Pre-analytical Considerations in Phlebotomy
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Physiological Variables
Factors affecting laboratory test results.
Vascular Access Sites
Locations for blood collection or device placement.
Complications in Blood Collection
Issues arising during blood draw procedures.
Specimen Quality
Integrity of samples for accurate testing.
Procedural Error Risks
Potential mistakes during blood collection.
Failure to Draw Blood
Inability to obtain a blood sample.
Age Effect on RBC Count
Higher in younger patients.
Altitude Effect on Hemoglobin
Elevated levels at higher altitudes.
Dehydration Effect on RBC Count
Elevated due to reduced plasma volume.
High Protein Diet
Elevates non-protein nitrogen compounds.
Caffeine Impact
Increases cortisol and ACTH levels.
Diurnal Variation
Fluctuations in test results based on time.
Chemotherapy Drugs
Decrease blood cell counts.
Inappropriate Venipuncture Sites
Locations to avoid for blood draws.
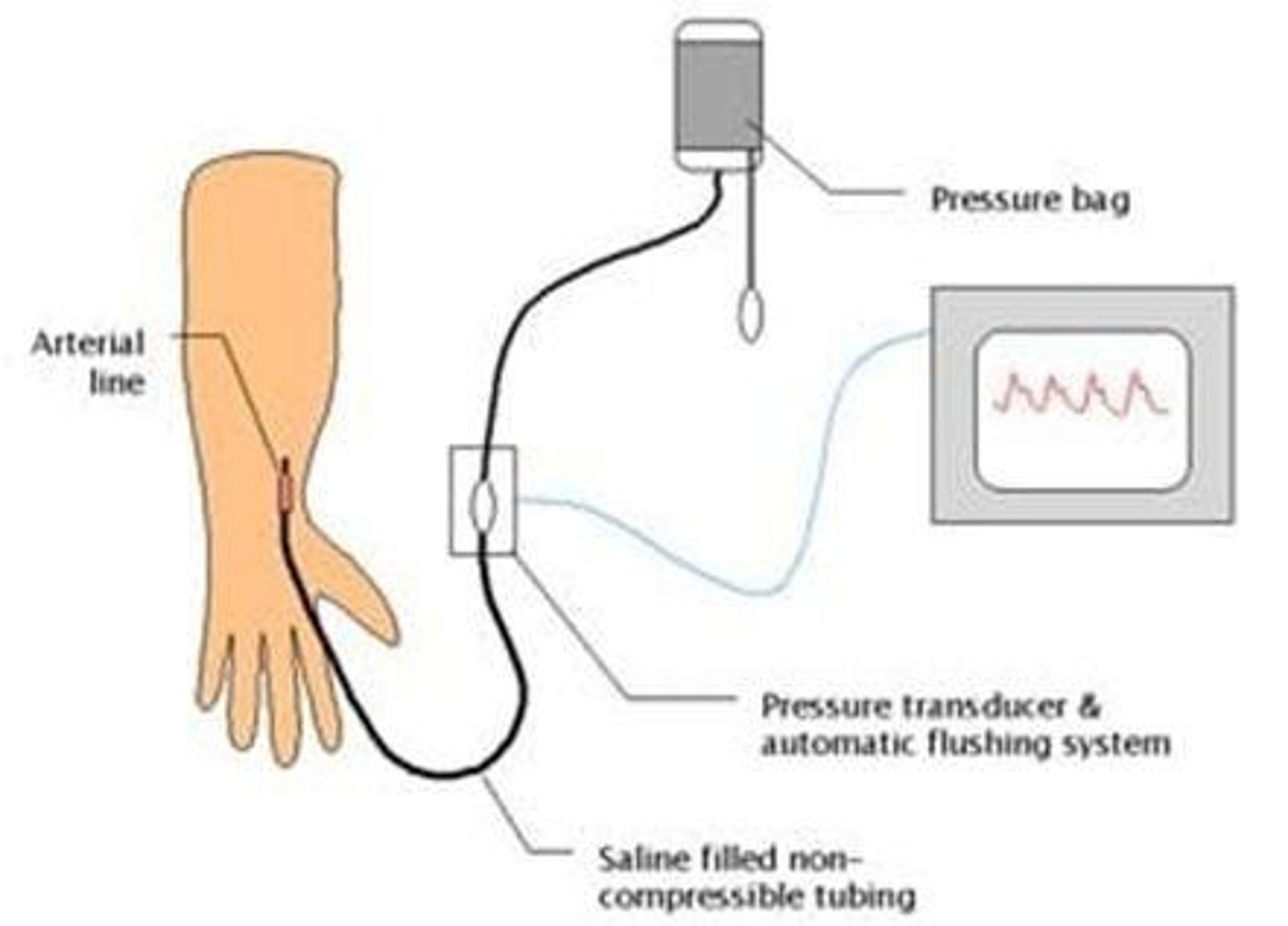
Arterial Line
Catheter for continuous blood pressure monitoring.
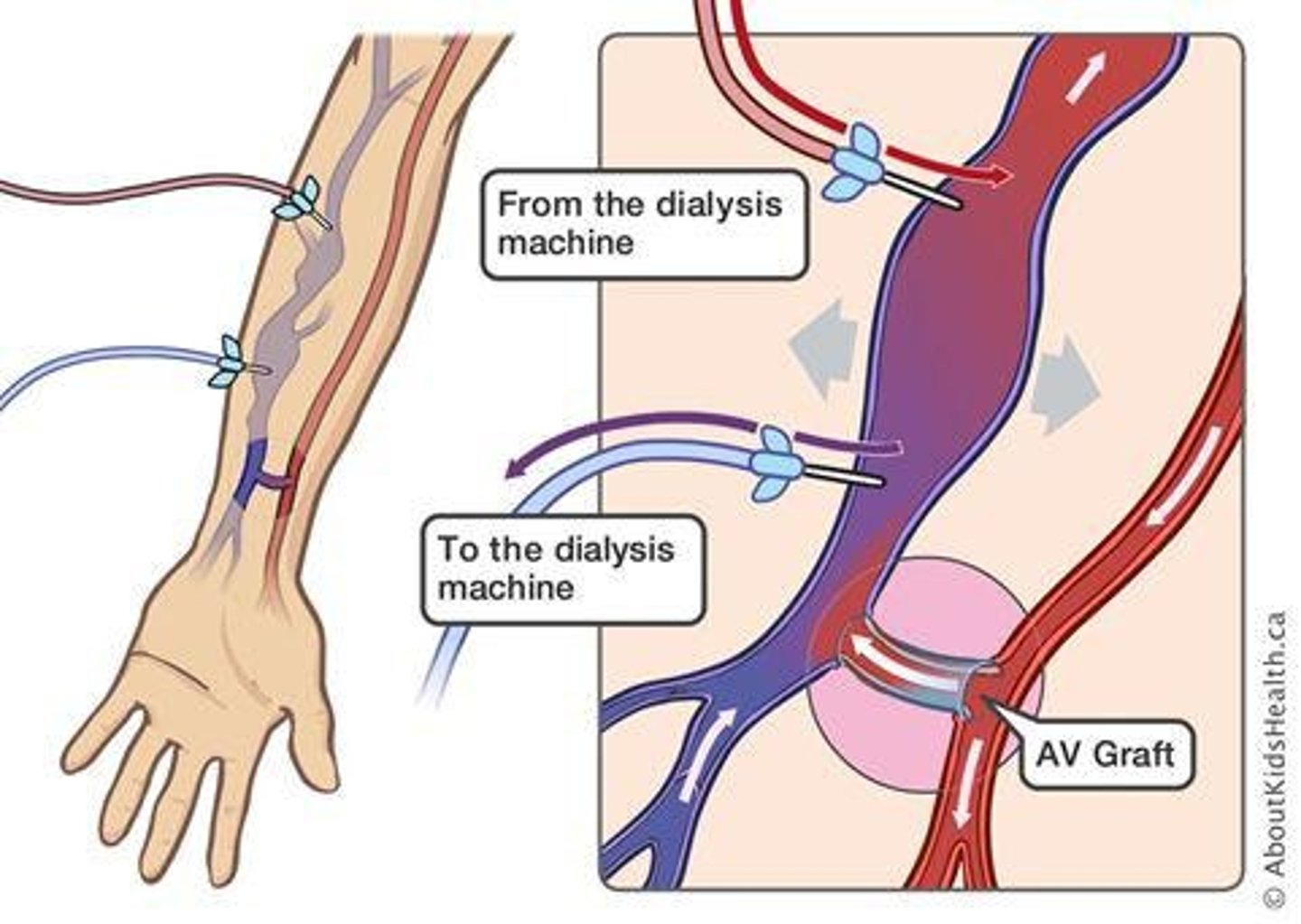
Arteriovenous Shunt
Surgical connection for dialysis access.
Blood Sampling Device
Needleless device minimizing infection risk.
Heparin Lock
Access for medication or blood drawing.
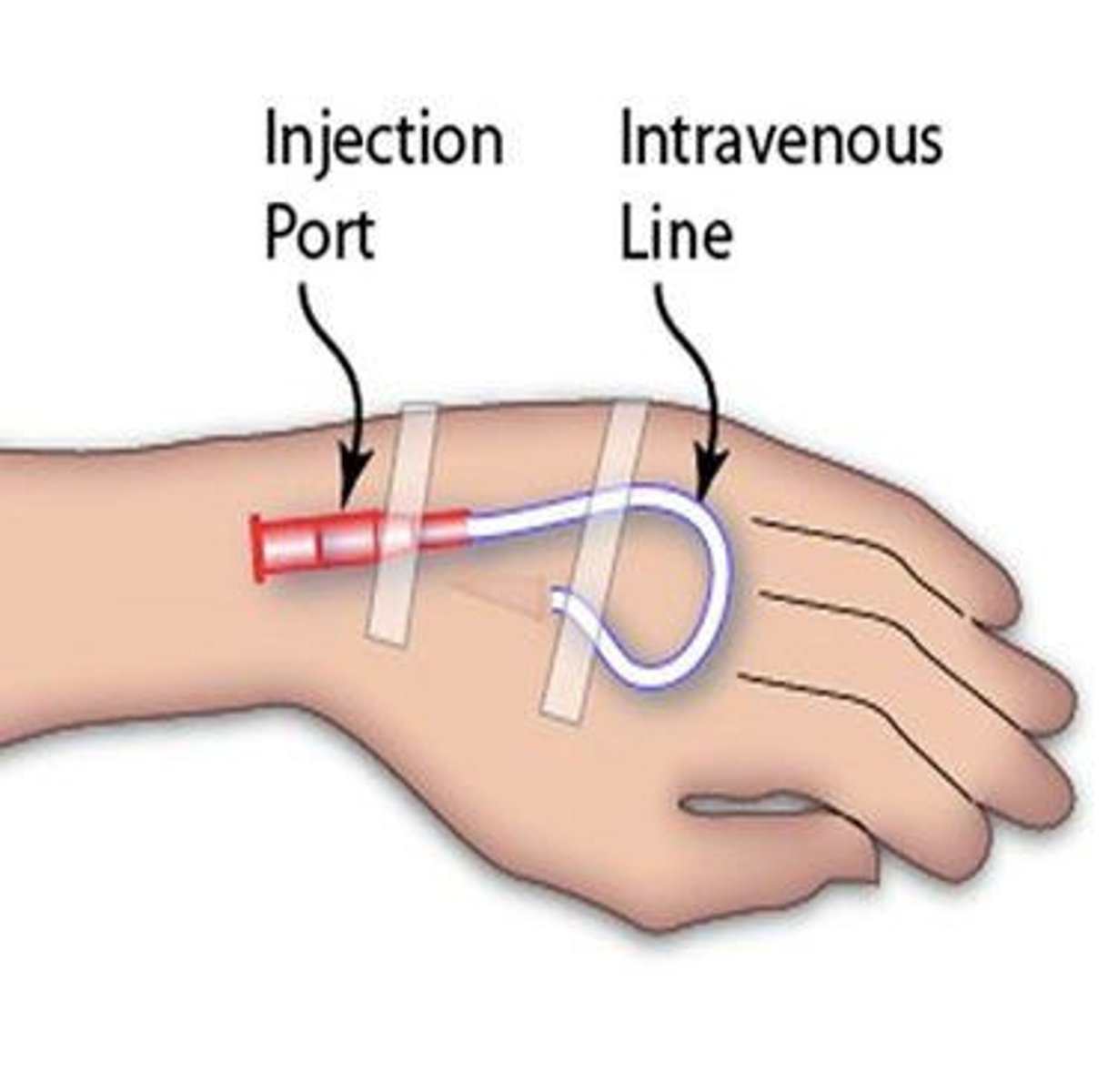
Intravenous Sites
Used for fluid administration, not blood sampling.
Hematoma
Swelling from blood leakage at puncture site.

Iatrogenic Anemia
Anemia resulting from medical treatment.
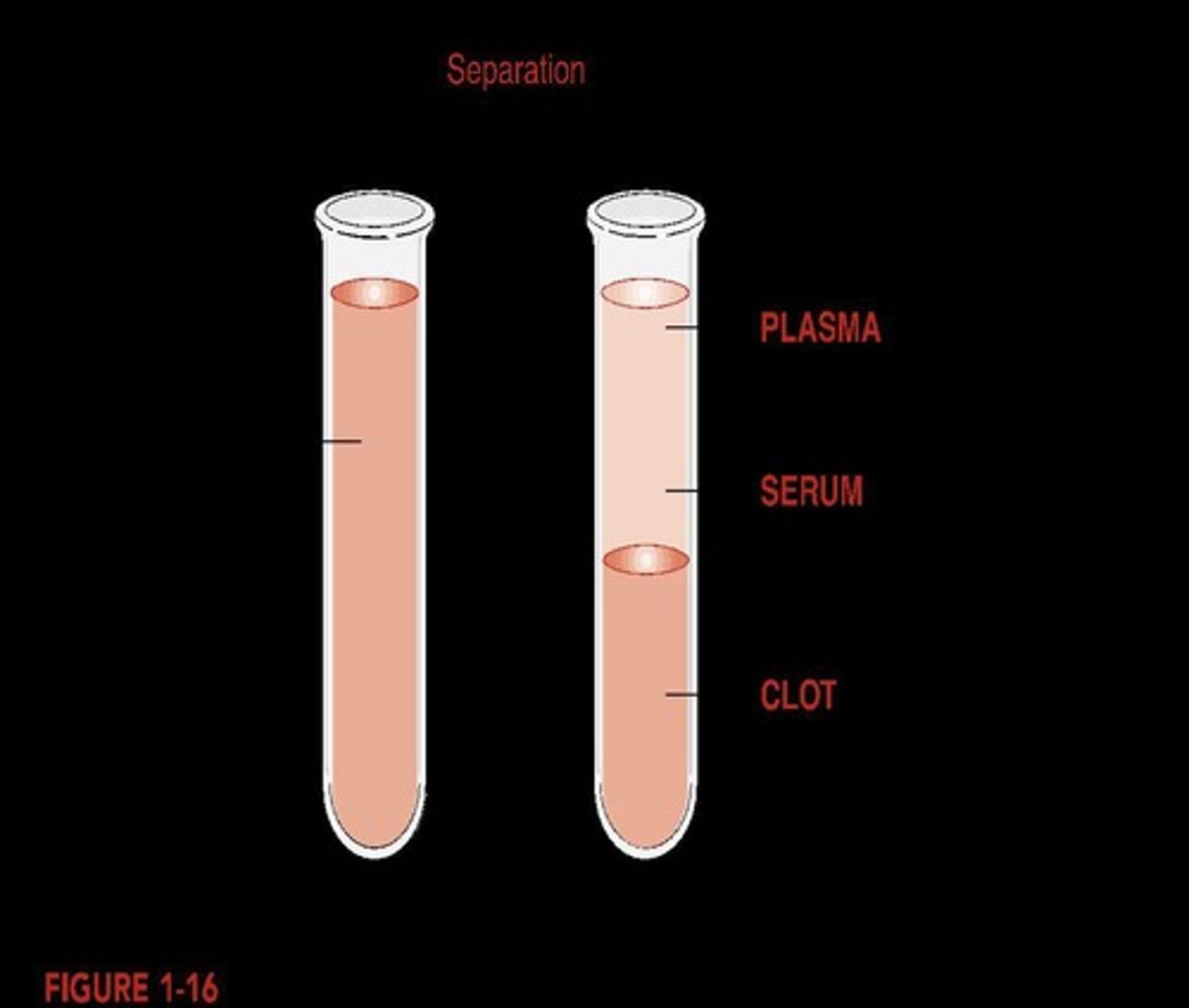
Types of Blood Specimen
Serum, plasma, and whole blood definitions.
Glycolysis Delay Effects
Changes in glucose levels due to delay.
Bacterial Changes in Specimen
Alterations due to bacterial growth.