Module 2-Foundations in Chemistry
1/236
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
237 Terms
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element with the same number of electrons and protons but a different number of neutrons and masses
What are the different sub atomic particles of an atom?
-protons
-neutrons
-electrons
What does the top number of an element tell you?
Mass number(bigger)-num of protons and neutrons
What does the bottom number of an elements tell you?
Atomic number(smaller)-number of protons/electrons in an atom
What are the masses of the subatomic particles?
P=1
N=1
E=1/2000
How do you calculate the number of neutrons?
Mass no-Atomic no
What is an ion?
Atoms that have lost or gained electrons to become positively or negatively charged
Eg.O2- has gained 2 electrons
How did JJ Thompson describe the atom in 1897?
-discovered the electron
-atom isn’t solid and made up of other particles
-plum pudding model developed
How did Ernest Rutherford describe the atom in 1909 and what experiment was used to prove this?
-discovered the nucleas
-nucleus=very small and positively charged
-collided atom was mainly empty space making up a negative cloud
Gold Leaf Experiment-
Positive alpha particles fired at thin gold leaf
Most went through the gold leaf(mainly empty space)
Small number deflected back(hit a small positive nucleas)
How did Neil’s Bohr describe atoms inn1913 and what experiment did he use to prove it?
-descovered a problem with Rutherford model
Cloud of electrons could collapse into the positive nucleas
-proposed electrons were in fixed energy shells
Experimental proof:
When EM radiation is absorbed, electrons move between shells
They emit EM radiation when electrons move down to lower energy shells
What model is referred to most today?
Atomic model:
Electrons don’t have the same energy in shells
They have sub shells
This explains ionisation trends
What is relative atomic mass(AR)?
Weighted mean mass of an atom of an element ,compared to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon 12
What is relative isotopic mass?
Mass of an atom of an isotope, compared to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon 12
What is mass to charge ratio(m/z)?
Mass of an isotope divided by the charge
As most just have a +1 charge, it’s the same as the isotopic mass
Isotopes lose an electro when going through the mass spectrometer
What axis is abundance always shown on?
Y-axis
Can be a percentage or a nominal value
What does a mass spectrometer do?
-finds percentage abundances of the isotopes in a sample of an element
-can record mass to charge ratio for each isotope
What is the formula of relative atomic mass?
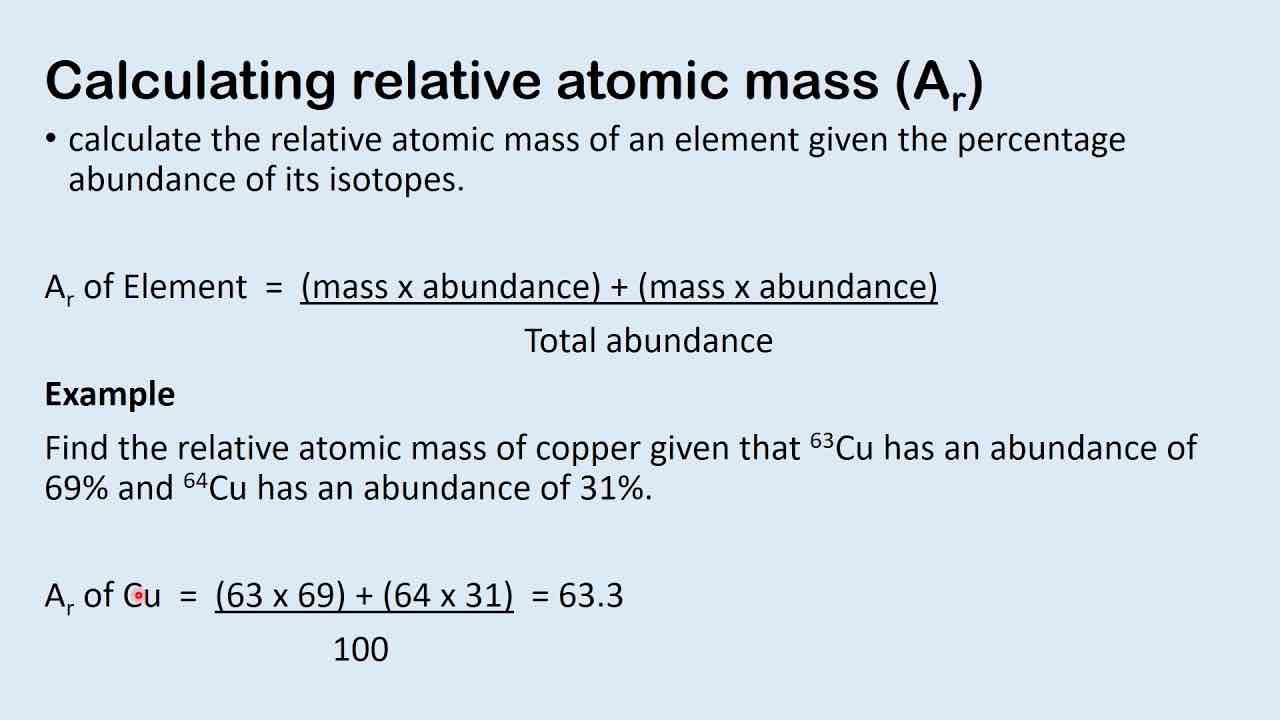
How do you find relative molecular mass?
Add all of the relative atomic masses of all the atoms in the molecule(simple molecules)
How do you find relative formula mass?
The sum of the relative atomic masses of the atoms in the numbers shown in the formula
How many electrons can fill the 1st shell?
2=1s
How many electrons can fill the 2nd shell?
8=2s,2p
2+(3×2)=8
How many electrons can fill the 3rd shell?
18=3s,3p,3d
2+(3×2)+(5×2)=18
How many electrons can fill the 4th shell?
32
What are the shell numbers also known as?
Principal quantum numbers
The higher the shell number…
-the further away from the nucleus
-they also have higher energy
What is spin pairing?
When 2 electrons occupy 1 orbital they ‘spin’ in opposite directions
What is an orbital?
A region around the nucleus that can hold up to 2 electrons, with opposite spins
What is the shape of an s orbital and how do you draw it?
-sphere
-electrons can move anywhere writhing the spherey
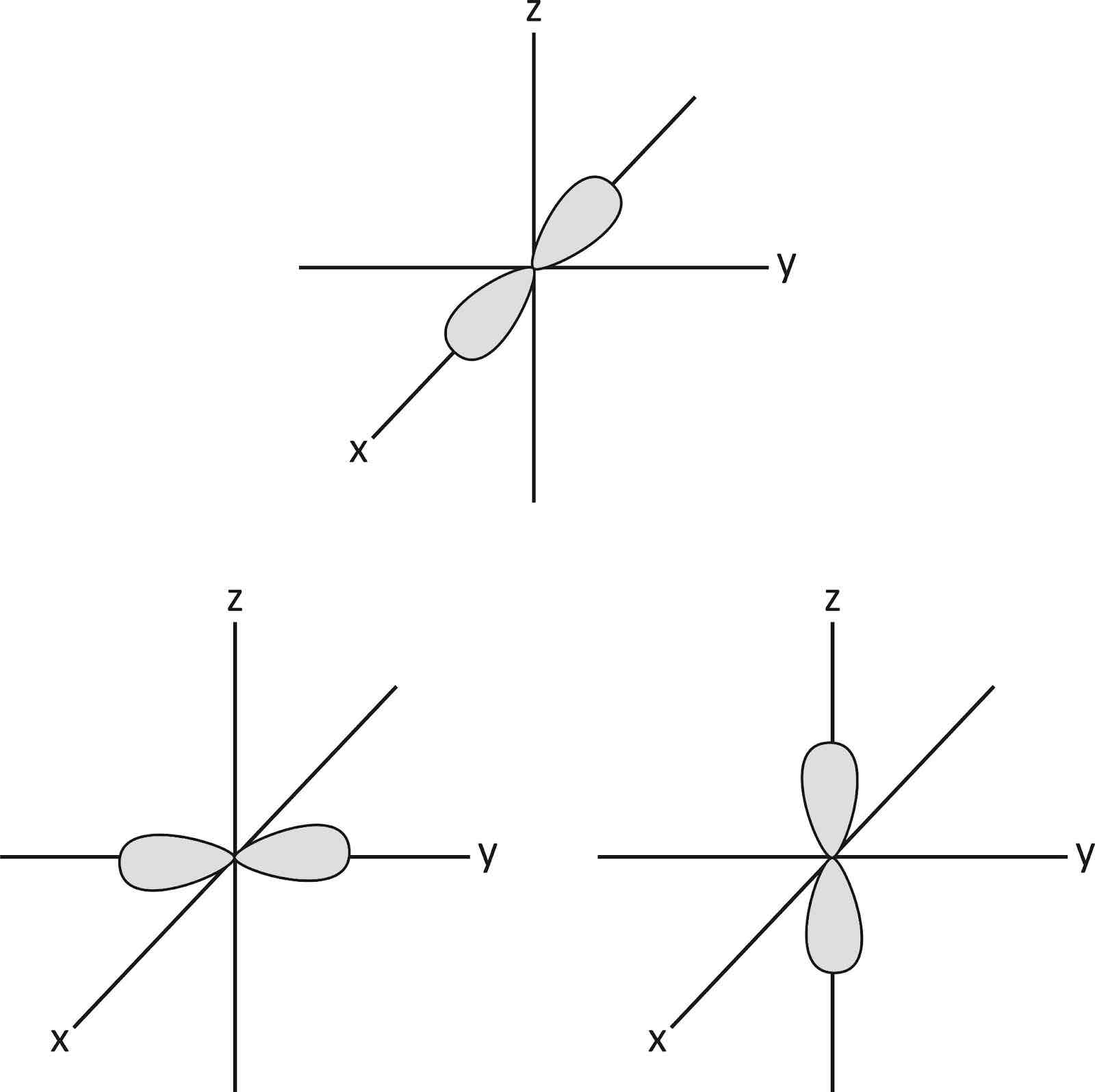
What is the shape of a p orbital and can you draw the 3 different types?
-dumb bell shaped
-electrons can move anywhere within these shapes y
How many orbitals do the s,p,d and f sub shells have?
-S=1 orbital
-P=3 orbitals
-D= 5 orbitals
-F=7 orbitals
How many electrons can each orbital have?
2
How many electrons can fill the s,p,d and f sub shells?
-S=2 electrons
-P=6 electrons
-D=10 electrons
-F=14 electrons
How do the orbitals fill up?
In order of increasing energy
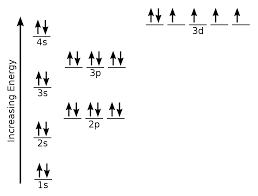
Draw the electron configuration of iron?
-4s fills up before 3d as it is a transition metal
-arrows should add up to 26
-fill up from the bottom up
-electrons fill up singly first then pair up
What can you use to write short hand electron configurations?
Noble gas symbols
Give the short hand for potassium’s electron configuration
K=1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s1
First 4 sub shells have the same configuration as argon
K=[Ar]4s1
In what order do the shells fill up?
1s,2s,2p,3s,3p,4s,3d,4p,5s,4d,5p,6s
How do orbitals fill up for orbitals with the same energy?
Fill the orbitals singly as far as possible before pairing up
Give an example for sub shell notation for oxygen
8 protons-1s2, 2s2, 2p4
What does each part of the sub shell notation mean?
1=energy level(shell)
S=sub shell
2=num of electrons
What would the sub shell notation be for the ion Be2+?
1s2=beryllium has lost 2 electrons
What is ionic bonding?
Electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions.
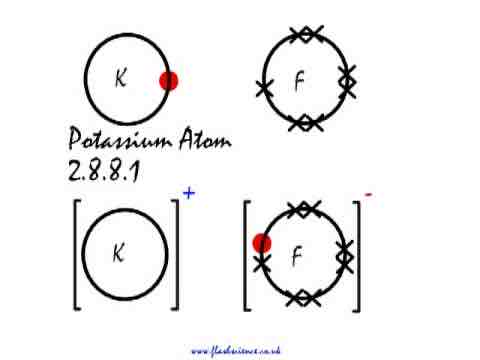
Draw the dot and cross diagram for potassium fluoride
What are the molecular ions?
-OH- hydroxide
-NO3- Nitrate
-NH4+ Ammonium
-SO42- Sulfate
-CO32- Carbonate
Describe the swap and drop method to write the formula for an ionic compound
-write the 2 ions
-swap the charges
-drop the charges(they literally go down)
-simplify to the lowest whole number ratio
What would you call an ionic structure?
Giant ionic lattice
How does a giant ionic lattice form?
Each ion is electrostaticslly attracted in all directions to ions of the opposite charge
Describe a giant ionic structure
-regular structure
-cubic shape
-giant repeating pattern
What are the characteristics of ionic compounds?
-can dissolve in water
-can conduct electricity when molten
-have high melting and boiling points
Why can ionic compounds dissolve in water?
-water molecules are polar
-they attract the positive and negative ions
-they break up the structure
Why can ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in solution?
-ions are free to move around and carry charge
Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points?
-many electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions
-lots of energy needed to overcome these forces
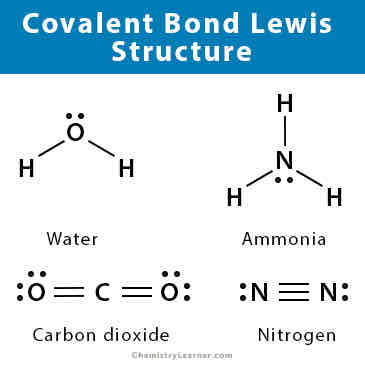
What is covalent bonding?
Sharing of outer electrons in order for atoms to obtain a full outer shell.There is an electrostatic attraction between the shared electrons and the positive nucleus.
How many different kinds of covalent bonds are there?
3-single,double,triple
How can covalent bonds be represented other than dot and cross diagrams?
With lines
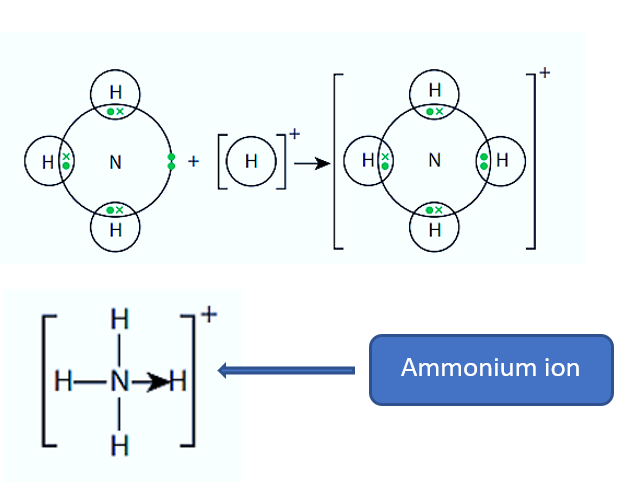
What are dative covalent/co ordinate bonds?
Where an atom donates 2 electrons to an atom or ion to form a bond
What rules are followed when doing the electron configuration for chromium and copper?
-4s fills up before 3d
-provides either half filled or full sub shells
What electron configuration would you expect for chromium and what is it actually?
-expected=[Ar]4s2, 3d4
-actually=[Ar]4s1, 3d5
-one electron moves from 4s to 3d, which achieves a half filled 3d level making it more stable
What electron configuration would you expect from copper and what is it actually?
-expected=[Ar]4s2, 3d9
-actually=[Ar]4s1, 3d10
-by moving one electron from the 4s orbital to the 3d orbital, copper achieves a fully filled 3d sub level which is more stable.
When are ions created?
When electrons are transferred from one atom to another. They attract to each other to form compounds.
What is the ion for zinc and silver?
-Zn2+
-Ag+
what is salt an example of and what can it do?
-ionic compound
-can be hydrated or anhydrous
What is water attracted to because of its polar nature?
-ions in a salt
-delta negative oxygen is attracted to positive ions
-delta positive is attracted to negative ions
Where can water molecules exist and what would call this?
-within crystal structures
-called water of crystallisation
What does .H2O mean?
For every mole of slat you have a certain number of moles of crystallisation
What is the mole(mol)?
A way of measuring the amount of a substance in chemistry
What is avogadros number ?
6.02×10²³ atoms/molecules
How do you calculate water of crystallisation?
1)write out the 2 molecules involved
2)write the masses of each molecule
3)divide these by the relative molecular mass to get the number of moles
4)divide all numbers by the smallest number of moles
What is the equation for moles in terms of particles?
Mole=no of particles/6.02×10²³
What is the equation for moles in terms of mass and Mr?
Mole=mass(g)/Mr or Ar
What is molar mass?
The mass of one mole of something
What is molar mass the same as?
Relative molecular mass,Mr
How much CaO can be made when 34g of Ca is burnt completely in oxygen?
-2Ca+O2=2CaO
40×2=80g = 56×2=112g. /80
1g. = 1.4g. * 34
34g. = 47.6g
How do you work out masses using equations?
1)write out equation and balance it
2)work out Mr/Ar of species involved.write these as mass in grams
3)divide one side by the mass you already know then multiply by the amount of substance used
4)do the same on both sides of the equation
The result is the theoretical mass
What is empirical formula?
Simplest whole number ratio of elements in a compound
How would you find the empirical formula of a compound?
1)write out the elements involved
2)write the percentages as masses
3)divide these by relative atomic mass to get numbers of moles
4)divide all the numbers by the smallest number of moles
How do you work out the molecular formula?
1)work out the Mr of the empirical formula
2)divide by the Mr of molecular formula
3) use this number to multiply all the atoms in the empirical formula
How would you find the empirical formula of a hydrocarbon?
1)write H2O and CO2 as headings
2)write the masses of each molecule
3)divide these by relative molecular mass to get number of moles
4)divide the number of C and H atoms by the smallest number of moles
Only the hydrogen and carbon come from the hydrocarbon not the oxygens
1 mol of CO2 has 1 mol of C
1 mol of H2O has 2 moles of H
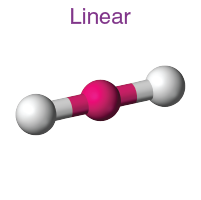
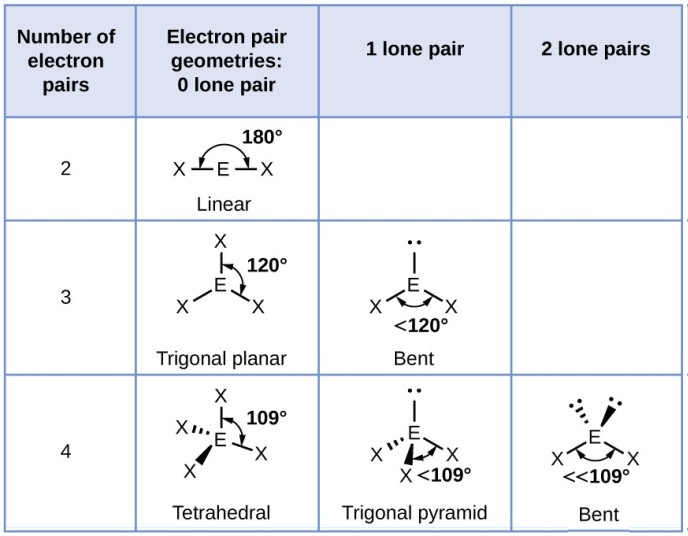
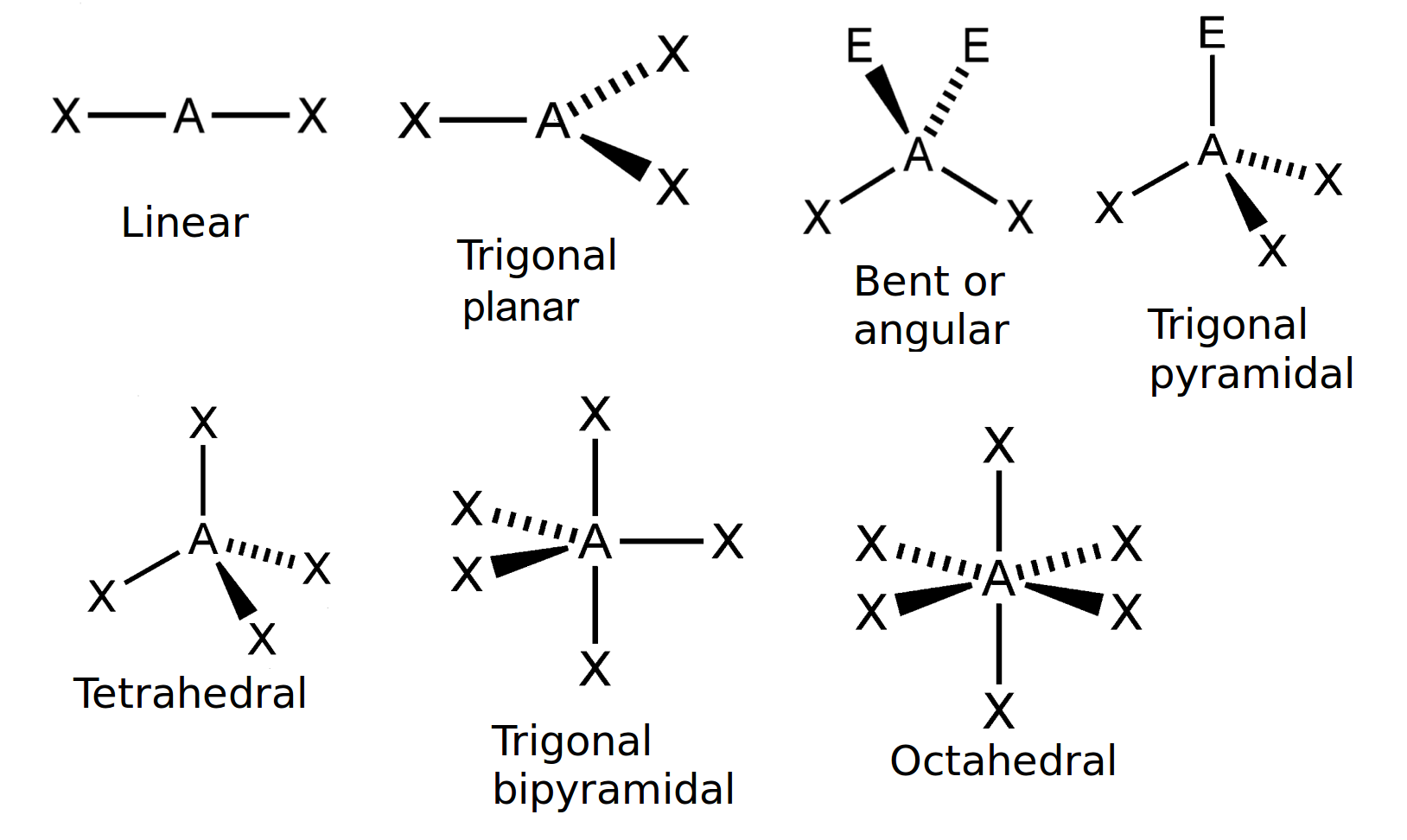
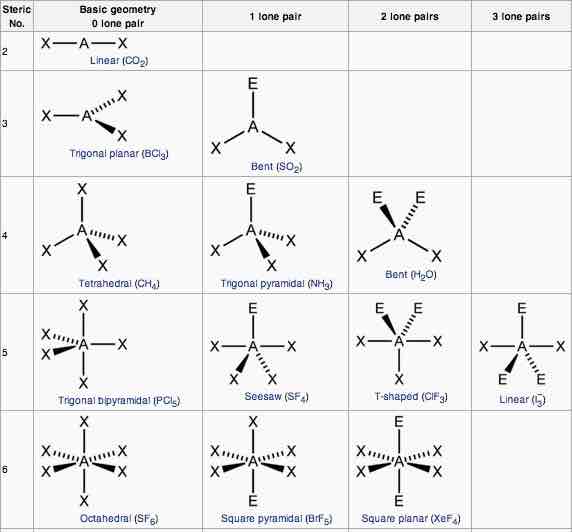
Explain the characteristics of the linear shape of molecules
-no of bonding pairs= 2
-no lone pairs=0
-bond angle=180 degrees
-examples=CO2, CS2, HCN, BeR2
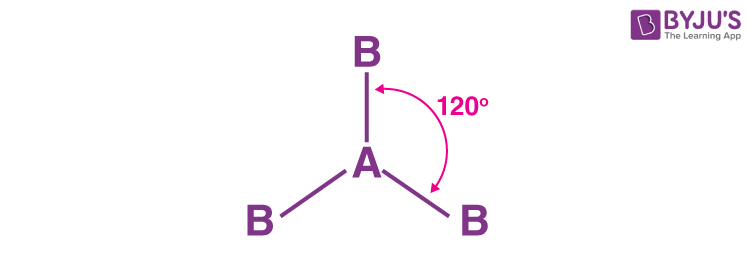
Explain the trigonal planer shape
No of bonding pairs=3
-no of lone pairs= 0
-bond angle=120 degrees
-examples=BF3, AlCl3, SO3
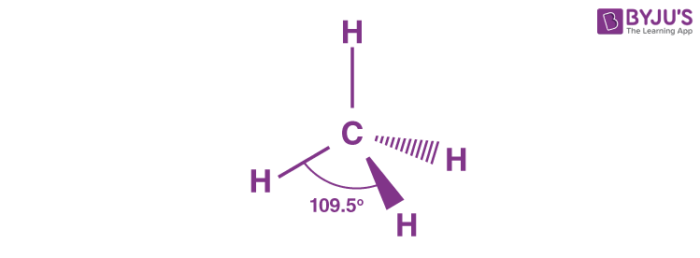
Describe the tetrahedral shape of molecules
-no of bonding pairs=4
-no of lone pairs= 0
-bond angle=109.5 degrees
-examples= SiCl4, SO42+, NH4+
Explain the trigonal bipyramidal shape molecules
-no of bonding pairs= 5
-no of lone pairs= 0
-bond angle= 90 degrees and 120 degrees
-example=PCl5
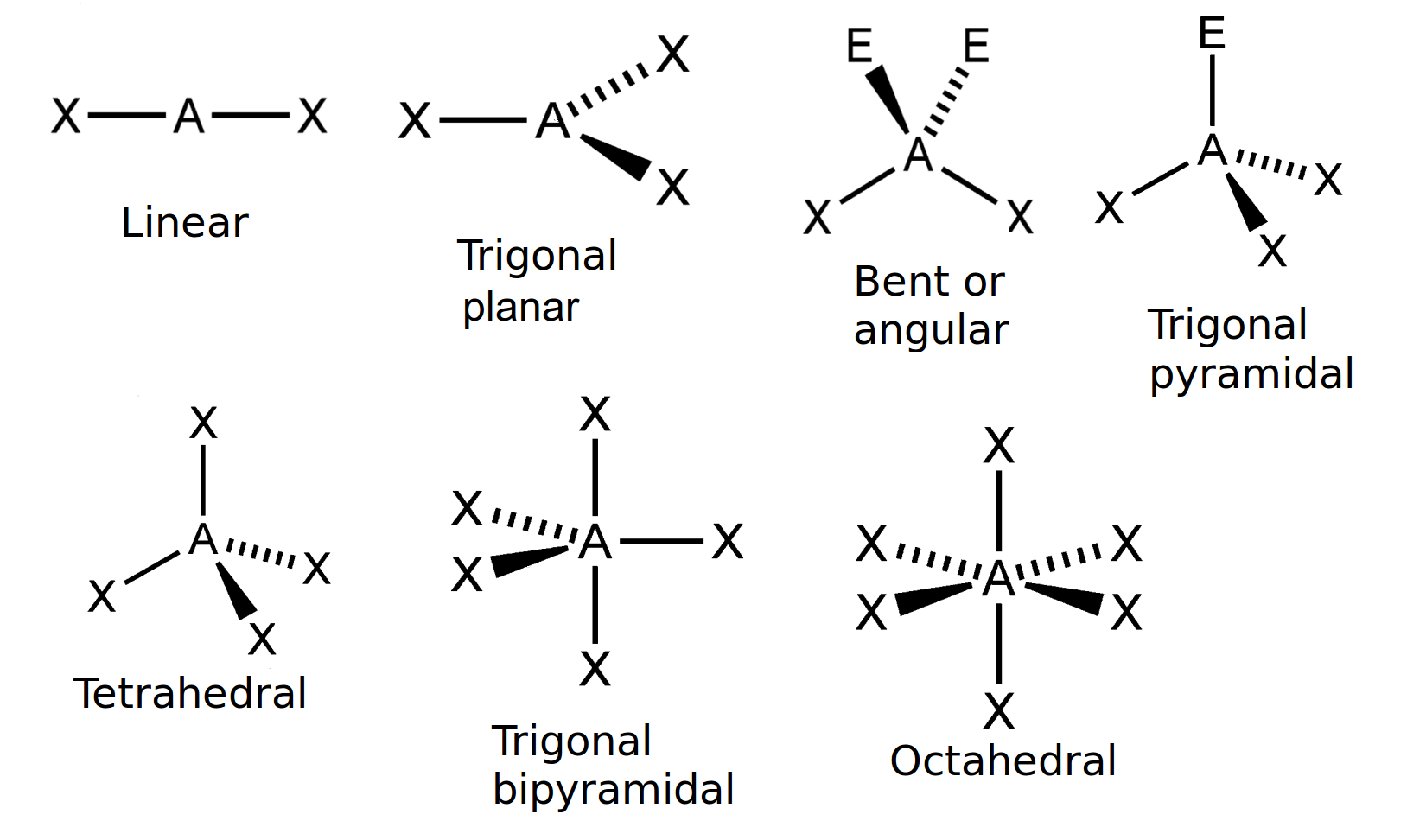
Explain the trigonal pyramidal shape of molecules
-no of bonding pairs=3
-no of lone pairs=1
-bond angle=107 degrees
-examples=NCl3, PF3, ClO3
Explain the bent shape of molecules
-no of bonding pairs=2
-no of lone pairs= 2
-bond angle=104.5 degrees
-examples= OCl2, H2S, OF2
Explain a square planar shape molecules
-no of bonding pairs=4
-no of lone pairs= 2
-bond angle= 90 degrees
-example= XeF4
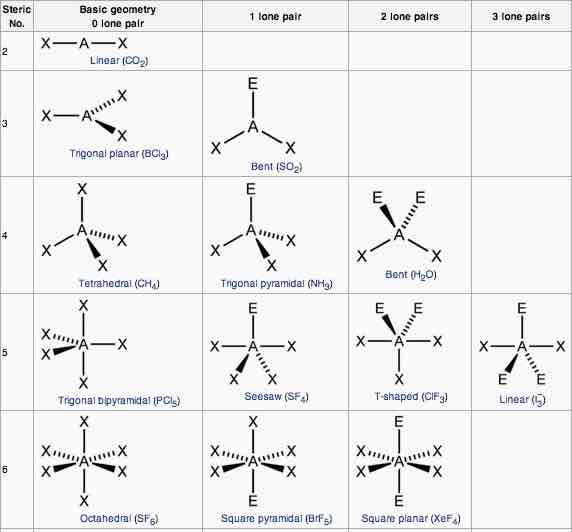
Explain the octahedral shape molecule
-no of bonding pairs=6
-no of lone pairs= 0
-bond angle= 90 degrees
-Example= SF6
How do you explain the shape of molecules?
1)state the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons
2)state that electron pairs repel and try to get as far as possible
3)if there are no lone pairs, state that the electron pairs repel equally
4)if there are lone pairs of electrons, then gate that lone pairs repel more than bonding pairs
5)state the actual shape and bond angle
What do lone pairs do more than bonding pairs?
They repel more than bonding pairs and so reduce bond angles by about 2.5 degrees per lone pair
How do you determine the shape of molecules?
1)determine the number of outer shell electrons in each of the atoms in the molecule
2)draw a dot and cross diagram to show the bonding in the molecule
3)count the number of electron pairs around the central atom
4)predict the shape of bond angle
What do the lines showing molecule shapes mean?
-solid line= bond in the plane of the paper
-solid wedge= bond coming out of the paper
-dotted wedge= bond going into the paper
What does electronegativity mean?
The ability of an atom to attract the bonding electrons in a covalent bond towards itself
What atoms are most electronegative?
F, O, N and CL
When does electronegativity increase?
Increases across a period as the number of protons increases and the atomic radius decreases because the electrons in the same shell are pulled in more.
When does electronegativity decrease?
Down a group because the distance between the nucleas and the outer electrons increases and the shielding of inner shell electrons imcreases
When will a compound be purely covalent?
When the compound contains elements of similar electronegativity and hence a small electronegativity difference.
When does a permanent dipole (polar covalent) bond form?
When the elements in the bond have different electronegativities
What happens when a polar covalent bond is formed?
Has an unequal distribution of electrons in the bond and produces a charge separation (Dipole)
Delta negative and positive ends
What is a symmetric molecule?
All bonds identical and no lone pairs
When will a symmetric molecule not be polar?
Even when individual bonds within the molecule are polar
What happens because of the symmetrical shape of a molecule?
-Dipoles on the bonds cancel out
-there is no net dipole moment
-the molecule is non polar