week 3 Motor Learning and Neurodevelopment Treatment Approach (NDT)
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
principles of movement, positioning, handling and facilitation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Motor learning theory
acquisition of new motor skills, the improvement of existing and long term retention through practice
contains the cognitive, associative, and autonomous stage
Cognitive stage in the Motor Learning Theory
movements are slow, inconsistent and inefficient
learners focus on aspects of movement and require mental effort
goal is to understand the task, develop strategies and problem solve.
Associative stage in the Motor Learning Theory
movement are fluid, reliable, efficient and with fewer errors
learner perform parts of movement automatically but still need focus
goal is to refine movements, improve consistency and reduce errors.
Autonomous stage in the Motor Learning Theory
movements are accurate, consistent and efficient
decrease cognitive effort, may multi task
maintain skill and adapt to new situations/generalize
Dynamic systems theory
interaction between organism (and their ability), task (requirement) and enviroment contribute to motor development.
Neurodevelopment Treatment Approach NDT
a FOR
The Bobath Concept (question how does posture and movement impact function)
framework for understanding how movement is learned and adapted
Evolution of NDT
first inspired by Reflex higherarchial model then moved to Dynamic systems model
Reflex Higherarchical Model
First model to contribute to the evolution of NDT
Motor control is a strict hierarchy
movement is triggered by a series of reflexes AND is a response to sensory stim
fails to explain voluntary movement
Dynamic Systems Model
Model that NDT is currently inspired by
a complex interaction between multiple subsystems
movement is guided by functional goals
explains multifaceted nature of motor control
Core principles of NDT
brain had plasticity (ability to change)
children needs to feel typical movement patterns using positioning, facilitation and handling techniques
learning movements patterns should occur in natural enviroment
remediation of foundational skills will make normal skills acquisition possible
cannot impose normal movement w abnormal muscle tone
children should learn/experience normal movement pattern during meaningful activities
targeting postural control through key pts of control
Proximal points of control
shoulders, hip, trunk, pelvis
distal points of control
hands, feet, head
Passive elongation of muscle, reflex inhibiting pattersn, positioning and weight shifts can be used to…
inhibit hypertonia (the increase of muscle tone/stiffness)
joint compression, traction, manuel resitiance and weight shifts can be used to…
increase hypotonia
axial control can be achieved through
elongation, weight shifts, passice pelvis tilt, and truck rotation
automatic reaction can be achieve through
inhibitng reflexes and use of normal movement patterns
weight shifts can occur through
dissociation of synergistic patterns and inhibiting reflexes
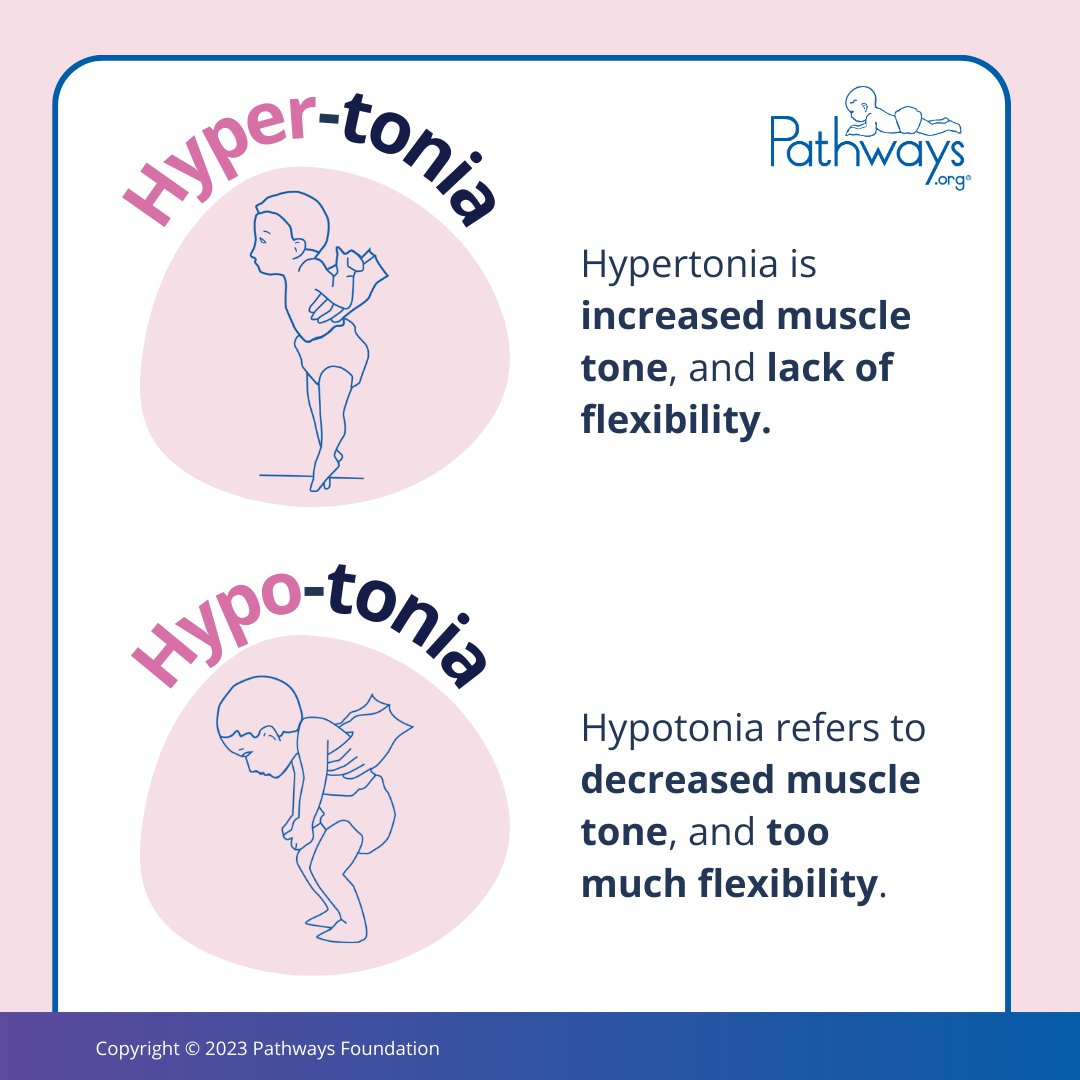
Muscle tone
muscle readiness for passive strength, tested passively
NDT assessment objectives understand an individuals….
muscle tone
functional abilities/limitations
analysis of movement patterns and compensatory movement
absent components of movement
impact of movement on participation in occupational roles.
decreased BOS
increases truck control
increased BOS
decrease truck control
The NDT assessment looks to understand a child’s…
functional skills
quality of movement
structural limitations and deformities
Handling Technique
NDT intervention strategy that can be preparatory or used to facilitate typical movement patterns. When done correctly, changes in sensory input is achieved.
As a part of NDT intervention strategies, abnormal movement patterns can be changed through..
altering sensory input (which changes motor output)
hand placement
directs, organizes, and facilitates initiation , activation of muscles and response to muscles
therapeutic touch
requires a respect and knowledge of the child’s sensory systems and how they process tactile, proprioceptive and kinesthetic input
Ways to increase tone…
intermittent joint compression ( to provide proprioceptive input)
vibration
resistance (through gravity or heavy work)
weight bearing in small ranges
tapping
Decreasing tone
muscle elongation
muscle activation within new length
trunk rotation
dissociation
weight bearing.shifting in large ranges
fine manual vibration
traction
Developmental transition Sequence
Supine → side lying/roll → prone → side sit → quadruped → short kneel → tall kneel → 1 point kneel → stand