perfect competition in the short-run
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
profit
total revenue - total cost
profit alt. equation 1
(P Q produced) - (ATC Q produced)
profit alt. equation 2
(P - AC) * Q produced
characteristics of perfect competition:
- many firms but identical product
- many buyers
- all relevant info is available about price, quantity, and quality
- each seller has minimal market impact
- sellers are price takers
- no barriers to entry
what does being a price taker mean for product elasticity?
the firm faces a perfectly elastic demand curve for its product
- buyers are willing to buy any number of units of output from the firm at the market price
1st way of determining the profit maximizing amount of output:
calculate the total profit at each quantity for comparison
- MR = MC
2nd way of determining the profit maximizing amount of output:
use the optimal output rule
optimal output rule
the application of the principle of marginal analysis to the producer's decision of how much to produce
MR = MC
- profit is maximized by producing the quantity at which the marginal revenue of the last unit produced is equal to its marginal cost
where is max profit on a graph?
it is located where the MC curve crosses the MR curve (the horizontal line at market price)
when will the firm earn profits?
if the price that a producer charges is higher than its ATC of production for that quantity produced
when will the firm suffer losses?
if the price that a producer charges is lower than its ATC of production for that quantity produced
- however the firm may not shut down after already paying FC
if p > ATC then
profit occurs
if p = ATC then
zero profit
if p < ATC then
loss occurs
breakeven point
the point where P = ATC
- the firm is covering all of its economic costs
- also called earning a 'normal profit'
shut down point
the intersection of the AVC curve and the MC curve
what does the shut down point show?
the price where the firm would lack enough revenue to cover its variable costs
what happens if price is above the shut down point?
VC and FC are covered; so losses are smaller
what happens if price is below shut down point?
VCs are not covered and losses are larger
if p < min AVC then
the firm will shut down
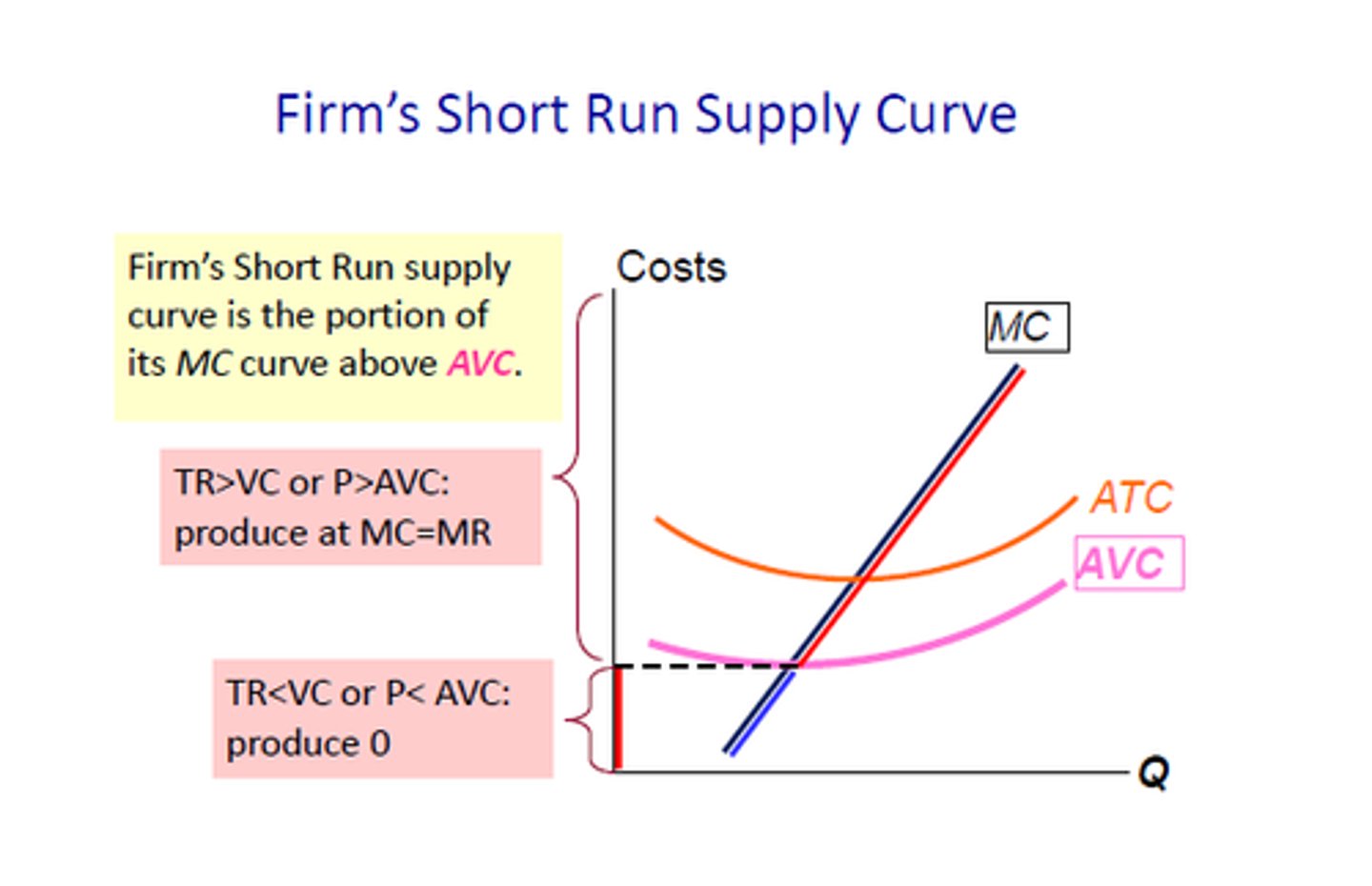
supply curve in the short run
- below AVC: shutdown
- between AVC and ATC: loss but can continue operating
- above AVC: zero-profit point
firms SR decision to shut down:
refers to a temporary stop in product
- must still pay FC (aka sunk costs)
shut down points:
- TR < VC
- TR/Q < VC/Q
- AR < AVC
- P < AVC
where is competitive firm's SR supply curve?
the portion of the MC curve that lies above the AVC curve
if MR > MC then
increase production
if MR < MC then
decrease production
if MR = MC then
at profit maximizing point