Pathophysiology exam 1: Inflammation
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is inflammation in response to?
Cell injury (tissue irritation) or death
What is the result of inflammation?
Minimizes effects if infection or injury
Removes damaged tissue
Generates new tissue
"-itis”
inflammatory response
Inflammation is caused by…
Inflammatory mediators
Fluid movement and leukocytes migration to extravascular tissues
What are the 3 types of cells of inflammation?
Endothelial cells
Platelets
Leukocytes
Roles of endothelial cells in inflammation
Selective barrier to microbes and inflammatory stimuli via tight junctions
Regulate immune cell proliferation
Repair process
What do the tight junctions between endothelial cells regulate and release?
Leukocyte extravasation (leak out of BV)
Release inflammatory mediators (i.e., cytokines like IL-8)
What type of leukocyte is the 1st to appear in the inflammatory response?
Neutrophils
present at injury site after about 90 minutes
What leukocytes are there? Which are granulocytes and which are agranulocytes?
Granulocytes:
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils —> Mast cells
Agranulocytes
Monocytes/macrophages
Lymphocytes
Neutrophil function
Phagocyte
Attack bacteria
(short lifespan so they must be regenerated by BM often)
Eosinophil function
Phagocyte
Protect against parasites
A response in allergic reactions
(longer life span — seen in chronic inflammation)
Basophil function
Release histamines during allergic reactions
When do mast cells form?
When a basophil leaves BV circulation and goes into the tissue “tracts” to find the invader and destroy it
Monocyte function
Phagocyte
Produce vasoactive mediators
once they leave the blood stream and go into the tissues, they turn into macrophages
***Macrophage function
***Phagocytes that are part of the innate to the inflammatory process
Antigen presenting cells
What are mediators of inflammation?
When released, they tell other cells what to do
Where do mediators of inflammation come from?
They are a result of acute inflammation and they come from either the liver (plasma-derived mediators) or surrounding cells (cell-derived mediators)
What two cellular mediators of inflammation are released? Where do they come from?
Histamine — mast cells
Serotonin — platelets
Leukotrienes
Prostaglandins
When are cellular mediators of inflammation released?
Released in acute inflammatory response
Role of histamine and serotonin release
Dilate BVs and increase permeability of BVs
Process of microorganism movement
Histamine/serotonin released
BVs contract initially
BVs relax
gap btwn endothelial cells
plasma leaks out
helps move microorganisms
Role of leukotrienes and prostaglandin cellular mediators
Potentiate (make more powerful) the effect of histamine and serotonin
more vasodilation and increased permeability
Cytokine
Is a cellular mediator of inflammation involved in acute inflammation
Intracellular signaling proteins that regulate inflammatory responses by facilitating communication between cells
What type of inflammation is cytokines involved in?
Acute
Types of cytokines (3)
Interleukins (IL-1)
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-a)
Chemokines
Process of acute inflammation
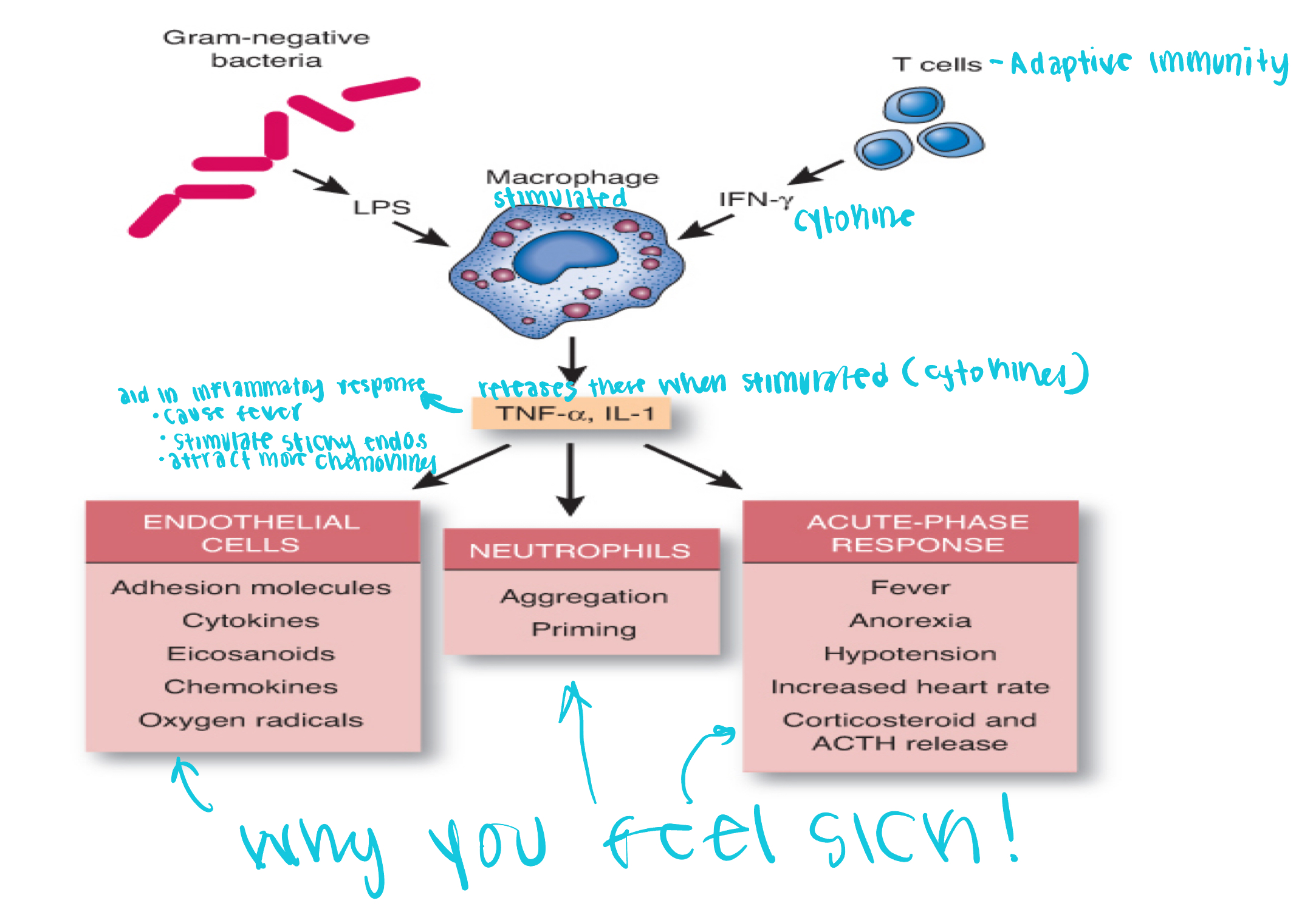
Bacteria enters body which has an antigen on the surface
T-cells are made aware of the bacteria via the antigen
Cytokine is released, stimulating the macrophage
Macrophage releases TNF-a and IL-1 cytokines
The cytokines signal for endothelial cells, neutrophils, and acute-phase response to activate
Now you feel sick
What is acute inflammation triggered by?
Tissue injury or infection
What is acute inflammation characterized by?
Plasma leaking out from BVs to tissues to aid in detoxifying cells
Emigration of leukocytes, signaling for other immune cells to come help
What are the most common signs of acute inflammation?
Redness
Swelling
Heat
Pain
Loss of function (i.e. Crohn’s disease = can’t absorb nutrients)
Systemic (affects whole body) signs of acute inflammation (when it gets really bad)
Fever
Leukocytosis
May see an increase in ESR and CRP (proteins that can be secreted from the liver)
Process of acute inflammation
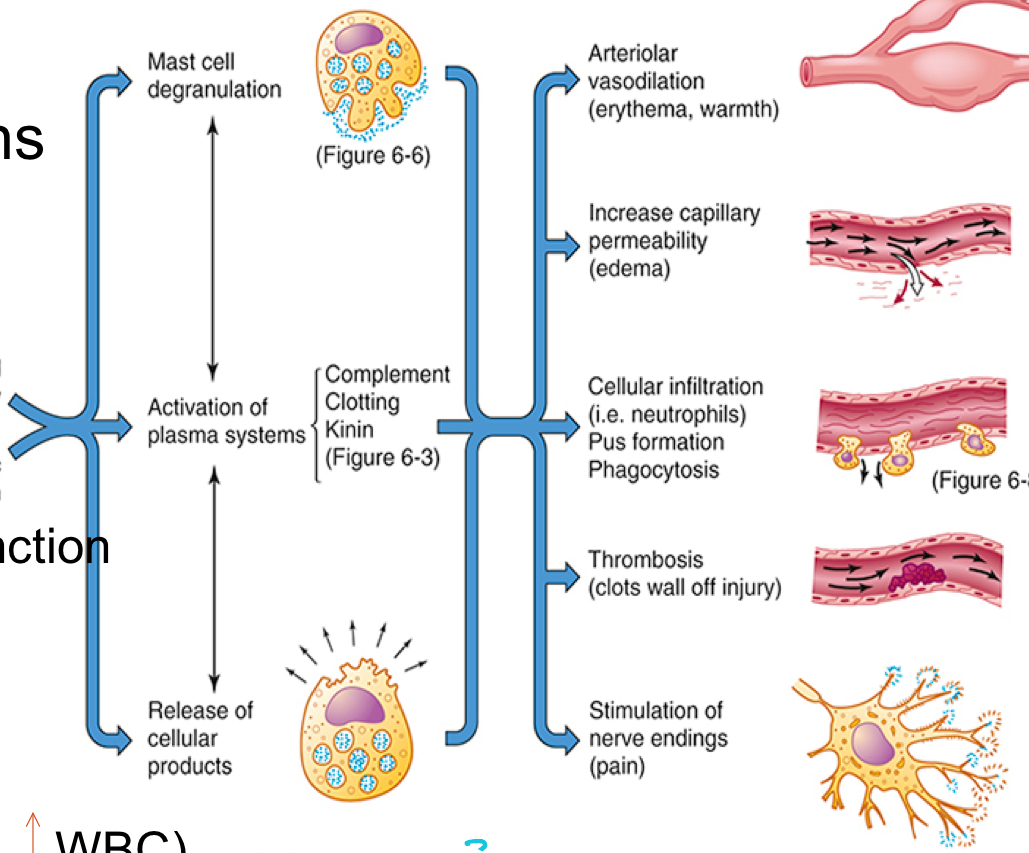
Purpose of vascular phase
Bring more blood flow
Steps of vascular phase
Brief vasoconstriction in response to injury
Vasodilation — caused by histamine and NO, resulting in warmness and redness
Increased permeability