Kinship & Parentage Testing
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are the possible outcomes of a typical paternity test?
1. Cannot be excluded (inclusion) - the obligate paternal alleles in the child all have corresponding alleles in the alleged father
2. Exclusion - the obligate paternal alleles in the child DO NOT correspond to those of the alleged father
Examples of statistical value used to assess strength of the genetic evidence
1. Paternity Index (PI)
2. Combined Paternity Index (CPI)
What is the likelihood expression for PI?
Probability of alleged father being able to produce a child of a given type with the mother OVER Probability of a random man being able to produce a child of a given type with the mother
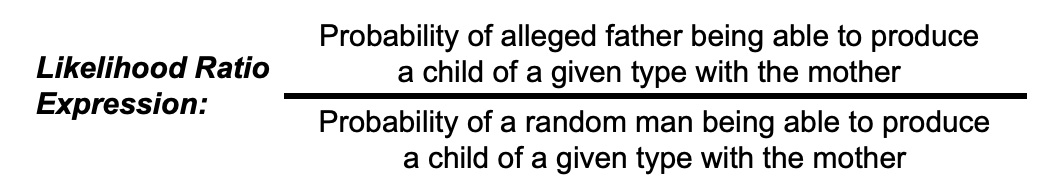
LR Numerator
Assumes paternity
LR Denominator
Assumes random man is the father
PI Numerator
A woman randomly selected from a population is type BD, AND a man randomly selected from a population is type AC, AND their child is type AB.
PI Denominator
A woman randomly selected from a population is type BD, AND a man randomly selected and unrelated to either mother or child is type AC, AND their child is type AB.
Probability statements for PI
a) Numerator is the probability of observed types, given the tested man is the father, and
b) Denominator is the probability of observed types, given a random man is the father
CPI Equation
Total PI (CPI) = PI (locus1) x PI (locus2) x PI (locus3) x PI(n)
CPI results
CPI = 1 -> genetic tests provide no info
CPI <1 -> genetic evidence is more consistent with non-paternity
CPI >1 -> genetic evidence supports the assertion that the tested man is the father
What is the minimum accepted standard for inclusion?
PI > 100
Verbal expression of PI
It is (X/Y) times more likely to see the genetic results if the tested man was the true biological father than if an untested random man was the father
________ inconsistencies have been traditionally considered genetic evidence to exclude a tested man and to issue a finding of non-paternity (<12 STR System)
2
________ inconsistencies have been traditionally considered genetic evidence to exclude a tested man and to issue a finding of non-paternity (>12 STR System)
3
T/F: Unrelated individuals have a very low probability of sharing the same DNA profile
TRUE
What is the closest relationship that has an impact on calculations?
Full siblings
How many loci is sufficient to assert uniqueness?
11
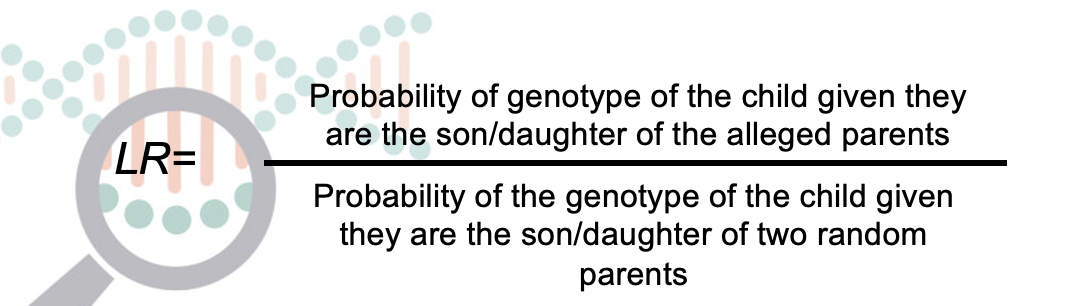
Reverse parentage LR expression
Probability of genotype of the child given they are the son/daughter of the alleged parents OVER Probability of the genotype of the child given they are the son/daughter of two random parents
Possible explanations when loci are inconsistent
1. The alleged father is excluded as the biological father of the child and is unrelated to the true biological father.
2. The tested man is not the biological father but is a 1st order relative of the true biological father and shares the majority of alleles contributed to the child with the biological father.
3. A mutation event has occurred altering the allele inherited from the AF by the child.
T/F: In cases with a single non-matching system, the laboratory should ignore the inconsistent locus.
FALSE. In cases with a single non-matching system, the laboratory cannot simply ignore the inconsistent locus. A paternity index must be calculated for the inconsistent locus, which takes into account the possibility of a mutation