Esters Slides
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Ester Definition
Derivatives of carboxylic acids where the hydroxyl group (OH)
is replaced by an alkoxyl group (OR)
Combination of carboxylic acid and an alcohol with loss of water
Ester Properties
They are presented as liquids and solids depending on the amount of
carbons
Low molecular weight – colorless liquids with pleasant odors
Increases molecular mass – they become viscous and more solid (like
waxes) and odorless
Ester Properties 2
Insoluble in water
Soluble in alcohol, ether and chloroform
Boiling and melting points are lower than
alcohols and acids of equal molecular mass
Density lower than water
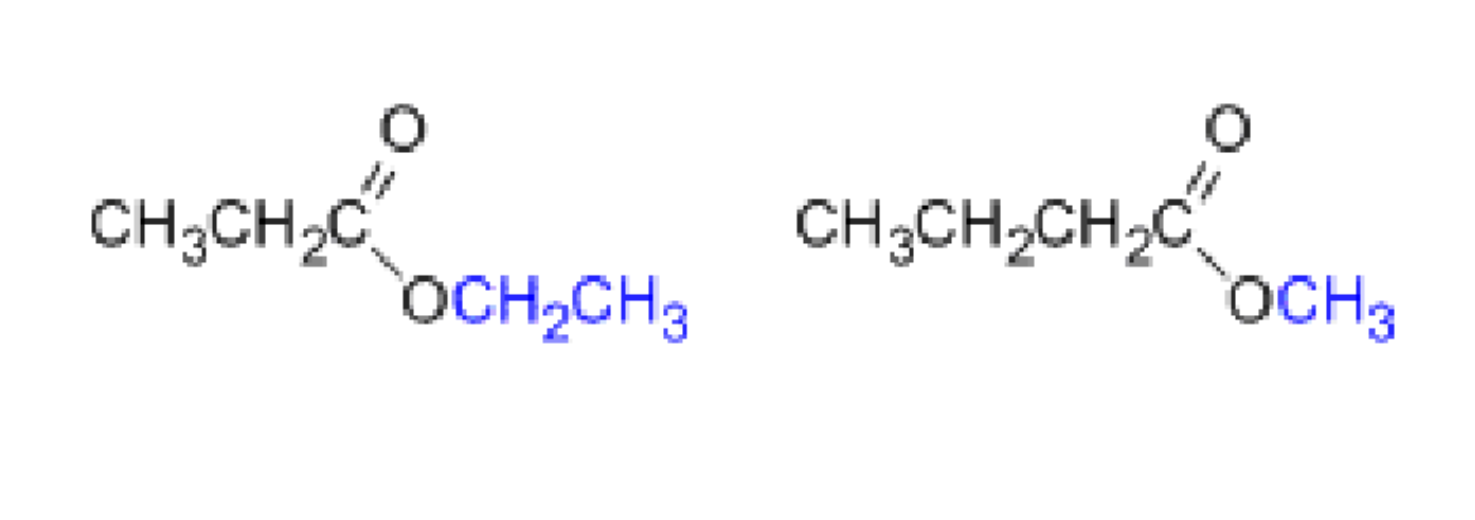
Ester Nomenclature. Ethyl Propanoate and methyl butanoate
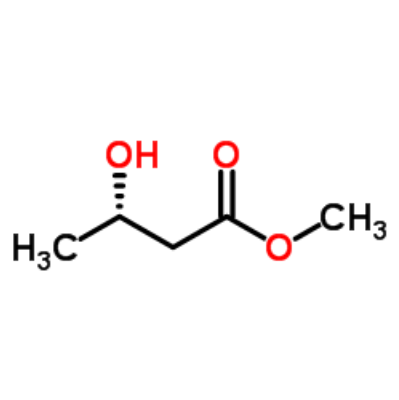
Methyl (R)-3-hydroxybutanoate
Methyl (R)-3-hydroxybutanoate

Methyl (3S)-3-hydroxybutanoate
Methyl (3S)-3-hydroxybutanoate.
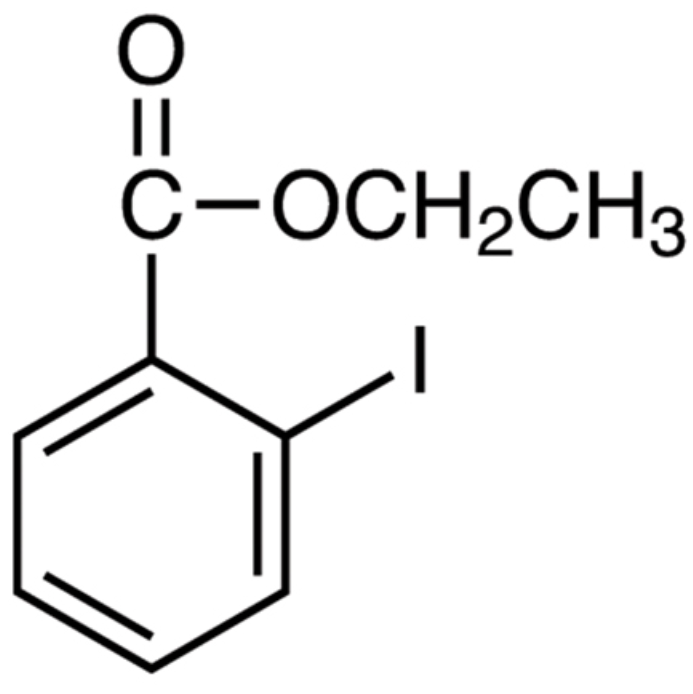
Ethyl-2-IodoBenzoate
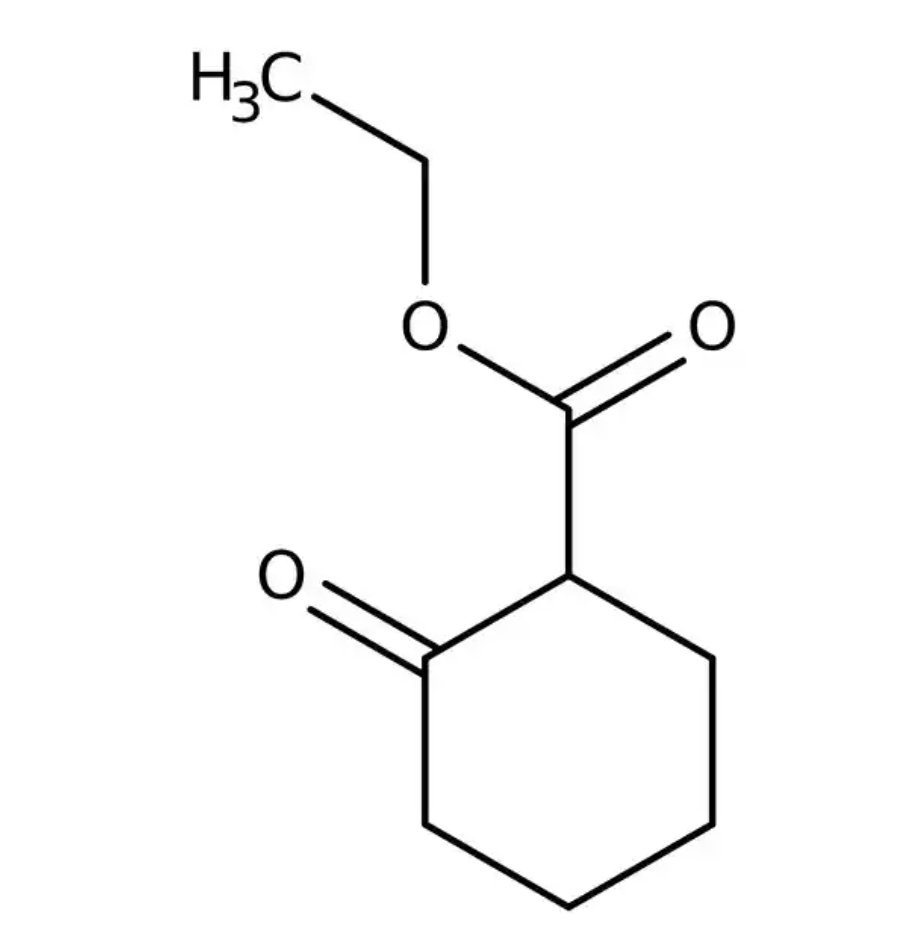
Ethyl 2-Oxocyclohexanecarboxylate
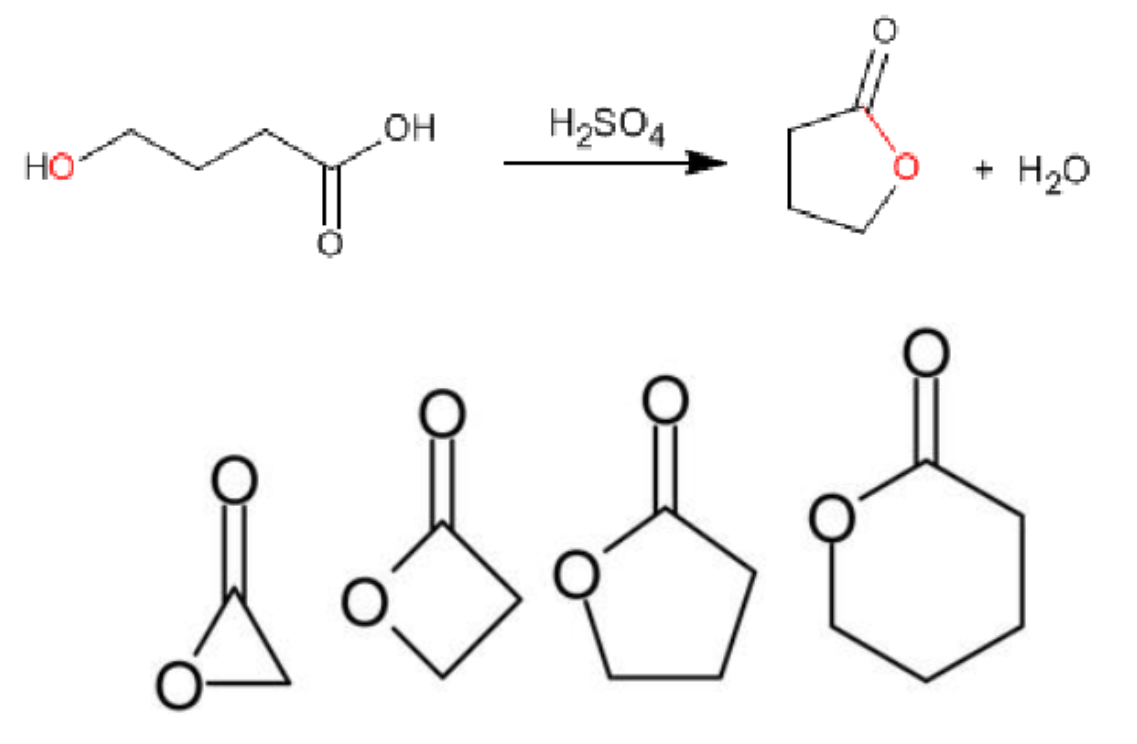
Cyclic Esters
Cyclic esters are called Lactones
It is formed from an open chain hydroxy acid where the hydroxyl
group reacts with the acid group.
Applications of Esters
🍬 Artificial flavors
💊 Medications
🧼 Soap manufacturing
💄 Beauty products
🧪 Solvents
🧵 Fiber manufacturing