a specifies vertical portion of the firewall and shall not be more than 3m in clear width and minimum depth of 1.5 meters
Vent Well
11
New cards
unoccupied space between the faces of the building lines and a yard or another court, free, open and unobstructed.
Court
12
New cards
bounded on all sides
Inner court
13
New cards
\- bounded on 3 sides
Open Court
14
New cards
bounded by 2 opposite sides
Through Court
15
New cards
paved and unpaved
\
\
TOSL
16
New cards
water content in the air that does not evaporate
Humidity
17
New cards
tells us how much water vapor is in the air compared with the maximum possible
Relative humidity
18
New cards
passive strategy using both wind and temperature differences to cool or ventilate spaces
Natural Ventilation
19
New cards
maximum performance when inlet and outlet areas are equal, and minimum stack height is 11 feet.
Stack Ventilation
20
New cards
maximum performance when inlet and outlet are placed at diagonal in both plan and section
Cross Ventilation Section
21
New cards
wind wall size should be 0.5 – 1 x width of window
Cross Ventilation Plan
22
New cards
Prevent Unecessary Increase in Humidity Levels
AIR CONDITIONER
23
New cards
Maximize Ventilation
PASSIVE COOLING
24
New cards
High precipitation levels during rainy days resulting to typhoons
Have good drainage system to accommodate high precipitation during the year
25
New cards
Protect spaces from insects and rodents
GROOVES
26
New cards
prevent moisture from building up on ground
\
\
Damp ground
27
New cards
Earth receives almost all its energy from the sun in the form of radiation
Solar Radiation
28
New cards
290 to 380; producing photochemical effects, bleaching, sunburn, etc
Ultra-violet radiation
29
New cards
380 (violet) to 700 nm (red)
\
\
Visible light
30
New cards
700 to 2300 nm, radiant heat with some photochemical effects.
Short infrared radiation
31
New cards
The axis of this rotation is tilted to the plane of the elliptical orbit at an angle of ….. and the direction of this axis is constant.
66\.5 dg
32
New cards
longest day, falls around June 21
\
\
Summer solstice
33
New cards
shortest day, falls around Dec 22
Winter solstice
34
New cards
when day and night are of equal length, twice around March22 and Sept 22
Equinox
35
New cards
angle of incoming solar radiation influences seasonal temperatures of locations at different latitudes.
Angle of incidence/insolation
36
New cards
the absorption of radiation by ozone, vapors and dust particles in the atmosphere
Atmospheric depletion/absorption
37
New cards
the length of daylight period
\
\
Duration of sunshine
38
New cards
to cold outer space
long-wave radiation-
39
New cards
– the earth’s surface is cooled, as liquid water changes into vapor and mixed with air
By evaporation
40
New cards
– air heated by contact with warm earth becomes lighter and rises to the upper atmosphere where it dissipates its heat to space
By convection
41
New cards
the only way the earth loses energy in space is
Electromagnetic Radiation
42
New cards
convection currents in the atmosphere, tending to even out the differential heating of various zones.
Winds
43
New cards
The area where the air rises, where these northerly and southerly winds meet, where the tropical front is formed, is reffered to as
Inter-tropical convergence zone (ITCZ)
44
New cards
area experiences either completely calm conditions or only very light breezes of irregular directions and is referred to by sailors.
\
\
Doldrums
45
New cards
Influences the force of air, direction of air flow, moisture content of air
Topography
46
New cards
Measured in degrees Celsius
Temperature
47
New cards
\- instrument measure air temperature
Thermometer
48
New cards
\- reading taken in the shade with a thermometer
Dry-bulb/”true air temperature”
49
New cards
\- a louvered box mounted at a height range of 1.20 m to 1.80 m. to meteorological instruments against precipitation and direct heat radiation from outside sources
Stevenson screen
50
New cards
Can be described as absolute humidity (AH)
\
\
Humidity
51
New cards
more useful from of expression, as it gives a direct indication of evaporation potential.
Relatively humidity (RH)
52
New cards
an instrument used to measure humidity
Wet-and-dry buld hygrometer
53
New cards
amount of moisture actually present in unit mass or unit volume of air, in terms of gram per kilogram or gram per cubic meter
Absolute Humidity (AH)
54
New cards
the amount of moisture the air can hold
Saturation-point Humidity (SH)
55
New cards
ratio of the actual amount of moisture present, to the amount of moisture that the air could hold at the given temperature
Relative Humidity (RH)
56
New cards
All forms of water deposited from the atmosphere, such as rain, snow, hail, dew, and fros
Precipitation
57
New cards
\- instrument used to measure precipitation
Rain gauge
58
New cards
a device that records the amount of sunshine at a given location; reading is expressed in number of hours per day
Sunshine recorder
59
New cards
metric unit for the instantaneous intensity of solar radiation, or the incidence of solar energy received by a surface
Watt per square meter (W/m^2)
60
New cards
measured by a cup-type or propeller anemometer
Wind velocity
61
New cards
direction is measured by
Wind vane
62
New cards
instrument used to measure wind velocity and directional changes
Anemograph
63
New cards
covers a considerable portion of the earth and has an effect on weather and climate
Vegetation
64
New cards
usually provide enough information for the designer to make a preliminary assessment of the climate and may be sufficient to form the basis of sketch designs.
\
\
Deviation within the zone
65
New cards
\- information may be useful guide to the climate of the site.
\
\
Macroclimate
66
New cards
small scale patterns of climate resulting from the influence of topography, urban forms, water bodies, vegetation, etc
Microclimates
67
New cards
\- falls between micro and macro climates
\
\
Meso-climate
68
New cards
slope, orientation, elevation, exposure, hills/valleys
Topography
69
New cards
whether natural or man-made, its reflectance, permeability
\
\
Ground Surface
70
New cards
trees, fences, walls, buildings – may influence air movement, etc.
Three-dimensional objects
71
New cards
\- dependent upon the amount of heat gained or lost at the earth’s surface
Air temperature
72
New cards
depends as much on the air temperature as on the actual amount of water vapor present in the air.
Humidity
73
New cards
wind speed is always near the ground than with the higher portion
Air movement
74
New cards
top of hills or tall buildings are subject to lighting strikes
Thunderstorms
75
New cards
influenced by the ground surface providing sand and dust
Dust and sandstorms
76
New cards
small-scale whirlwind carrying dust
Smaller dust-storm
77
New cards
form an intermediate layer between the earth’s surface and the atmosphere
Vegetation
78
New cards
man-made environments can create microclimates of their own, deviating from the urban climate the macroclimate of the region to a degree depending on the extent of man’s intervention
Urban Climate
79
New cards
Classifications that influence human comfors
air temperature and humidity
80
New cards
subgroup: warm-humid island or trade-wind climate
Warm-humid equatorial climate
81
New cards
subgroup: hot-dry maritime desert climate
Hot-dry desert / semi-desert climate
82
New cards
subgroup: tropical upland climate
\
\
Composite or monsoon climate
83
New cards
warm humid island
caribbean, Philippines, Pacific islands
84
New cards
air temperature of the philippines at day
29-32 c
85
New cards
air temperature of the philippines at night
18-24 c
86
New cards
humidity level in philippimes
55-100%
87
New cards
Tropical Moist Climates (Af)
\
\
Tropical Rainforest & savanna
88
New cards
Mediterranean Climates (Cs)
\
\
Chaparral Biome
89
New cards
receive the greatest amount of rainfall
Baguio City, eastern samar, and eastern Surigao
90
New cards
least rainfall
Cotabato
91
New cards
locally known as Amihan
Northeast Monsoon
92
New cards
Locally known as Habagat
Southwest Monsoon
93
New cards
Wet season
from June to November
94
New cards
Dry season
from December to May
95
New cards
Great influence on the climate and weather conditions
Typhoons
96
New cards
\- take advantage of the environment to provide tha maximum comfort for its occupants
Passive design concepts
97
New cards
is designed as an adaptation to its tropical environment.
Bahay kubo
98
New cards
can be seen as an evolution of a structure to adapt to the local environmental conditions in the Philippines.
\
\
Bahay na bato
99
New cards
since Batanes experience strong winds, the local thatch and wood evolve to stringer materials like stone with lime
Ivatan house
100
New cards
design ed with thick layers of cogon to serve as insulation from the heat of the sun and rains
Ifuago house