Photosynthesis
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Light Dependent Reaction
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What pigments do they thylakoids contain in photosynthesis?
Chrolorplasts
What do different pigments absorb within thylakoids?
Different wavelengths of light
What do more pigments available in leaf mean?
More light absorbed available for photosynthesis
What is the name of the pigments that surround chloroplasts?
Accessory pigments
What is chlorophyll + acessory pigments called?
Light Harvesting clusters
What is the name given to the arrangement of acessory and primary pigments to gather and use light energy?
Photosystem
Why do leaves appear green?
Red and Blue light can be absorbed but Green light is relected
What is a limiting factor?
A factor that will limit the rate of a reaction when it is at a suboptimal level.
What 3 factors limit photosynthesis?
Light Intensity
Co2 concentration
Temperature
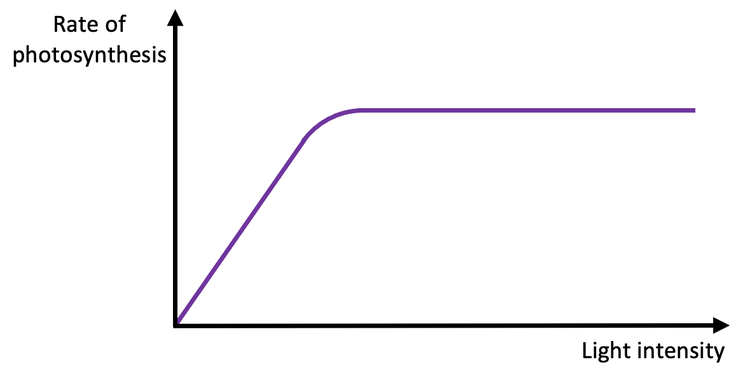
What do light intensity and co2 concentration graphs look like
Plateu is another factor becomes limiting
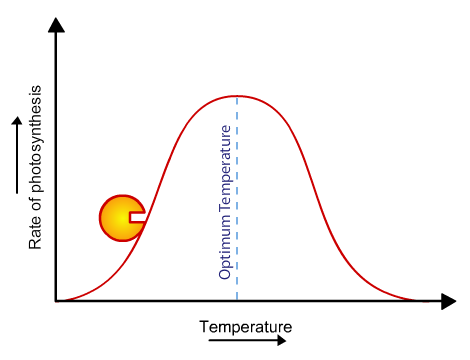
What does temperature graph look like?
How can limiting factors be overcome? X3
Artifical lighting
Co2 Waste
Greenhouses kept as specific temperatures
Why is temperature limiting?
Denatures the enzymes
What is the 1st stage of photosynthesis called?
Light dependent reaction
What does the light independent reaction (2nd) still rely on?
Products from light dependent reaction
Where does the light dependet reaction take place?
Thylakoid membrane
Where is the thylakoid membrane?
Between thylakoid space and stroma
What is the name of the enzyme needed to produce ATP?
ATP synthase
What is the reaction to form ATP?
ADP + Pi ——> ATP
Where does the energy come from to catalyse ADP?
Protons (H+ Ions)
Is there a higher concentration of H+ ions in the Stroma or Thylakoid Space? what does this mean
Thylakoid space making a conc gradient alllowing H+ ions to move acorss
What is the a higher concentration of H+ ions in the Thylakoid Space called?
Proton Gradient
Where does H+ move from thylakoid space the stoma by?
ATP Synthase
What is does H+ move from thylakoid space the stoma know as?
Chemiosmosis
What is H+ giving energy for ADP synthase to catalyse to ATP known as?
Photo phosphorylation
How is the Proton Gradient maintained?
Protons are actively transported from stroma to thylakoid space
How is energy provided to maintain proton gradient?
Redox reaction
How do you rememebr Redox reaction?
Oxidation
Is
Loss
Reduction
Is
Gain
Where are electrons provided by and how?
Chlorophyll absorbs light which exites 2 electrons
When electrons are excited from the chlorophyll where do they go?
Leave the chlorophll leaving it oxidised
What is the process of light oxidisng chlorophyll known as?
Photoionisation
What passes electrons along the membrane?
Electron transfer chain
How are electrons moved along the Electron transfer chain?
Oxidation Reduction Reactions
What would happen if protons werent actviely tansports back to thylakoid ,enbrane?
No gradient so no ATP Synthase so no ATP
What type of molecule is NADP?
Coenzyme
When electrons reach the final stage in the electron transfer chain what reacts with them to move them so more electrons can be passed?
NADP
What is NADP reduction reaction
NADP + H+ → Reduced NADP (NADPH)
What 2 molecules are made in light dependent reaction needed for light independenct reactio?
ATP
Reduced NADP
What do the electrons lost by photoionisation need to do?
Be replaced
How are electrons replaced in chlorophyll?
Photolysis
What is photolysis?
When electrons are lost during photoionisation they are replaced by water
What does light split the water into in photolysis?
Protons
Electrons
Oxygen
What is oxygen used replaced in photolysis used for?
Diffuse out of the plant
Used in respiration
What are protons replaced in chlorophyll used for?
Maintain a high concentration in the thylakoid space
What are the electrons from photolysis used for
Replace those lost in chlorophyll
How many photosystems does the thylakoid membrane have?
2
What is excited electrons in PSI used for?
Transferred along electrons transfer chain and used for channel protein to actively transport a proton
Where does electrons from PSI go after providing energy for active transport?
Back to chlorophyll to be excited again and repeat the process
What is PSI an example of?
Cyclic photophosphorylation
Why does the plant have PSI if it doesnt create NADP or ATP?
Absorbs different wavelengths of light
Useful when there is enough ATP for light independent but not enough NADP as other reactions can occur
What is PSII an example of?
Non Cyclic photophosphorylation
How is the chloroplast well adapted for photosynthesis?
Large SA
Proteins in the grana hold the chlorophyll so the max amoutn of light can be absorbed at one time
Thylakoid contrains ATP for productions and the membrane is selectively permeable
Contain both DNA and Ribosomes
Why is a Large SA important for chloroplasts in photosynthesis?
Maximises the amount of ATP and NADPH that can be made at once
Why is a Proteins in the grana hold the chlorophyll important for chloroplasts in photosynthesis?
Maximum amount of light is able to be absorbed at one time
Why is Thylakoid membrane being selectively permeable improtnat?
Allows them to establish and maintain a proton gradient
Why is chloroplast contain both DNA and Ribosomes improtant?
Protins in light dependent reaction can be easily and quickly produces