Transport in plants (2)
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Transport of water and mineral ions
Froom root upwards
soil
root hair
cortex
endodermis
xylem (in root to stem to leaves)
mesophyll cells (in leaves)
stomata
atmosphere
Movement of water from soil to root hair
root hairs are permeable to water
mineral ions are taken up by facilitated diffusion and active transport
they are long thin extensions of epidermal cells
able to reach into spaces between soil particles
has very large surface area for increased area of absorption
Water travels down the ____
water potential gradient
Movement of water from soil to root hair in terms of water potential
soil has a higher water potential than the root hairs cytoplasm (so water can move from high to low water potential)
soil has a higher water potential because the cytoplasm has more concentration of ions
therefore water diffuses down the water potential gradient via osmosis through the partially permeable cell surface membrane
into the vacuole & cytoplasm of root hair
Movement of water from root hair to cortex
root hairs have a higher water potential than cortex
water moves down the water potential gradient via osmosis (root hair → cortex)
three possible pathways for water to travel from the root hair to the cortex
Apoplastic pathway: (cell wall)
water travels between the cellulose fibers → there is adhesion of water to cellulose
Symplastic pathway: cell membrane, travels cell-to-cell via plasmodesmata
Vacuolar pathway
Movement of water from the root hair to the cortex to the endodermis
the endodermis has a Casparian strip = suberized cell wall (Casparian strip is made up of suberin which is impermeable to water)
in endodermal cell apoplast pathway is blocked because of the casparian strip
the only way for water to travel is through the endodermis is by symplast pathway
water and ions must pass through endodermal cells so that transport of mineral ions can be controlled
Movement of water from endodermis to xylem
water continues to move down the water potential gradient
from the endodermis to the xylem you have to cross the pericycle (layer of cells just below the endodermis)
water gets into xylem vessels through the pits in the cell wall
Movement of water in xylem vessels from roots to leaves
roots have a higher water potential than leaves
water moves down the water potential gradient travelling up xylem from roots to leaves
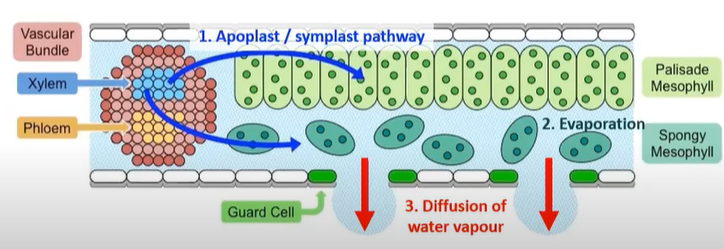
Movement of water from xylem in leaves to atmosphere
xylem vessel in leaves
water moves through the pits
arriving at the palisade/spongy mesophyll cells via apoplastic or symplastic pathway
water gathers onto the surface of spongy mesophyll cell walls
evaporates into air spaces
diffusion of water vapour from stomata into atmosphere
Transpiration
is the loss of water from leaves (side effect is the cooling of plant)
Two ways for transpiration to occur
via the stomata
→ diffusion of water vapour from air space to atmosphere, occurs only when stomata is open for gas exchange
via the cuticle, only a small amount of water is lost