Lab Book Exercise 24 - Activities
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
---Activity 1: The Optic Disc---
In activity 1, you will perform several visual tests and experiments focusing on what?
physiology of vision
The optic disc test involves demonstrating what?
the blind spot (optic disc), the site where the optic nerve exits the eyeball
What is the name of the optic nerve test (Activity 1)?
Demonstrating the Blindspot
What is the name of this blind spot test figure used to find your blindspot?
Biuret test
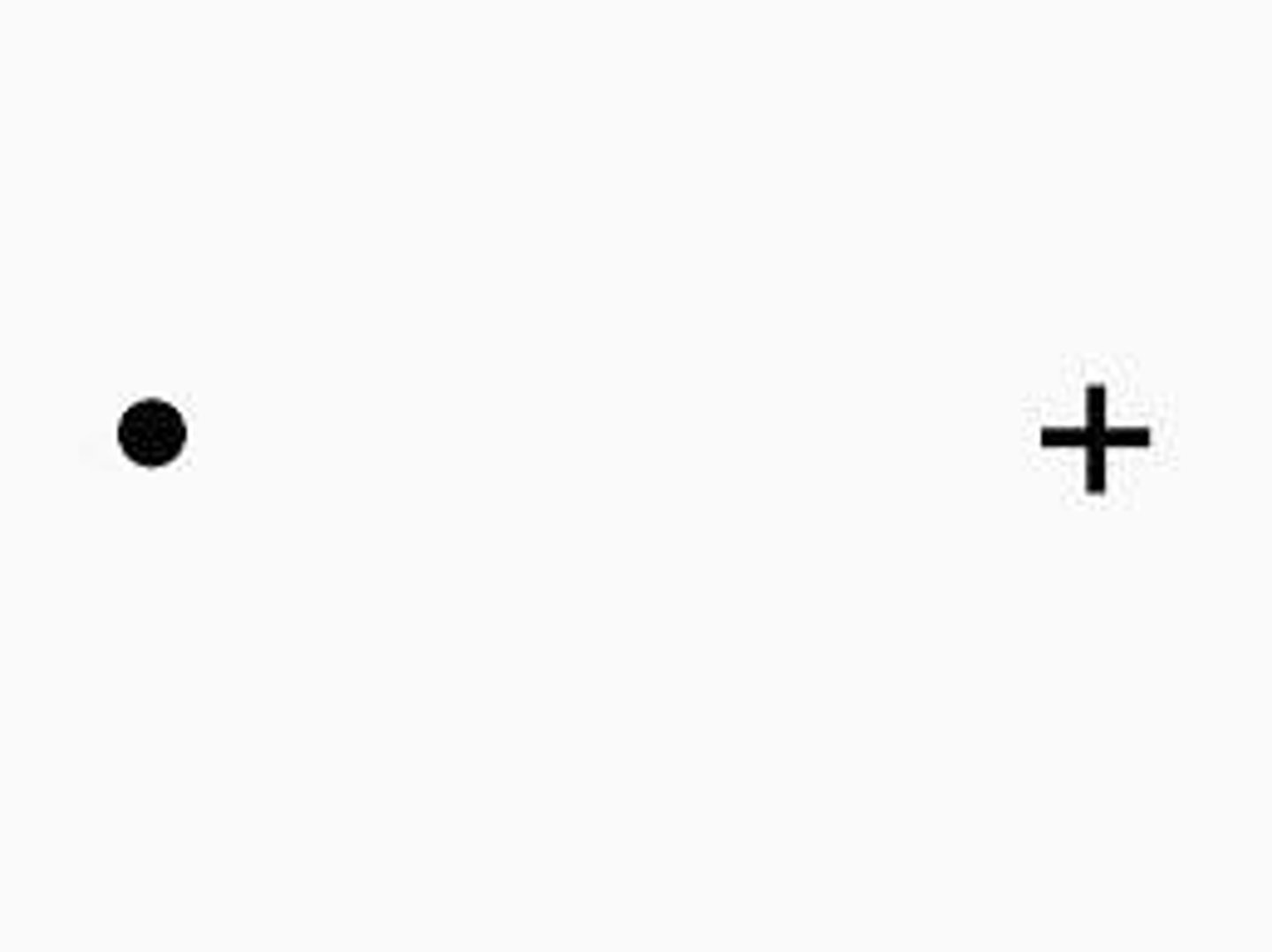
How do you test your blindspot?
Hold the blind spot test figure about 18 inches from your eye. Close your left eye and focus your right eye on the x which should be directly in line with your right eye (open eye). Keep your right eye (open eye) focused on the x and move the figure slightly towards your face. When the dot focuses on the blindspot, it will disappear. Repeat on other eye switching x to dot.
What is the blind spot (optic disc test) measuring/results?
Distance at which the dot disappears in inches.
---Activity 2: Refraction, Visual Activity, and Astigmatism---
Refraction
When light rays pass from one medium to another, their speed changes and the rays are bent
Light rays in the visual field are refracted as they encounter what?
cornea, aqueous humor, lens, and vitreous humor of the eyes.
Refractive index "bending power" is
constant
When is the refractive index not constant?
When it is varied by changing the lens shape
The greater the lens convexity or bulge
The more light will be bent
The less convex the lens (flatter it is)
the less light will be bent
Light from a distant source (6m or 20ft) approaches the light as what type of rays
parallel
Is change made when parallel rays approach the eye from a distant source?
nope, no change in lens convexity is necessary for it to focus properly on the retina
Light from a close source tends to do what?
diverge and convexity of the lens must increase to make close vision possible
Accommodation
the ability of the eye to focus differently for objects of close vision (less than 6m or 20ft)
emmetropic eye
normal eye
astigmatism
irregular curvature of cornea or lens leading to a blurred vision problem
presbyopia
impairment of vision as a result of old age
How can you test lens elasticity?
Measuring near point of vision
Near point of vision is about how many cm away from the eye in young adults?
10
The near point of vision is ____ in children and ____ in old age
closer in children and farther in old age
myopic eye
eyeball too long, causes nearsightedness. focal point in front of the retina
How to correct myopia (nearsightedness)?
concave lens
hyperopic eye
eyeball too short, causes farsightedness. focal point behind the retina
how to correct hyperopia (farsightedness)?
convex lens
What is the name of Activity 2 about refraction?
Determining Near Point of Vision
How do you determine Near point of vision?
hold a common straight pin at arms length in front of ones eye. Slowly move the image away until it becomes distorted.
What is near point of vision measuring / results
distance in cm from your eye to the pin at the point it becomes distorted
---Activity 3: Visual Acuity---
visual acuity
sharpness of vision
What type of test do you use to measure visual acuity?
Snellen eye chart
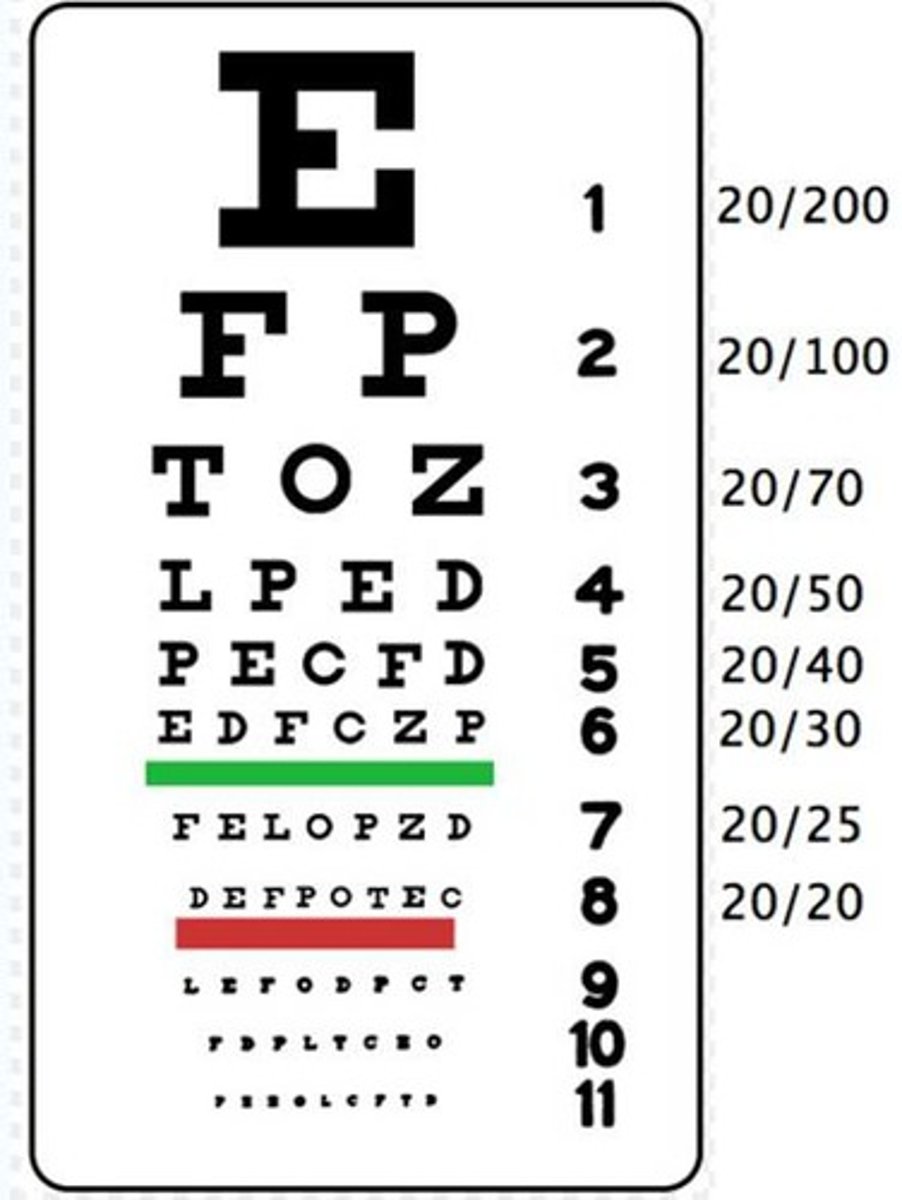
What should happen when you read the snellen eye chart with normal vision?
letters of a certain size should be clear
What is the name of exercise 3 visual activity?
Testing Visual Acuity
How do you test visual acuity?
have someone stand 20 feet away from the posted snellen eye chart and cover one eye with a card or hand. As the person reads each consecutive line out loud check for accuracy. If they wear glasses do the test twice once with glasses and then one without. Do not remove contacts but note if they were in during the test.
What does the visual acuity measure?
Refers to the clarity of vision—measure of a person's ability to discern small details, with precision, at a given distance.
What does 20/20 vision mean?
normal vision
What does 20/40 or any ratio less than one mean for visual acuity?
he/she has less than normal visual acuity
What does a 20/15 mean in Snellen eye chart?
vision is better than normal, because this person can stand at 6m (20 ft) from the chart and read letters that are discernable by the normal eye only at 15 ft.
What is the second activity called that is the second half to visual acuity?
Testing for Astigmatism
what figure do you use to test for astigmatism
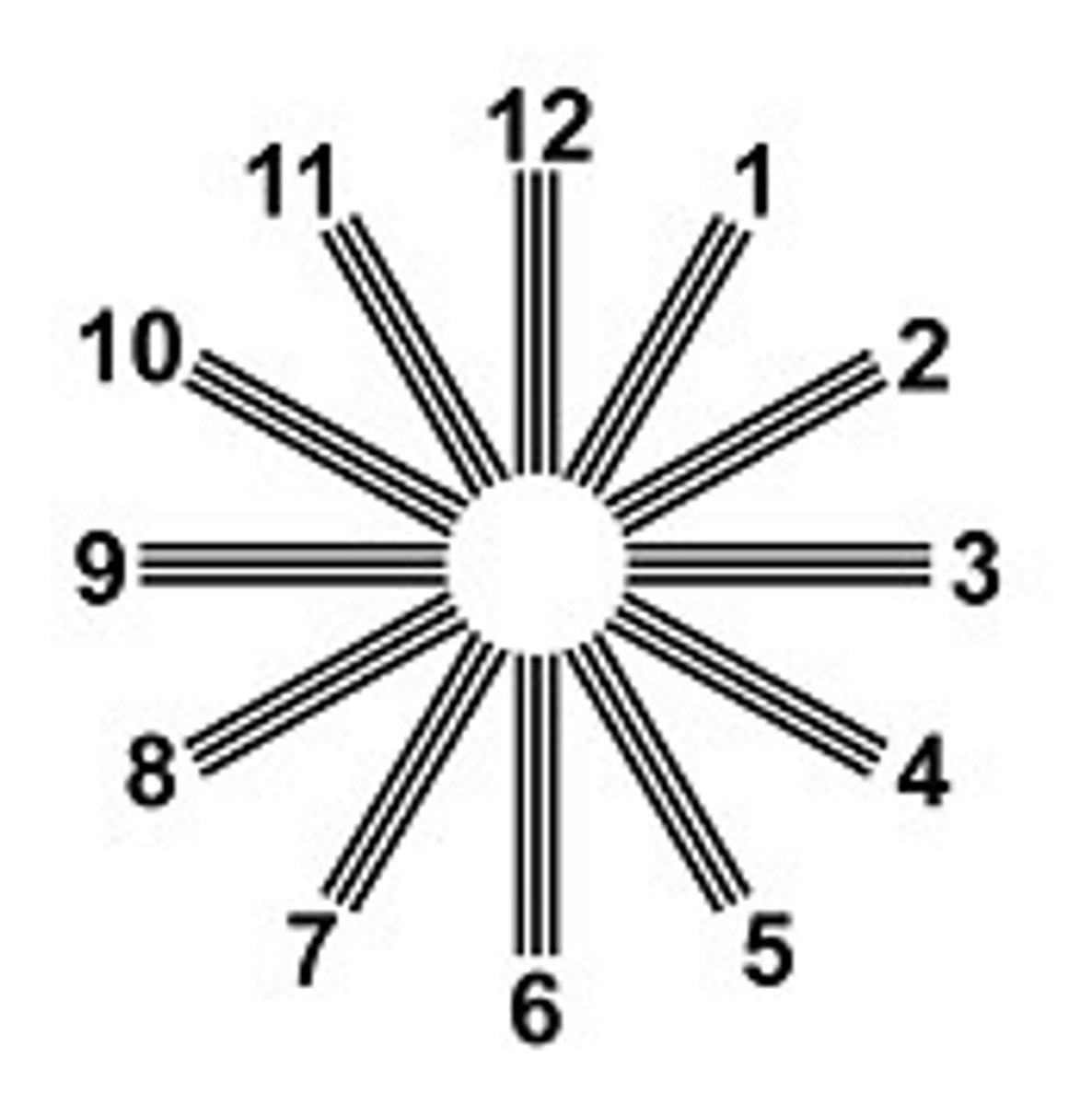
what is the process of testing for astigmatism/results?
view the chart from 20ft away with one eye then with the other focusing on the center of the chart. If the radiating lines appear equally dark and distinct then there is no distortion, if some lines are blurred or less dark then there is some degree of astigmatism present
what are you testing during astigmatism
unequal curvatures of the lens and/or cornea
---Activity 5: Colorblindness---
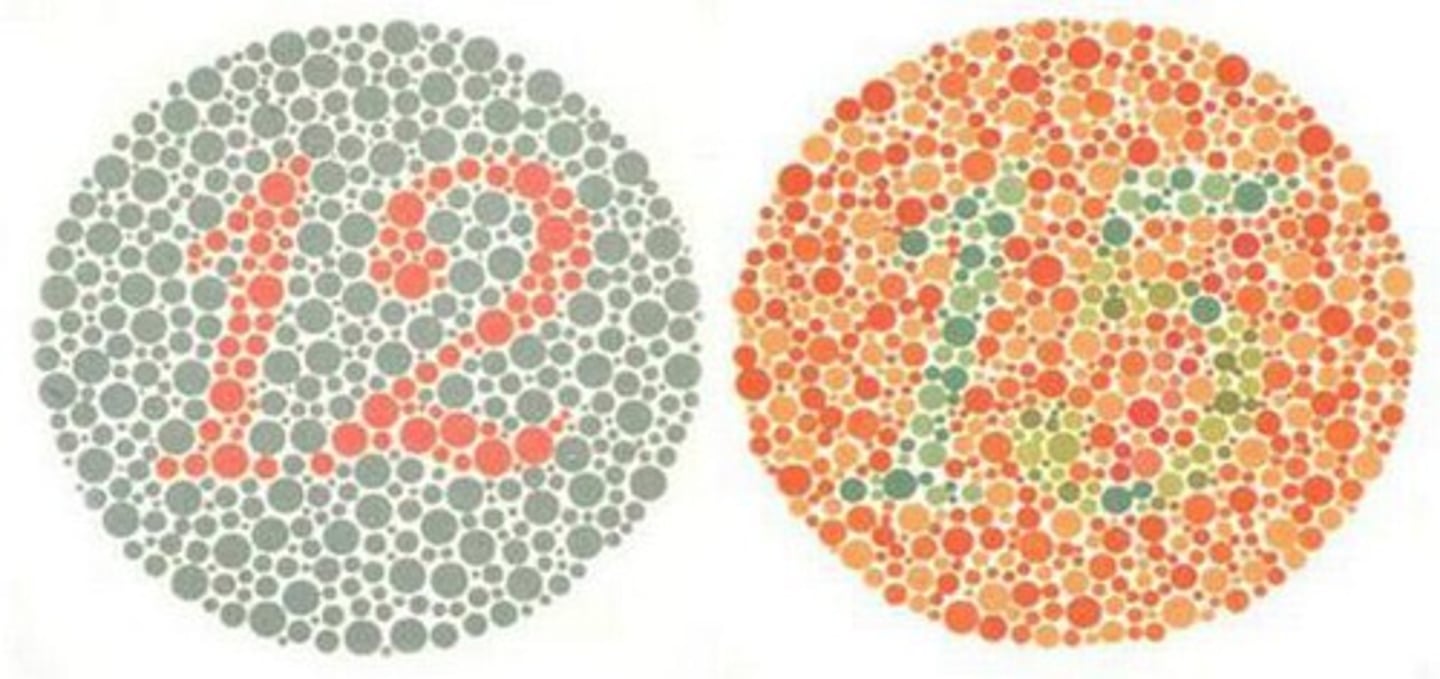
How do you test for colorblindness
Ishihara's color plates
There are three cone types each containing a different light-absorbing pigment, what are they?
red wavelengths, blue wavelengths, and green wavelengths
overlapping input from more than one cone type leads to what?
brain interprets the intermediate colors of the visible light spectrum
how to test for colorblindness
view the color plates in bright light or sunlight while holding them 30 inches away at right angles to your line of vision then report what you see on each plate. Take no more than 3 seconds for each number
---Activity 6: Binocular Vision---
humans visual fields are how many degrees
170
depth perception/three-dimensional vision
the primary visual cortex fuses slightly different images
eyes in the front
like to hunt
Eyes to the side
like to hide
What is the name of activity 6 that test for binocular vision?
Testing for depth perception
how do you test for depth perception?
to demonstrate the importance of binocular vision, have someone hold a lab test tube in front of you about arms length away. with both eye open quickly insert the pencil into the test tube. Remove the pencil and bring it back towards your body. Close one eye and do the same thing but do not feel for the test tube. Repeat with the other eye.
what does depth perception measure
Binocularity and how well the eyes work together/ if it was as easy to dunk the pencil with eyes closed as with both eyes open
---Activity 7: Eye Reflexes---
what is necessary for proper eye functioning
intrinsic (internal) and extrinsic (external) muscles
The intrinsic muscles are controlled by what
autonomic nervous system
Exterinsic eye muscles
rectus and oblique muscles which are attached to the eyeball exterior
convergence
medial eye movements which is essential for near vision responsible of the exterinsic eye muscles
what happens when convergence occurs
both eye are directed toward the near object viewed
the extrinsic eye muscles are controlled by what
somatic nervous system
what is the name of activity 7 which tests eye reflexes
demonstrating reflex activity of intrinsic and extrinsic eye muscles
Involuntary activity of both the intrinsic and extrinsic muscle types is brought about by three Flix actions that can be observed in the following experiments. What are they?
pulpillary light reflex, accommodation pupillary reflex, and convergence reflex
pupillary light reflex
protective response of pupil constriction when a bright light is flashed in the eye to prevent damage to the photoreceptor cells
how to test for pupillary light reflex
turn on the light and position it so that it shines in your partners right hand. After one minute ask your partner to remove the hand covering the eye and observe the pupil of the eye
What happens to the pupil in bright light?
constricts
what happens to the pupil in dark light
it gets bigger
During the accommodation pupillary reflex (staring one min at distant object - printed material held at partners face - observe pupils), how does the pupil size change as your partner focuses on the printed material?
smaller at first
Explain the value of this reflex
This reduces divergent light rays and aids in formation of sharper image. It also restricts amt. of light entering eye.
During the convergence reflex experiment (same experiment but with pen this time), note the position of your partner's eyeballs while he or she gazes at the distant object, and then at the close object. Do they change position as the object of focus is changed?
Eyes move medially. In what way? This reflex keeps image focused on fovea.