Chapter 10.2
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/30
Last updated 5:38 AM on 1/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1
New cards
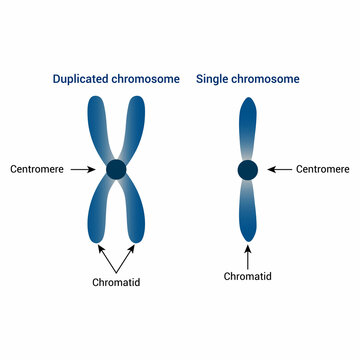
What are chromosomes?
Packages of genetic information (DNA) bundled together.
2
New cards
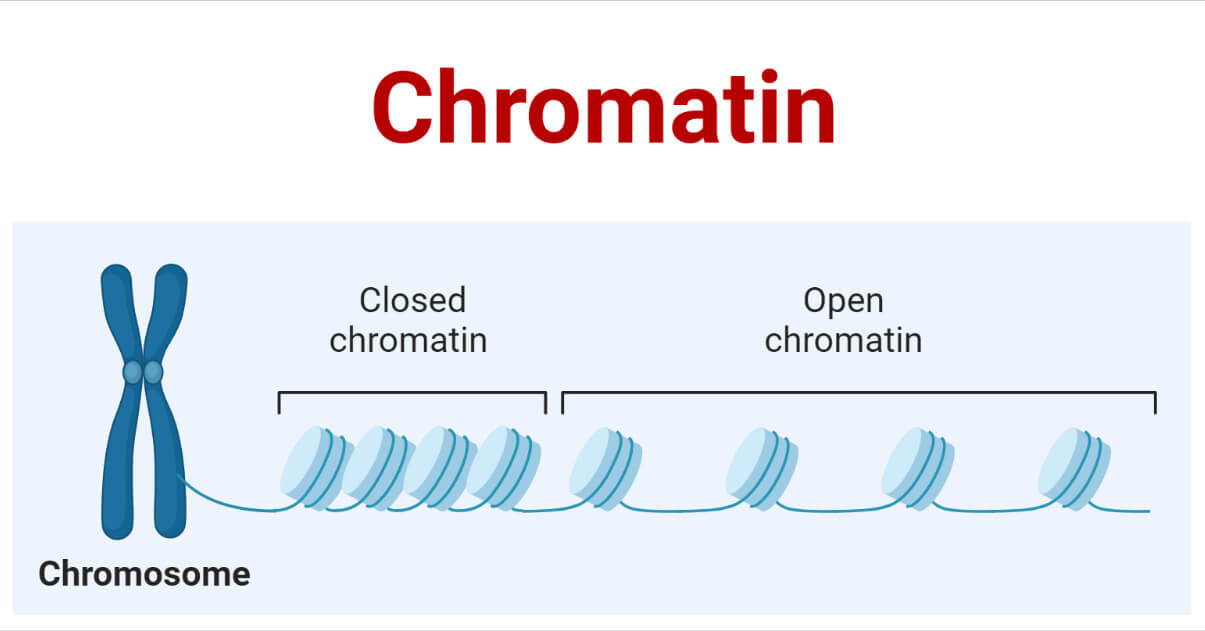
What is chromatin?
Complex of DNA.
3
New cards
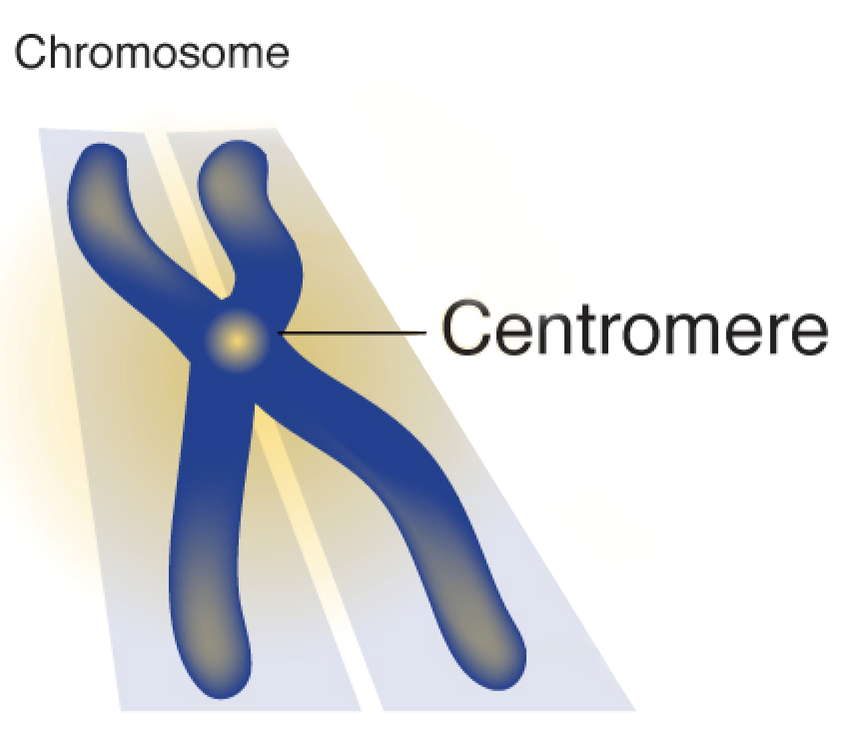
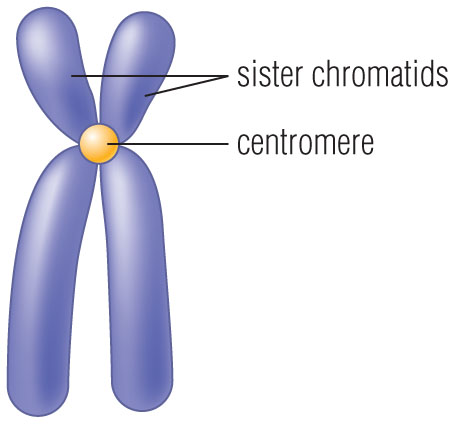
What is the centromere?
Center of a chromosome.
4
New cards
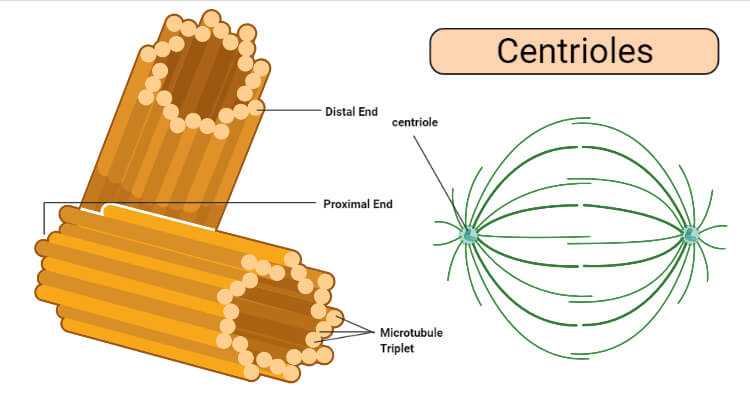
What are the centrioles?
2 organelles that produce the spindle fibers that pull the chromosomes apart during anaphase.
5
New cards
What is a chromatid?
One half of a duplicated chromosome.
6
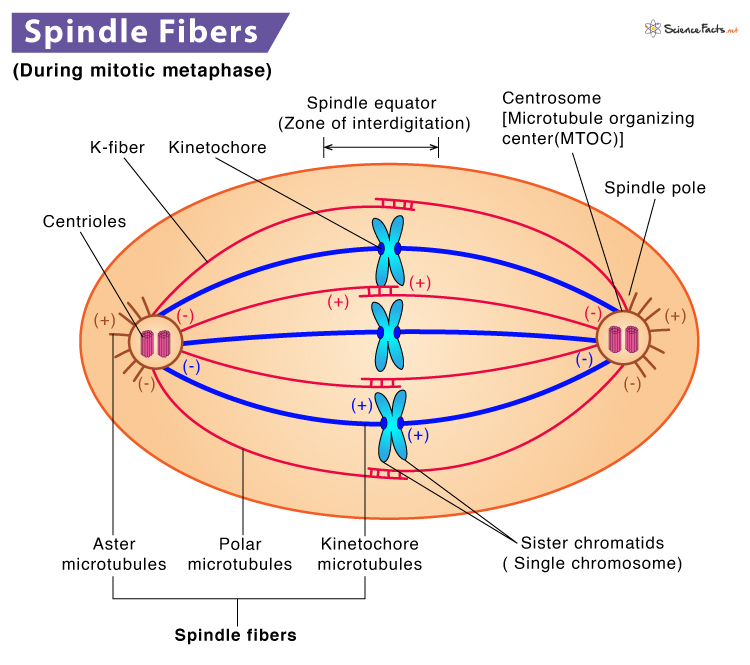
New cards
What are spindle fibers?
Fibers that attach to the centromeres and separate chromosomes to opposite sides of the cell.
7
New cards
Describe prokaryotic chromosomes.
Prokaryotes have no nucleus, but they have one circular chromosome in the cytoplasm.
8
New cards
Describe eukaryotic chromosomes.
They are made of chromatin; during cell division, it coils into chromosomes.
9
New cards
What is the Cell Cycle?
A series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. It begins when the cell is formed and ends when the cell divides.
10
New cards
What is another name for the prokaryotic cell cycle?
Another name for it is "binary fission" (asexual reproduction).
11
New cards
What are the steps for the prokaryotic cell cycle (binary fission)?
First the cell grows; then the DNA doubles; finally it splits in two.
12
New cards
True or false: Eukaryotic cells contain more DNA than prokaryotic cells.
True.
13
New cards
True or false: Eukaryotic cells have chromosomes in the nucleus.
True.
14
New cards
What are ALL the stages of the cell cycle in order?
Interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis.
15
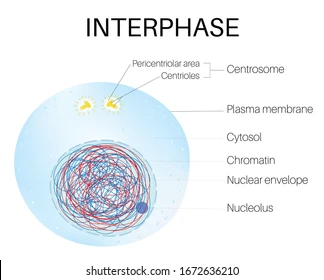
New cards
What is interphase?
The period of cell growth in between cell division.
16
New cards
What are the stages of interphase?
G1, S, and G2.
17
New cards
What is the G1 phase of interphase?
Cell growth.
18
New cards
What is the S phase of interphase?
DNA replication; new DNA is synthesized.
19
New cards
What is the G2 phase of interphase?
Preparation for cell division; there is cell growth and organelle production, and the cell is ready to divide.
20
New cards
What is the M phase?
Cell division and the making of 2 daughter cells; very quick compared to interphase.
21
New cards
What are the phases of the M phase?
Mitosis and cytokinesis.
22
New cards
What is mitosis?
The division of the nucleus.
23
New cards
What is cytokinesis?
The division of the cytoplasm; usually occurs at the same time as telophase.
24
New cards
True or false: In eukaryotic cells, the M phase is the only phase where cell division actually occurs.
True.
25
New cards
What are the phases of mitosis in order?
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase (PMAT).
26
New cards
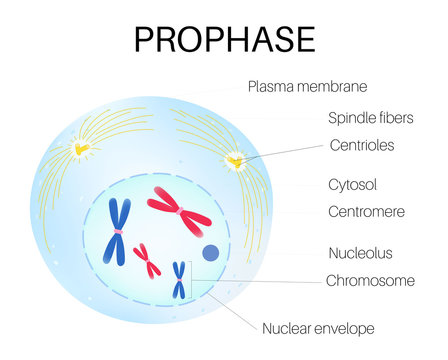
What is prophase?
It is the longest phase of mitosis; DNA is duplicated and condenses into chromosomes afterward. Spindles form outside the nucleus produced by centrioles and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
27
New cards
What is metaphase?
It is the shortest part of mitosis; chromosomes line up across the center of the cell and spindle fibers connect each centromere.
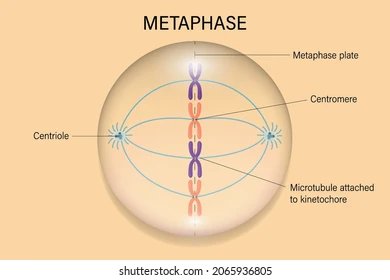
28
New cards
What is anaphase?
It is the part of mitosis when chromatids separate and begin to move apart to opposite sides of the cell.
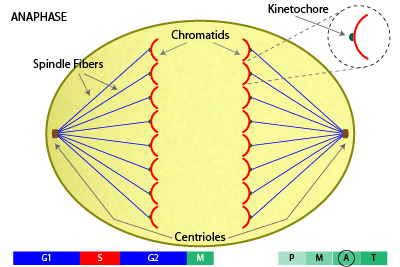
29
New cards
What is telophase?
It is the part of mitosis where the condensed chromosomes begin to spread out into chromatin again; spindles release and the nuclear envelope/nucleolus reform in each daughter nucleus.
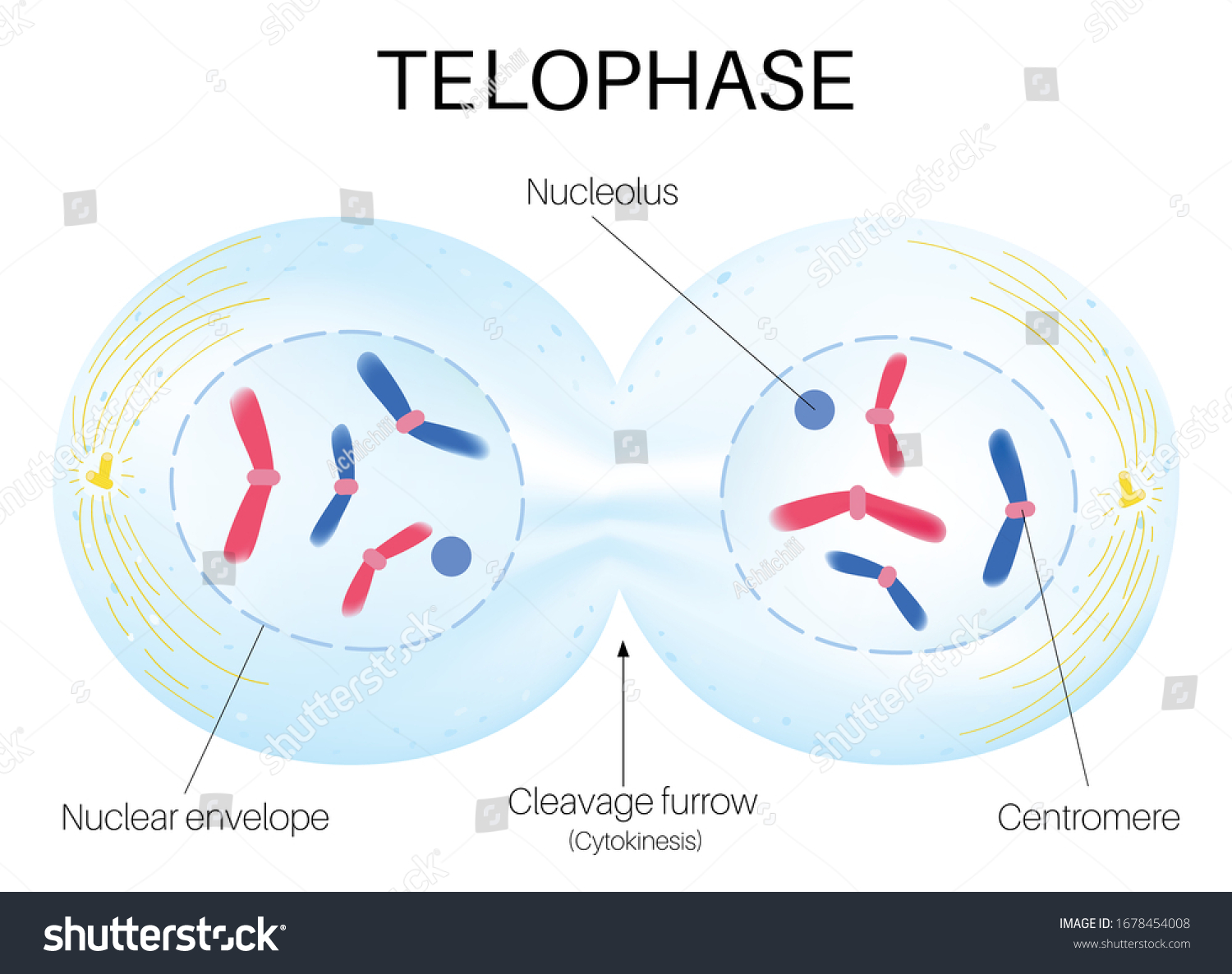
30
New cards
Describe cytokinesis in animal cells.
In animal cells, the cell membrane is drawn inward, creating a cleavage furrow. The cytoplasm pinches into 2 parts until the daughter cells separate.
31
New cards
Describe cytokinesis in plant cells.
In plant cells, a cell plate forms between the daughter cells. The cell membrane and cell wall form at the cell plate to separate the cells.