LAB EXAM EVERYTHING AHHHHHHHHHHHH
1/266
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GOOD LUCK TO EVERYONE <3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
267 Terms
At its current setting, what volume will this pipette dispense?
A. 157.8 microliters
B. 8751 microliters
C. 1578 microliters
D. 8.751 microliters
A. 157.8 microliters
Which of the following options is closest to the volume of solution in this 10 mL graduated cylinder?
A. 6.8 mL
B. 6.9 mL
C. 6.7 mL
D. 6.6 mL
D. 6.6 mL
How many mL are in 1 dL?
A. 0.01 microliters
B. 100 microliters
C. 100 milliliters
D. 0.01 milliliters
C. 100 milliliters
How many microliters are in 0.076 mL
A. 0.076 microliters
B. 76 microliters
C. 7.6 microliters
D. 0.76 microliters
B. 76 microliters
Which of the following statements is false?
A. temperature change of 1 degree Fahrenheit is a larger change than a temperature change of 1 degree Celsius.
B. Normal human body temperature is 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit.
C. 100 degrees Celsius is equivalent to 212 degrees Fahrenheit.
D. Normal human body temperature is 37 degrees Celsius.
A. temperature change of 1 degree Fahrenheit is a larger change than a temperature change of 1 degree Celsius.
What is the maximum volume this micropipette can accurately dispense?
A. 200 microliters
B. 20 microliters
C. 1578 microliters
D. 8751 microliters
A. 200 microliters
There are __________ mL in one liter and there are _________ grams in one mg.
a. 1000; 0.001
b. 0.0001; 1000
c. 0.001; 0.001
d. 1000; 1000
Which of the following options is closest to the volume of liquid that has been drawn into this 5 mL syringe?
a. 3.1 mL
b. 2.3 mL
c. 2.8 mL
d. 2.4 mL
C. 2.8 mL
Which of the following statements is false?
A. There are 100 centimeters in a meter.
B. A person who weighs 100 lbs is heavier than a person who weighs 100 Kg.
C. An object that has a diameter of 15 micrometers is too small to see with the naked eye.
D. There are 100,000,000 micrometers in a meter.
B. A person who weighs 100 lbs is heavier than a person who weighs 100 Kg.
Assume your patient weighs 186 lbs and requires a certain drug at a dose of 10mg/kg*. What quantity (i.e. how many milligrams) of the drug do you need to administer to your patient?
* This means your patient requires 10 mg of the drug for every kg she weighs.
837 mg
1860 mg
837 kg
186 mg
Which specific structure labeled below should you adjust to focus this microscope if the image you see is blurry?
A. The structure lableled "A"
B. The structure lableled "C"
C. The structure lableled "D"
D. The structure lableled "B"
Adjusting which of the following will help you increase contrast when looking at a tissue under the microscope?
Hint: Recall that the contrast is the difference in brightness between the darkest and lightest parts of the microscope slide.
A. the lamp (illuminator knob)
B. the condenser
C. the iris diaphragm
D. the coarse focus knob
C. the iris diaphragm
Adjusting which of the following structures can help increase the amount of light that reaches the cells you are observing with your microscope?
(Choose all that apply.)
A. iris diaphragm
B. arm
C. ocular lens
D. revolving nosepiece
E. lamp (illuminator knob)
A. E
When you are finished using a microscope, all of the following should be true:
(Choose all that apply.)
A. The stage should be in its lowest position.
B. The slide should be removed from the stage and returned to the tray where you found it.
C. The 40x objective lens should be in the light path.
D. The lamp should be turned off.
A, B, D
Identify the specific structure at the end of the pointer:
A. occular lens
B. objective lens
C. condenser lens
D. coverslip
A. occular lens
Imagine that instead of viewing a "letter e slide" like we did in this lab, you view a "letter d" slide. In other words, you see a lower-case letter "d" when you hold the slide up to the light and look at the slide with your naked eye.
What letter will you appear to see when you use your microscope to view this slide?
(Choose the best answer.)
A. "d"
B. "b"
C. "q"
D. "p"
D. "p"
When you move the compound microscope we use in lab, you should always have one hand supporting the __________ and the other hand under the hand supporting the __________.
(Choose the best answer.)
A. arm; base
B. stage; base
C. stage; arm
D. objective lens; ocular lens
A. arm; base
The area of the microscope slide that you can see when you look through the eyepieces of your microscope is called the __________.
(Choose the best answer.)
A. stage
B. field of view
C. objective lens
D. target
B. field of view
If you are using the 40x objective to view a microscope slide and the image is out of focus you should _________.
(Choose all that apply.)
A. You should adjust the lamp (illuminator knob).
B. You should switch to the 100x objective.
C. Adjust the coarse focus knob and then the fine focus knob.
D. Adjust the fine focus knob.
D. Adjust the fine focus knob.
What is the total magnification of the microscope shown in the image below?
(Note that the 10x objective is currently in the light path.)
A. 400x
B. 10x
C. 100x
D. 4x
C. 100x
Assume you take your resting pulse (heart rate) 10 different times. Each time, your record a different value (i.e. a different number of heartbeats per minute). Your measurements vary anywhere from a low of 66 beats per minute to a high of 85 beats per minute, but when you average all of your pulse measurements together, your average heart rate is 74 beats per minute.
Which of the following is correct?
(Select all correct options.)
A. Based the information above, we can conclude that heart rate is regulated by negative feedback
B. Your setpoint for heart rate is approximateily 74 beats per minute
C. Your normal range for heart rate is probably between 66 and 74 beats per minute.
D. Your normal range for heart rate is probably between 66 and 85 beats per minute.
A, B, D
The ability to maintain a relatively stable internal environment even when the external environment is unstable is called _________.
(Choose the best answer.)
A. homeostasis
B. the setpoint
C. the range
D. negative feedback
A. homeostasis
Assume your hypothesis is that students who exercise regularly will have a lower resting heart rate than students who do not exercise regularly. You divide the class into two groups and average the resting heart rate of all students in each group. You find that the average resting heart rate of students who exercise regularly is 64 beats per minute and the average resting heart rate of students who do not exercise regularly is 79 beats per minute.
Select all of the possible explanations that could help account for this result.
A. Students who exercise regularly have more free time to exercise and (therefore, on average) less stress. (Note that stress can increase heart rate.)
B. Students in the group that does not exercise regularly drink more coffee than students in the group that exercises regularly.
C. The red blood cells of the students who exercise regularly have more hemoglobin (the molecule in your red blood cells which transports oxygen) can transport more oxygen to their tissues.
D. The students who exercise regularly have stronger and more efficient hearts than students who do not exercise regularly.
E. Students who exercise regularly have red more blood cells.
All the above
The range (and set-point) for a regulated variable such as heart rate could change during the course of a 24 hour period because ________.
(Choose all that apply.)
A. heart rate increases during strenuous activity.
B. heart rate increases during stressful situations.
C. heart rate increases when you drink coffee, alcohol, or smoke.
D. heart rate decreases when you sleep.
All the above
Select all the examples of negative feedback below.
A. The concentration of glucose in your blood rises quickly after you eat a bowl of white rice. But the concentration of glucose in your blood soon falls when insulin is released and causes your skeletal muscle cells and adipocytes to take up glucose from the blood.
B. You stand up too quickly and your blood pressure drops. But you do not faint because your heart beats faster and more forcefully and increases your blood pressure.
C. During blood clotting, activated platelets (which stick to each other) release chemicals that activate other platelets (which then also stick together). These activated plates release chemicals with activate still other platelets (which then also stick together).
D. You walk outside on a cold day and your body temperature drops. You quickly start to shiver and generate heat that warms your body.
A, B, D
If you add 23 grams of NaCl to 750 mL water, what is the molarity of the solution you have created?
A. 0.031 M
B. 0.39 M
C. 0.52 M
D. 30.6 M
C. 0.52 M
Patients suffering from diabetic ketoacidosis may be given an intravenous 0.45% saline solution.
How many grams of NaCl would you need to add to 2.5 liters of water to produce 2.5 liters of 0.45% saline solution?
A. 58.5 g NaCl
B. 22.5 g NaCl
C. 0.9 g NaCl
D. 11.25 g NaCl
D. 11.25 g NaCl
After grading 100 anatomy and physiology exams, Dr. Long enjoys two of his favorite IPAs (beer). Assume that 1.8 grams of ethanol (alcohol) are absorbed into Dr. Long's blood and that he has a total of 6.0 liters of blood in his body. What is Dr. Long's BAC (blood alcohol content) as he assigns grades?
Note: BAC is an example of "mass percent" which we learned about in our "Concentrations and Dilutions" worksheet. Since the units for mass percent are grams of solute divided by deciliters of solution, this quesiton is basically asking you to convert the information you are given (1.8 grams of ethanol in 6 liters of solution) to units of grams per deciliter.
A. BAC = 0.02 (grams of ethanol / dL blood)
B. BAC = 0.01 (grams of ethanol / dL blood)
C. BAC = 0.04 (grams of ethanol / dL blood)
D. BAC = 0.03 (grams of ethanol / dL blood))
D. BAC = 0.03 (grams of ethanol / dL blood))
Consider the following chemical reaction:
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O
How many moles of water are produced for every mole of C6H12O6 that is consumed?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 6
D. 12
C. 6
What is the molarity of a solution that contains 13 grams of carbonic acid (H2CO3) dissolved in 125 mL of water?
A. 0.43 M
B. 1.68 M
C. 0.0065M
D. 6.45 M
B. 1.68 M
Consider the following chemical reaction:
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O
How many grams of water are produced for every gram of C6H12O6 that is consumed?
A. 0.6 grams of H2O
B. 0.033 grams of H2O
C. 1.2 grams of H2O
D. 6 grams of H2O
A. 0.6 grams of H2O
Consider the following chemical reaction which describes how carbon dioxide in your blood can affect the pH of your blood:
H2O + CO2 --> H+ + HCO3-
How many moles of hydrogen ions (H+) are produced for every gram of CO2 that is consumed?
A. 0.023 grams H+
B. 0.023 moles H+
C. 0.74 moles H+
D. 44 moles H+
B. 0.023 moles H+
If you dilute 0.15 liters of a 3.0 M glucose solution to a final volume of 4.0 liters, what is the final concentration of this diluted solution?
A. 4.0 L
B. 0.202 M
C. 3.0 M
D. 0.113 M
D. 0.113 M
Assuming you have not recently eaten a meal, a normal concentration of glucose in the blood is approximately 5 mM. What is a normal concentration of glucose in the blood using units of "milligram percent"?
Note 1: "mM" is an abbreviation for millimolar. 1 mM means there is 1 millimole (abbreviated mmol) of solute (i.e. glucose) per liter of solution, or equivalently, one thousandth of a mole of solute per liter of solution.
Note 2: "milligram percent" has units of mg/dL and is a short-hand way of saying "milligrams of solute per deciliter of solution" or equivalently "milligrams of solute per 100 mL of solution. In this case we are looking for the number of milligrams of glucose per liter of blood. "Milligram percent" is sometimes abbreviated mg%.
Note 3: Don't panic. Remember just use dimensional analysis and apply conversion factors until get from the units you have to the units you want.
A. 70 mg/dL
B. 100 mg/dL
C. 90 mg/dL
D. 80 mg/dL
C. 90 mg/dL
How many oxygen atoms are in 1 mole of carbon dioxide (CO2)?
Note 1: Remember that one mole of any substance contains 6.02 x 1023 (Avogadro’s number) of that substance. For example, if you have a mole of carbon atoms, you have 6.02 x 1023 carbon atoms. If you have 2 moles of carbon atoms you have (2 * 6.02 x1023) = 1.204 x 1024 carbon atoms. In a way, the idea of a mole is similar to the idea of “a dozen”: If you have a dozen donuts, you have 12 donuts. If you have a mole of donuts, you have 6.02 x 1023 donuts. (Even Dr. Long would not want to eat that many donuts!)
Note 2: There are 2 oxygen atoms for every molecule of CO2. This means that there are two moles of oxygen atoms for every mole of CO2 molecules.
Note: 3: As always, use dimensional analysis and apply conversion factors until we go from the units we start with to the units we want.
A. 1.204 x 1024 oxygen atoms
B. oxygen atom
C. 6.02 x 1023 oxygen atoms
D. 2 oxygen atoms
A. 1.204 x 1024 oxygen atoms
Based on random and independent assortment alone, how many genetically distinct gametes can be produced by meiosis of a diploid (2n) cell that has 12 chromosomes?
A. 4096
B. 24
C. 64
D. 6
E. 12
C. 64
Here are some beads that represent a phase of meiosis. Yellow beads represent chromosomes that this organism inherited from its mother and red beads represent chromosomes that it inherited from its father.
This cell contains _____ chromosomes and _____ molecules of DNA.
A. 12; 6
B. 6; 12
C. 6; 6
D. 12; 12
B. 6; 12
During what stage in the cell cycle is DNA replicated?
A. anaphase
B. G1
C. metaphase
D. S-phase
D. S-phase
What disorder does a person with this karyotype have?
A. Down syndrome
B. Turner syndrome
C. Trisomy 18
D. Jacob's syndrome
A. Down syndrome
Here are some beads that represent a phase of meiosis. Yellow beads represent chromosomes that this organism inherited from its mother and red beads represent chromosomes that it inherited from its father.
What stage of meiosis is represented here?
A. metaphase I
B. anaphse II
C. metaphase II
D. anaphse I
D. anaphse I
What is the sex of the person with the karyotype below?
A. female
B. male
C. There is not enough information to answer this question.
A. female
What is/are important function(s) of the main tissue in the field of view?
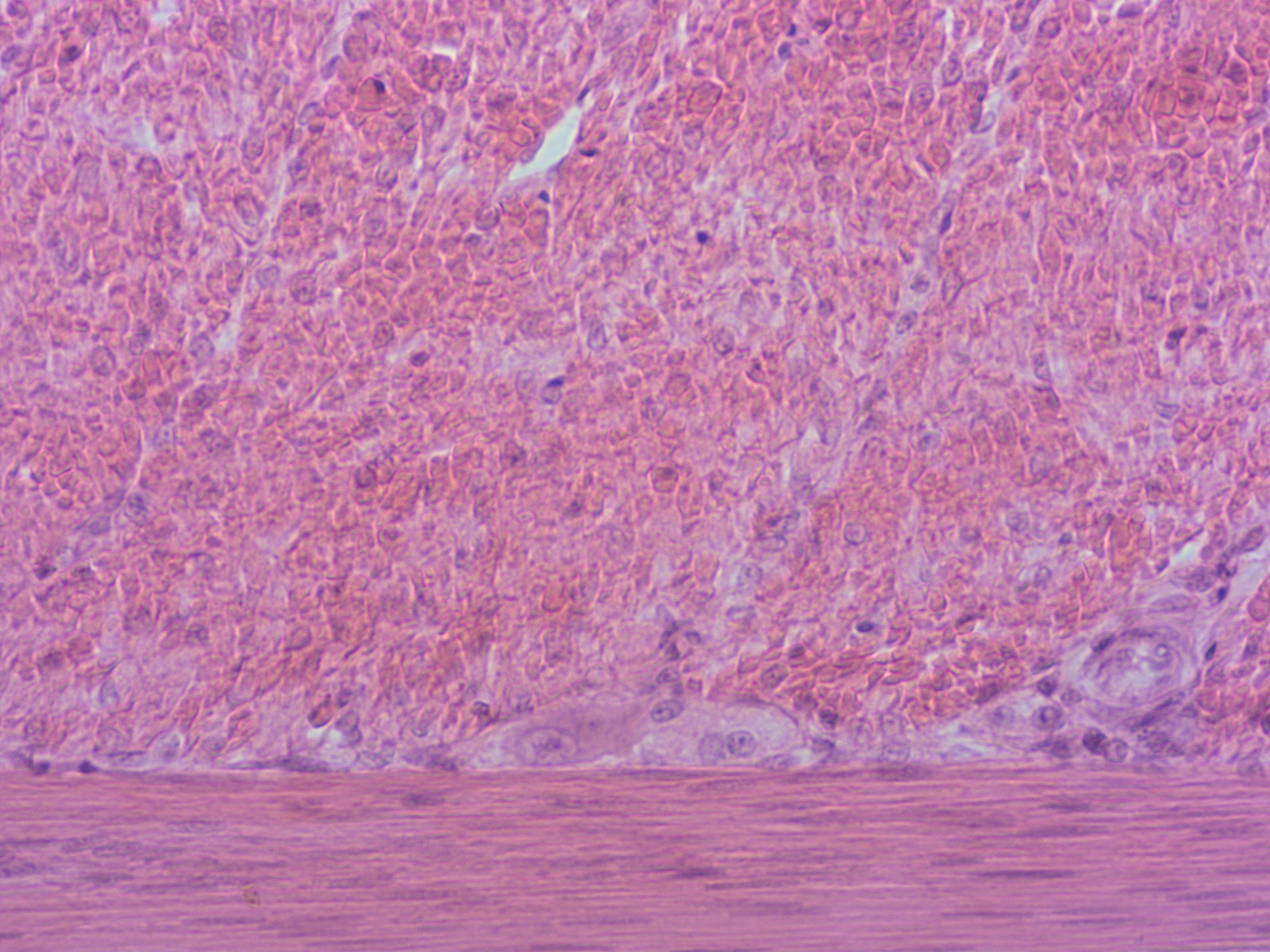
A. contracts forcefully to produce voluntary movement
B. contracts forcefully to maintain body posture
C. contracts forcefully to propel fluids through hollow spaces within the body
D. contracts forcefully to propel blood into arteries
C. contracts forcefully to propel fluids through hollow spaces within the body
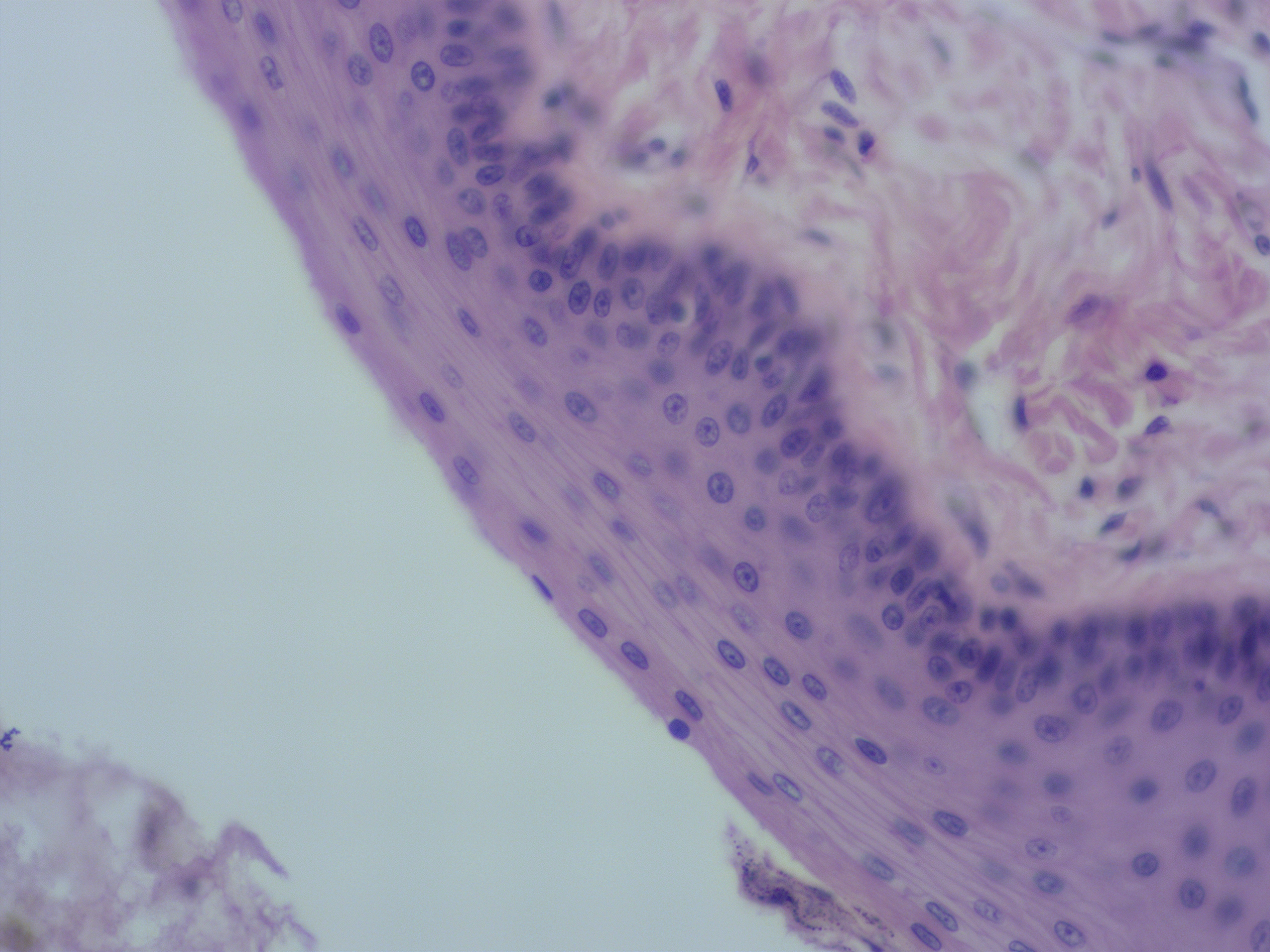
Identify the main tissue in the field of view:
A. stratified squamous epithelial tissue
B. dense irregular connective tissue
C. hyaline cartilage
D.(compact) bone tissue
C. hyaline cartilage
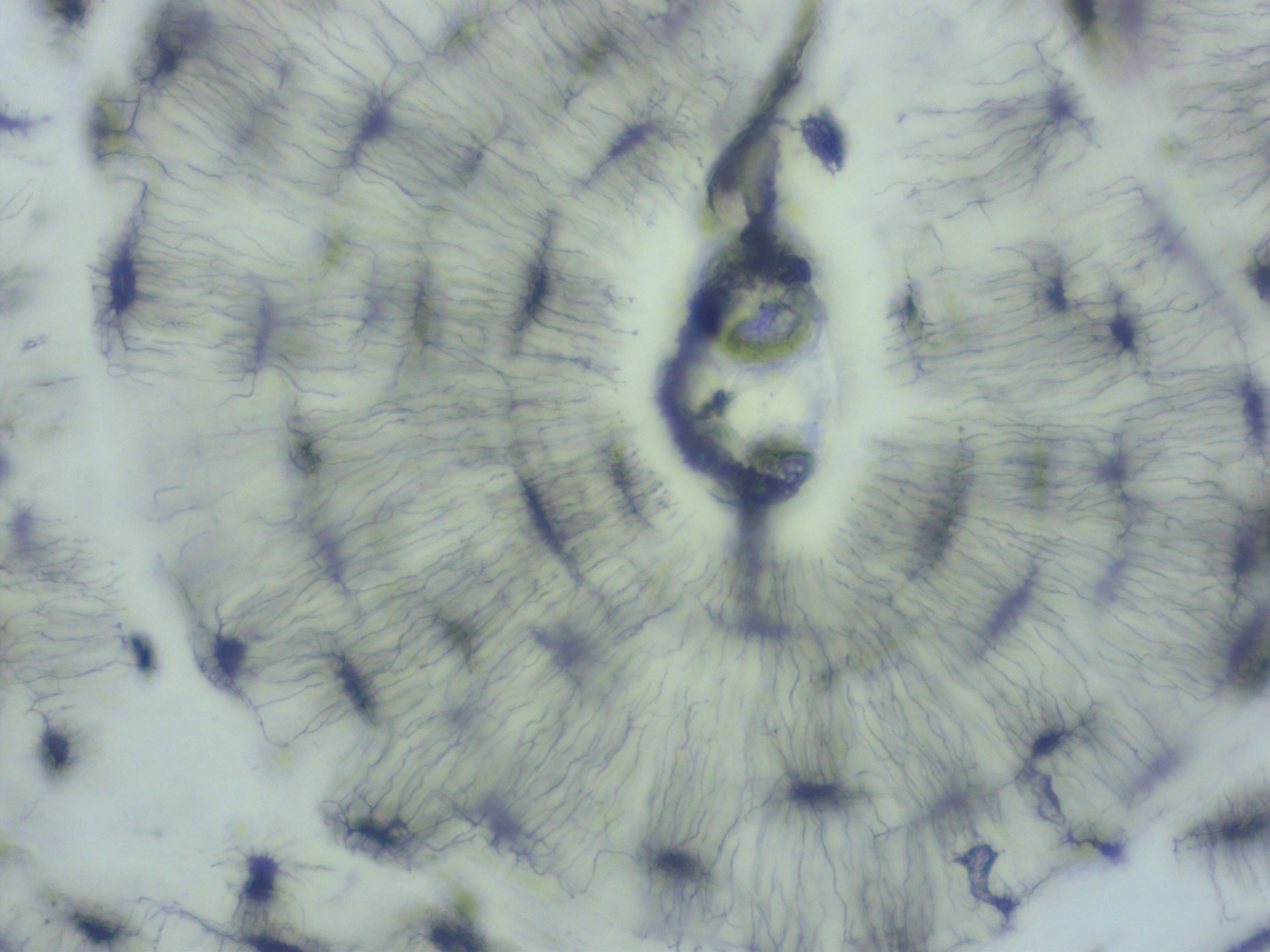
Where in the body can the tissue below can be found?
A. the skin
B. the stomach
C. the esophagous
D. the trachea
E. the urinary bladder
C. the esophagous
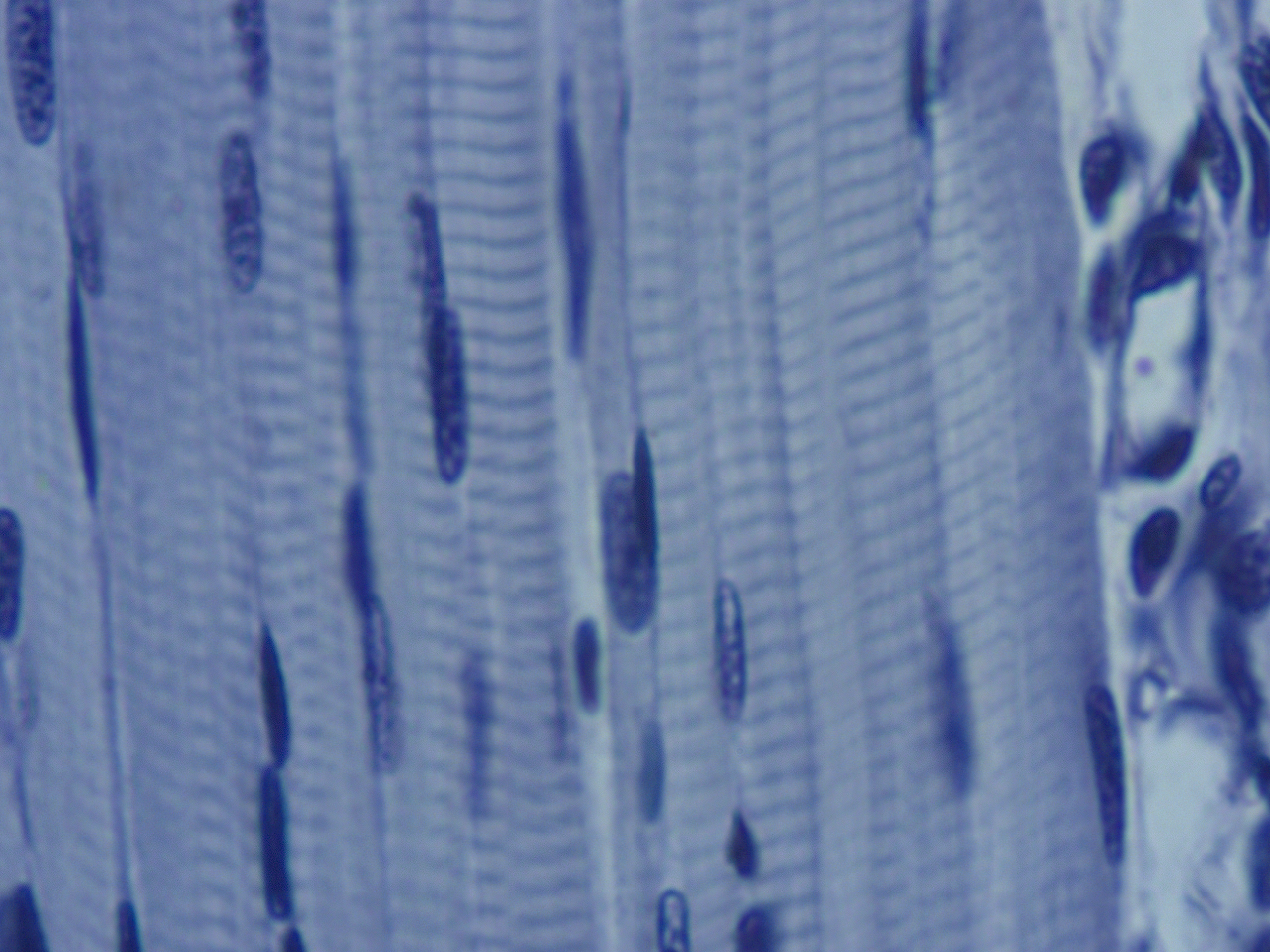
Where in the body might the tissue below be found?
A. the renal medulla
B. the skin (epidermis)
C. the biceps brachii
D. the heart
D. the heart
What is/are important function(s) of the main tissue in the field of view?
A. provides structural support and cushioning; also grows quickly during embryonic development
B. contracts forcefully to produce movement
C. allows for diffusion and filtration
D. provides structure and support; also stores calcium and other minerals
D. provides structure and support; also stores calcium and other minerals
Where in the body can the tissue below can be found?
A. hypdermis / surrounding and cushioning organs
B. the lumen of arteries and veins
C. the central nervous system
D. the renal cortex
A. hypdermis / surrounding and cushioning organs
Identify the main tissue in the field of view:
A. areolar connective tissue
B. adipose tissue
C. dense irregular connective tissue
D. hyaline cartilage
A. areolar connective tissue
Where in the body can the tissue below can be found?
A. the biceps brachii
B. the wall of the small intestine
C. the heart
D. the wall of a large artery
A. the biceps brachii
What is/are important function(s) of the main tissue in the field of view?
A. contract forcefully
B. diffusion and filtration
C. store energy and provide cushioning
D. absorption and secretion
D. absorption and secretion
What is/are important function(s) of the main tissue in the field of view?
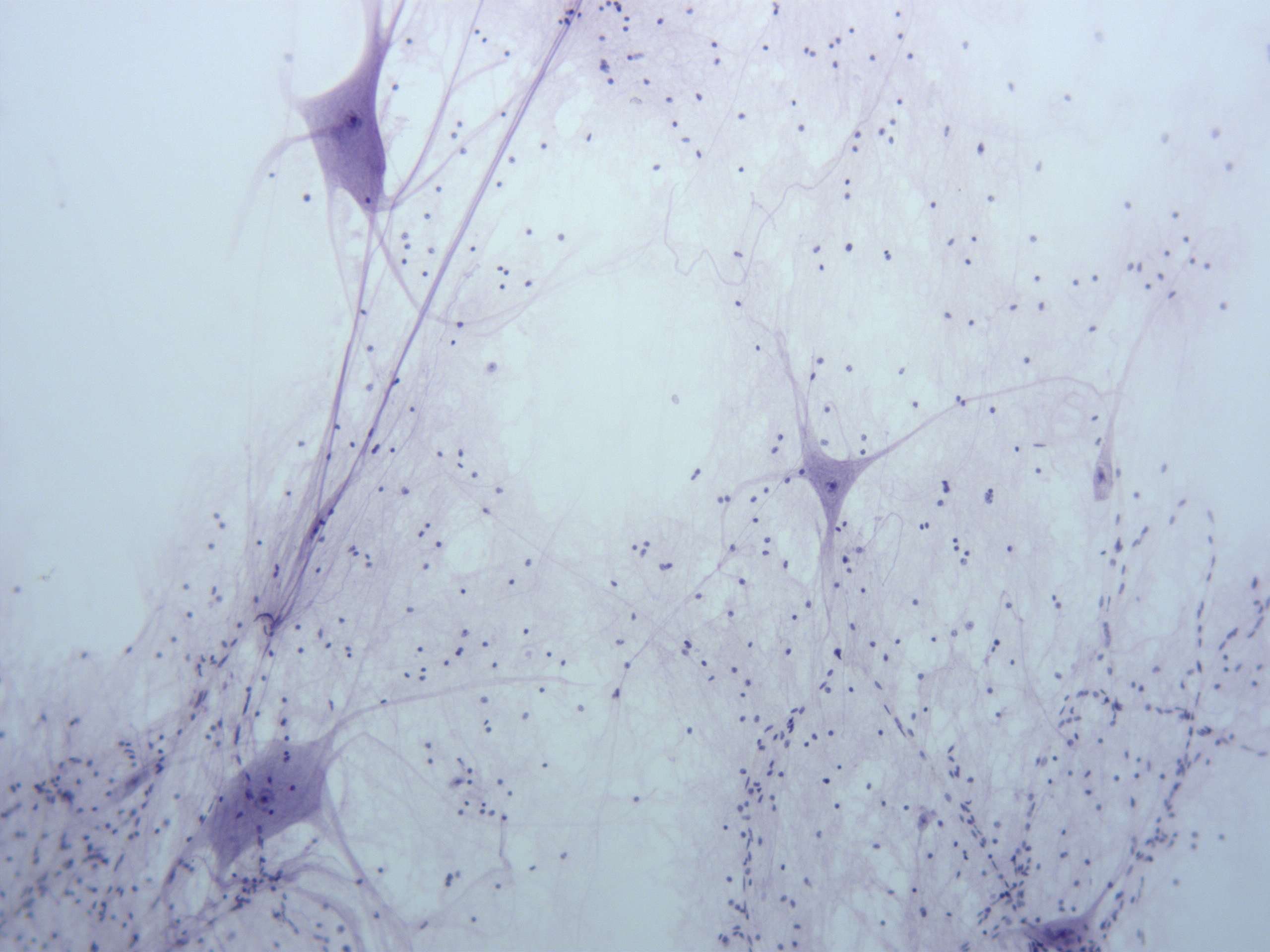
A. contracts forcefully to produce voluntary movement
B. provides structural support and cushioning; also grows quickly during embryonic development
C. communication; rapidly transmits and integrates information in the body
D. resists tension from multiple directions
C. communication; rapidly transmits and integrates information in the body
Select all of the statements below that are true.
A. If you inherit a dominant allele for a particular gene from your mother and a recessive allele for the same gene from your father, the recessive allele from your father will not contribute to your phenotype but it may be passed on to your children and contribute to their phenotypes.
B. Sons recieve an X chromosome from thier mother.
C. Daughters receive a Y chromosome from thier fathers.
D. It is theoretically possible for a woman to have hemophilia A. (Note that hemophilia A is an X-linked recessive trait
A, B, D
Assume the allele for the ability to roll one’s tongue is dominant (‘R’) and the allele for the inability to roll one's tongue is recessive (‘r’).
Also assume that the ability to roll one's tongue exhibits autosomal inheritance. In other words, the gene associated with this trait is not located on a sex chromosome.
If two individuals who are heterozygous (‘Rr’) mate and produce offspring, what are the predicted genotypic ratios of the offspring?
A. 25% of the offspring can roll their tongue, 50% of the offspring can roll their tongue somewhat; 25% of the offspring cannot roll their tongue.
B. RR: 25%; Rr: 50%; rr: 25%
C. RR: 75%; rr: 25%
D. 75% of the offspring can roll their tongue; 25% cannot roll their tongue.
B. RR: 25%; Rr: 50%; rr: 25%
Assume the allele for the ability to roll one’s tongue is dominant (‘R’) and the allele for the inability to roll one's tongue is recessive (‘r’).
Also assume that the ability to roll one's tongue exhibits autosomal inheritance. In other words, the gene associated with this trait is not located on a sex chromosome.
If two individuals who are heterozygous (‘Rr’) mate and produce offspring, what are the predicted phenotypic ratios of the offspring?
A. 25% of the offspring can roll their tongue, 50% of the offspring can roll their tongue somewhat; 25% of the offspring cannot roll their tongue.
B. RR: 75%; rr: 25%
C. RR: 25%; Rr: 50%; rr: 25%
D. 75% of the offspring can roll their tongue; 25% cannot roll their tongue.
D. 75% of the offspring can roll their tongue; 25% cannot roll their tongue.
The genetic makeup of a cell or individual.
genotype
Either of the two identical condensed DNA molecules, with both identical copies joined together at the centromere.
sister chromatid
The set of observable characteristics of an individual (resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment)
phenotype
A single set of all the genes associated with a particular organism.
genome
A type of nuclear and cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth or development
mitosis
A type of nuclear and cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes.
meiosis
The region of a chromosome where two sister chromatids are attached to each other. Also the location at which the chromosome is attached to a spindle fiber (microtubule) during cell division.
centromere
An organelle (normally near the nucleus of a cell) that contains the centrioles (in animal cells) and from which the spindle fibers extend in cell division.
centrosome
A distinct structure made of DNA and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. (This structure may consist of one or two chromatids at various points in the cell cycle.)
chromosome
What level of protein structure would be least affected by a disruption of hydrogen bonds?
A. secondary structure
B. tertiary structure
C. quaternary structure
D. primary structure
D. primary structure
Which statements about the induced-fit mechanism of enzyme activity are true?
(Select all that apply.)
A. An enzyme must have the precise correct three-dimensional shape to efficiently catalyze a chemical reaction.
B. When substrate is converted to product, the product no longer properly fits in the active site of the enzyme, so it is quickly released.
C. When an enzyme binds its substrate, the enzyme changes shape and stresses (weakens) the chemical bonds of the substrate.
A, B, C
Pancreatic lipase catalyzes a reaction in which triglycerides (fats and oils) are converted to fatty acids so they can be absorbed into the body. What is the substrate in this reaction?
A. fatty acids
B. bile salts
C. chylomicrons
D. pancreatic lipase
E. triglycerides
E. triglycerides
If the temperature of the solution surrounding a protein decreases:
parts of the protein that normally have enough energy to move back and forth are able to move ____ ,
the protein is ___ able to change shape as it binds it substrate.
Less; Less
Which statements about bile salts are true?
A. Bile salts are broken down by pancreatic lipase.
B. Bile salts emulsify hydrophobic lipids.
C. Bile salts increase the surface area of fat droplets.
D. Bile salts are amphipathic.
E. Bile salts are enzymes.
B, C, D
Why did we run our gels under basic (pH ≥ 8.3) conditions?
A. so the poteins would have a negative charge and migrate toward the cathode
B. so the poteins would have a positive charge and migrate toward the cathode
C. so the poteins would have a positive charge and migrate toward the anode
D. so the poteins would have a negative charge and migrate toward the anode
D. so the poteins would have a negative charge and migrate toward the anode
All of the following plasma proteins are primarily produced in the liver, except ____________, which are produced by B-lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell).
A. alpha 1 globulins
B. albumins
C. alpha 1 globulins
D. gamma globulins
E, beta globulins
D. gamma globulins
What is the difference between serum and plasma?
A. Serum contains blood cells but plasma does not.
B. Plasma contains clotting factors but serum does not.
C. Plasma contains blood cells but serum does not.
D. Serum contains clotting factors but plasma does not.
B. Plasma contains clotting factors but serum does not.
Explain why the band at location A is not as dark as bands at locations B, C, and D.
A. The proteins at location A are very small.
B. The proteins at location A are very large.
C. The proteins at location A are very homogeneous.
D. The proteins at location A are not as concentrated.
D. The proteins at location A are not as concentrated.
Explain why the proteins at location C moved farther than the proteins at location B.
A. The proteins at location C are more hetrogeneous than the proteins at location B
B. The proteins at location C are smaller than the proteins at location B
C. The proteins at location C are more homeogeneous than the proteins at location B
D. The proteins at location C are more concentrated than the proteins at location B
E. The proteins at location C are larger than the proteins at location B
F. The proteins at location C are less concentrated than the proteins at location B
B. The proteins at location C are smaller than the proteins at location B
When the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution is higher than normal, this means that the pH is ____ than normal, and the solution is described as being _____.
Lower, acidic
What is the general name for this type molecule?
A. a carboxyl group
B. an alpha globulin
C. a nucleic acid
D. an amino acid
D. an amino acid
Why did we run our gels under basic (pH ≥ 8.3) conditions?
A. so the poteins would have a positive charge and migrate toward the anode
B. so the poteins would have a negative charge and migrate toward the anode
C. so the poteins would have a positive charge and migrate toward the cathode
D. so the poteins would have a negative charge and migrate toward the cathode
B. so the poteins would have a negative charge and migrate toward the anode
Why did we use a cuvette with distilled water to blank the spectrophotometer?
A. To clean the cuvette in case there is residue from solutions leftover from previous experiments.
B. Distilled water has the same absorbance as martian hemoglobin.
C. So that we can subtract (i.e. not count) the absorbance of water (the solvent) when measuring the absorbance of martian hemoglobin.
D. To make sure the spectrophotometer is working properly so we do not waste our unknown solutions.
C. So that we can subtract (i.e. not count) the absorbance of water (the solvent) when measuring the absorbance of martian hemoglobin.
This is a standard curve similar to the one you created in the spectrophotometry lab.
What was the dependent variable in this experiment?
A. the point 0,0 on this graph
B. concentration
C. absorbance
D. Beer's law
C. absorbance
Assume your instructor gives you a sample of martian hemoglobin at the beginning of lab.
You create a standard curve and use it to estimate that the concentration of your sample is 3.25 M.
At the end of the lab, your instructor informs you that the actual concentration of the sample of martian hemoglobin he gave you is 3.0 M.
What is the percent error for your estimate of the concentration of your martian hemoglobin sample?
A. 108%
B. 25%
C. 92%
D. 6%
E. 8%
E. 8%
Why might we need to carry out serial dilutions when using spectrophotometry to measure the concentration of an unknown solution?
A. We can only use spectrophotometry when a solution is dilute enough so that no molecules are shielded or blocked from absorbing light by other molecules in that solution.
B. If an unknown solution is too concentrated, it will stick to the cuvette and possibly damage the spectrophotometer.
C. Beer's law states that absorbance is proportional to concentration.
D. No answer text provided.
A. We can only use spectrophotometry when a solution is dilute enough so that no molecules are shielded or blocked from absorbing light by other molecules in that solution.
This is a standard curve similar to the one you created in the spectrophotometry lab.
Which answer below is closest to the concentration of an unknown sample with an absorbance of 0.5?
A. 0.85 M
B. 0.5 M
C. 3 M
D. 5 M
C. 3 M
Assume that a beaker is filled with water and divided in half by a membrane that is only permeable to water.
Now suppose glucose is added to the water on the left side of the membrane until the concentration of glucose on the left side of the beaker is 0.25 M. In other words, there is now a 0.25 M glucose solution the left side of the membrane.
Further suppose that NaCl is added to the water on the right side of the membrane until the concentration of NaCl on the right side of the beaker is 0.15 M. In other words, there is now a 0.15 M NaCl solution the right side of the membrane.
Over time, what will happen to the water in this beaker?
Hint: Draw and label a diagram depicting the experiment described above.
A. There will be a net movement of water across the membrane from the right side of the beaker to the left side of the beaker.
B. There will be a net movement of water across the membrane from the left side of the beaker to the right side of the beaker.
C. There is not enough information available to answer this quesiton.
D. There will be no net movement of water across the membrane in this beaker.
B. There will be a net movement of water across the membrane from the left side of the beaker to the right side of the beaker.
The water in beaker A is at room temperature (22 degrees C) and the water in beaker B is warm (heated to 50 degrees C).
Assume you add equal amounts of dye to each beaker. In which beaker will diffusion occur most rapidly?
A. Diffusion will occur more rapidly in beaker B
B. Diffusion will occur at the same rate in each beaker.
C. Diffusion will occur more rapidly in beaker A
D. There is not enough information to answer this question.
A. Diffusion will occur more rapidly in beaker B
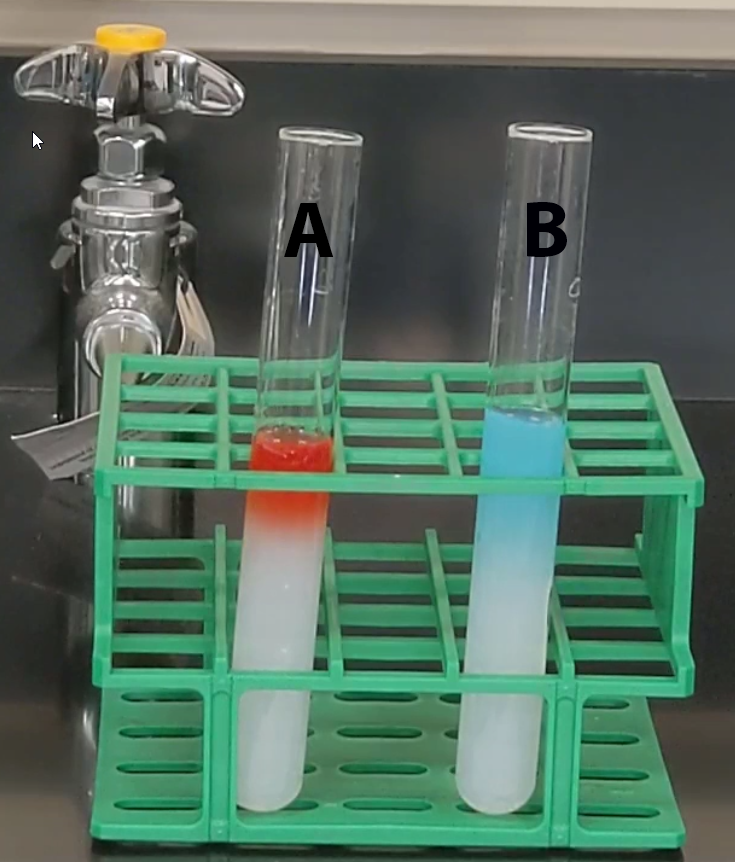

Which of the following is the most likely reason the dye in tube B diffused faster and farther than the dye in tube A?
A. The molecular weight of the dye in tube B is smaller than the molecular weight of the dye in tube A.
B. The dye in tube B has a higher temperature than the dye in tube A.
C. The dye in tube B has a lower temperature than the dye in tube A.
D. The molecular weight of the dye in tube B is larger than the molecular weight of the dye in tube A.
A. The molecular weight of the dye in tube B is smaller than the molecular weight of the dye in tube A.
The water in beaker A is at room temperature (22 degrees C) and the water in beaker B is warm (heated to 50 degrees C).
Assume you add equal amounts of dye to each beaker. In which beaker will diffusion occur most rapidly?
A. Diffusion will occur more rapidly in beaker A
B. Diffusion will occur more rapidly in beaker B
C. There is not enough information to answer this question.
D. Diffusion will occur at the same rate in each beaker.
B. Diffusion will occur more rapidly in beaker B
What word best describes a solution that has a higher osmolarity than the cytoplasm of a red blood cell placed in that solution?
A. hyposmotic
B. hypotonic
C. isosmotic
D. hyperosmotic
E. isotonic
F. hypertonic
D. hyperosmotic
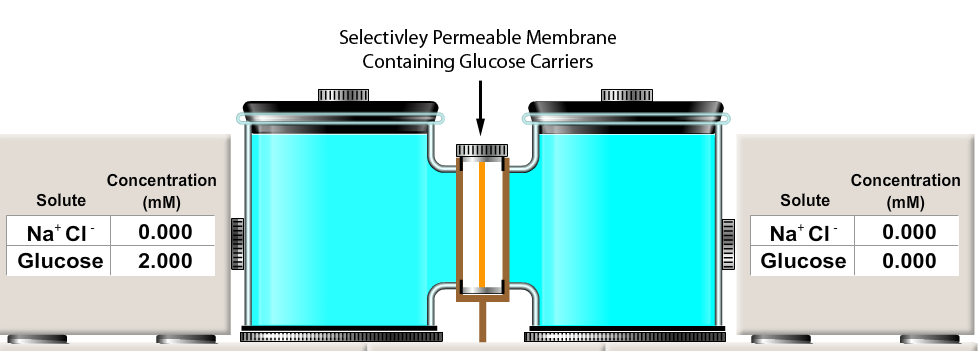
Consider the facilitated diffusion experiment similar to the one you completed in Physio Ex Exercise 1 -- Activity 2.
Two solutions were separated by a membrane containing glucose carriers. In the experiment shown below, what will be the final concentration of glucose in both chambers?
A. left chamber: 0 mM glucose; right chamber 2 mM glucose
B. left chamber: 2 mM glucose; right chamber 0 mM glucose
C. left chamber: 2 mM glucose; right chamber 2 mM glucose
D. left chamber: 0 mM glucose; right chamber 0 mM glucose
E. left chamber: 1 mM glucose; right chamber 1 mM glucose
E. left chamber: 1 mM glucose; right chamber 1 mM glucose
What word best describes a solution that causes a red blood cell to crenate (shrivel) when placed in that solution?
A. hypotonic
B. isosmotic
C. isotonic
D. hyperosmotic
E. hypertonic
F. hyposmotic
E. hypertonic
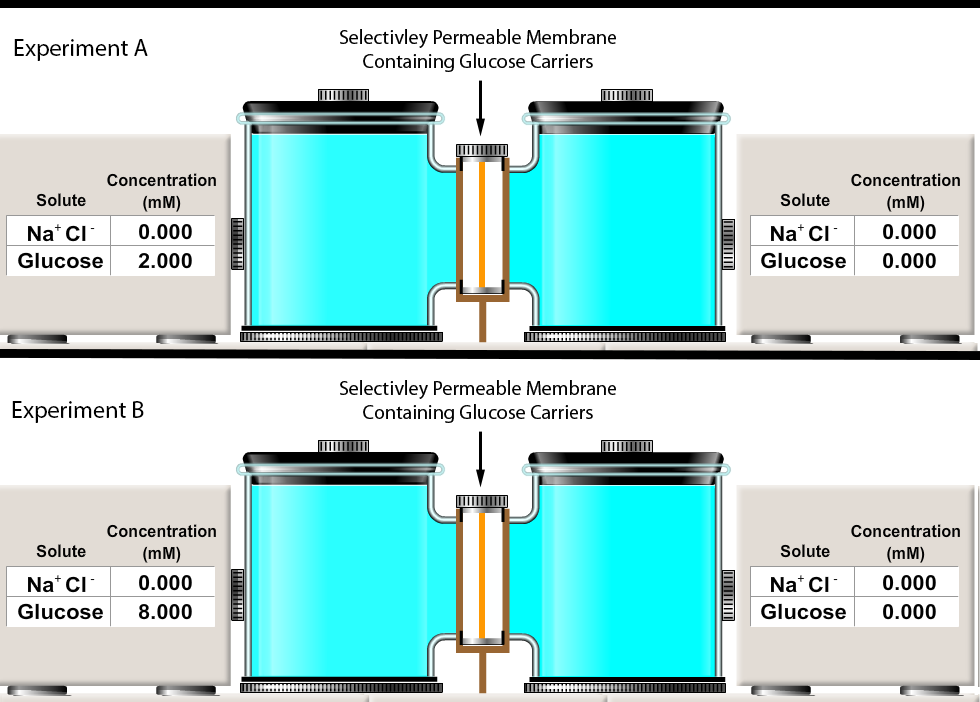
Consider the facilitated diffusion experiment similar to the one you completed in Physio Ex Exercise 1 -- Activity 2.
Experiments A and B both contain solutions separated by a membrane containing glucose carriers. Once this experiment starts (i.e. once glucose is allowed to move across the membrane containing glucose carriers), which of the following will most likely occur?
A. Glucose will diffuse more quickly in experiment A than in Experiment B
B. Glucose will diffuse more quickly in experiment B than in Experiment A
C. Glucose will diffuse at equal rates in in experiments A and B.
D. It is not possible for glucose to move between the two chambers in either experiment.
B. Glucose will diffuse more quickly in experiment B than in Experiment A
[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]
The EEG wave that is most readily recorded from the parietal and occipital lobes of a patient when they are awake and relaxed with their eyes closed is called the ____ wave.
Alpha
[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]
The EEG wave that is most readily recorded from the frontal lobes of a patient who is engaging in mental activity with thier eyes open is called the ____ wave.
Beta
![<p><em>[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]</em><br><strong>ID specific structure (light) at the end of the pointer.</strong></p><p>a. myelin sheath</p><p>b. Schwann cell</p><p>c. reticular fiber</p><p>d. node of Ranvier</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0ee3197a-89b6-49d1-9fdd-27cbbc9b3e67.jpeg)
[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]
ID specific structure (light) at the end of the pointer.
a. myelin sheath
b. Schwann cell
c. reticular fiber
d. node of Ranvier
d. node of Ranvier
[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]
The time interval when a neuron requires a stronger than normal stimulus to fire an action potential because some voltage-gated Na+ channels are inactivated and some voltage-gated K+ channels are open is called ___________.
a. the absolute refractory period
b. initiation
c. the relative refractory period
d. the latent period
c. the relative refractory period
![<p><em>[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]</em></p><p><strong>ID specific cell at the end of the pointer:</strong></p><p>a. multipolar neuron</p><p>b. bipolar neuron</p><p>c. neuroglial cell</p><p>d. unipolar neuron</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8b57cf92-a867-4fd7-9f83-1d5bbc383a6e.jpeg)
[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]
ID specific cell at the end of the pointer:
a. multipolar neuron
b. bipolar neuron
c. neuroglial cell
d. unipolar neuron
a. multipolar neuron
![<p><em>[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]</em></p><p><strong>Identify the connective tissue sheath at the end of <u>both</u> pointers:</strong></p><p>a. perineurium</p><p>b. epineurium</p><p>c. fassicle</p><p>d. endoneurium</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d8f6803d-2095-48b0-b45e-e7101a19faa8.jpeg)
[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]
Identify the connective tissue sheath at the end of both pointers:
a. perineurium
b. epineurium
c. fassicle
d. endoneurium
a. perineurium
[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]
The membrane potential at which enough voltage-gated Na+ channels open to cause positive feedback is called the __________ .
a. resting membrane potential
b. threshold
c. rising phase
d. initiation
b. threshold
[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]
When you apply lidocaine or TTX to the axon of a neuron, its ability to fire an action potential is ____ because it binds to and blocks ______
eliminated, voltage-gated sodium channels
![<p><em>[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]</em></p><p><strong>At which number (1-7) is membrane potential most <u>positive</u>?</strong></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9d1712f8-d7df-463c-b0a2-f8e24c0ef8e5.jpeg)
[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]
At which number (1-7) is membrane potential most positive?
5
[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]
The height of a wave, or more specifically, the vertical distance between the peak of a wave and the point of equilibrium is called the ______.
amplitude
[Quiz - Lab 2.1 (Neurophysiology and EEG): Check Your Understanding]
The number of waves that are generated or pass a certain point each second is called the ______.
frequency