A&P Exam 3 - Bone Physiology Part 1
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Functions of the skeletal system
Support
Protection
Movement
Storage
Blood cell production
Function of the skeletal system - support
Bone is hard and rigid, cartilage is flexible yet strong
Function of the skeletal system - protection
Examples: Skull around brain; ribs; sternum, vertebrae protect organs of thoracic cavity (vital organs)
Function of the skeletal system - movement
Produced by muscles on bones, via tendons (muscle to bone)
Ligaments (bone to bone) allow some movement between bones but prevent excessive movement
Function of the skeleton system - storage
Calcium (Ca2+) and Phosphorus (PO4-)
Stored then released as needed
Adipose tissue stored in marrow cavities
Function of the skeletal system - blood cell production
Bone marrow gives rise to
Red Blood Cells (Transport O2)
White Blood Cells (Immune defense)
Platelets (Clotting, Scab)
Components of skeletal system
Bone (spongy bone and compact bone)
3 types of cartilage: hyaline, fibrocartilage, elastic
Tendons and ligaments
Cartilage structure - specialized cells that produce matrix
Chondroblasts, chondrocytes
Chondroblasts
Form matrix
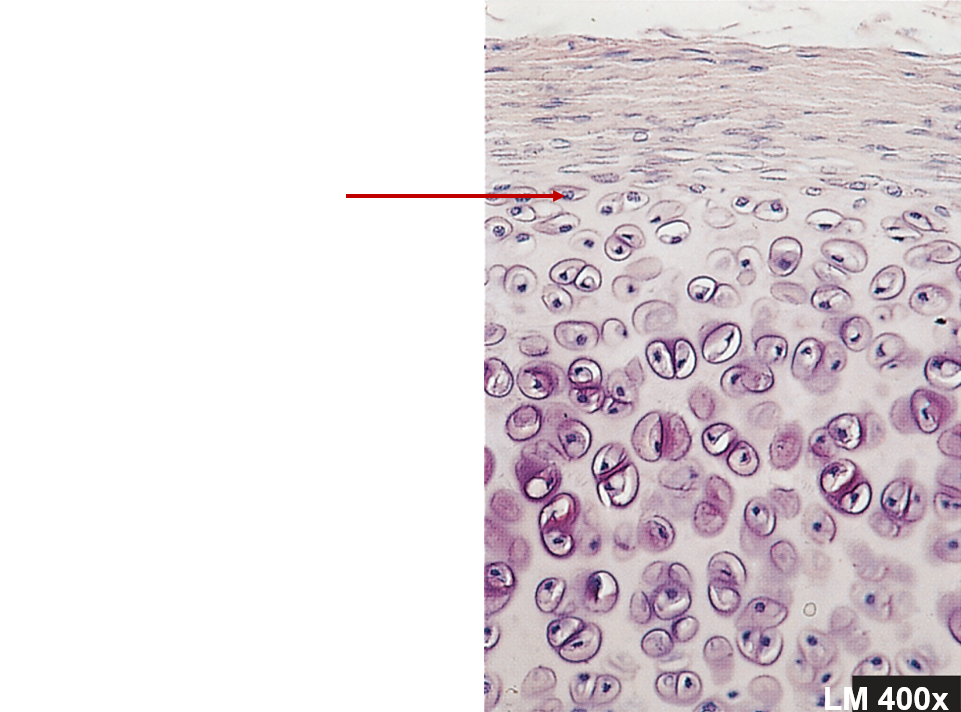
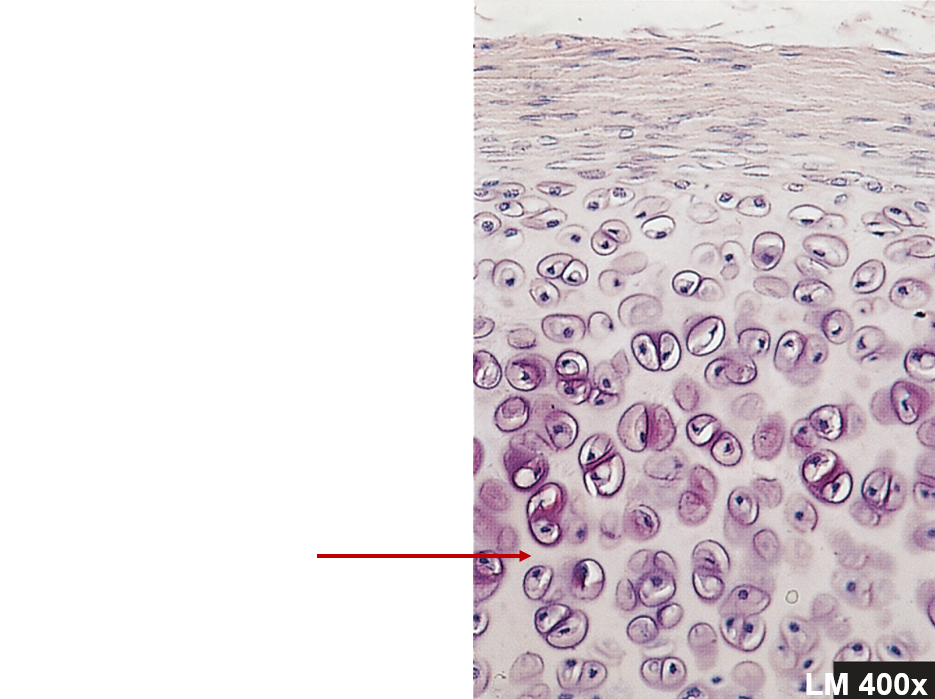
Chondrocytes
Surrounded by matrix, within lacunae
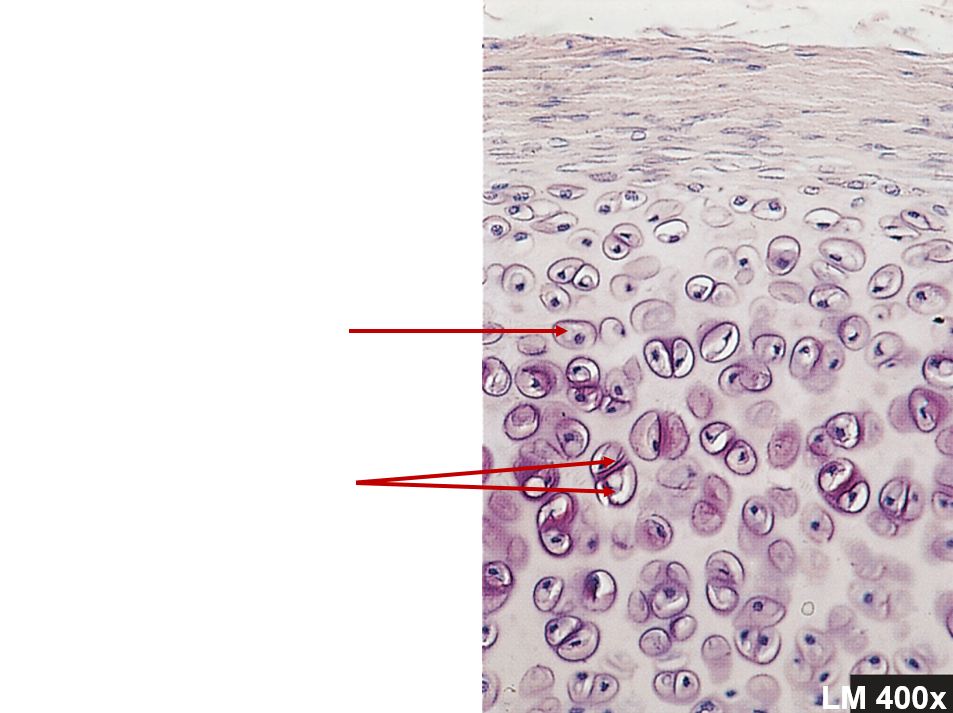
Matrix structure
Collagen fibers - strength
Proteoglycans - resiliency
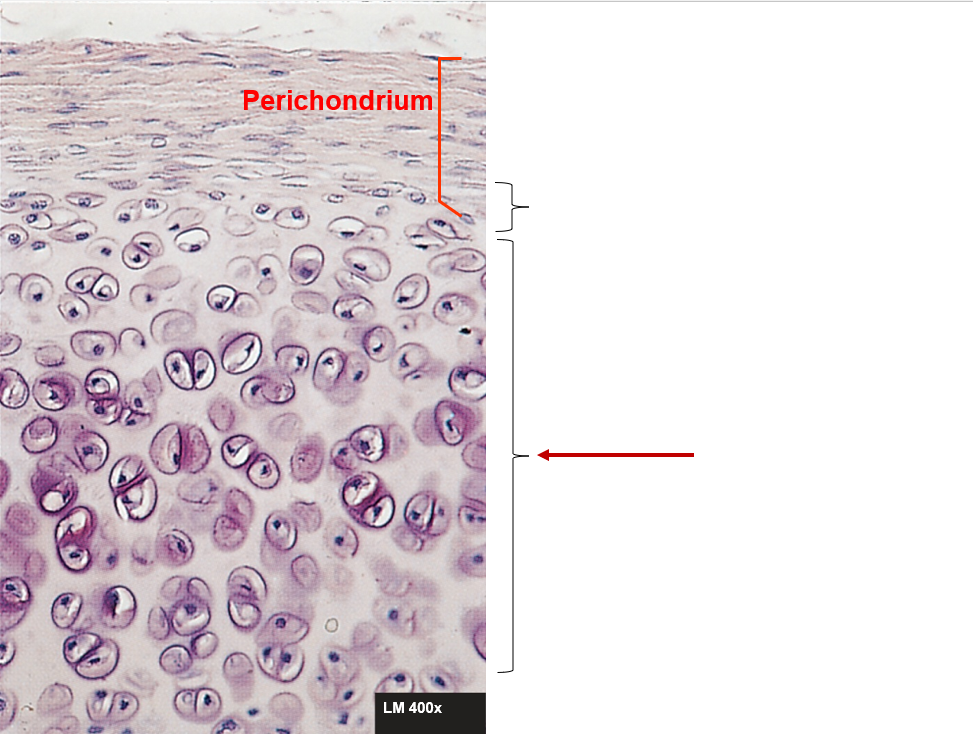
Perichondrium
Double-layered C.T. sheath, covers cartilage except at articulations
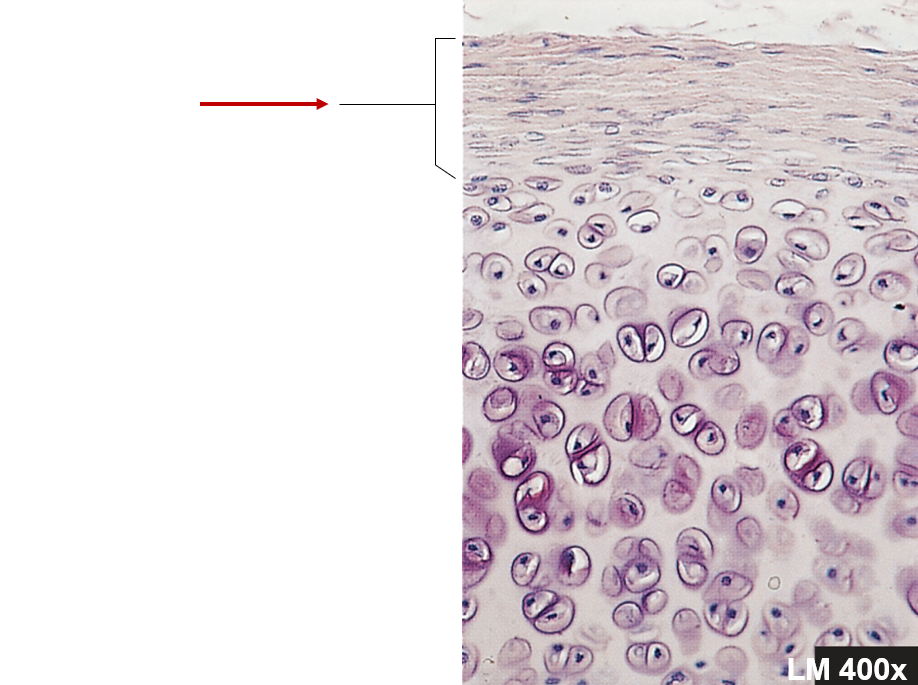
Perichondrium - inner layer
More delicate, fewer fibers, has chondroblasts
Perichondrium - outer layer
Blood vessels and nerves penetrate, no blood vessels in cartilage itself
Articular cartilage
Covers bones at joints, has no perichondrium
Thin layer of hyaline cartilage
Reduce friction
Cartilage growth - appositional
Location - inner layer of the perichondrium
Growth - chondroblasts and new matrix at the periphery (surface). At the edges
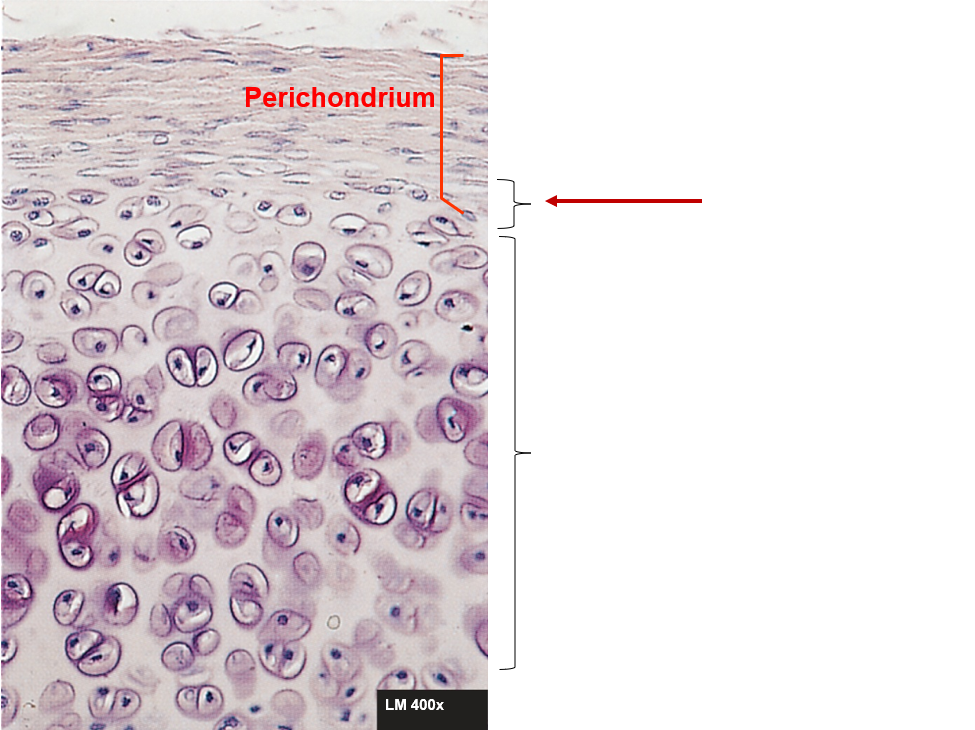
Cartilage growth - interstitial
Location - within the tissue
Growth - chondrocytes within the tissue divide. Add more matrix between the cells
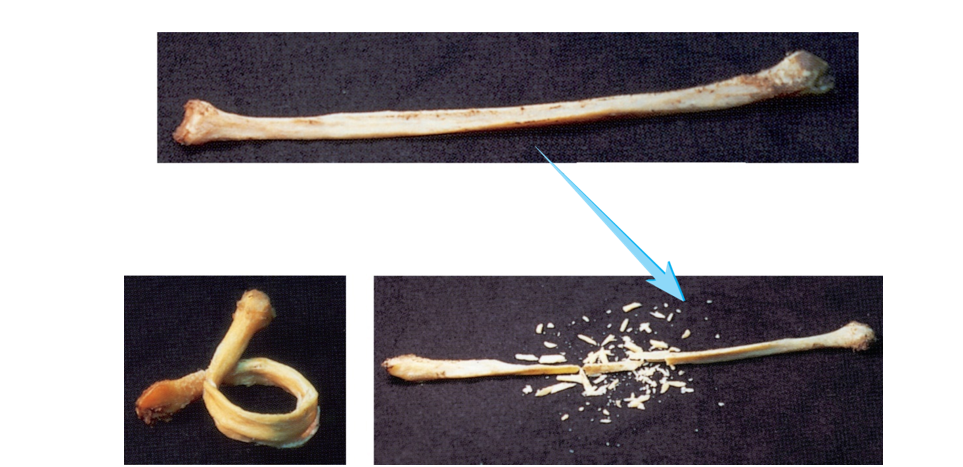
Bone matrix
Composed of organic and inorganic substances
Bone matrix - organic
Fibers
Composition: collagen and proteoglycans - Rebar
Function: flexibility and resistance
When removed: strength, but brittle because no flexibility
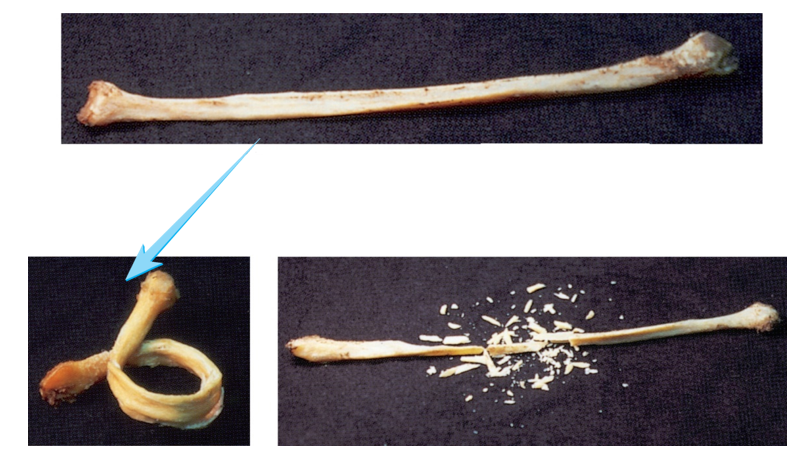
Bone matrix - inorganic
Matrix
Composition: hydroxyapatite. Composed of CaPO4 crystals - cement
Function: rigidity and resistance; withstand bending and weight-bearing forces
When removed: collagen bone, flexible
Osteoblasts - function
BUILD
Form bone by producing bone matrix
Collagen produced by ER and golgi. Released by exocytosis
Precursors of hydroxyapetite stored in vesicles, then released by exocytosis
Osteoblasts - origin
Arises from an osteogenic cell - stem cells that develop from embryonic mesenchyme
From endosteum and inner layer of the periosteum
Stem cells - starts as mesenchyme and becomes osteochondral progenitor cells which become chondroblasts or osteoblasts
Osteoblasts - location
Endosteum and inner layer of the periosteum
Osteoblasts - misc.
Ossification - formation of bone by osteoblasts
Communicate through gap junctions
Cells surround themselves by matrix
Become osteocytes afterwards
Osteocytes - function
MAINTAIN
Mature bone cells, stellate (star-shaped)
Maintains the matrix - surrounded by matrix, but can make small amounts of matrix to maintain it
Osteocytes - origin
Formed when osteoblast becomes surrounded by its own matrix and entrapped in a lacuna
Basically from osteoblasts
Osteocytes - location
Reside in lacunae - a small cavity or depression in a tissue such as bone or cartilage
Within bone matrix
Osteocytes - misc.
Lacunae - spaces occupied by osteocyte cell body
Canaliculi - canals occupied by osteocyte cell processes
Nutrients diffuse in liquid surrounding cell and filling lacunae and canaliculi
Then can transfer nutrients from one cell to the next through gap junctions
Osteoclasts - function
BREAK
Reabsorption of bone - break down bone matrix
Release acid and enzymes
H ions pumped across membrane, forming acid
Release enzymes that digest the bone
Derived from monocytes in red bone marrow
Osteoclasts - origin
Monocytes (white blood cells)
Form into osteoclast
Develop from same bone marrow stem cells as blood cells
Osteoclasts - location
Bone surfaces that are being broken down, in shallow depressions called Howship’s lacunae
Osteoclasts - misc.
Ruffled border - where cell membrane borders bone and reabsorption is taking place
Lacuna
Spaces occupied by osteocyte cell body, spaces that contain osteocytes
Canaliculi
Canals occupied by osteocyte cell processes, thin tubular connections between lacunae
Bone remodeling
Removing old bone and adding new bone
Woven bone
Collagen fibers randomly oriented
Formed during fetal development and fracture repair
Remodeled into lamellar bone
Lamellar bone
Mature bone in sheets called lamellae
Fibers are oriented in one direction in each layer, but in different directions in different layers for strength
Differences between spongy bone and compact bone
Spongy bone
Appears porous (lots of spaces filled with marrow)
Less bone matrix
More space
Compact bone
More dense
More bone matrix
Less space (very compact together)
Spongy bone - location
Within the ends of long bones, pelvic bones, ribs, skull bones, and vertebrae in the spine
Trabeculae
Interconnecting rods or plates of bone, like scaffolding
Spaces filled with marrow
Covered with endosteum (outer covering - layer within and lines spongy bone)
Oriented along stress lines
Spongy bone - structure
Most trabeculae are thin
Several lamellae
Blood vessels do not penetrate trabeculae
Surfaces covered with single layer of cells
Osteoblasts
Few osteoclasts
Compact bone - structure
Arranged in osteons
Osteon
Cylindrical unit of bone that is the functional unit of compact bone
Central (Haversian) Canal
Parallel to long axis, contains blood-vessels
Vessels of the central canal, receive blood from perforating canals
Surrounded by lamellae
Lamella
Tree rings
Concentric lamellae
Surrounds central canal
Circumferential lamellae
Around circumference, surrounds periphery of bone
Interstitial lamellae
Between osteons, remnants from bone remodeling
Perforating (Volkmann’s) Canal
Perpendicular to long axis, contains blood vessels
Blood vessels from periosteum penetrate bone
Not surrounded by lamellae
Nutrients and wastes travel to and from osteocytes via
Interstitial fluid of lacunae and canaliculi
From osteocyte to osteocyte by gap junctions
Epiphysis
End of the bone, spongy bone, develops from a center of ossification distinct from the diaphysis
Diaphysis
Shaft, compact bone
Epiphyseal lines (adult)
Bone stops growing in length, site of old growth plate
Epiphyseal plate (youth)
Plate of hyaline cartilage between epiphysis and diaphysis of long bone
Growth zone for bone elongation
Still capable of growing
Medullary Cavity
Hollow part of bone that contains red marrow in juveniles and yellow marrow in adults
Located within the diaphysis
Periosteum
Double-layered connective tissue membrane covering the outer surface of bone except where articular cartilage is present
Continous with ligaments and tendons
Periosteum - outer layer
Fibrous, dense irregular collagenous tissue
Periosteum - inner layer
Single layer of bone cells including osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteochondral progenitors
Periosteum - Sharpey’s Fibers
Tendon and ligament fibers penetrate through the periosteum into the bone, strengthen attachment of tendon to bone
Endosteum
Lines all internal spaces including spaces in spongy bone, such as trabeculae
Long bone
Longer than wide and serves as a lever
Anything that looks long
Ex: femur, humerus, ulna
Flat bone
Sandwich of spongy bone between compact bone
No diaphyses, small epiphyses
Ex: parietal bone from roof of skull, sternum, ribs
Irregular bone
Irregular shape
Ex: sphenoid bone from skull, sacrum, coccyx
Short bone
Short shape
Ex: carpal/wrist bone, tarsal/ankle bone, patella
Short and irregular bones - structure
Compact bone that surrounds spongy bone center, similar to structure of epiphyses of long bones
No diaphyses and not elongated
Some flat and irregular bones of skull have sinuses lined by mucous membranes
Sinus
Hollowed out spaces in skull lined with mucous membranes