stem cells
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
stem cell
undifferentiated cells that can differenitate into different cell types
what can stem cells do? (2)
-can replicate themselves to produce more stem cells [self-renewal]
-differentiate into different cell types
types of stem cells and what they can differentiate into and examples
Totipotent stem cells - can differentiate into any cell type and form whole organisms [e.g. fertilised egg]
Pluripotent stem cells - can differentiate into almost any cell types but cannot form whole organisms [e.g. embryonic stem cells (only present in embryo)]
Multipotent stem cells - can only differentiate into a few different cell types [e.g. bone marrow stem cells→can produce any type of blood cell]
Unipotent stem cells - can only differentiate into one cell type
embryonic stem cell
source?
what type of stem cell is it?
adult stem cell
source?(5)
what type of stem cell is it?
plant stem cell
source?
what type of stem cell is it?
embryonic stem cell
-blastocyst [early embryo]
-pluripotent
adult stem cell
-bone marrow, skin, muscle, brain, intestine etc
-multipotent
plant stem cell
-meristem
-pluripotent
why can adult stem cells replace damaged tissue?
they are multipotent so can differentiate into specific cell types needed for tissue repair
Where do erythrocytes and neutrophils derive from?
stem cells in the bone marrow
Where do xylem and phloem derive from?
stem cell in meristems
where are meristem found in plant?
tips of roots and shoots
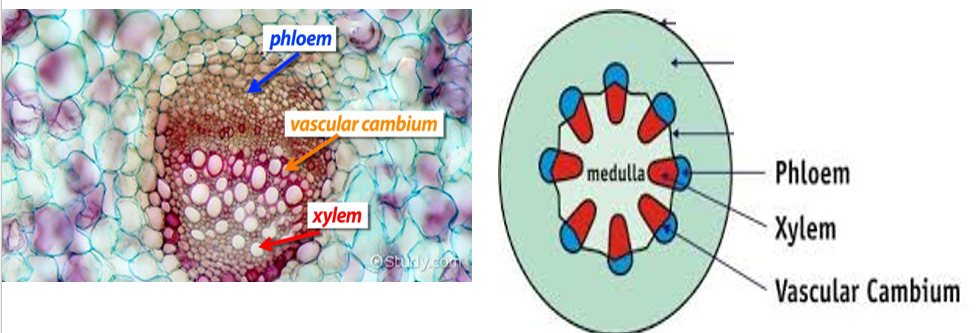
whats the name of the meristematic tissue that’s found between phloem and xylem?
vascular cambium→ produces xylem and phloem cells
uses of stem cells (4)
-repair damaged tissues
-treat neurological diseases (e.g. Parkinson's and Alzheimer's)→it regenerates nerve cells
-scientists use it to research developmental biology→help understand how organs develop
-test new drugs for toxicity and side effects
benefits of stem cell therapy (2)
-treats disease→ by replacing damaged cells
-using stem cells from the patient’s bone marrow reduces the risk of immune rejection, as they are genetically identical
disadvantages of stem cell therapy (2)
-The body may reject foreign stem cells so the treatment may not work
-may need immunosuppressive drugs
ethical issues of stem cell therapy
-against
-for
-The use of embryonic stem cells involves the destruction of embryos→some people view this as morally wrong because they believe that an embryo is a potential human life and that life begins at conception.
-Others argue that using these embryos for research is acceptable if it leads to medical advancements and treatments for serious diseases.