Immuno final
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
1
New cards
The first line of defense used by the immune system are
physical barriers
2
New cards
Which of the following is an antimicrobial susbtance produced by the Immune System?
Lysozyme
3
New cards
How do the Actions of the symbiotic microorganisms of the human microbiota assist the function of the immune system
They secrete substances that create an environment less conducive to pathogens ; they compete for nutrients in the same locations of the body pathogens might grow ; they secrete antimicrobial substances that prevent pathogens from growing.... the answer is all of the above.
4
New cards
a function of the innate immune system is pathogen ...
recognition and destruction
5
New cards
the rise in body temperature that occurs during a fever is caused during a fever is caused by
cytokines
6
New cards
All of the following are considered lymphoid tissue except
microbiota
7
New cards
autoimmune diseases occur when cells of the adaptive immune system are able to recognize ...
self molecules
8
New cards
which immune defense can both tag a pathogen for phagocytosis and create a membrane attack complex to create pores in the pathogen cell membrane
the complement system
9
New cards
which innate immune receptor family is composed of proteins that bind and recognize the pathogen associated molecular patterns such as LPS (lipopolysaccaride)
toll like receptors
10
New cards
Most pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that are recognized by PRRs
are molecules common to many pathogen external surfaces
11
New cards
\__________ are most abundant in blood circulation and specialize in engulfing and killing bacterial cells leaving behind a compound known as pus
neutrophils
12
New cards
When the body encounters a novel pathogen, which pathway of complement activation would activate last?
Classical pathway
13
New cards
The three pathways of complement activation first converge at the ....
cleavage of C3
14
New cards
Which pathway relies on C-reactive protein or antibody to initiate complement activation
the classical pathway only
15
New cards
Which member of the complement system is not a part of the membrane attack complex?
C4
16
New cards
Which cells have antigen receptors that are highly specific and can distinguish between different strains of bacteria or viruses?
B and T Lymphocytes
17
New cards
Which molecules have a variable region and one or more constant regions?
T-cell receptors and immunoglobulins
18
New cards
Which of the following can bind to a T-cell receptor?
Peptides bound to MHC Molecules
19
New cards
The B-cell receptor is an ...
Immunoglobulin with transmembrane domains
20
New cards
In which lymphoid organ are B and T cells produced?
Bone Marrow
21
New cards
Which cells would be absent in a mouse that has no thymus?
T-cells
22
New cards
A B-cell culture that is derived from a single B-cell clone will produce...
One antibody that binds to one antigen
23
New cards
During B cell development, negative selection ...
eliminates B-cells that recognize self-antigens
24
New cards
What occurs if the T-cell receptors of a developing T cell cannot recognize self-MHC molecules?
The T-cells undergo apoptosis from a lack of positive selection
25
New cards
Which cells of the body express MHC Class 1 molecules?
All nucleated cells
26
New cards
Which cells of the of the body express MHC Class 2 molecules
Professional antigen presenting cells (dendritic cells, macrophages, B cells)
27
New cards
MHC Class 1 molecules present peptides from \______ the cell to \______ T-cells
inside , CD8
28
New cards
MHC Class 2 molecules present peptides from \______ the cell to \_____ T-cells
outside , CD4
29
New cards
Which cells of the adaptive immune system kill virus-infected cells?
CD8 T-cells
30
New cards
T-Cell receptors rely on the cytosolic domains of \_____ for signaling events
CD3 chains
31
New cards
Which type of cells produce antibodies?
B cells (plasma cells)
32
New cards
Variable regions on immunoglobulins/antibodies are found on \________
both heavy and light chains
33
New cards
Immunological memory consists of
both memory B cells and memory T cells
34
New cards
The genes activated in lymphocytes whose products are important in VDJ recombinase activity are
RAG genes
35
New cards
The process used by activated B cells to change the heavy chain sequence to produce different antibody types is called
Isotype switching
36
New cards
Proper T cells complete their development in the
Thymus
37
New cards
Which cells play an important role in activating genes required for thymocyte development and in their maturation?
Thymic epithelial cells
38
New cards
A thymocyte is called a double negative thymocyte because it is
not expressing CD4 or CD8
39
New cards
Positive and Negative selection results in
Single Positive T Cells
40
New cards
Positive selection promotes the selection of thymocytes that can...
bind to self-MHC molecules with moderate affinity
41
New cards
Negative selection of thymocytes
prevent the release of thymocytes that recognize MHC molecules with high affinity
42
New cards
Failure of negative selection of T cells can lead to
Autoimmune disorders
43
New cards
T-Cells that recognize antigen presented on MHC class I typically are
activated to fight off intracellular pathogens
44
New cards
Which cells play an important role in pathogen clearance by activating other cells during an adaptive immune response?
T Cells
45
New cards
MHC Diversity is generated by
gene families and are genetic polymorphisms
46
New cards
a T-cell that has CD4 as a co-receptor is a ...
helper T cell
47
New cards
which of the following is paried correctly?
CD4 T-cell and MHC Class II
48
New cards
which protein provides a necessary costimulatory activation signal to Naiive T cells?
CD28
49
New cards
Both MHC class I and MHC class II molecules posses promiscuous binding specificity; this type of binding allows a \__________ molecule to bind to a variety of \_______________
MHC ; peptides to present to cells
50
New cards
Peptides generated by the destructio of intracellular cytosolic proteins are presented via \_______ molecules, and peptides derived via phagocytosis and the destruction of the phagolysosome are typically presented via \_______ molecules
MHC Class I ; MHC Class II
51
New cards
All nucleated cells in the body express MHC Class I because they
have the propensity to become infected with a virus
52
New cards
Transporter associated with antigent processing (TAP) carries \________ peptides into the ER where they can interact with \________ molecules
proteasome derived ; MHC class I
53
New cards
MHC class II molecules assembled in the ER bind to \______, which blocks the peptide binding groove and prevents binding of proteasomal peptides.
the invariant chain
54
New cards
In which of the following cases would MHC heterozygosity be detrimental?
Tissue and organ transplants
55
New cards
The three cells types that present antigen to T cells in secondary lymphoid tissues are dendritic cells, macrophages, and .....
B cells
56
New cards
Phagocytes of the innate immune system engulf pathogens at the site of infection and transport them to \______, where antigen presentation occurs.
secondary lymphoid tissue
57
New cards
The most important type of cells in T-cell activation are
dendritic cells
58
New cards
After entering secondary lymphoid tissue, mature dendritic cells express the coreceptor \_____, which is required for costimulation of naive T-cells
B7
59
New cards
Cytotoxic T cells cause the death of infected cells via ....
induction of apoptosis through cytotoxins or expression of Fas ligand
60
New cards
Which statement about effector functions of immunoglobulins is false?
They can trigger T-cell activation through binding to the T-cell receptor
61
New cards
\_____ T cells that aid in the activation and differentiation of B cells and granulocytes
TH2 Helper
62
New cards
The \_______ region of an antibody plays an important role in binding to receptors of certain immune system cells, including macrophages, dendritic cells, and granulocytes such as mast cells.
Fc
63
New cards
what is required to induce a naive B cell to express soluble antibody?
Antigen binding and cell activation
64
New cards
B cells activated by antigen undergo clonal expansion, during which some of the B cells experience somatic hypermutation. This in turn leads to ...
affinity maturation
65
New cards
Loss of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) activity can limit immunoglobulin repertoire diversity as well as isotype expression, leading to \______ syndrome.
hyper IgM
66
New cards
The first isotypes expressed in Naive B cells are \_____ and \_______
Igm ; IgD
67
New cards
Which of the following is expressed in a soluble form as a pentameric molecule?
IgM
68
New cards
TI-1 antigens can induce a T-independent response by ....
binding to an immunoglobulin and a pattern recognition receptor on the B-cell surface
69
New cards
TI-2 antigens can induce a T-independent response by
binding to multiple immunoglobulin receptors, leading to B-cell clustering
70
New cards
The secondary adaptive immune response to pathogens is faster than the first adaptive immune response due to the presence of
memory cells
71
New cards
The English physician Edward Jenner developed a method of prevention known as vaccination. He discovered that innoculation of individuals with \_______ prevented the disease known as small pox.
cow pox
72
New cards
The Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines against SARS-CoV-2, the causitive agent of COVID-19, are \______ vaccines
mRNA
73
New cards
Vaccine strategies are designed to
induce a primary response by activating lymphocytes to fight a pathogen without actual infection by the pathogen
74
New cards
The protection of unvaccinated individuals due to a large percentage of the population being vaccinated is know as
Herd Immunity
75
New cards
The Polio vaccince recommended by the CDC in the United States is an Example of an \__________ vaccine and used due to accidental vaccine reversions in the other vaccine type
inactivated
76
New cards
The MMR vaccine is an example of a \______ vaccine
live attenuated
77
New cards
A vaccine that involves coupling a weak antigen with a stronger antigen is known as a \________ vaccine
conjugated
78
New cards
Recombinant vector vaccines involve
a harmless bacterium or virus that is used to express a pathogenic antigen
79
New cards
The incorporation of \_____ into vaccines helps to elicit an inflammatory response
adjuvants
80
New cards
Clinical trials are performed to measure
vaccine safety and effectiveness
81
New cards
Molecules that can specifically trigger a type I hypersensitivity response are known as
allergens
82
New cards
Delayed type reactions caused by the activation of T cells by a foreign , but harmless, antigen are called type \_____ hypersensitivity reactions
IV
83
New cards
Reactions that occur when immunoglobulins stimulate an unwanted response following immune complex formation are called type \________ hypersensitivity reactions
III
84
New cards
Activation of \____________ due to allergen recognition can be a nuisance or even life threatening
eosinophils, basophils and mast cells
85
New cards
\_______ occurs when a persons first exposure to an allergen elicits a primary adaptive response resulting in the activation of allergen-specific helper T cells.
Sensitizing Exposure
86
New cards
Which type of reaction occurs when a small amount of allergen is injected into the skin via an insect bite or sting or as part of testing to diagnose specific allergies?
Wheal and Flare
87
New cards
Skin contact with an allergen can cause all of the following except
rhinitis
88
New cards
A sensitivity to innocuous material driven by the action of IgM and IgG immunoglobulins that recognize chemically active cell-surface molecules, and induce the targeting of cells that are mistakenly identified as foreign is known as
Type II hypersensitivity
89
New cards
IgG can serve as a trigger for antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, a mechanism by which an antibody induces destruction of the tagged cell through the action of
NK cells
90
New cards
Hemolytic disease of the newborn is often due to a mismatch of
Rh factors
91
New cards
Testing for tuberculosis in the US is dependent on whihc type of hypersensitivity reaction?
Type IV Hypersensitivity
92
New cards
Donors for tissue transplants can be
aoive or dead
93
New cards
Bone marrow transplants are primarily used to treat
leukemias
94
New cards
Hyperacute rejection of a transplant is due to
previously existing antibodies
95
New cards
Common anti-rejection medicines used by transplant recipients include:
Steroids
96
New cards
Identify 5 different physical or chemical barriers involved in innate immunity
Skin, mucosal membrane, stomach acid, vaginal pH, lysozymeW
97
New cards
What are the three complement pathways and what are the two outcomes they provide?
Pathways: alternative, lectin, classical
Outcomes: tag pathogens for phagocytosis, kill pathogens by forming holes in their cell membranes
Outcomes: tag pathogens for phagocytosis, kill pathogens by forming holes in their cell membranes
98
New cards
Draw an immunoglobulin. Identify 3 different protective actions an antibody provides.
neutralization of soluble particle/pathogen, opsonization, complement activation
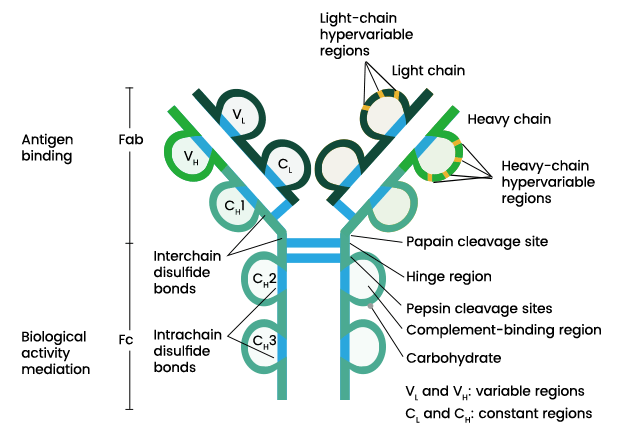
99
New cards
Describe how self-tolerance is developed through the interaction of T-cell receptors and MHC molecules. What are the 3 possible outcomes?
Self-tolerance is developed through the interaction of T-cell receptors and MHC molecules by negative selection. During development in the thymus, T-cells whose receptors bind too tightly to a self-MHC-peptide complex, or do not bind at all, are killed. Only T-cells who bind moderately to the self-MHC-peptide complex are allowed to survive.
Outcomes: binds too tightly=death, does not bind at all=death, binds moderately=survives
Outcomes: binds too tightly=death, does not bind at all=death, binds moderately=survives
100
New cards
What are the 5 different immunoglobulin isotypes?
IgM, IgG, IgE, IgD, IgA