Chemistry IGCSE - Metals
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Characteristics of metals
High MP/BP
Malleable
Ductile
Good conductor
Chemical reactions with metals + dilute acids
Metal + acid → salt + hydrogen gas
Chemical reactions with metals + cold water
Only very reactive metals form metal hydroxide + hydrogen
Chemical reactions with metals + steam
Less reactive metals form metal oxide + hydrogen
Uses of aluminium
manufacture of aircrafts → low density
manufacture of overhead cables → low density + good electrical conductivity
food containers → resistance to corrosion
Uses of cooper
electrical wiring → good electrical conductivity
Alloy
mixture of metals with 1 or more elements
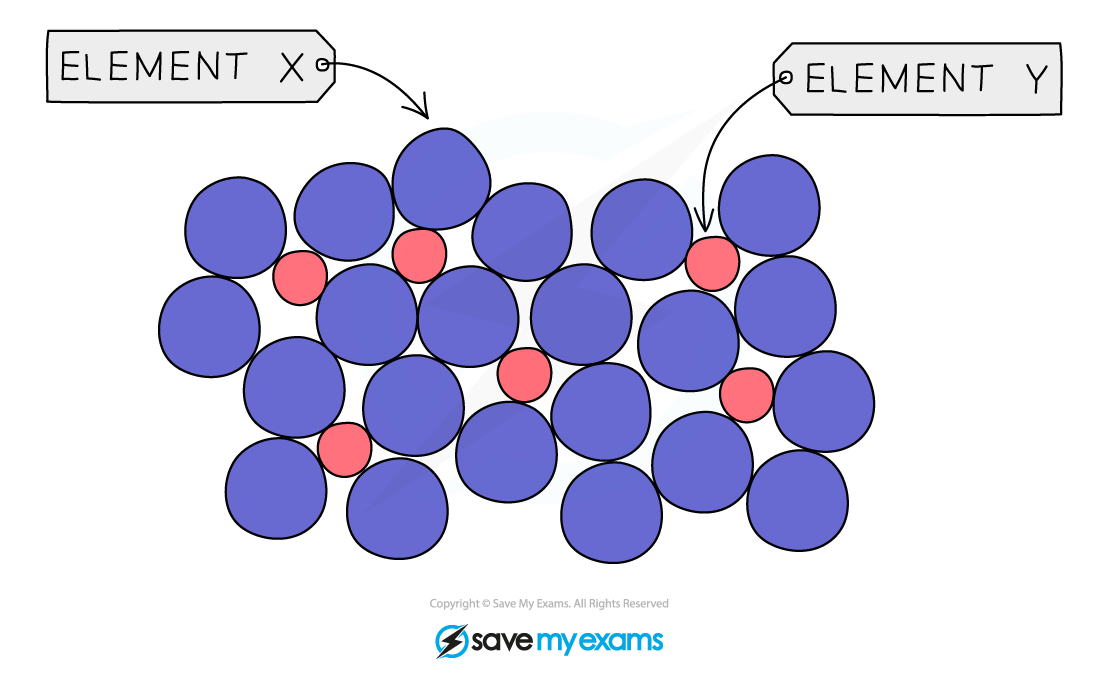
Common examples of alloys
Brass → mixture of copper + zinc
Stainless steel → mixture of iron + chromium + nickel + carbon
Alloys can be harder + stronger than pure metals → alloys more useful
Why stainless steel is used for cutlery
Hard + resistant to corroding → suitable for frequent use + washing
Why are alloys stronger in terms of structure
Alloys contain different sized atoms → distort regular layers in metal structure → layers can’t slide over each other easily → makes alloys stronger + harder
Order of reactivity
Reaction from potassium, sodium + calcium with cold water
react vigorously → produce metal hydroxide + hydrogen gas
Reaction from magnesium and steam
form magnesium oxide + hydrogen gas
Reaction from magnesium, iron, zinc, copper, silver + gold with dilute hydrochloric acid
Magnesium, zinc, iron react → form salt + hydrogen gas
Copper, silver, gold do not react → below hydrogen in reactivity series
Why some metals don’t react with acid or water
Metals below hydrogen in reactivity series → cannot displace hydrogen → no reaction
Displacement reaction in metals
more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal
Order of reactivity
Magnesium > Zinc > Iron > Copper > Silver
More reactive = more likely to form positive ions
Reaction from zinc in copper(II) sulfate solution
Zinc displaces copper → forms zinc sulfate + copper metal
Zn + CuSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Cu
Why some metals rom ions more easily than others
More reactive metals lose electrons more easily → form positive ions faster
Conditions needed for rusting of iron
Oxygen
Water
Barrier methods against rusting
Painting
Greasing
Coating with plastic
How barrier methods prevent rusting
Prevent oxygen + water from reaching iron surface
Galvanising
Coating iron or steel with zinc
How does galvanising prevent rusting
Zinc acts as a barrier → provides sacrificial protection
What is sacrificial protection
more reactive metal → losses electrons more easily → corrodes instead of iron → since it loses electrons more easily
How position of metal in reactivity series affect its extraction
Metals higher in reactivity series = harder to extract + usually require electrolysis
less reactive metals → extracted by chemical reduction
Iron hematite is extracted by reduction of iron in a blast furnace
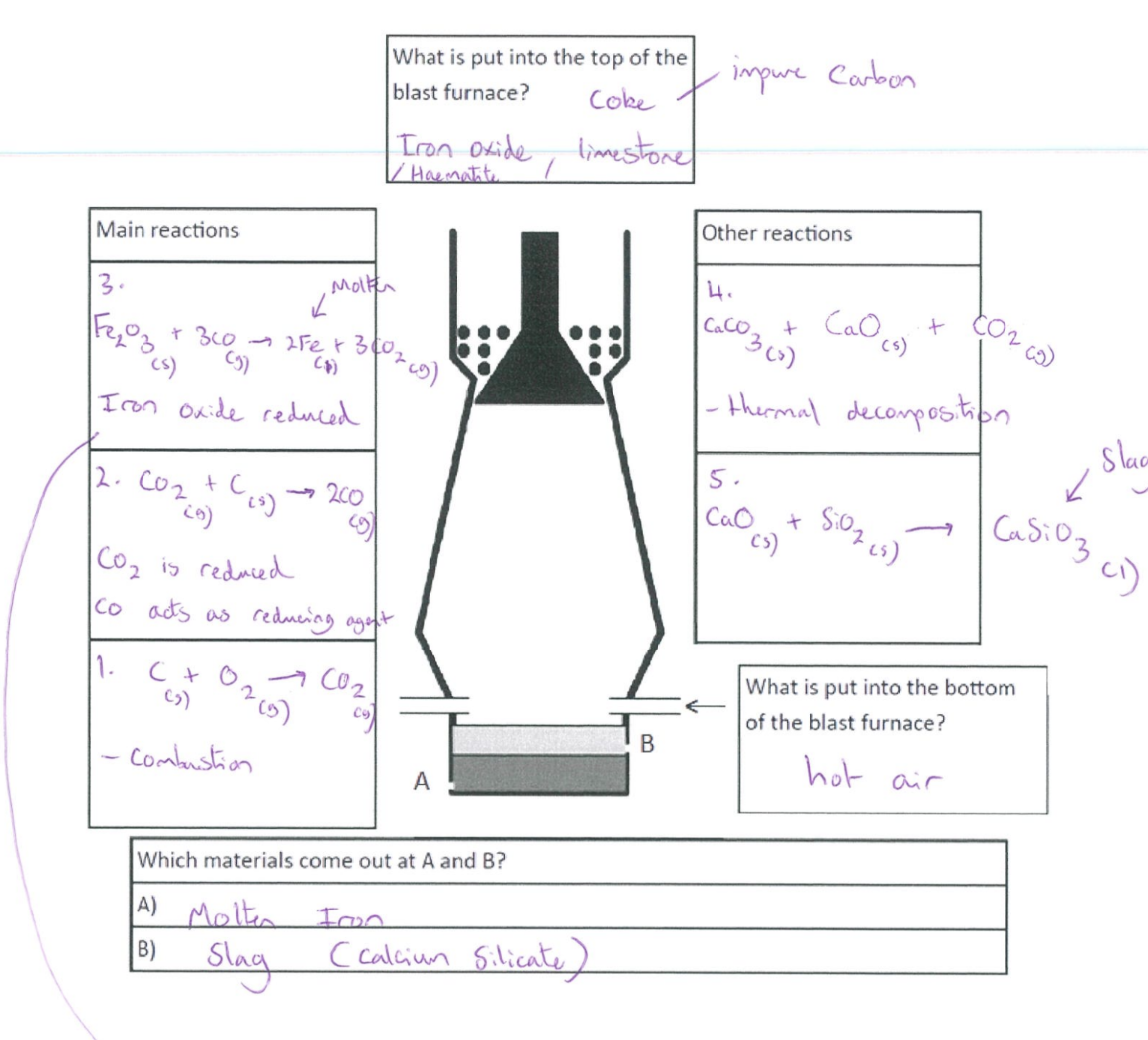
Blast furnace
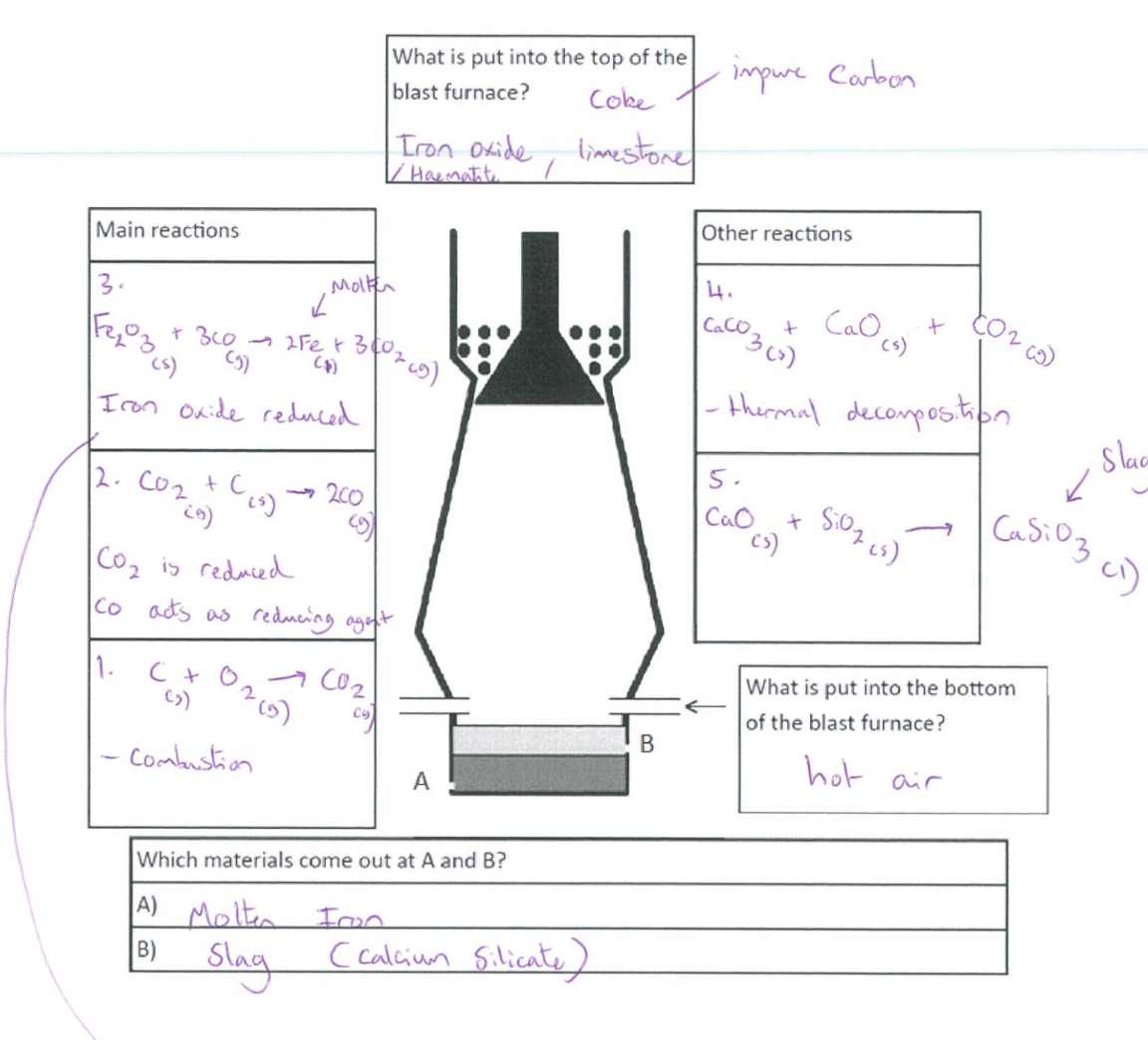
Burning of carbon (coke) → provide heat → produce carbon dioxide
C + O₂ → CO₂
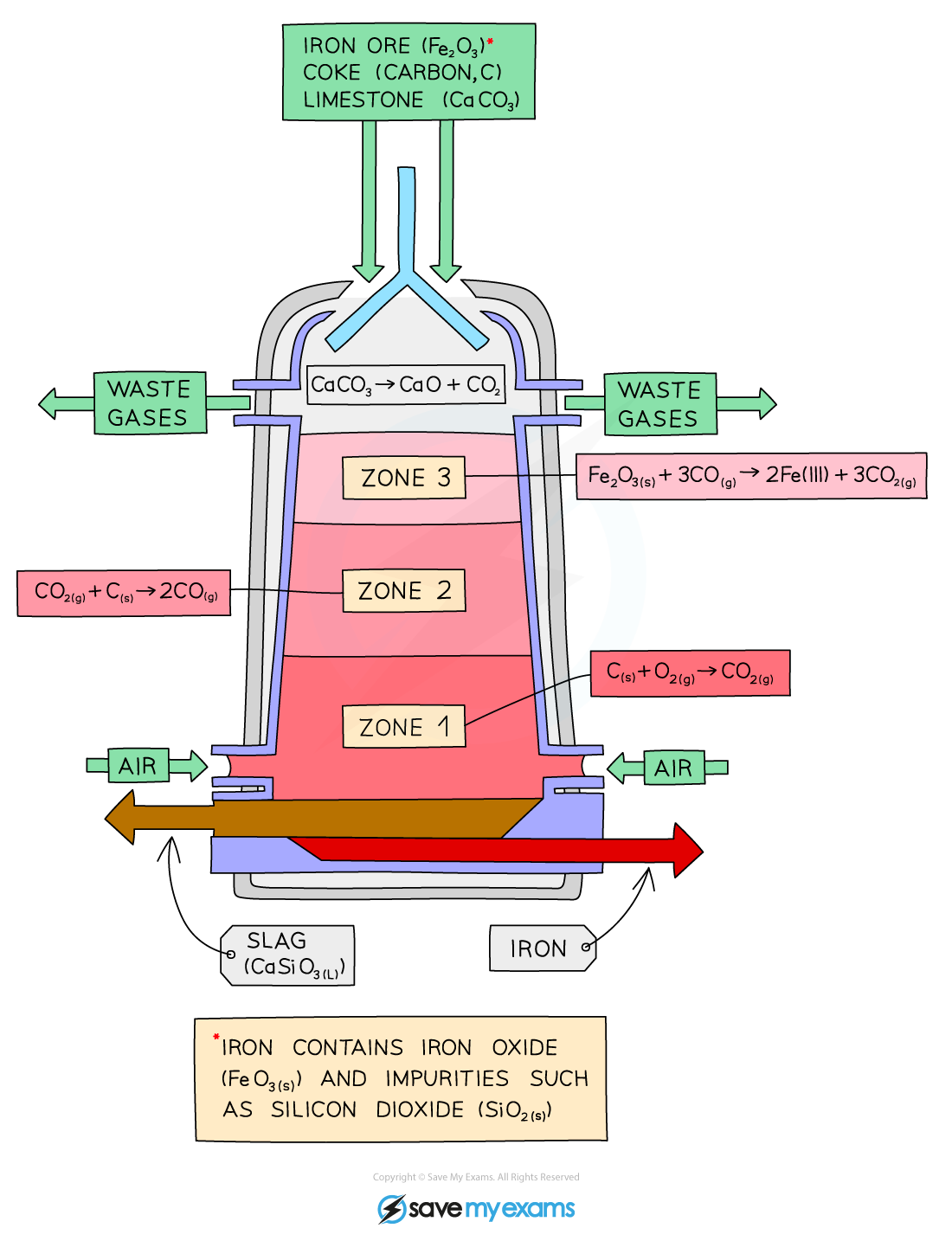
Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide
C + CO₂ → 2CO
Reduction of iron (III) oxide by carbon monoxide
Fe₂O₃ + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO₂
Thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate/limestone → produce calcium oxide
CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
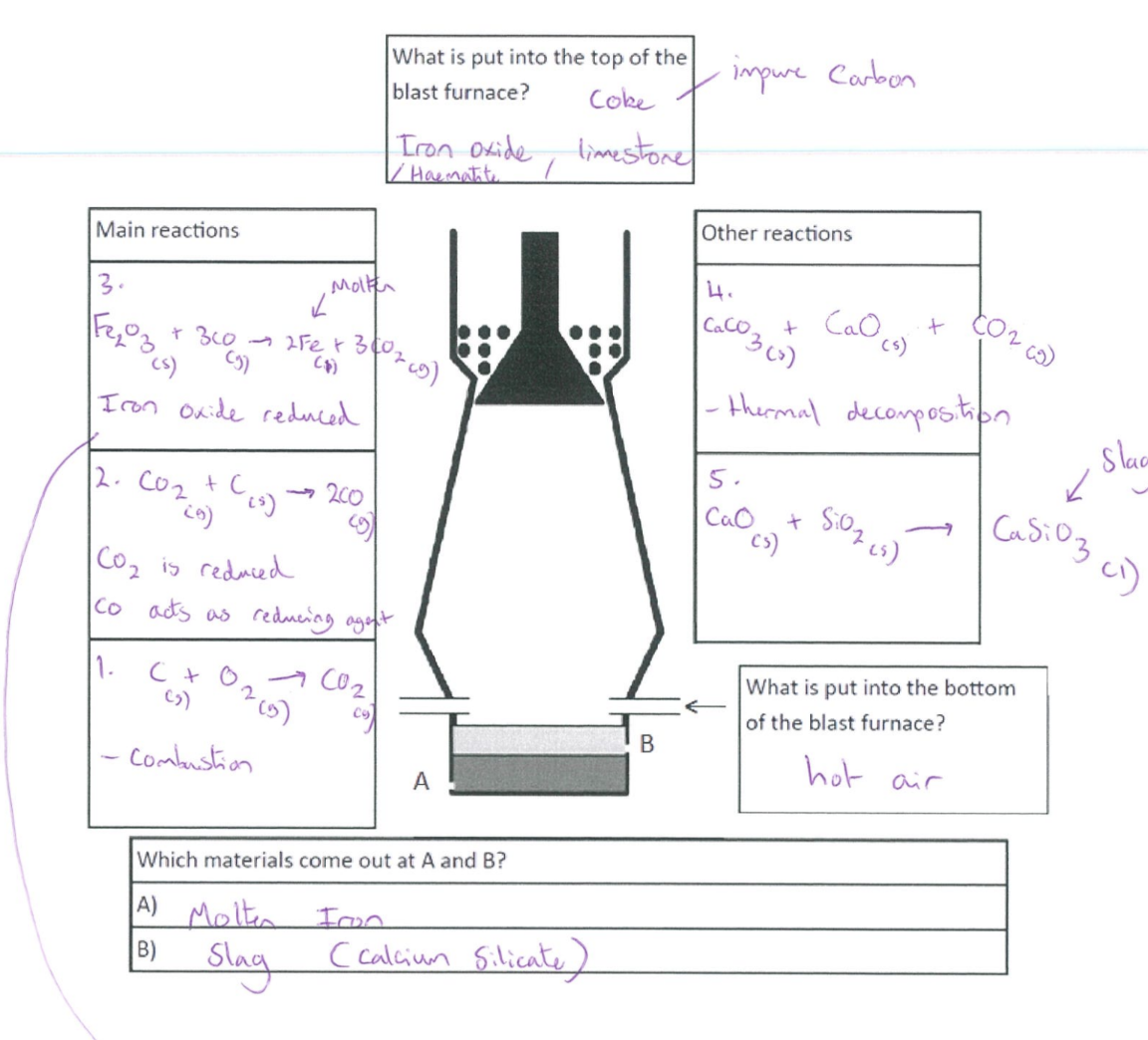
Formation of slag
CaO + SiO₂ → CaSiO₃