Adaptive immunity
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What are the main features of the adaptive immune system?
1. Specificity: the immune response is specific for individual antigens
2. Adaptation: the immune system functions only on contact with the antigen and its quality and quantity can be modified (adapted)
3. Memory: previous contact with an antigen changes the subsequent response both qualitatively and quantitatively
4. Discrimination of self vs non-self
How is the the response of the adaptive immune system mediated?
It is mediated by antigen-specific lymphocytes effective against a particular antigen.
How is efficiency of the adaptive immune system improved?
It is improved with repeated exposure to antigen.
What organs and tissues are associated with adaptive immunity?
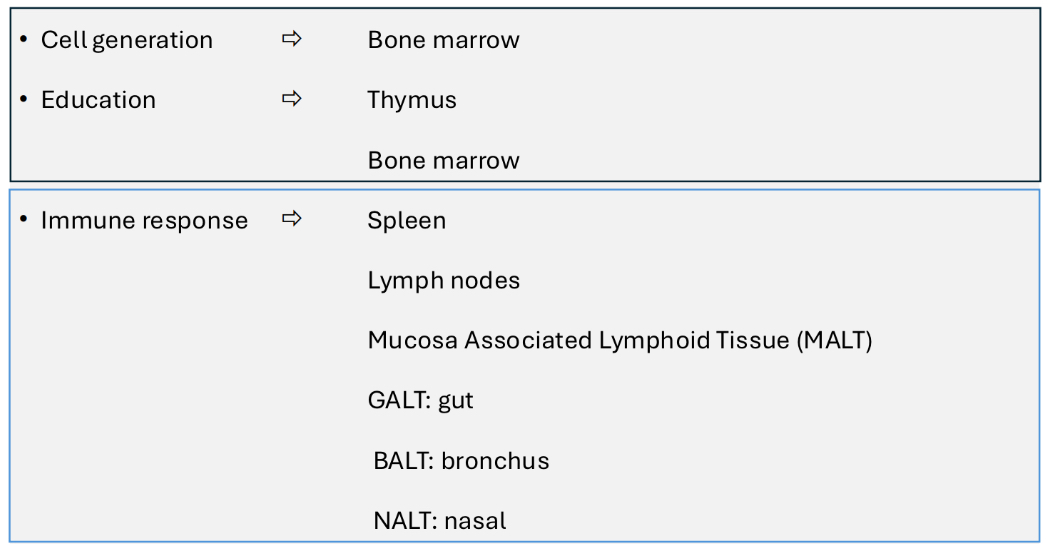
What blood cells are involved in adaptive immunity?
Small lymphocytes, T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes and plasma cells.
What features do T and B cells have in common?
Antigen-specific receptors and memory.
What do T cells do?
Regulation of adaptive immunity
Cytotoxic cell killing
Recognises antigen bound to MHC
What do B cells do?
Produce antibody
Recognises linear and 3D antigen structures.
How is specificity achieved in the adaptive immune system?
Through receptors. Immune receptors are cell-associated proteins.
Ligands that bind to immune receptors are called antigens.
An antigen binding to a receptor leads to cell signalling.
Cell signalling leads to a immune response.
How do T and B cells adapt?
By mutation of parts of the T and B cell receptors responsible for recognising Ag. Leading to:
Increased affinity and specificity of the T and B cell receptors
How does memory occur in the adaptive immune system?
During clonal expansion of activated T and B cells, a proportion of the population of cells will become long-lived memory cells.
How does the adaptive immune system determine self from non-self?
TOLERANCE (the lack of response to “self”) is established for T and B cells during maturation
Two types of tolerance are involved in the lack of self recognition:
• Central (thymus; during cell development and education)
• Peripheral (occurs during an ongoing immune response)
What molecular family are BCR and TCR a part of?
The immunoglobulin superfamily, they are structurally related.
What are BCR and TCR made of?
They are made up of related protein domains known as immunoglobulin domains, which are either constant (C) or variable (V) domains.
The V domains contribute to the antigen-binding site. The C domains are involved in antibody function.
All are transmembrane glycoproteins. All consist of two different linked, but separate chains that are genetically distinct from each other.
What is BCR?
Antibody
Small sections of whole molecules, usually proteins.
Can bind whole ,e molecules, whole cells, bacteria etc
What is TCR?
T cell receptor
Recognises peptides but only when presented by MHC molecules.
Therefore cannot bind whole molecules
Antigen must be digested before recognition
Structure of a BCR:
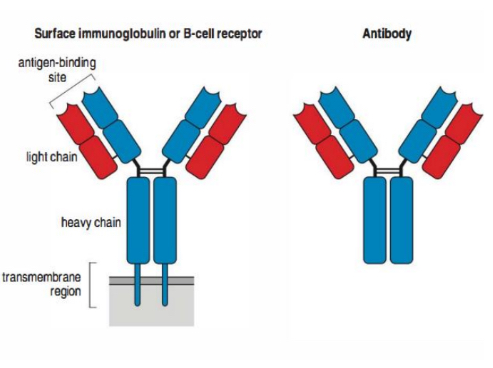
Where does antigen binding occur?
The variable domain; two binding sites per molecule.
Binding site = light chain and heavy chain
What does the constant domain of a BCR molecule do?
Constant domain (Fc fragment) –
linked to cytoplasmic tail and signal
delivery; in secreted antibody this
binds to Fc receptors on cells =
antibody function.
How is BCR diversity generated?
Somatic recombination. Antigen specificity is determined by the variable domain:
• Recombination events occur to join D and J genes.
• Further recombination joins V to DJ.
• This results in a functional VDJ gene.
• These are then expressed with the C region gene (m) to give IgM.
• Occurs in the bone marrow.
Class switching (change the class of antibody) to IgG (g), IgE (e) or IgA (a) occurs with T
cell help.
• Occurs in the secondary lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, Peyer's patch etc)
How do T cells develop and mature?
• Immature precursors migrate from bone
marrow to thymus
• Undergo developmental program
• Test receptors and reactivity to self
• Exit thymus as naïve, mature T cells expressing
either CD4 or CD8
• All T cells also express CD3
How do T cells circulate?
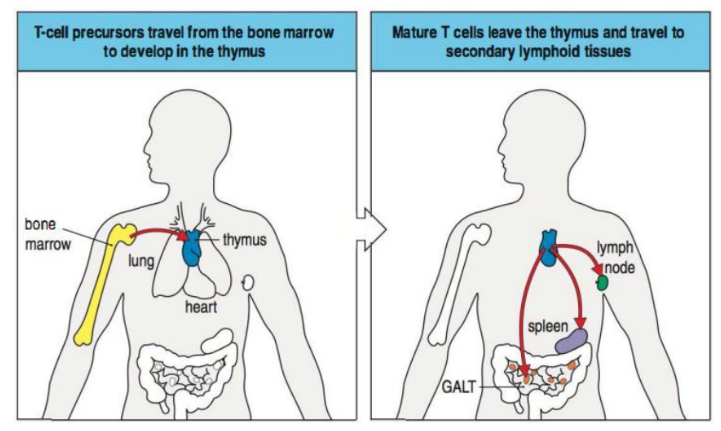
How are T cells activated in secondary lymphoid tissues?
Signal 1: Antigen Recognition
Signal 2: Co-stimulation
Signal 3: Cytokines from APCs
Responses- cell division/clonal expansion/cytokines
What are cytotoxic T cells?
CD8+ T cells antigen + MHC class I
What are helper/regulatory T cells?
CD4+ T cells antigen + MHC class II
What are the CD4+ T cell subsets?
T helper 1 (Th1)
T helper 2 (Th2)
T helper 17 (Th17)
T regulatory (Treg)
What do T helper cells do?
• CD4+ T cells that recognise antigen on MHC II
• Help/regulate immune response through effects on B & other T cells, myeloid cells, phagocytes
• Induced to differentiate into subsets by cytokines in combination with antigen presentation
• Subsets produce specific cytokines that confer function
• Major subsets T helper 1 and T helper 2 (Th1 and Th2)
What cytokines are produced by Th1 cells?
INF-y
What cytokines induce Th1 cells?
IFN-y, IL-12
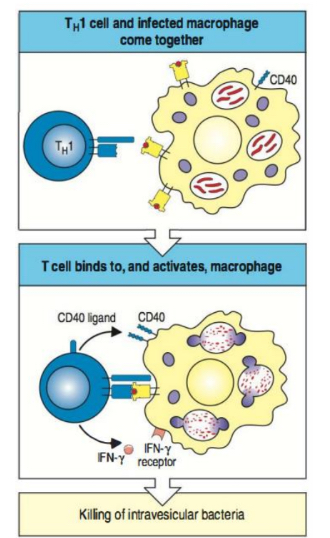
What immunological reactions are triggered by Th1 cells?
Macrophage activation
What is Th1 cells role in disease?
Immune-mediated chronic inflammatory diseases.
What do Th1 cells defend against?
Intracellular microbes
What do Th2 cells defend against?
Helminthic parasites
What cytokines do Th2 cells produce?
IL-4, IL-5, IL-13
What cytokines induce Th2 cells?
IL-4
What immunological reactions are triggered by Th2 cells?
Stimulation of IgE production, activation of mast cells and eosinophils
What are Th2 cells role in disease?
Allergies
How do Th1 cells kill intracellular microbes?
What is the function of cytotoxic T cells?
• CD8+ T cells = Cytotoxic T Cells = CTL
• Function to ‘kill’ virus-infected cells
• Kill by direct contact – interacting with antigen –
MHC class I via TCR
• CD8+ T cells have cytoplasmic granules
• Granules contain ‘perforin’ and ‘granzymes’
• TCR/MHC class I interaction triggers degranulation
• Perforin forms pore in target membrane – like
Complement C9
• Granzymes insert into target cell via pore
• Granzymes induce ‘apoptosis‘ in target – then
moves on to next cell
Where do B cells circulate?
B cells generate from, develop and mature in Bone Marrow
Mature BCR + B cells emigrate to secondary lymphoid tissues through blood to encounter their specific antigen
What do cytokines produced by Th cells do?
They induce class switching from IgM to IgG or IgA or IgE.
How are plasma cells produced?
• Some high-affinity B cells leave the
lymph node (via the efferent lymphatic
vessel), enter the blood and home back to
the bone marrow.
• During this they differentiate into plasma
cells and then secrete high affinity
antibody from the bone marrow (or sites
of inflammation) for months/years
What do B cells that don’t become plasma cells do?
They stay in germinal centres an become memory cells, these persist and quickly differentiate into plasma cells during secondary immune responses.
What are antibodies?
The secreted form of the B cell receptor (BCR)
5 antibody classes, each with different heavy chains.
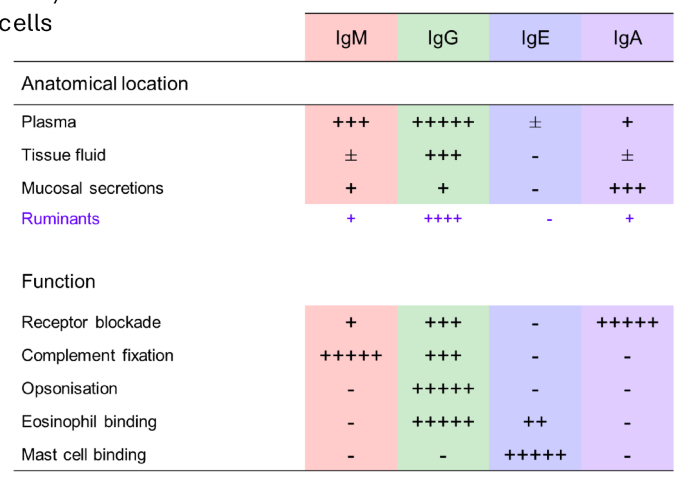
What are the antibody effector functions?
• Blockade and agglutination
• Promotion of phagocytosis (opsonization)
• Degranulation of eosinophils / mast cells
• Fixation of Complement
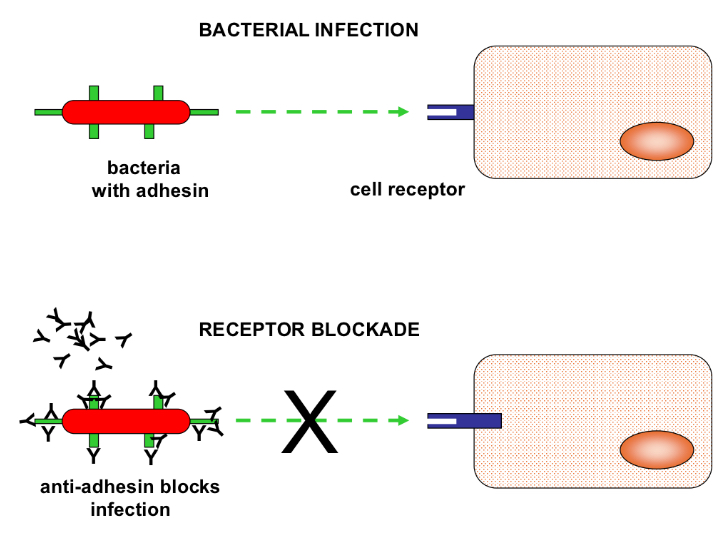
How do IgM and IgG form a blockade?
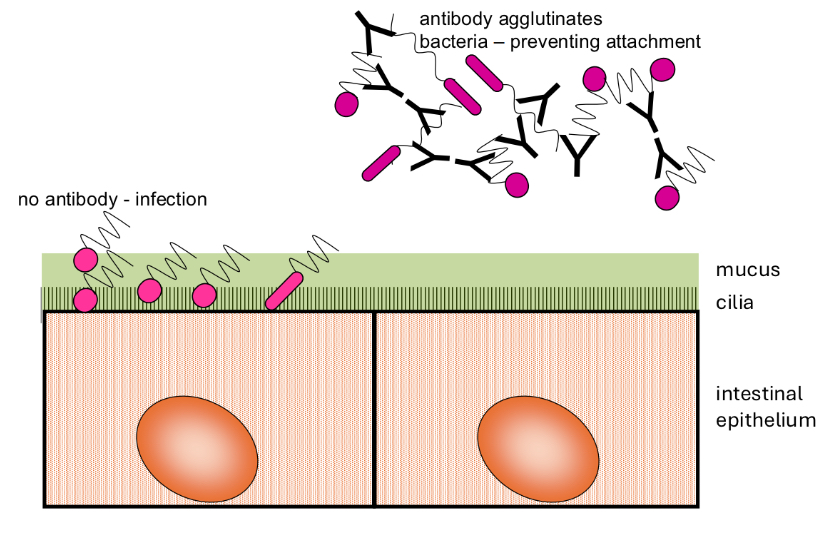
How does bacterial agglutination by IgA occur?
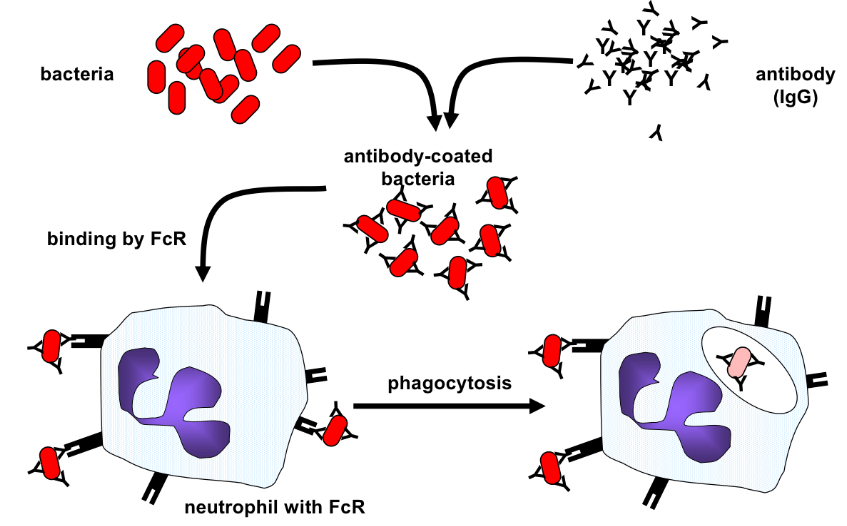
How doe opsonisation by IgG occur?
How does IgE mediated mast cell degranulation occur?
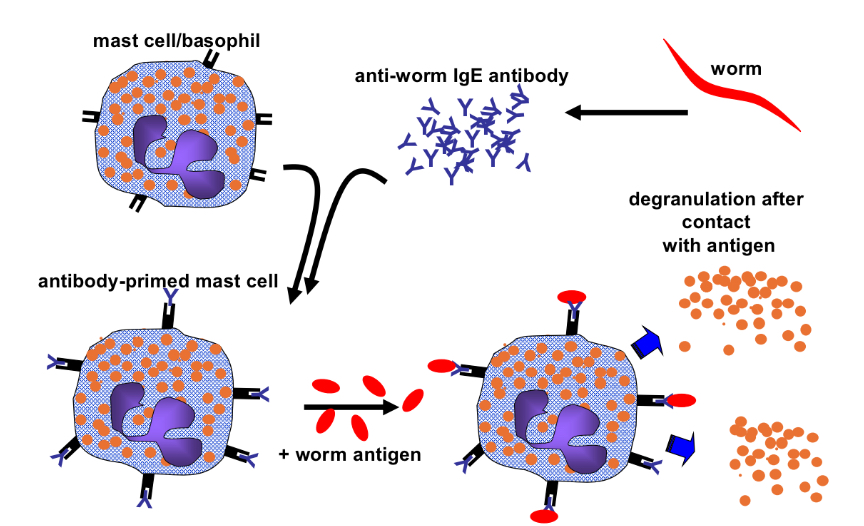
How does work expulsion by eosinophils and IgG occur?
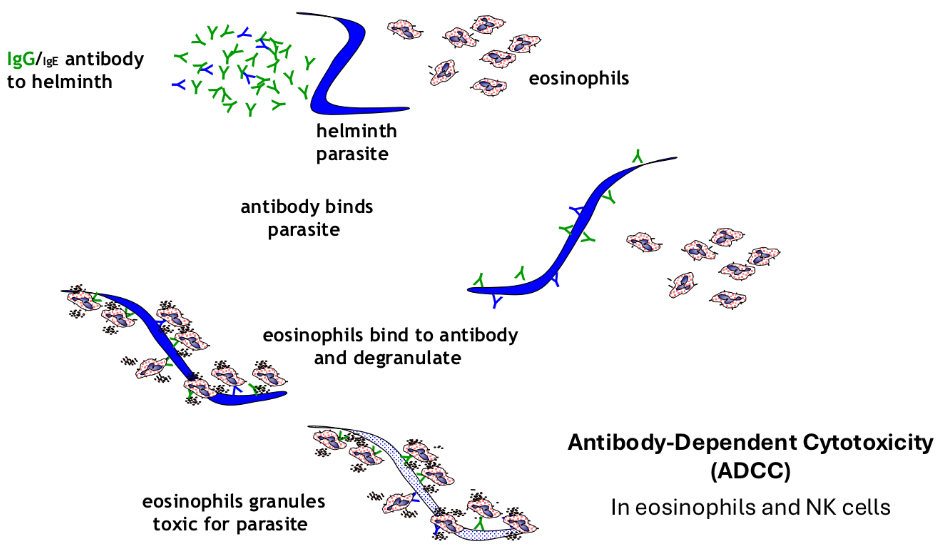
What are the functions of antibodies?
• Neutralisation of microbes and toxins
• Bacterial agglutination by IgA
• Blockade by IgM and IgG
• Opsonisation by IgG
• Mast cell/eosinophil degranulation
• ADCC
• Complement activation (cell lysis, enhanced
phagocytosis, inflammation)