Periodic table+Group 2 amd Group 7
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
The periodic table is in order of increasing …1? number and elements are put in columns (called …2?) of similar properties due to having the same number of …3? In their outer shell.
What does monoatomic mean?
1.proton. 2.groups. 3.electrons
Made up of 1 atom

Read the information then answer 1,2 and 3.

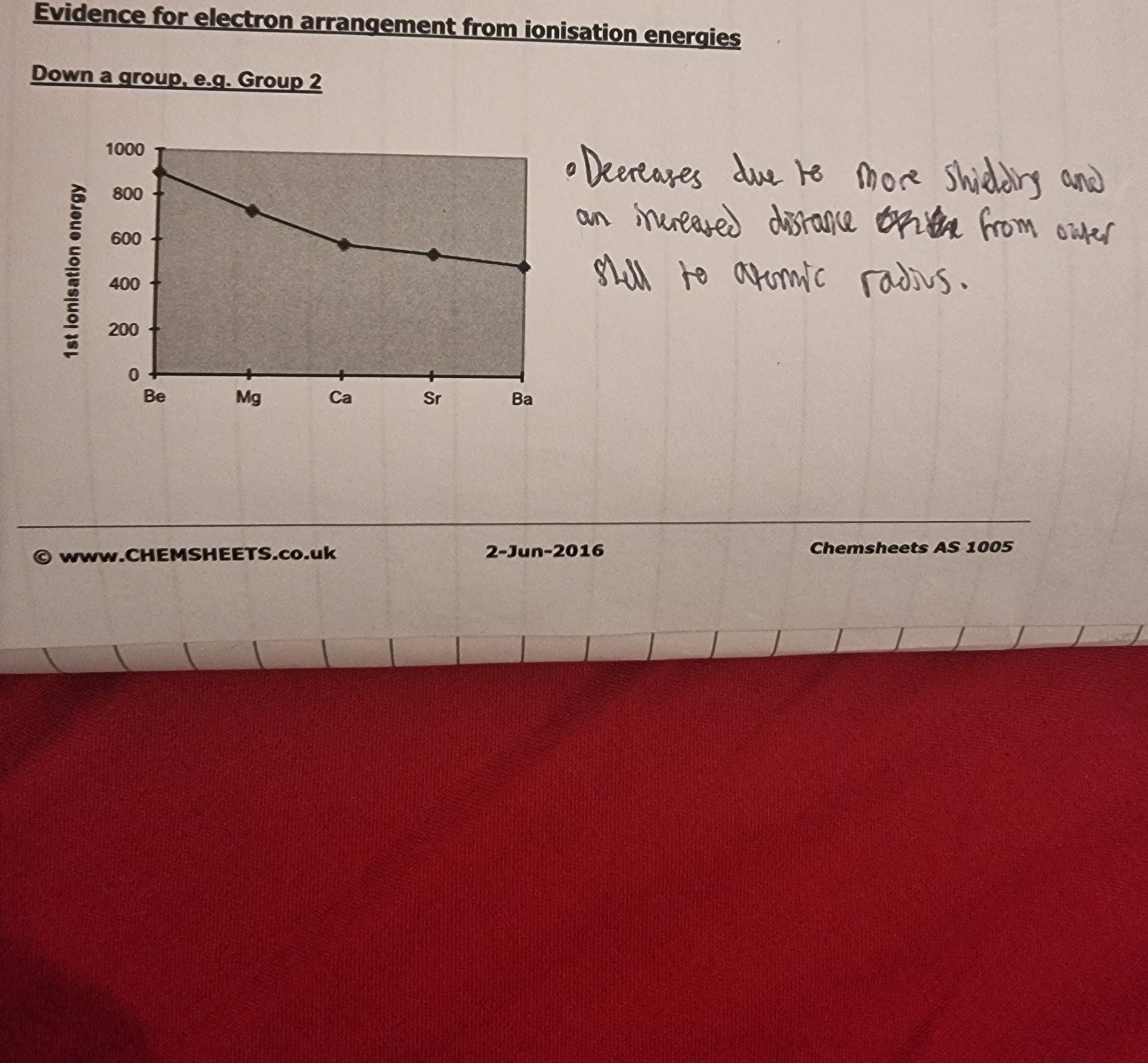
Explain the trend?
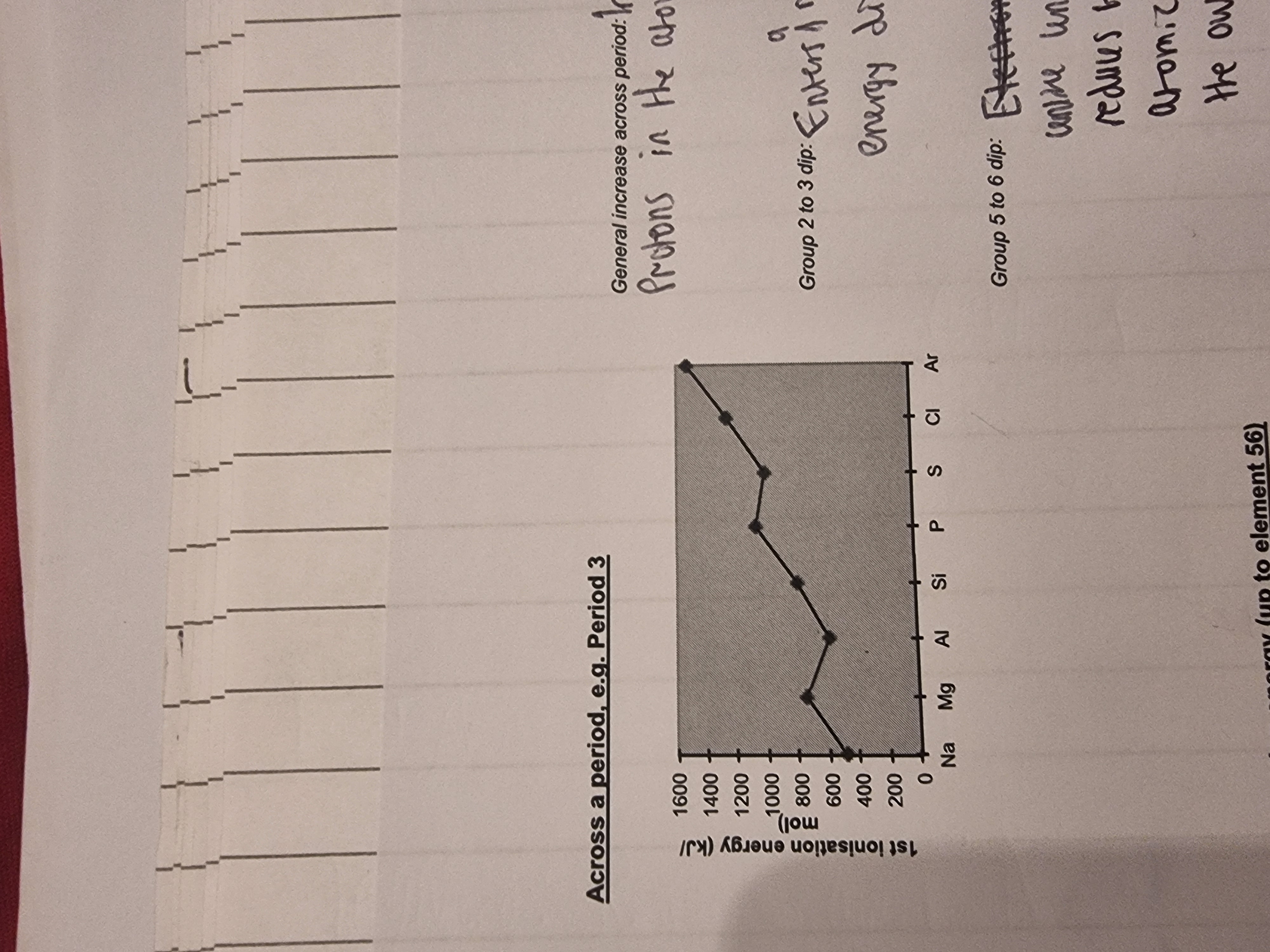
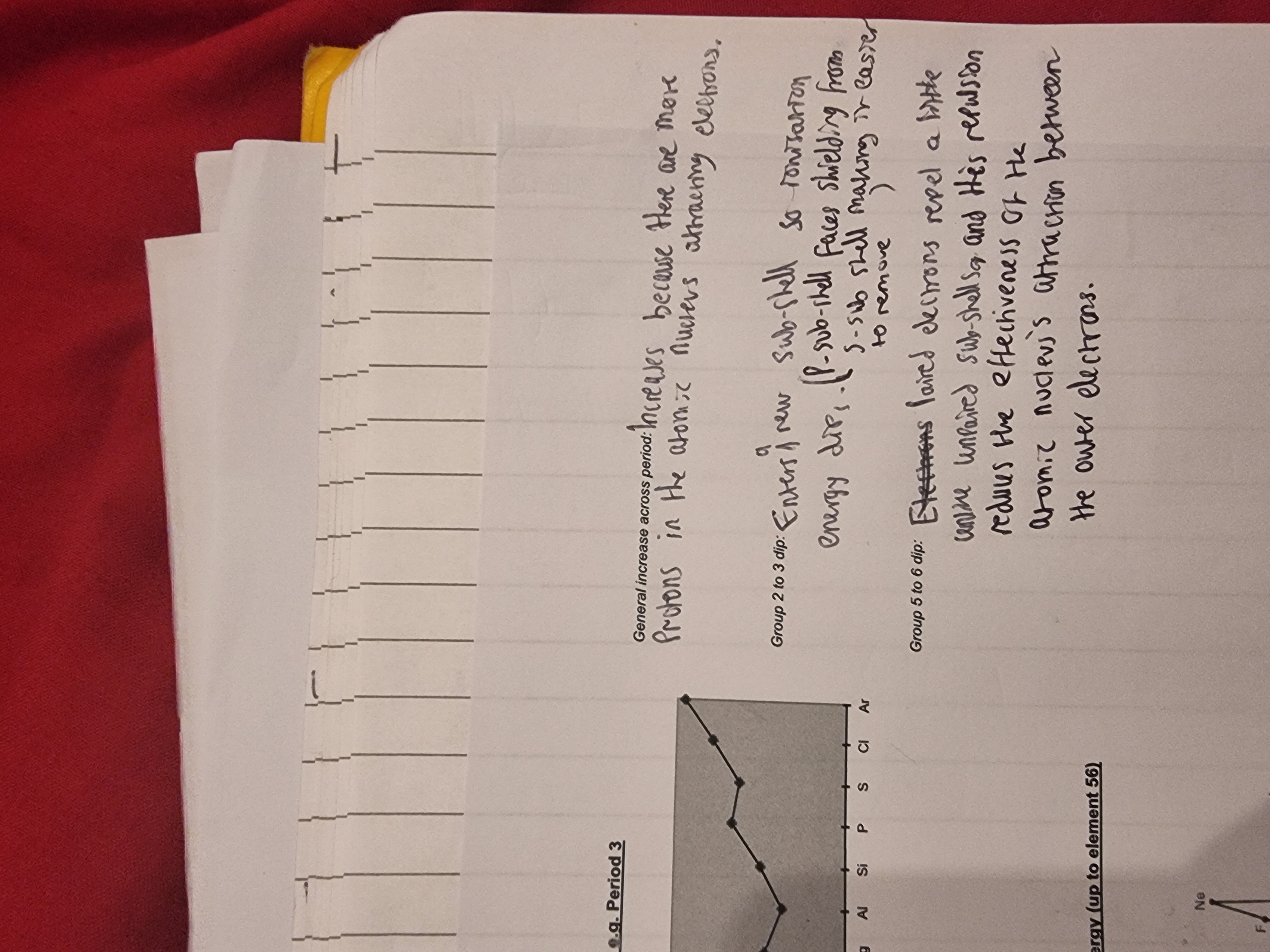
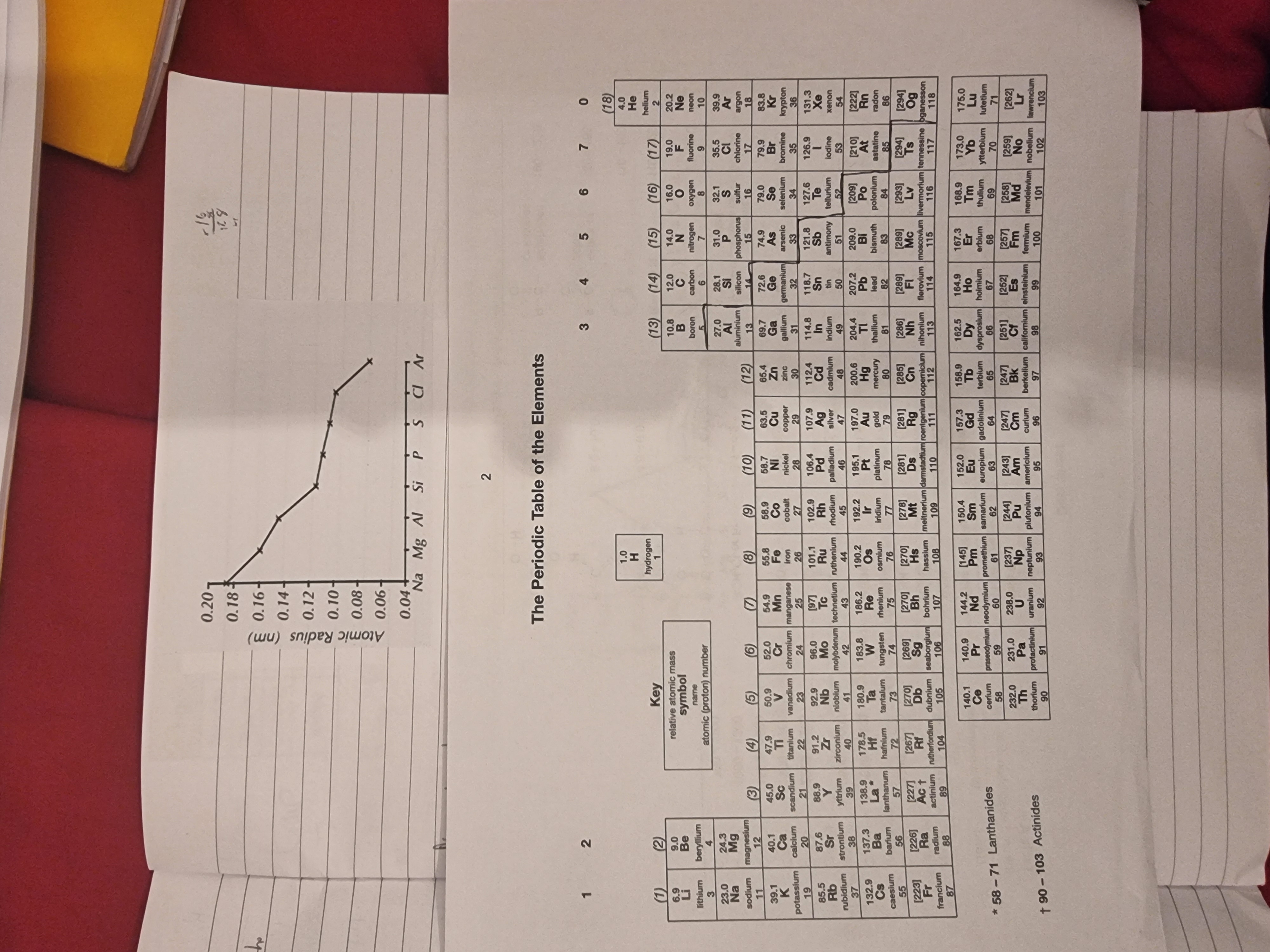
Explain the trend?
The atomic radius is decreasing because the proton number/ nuclear charge is increasing as you go across the period and this increased the atomic nucleus’s electrostatic attractions with the orbiting electrons. This stronger attraction decreses the atomic radius distance.
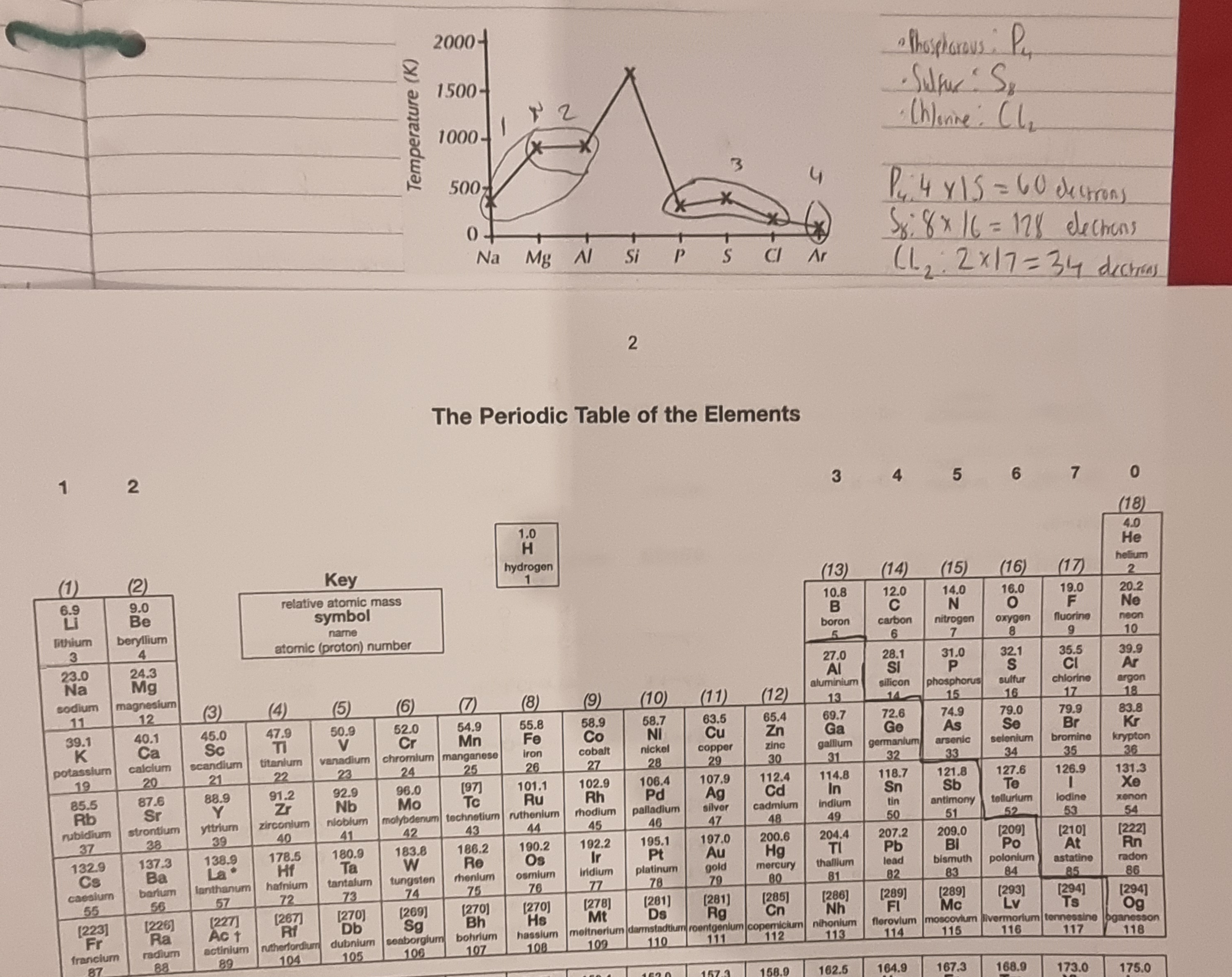
Explain the melting point trends?
Note •phosphorus exist as P4 molecules, Sulfur as S8 amd Chlorine as Cl2.
Both Na and Mg have metallic bonding but Mg has a higher nuclear charge so attraction between atomic nucleus and delocalised electrons increase which results in a higher melting point.
The melting point change from Mg to Al is very slim due to Mg having a higher melting point than expected since its atoms are packed together more closely.
•The melting point drops from silicon to phosphorus because silicon has a strong covalent network structure requiring much energy to break, while phosphorus exists as P₄ molecules held together by weak van der Waals forces, needing less energy to melt.
P has a lower melting point than S and Cl has a lower melting point than the other two because the more electrons an element has, the greater the van der waals, the molecules are P4(4X15=60 electrons), S8(128 electrons) and Cl2(34 electrons) so Cl2 has the fewest electrons and so has the weakest van der waals and lowest melting point.
Argon is monoatomic so it has the fewest electrons and less van der waals forces.
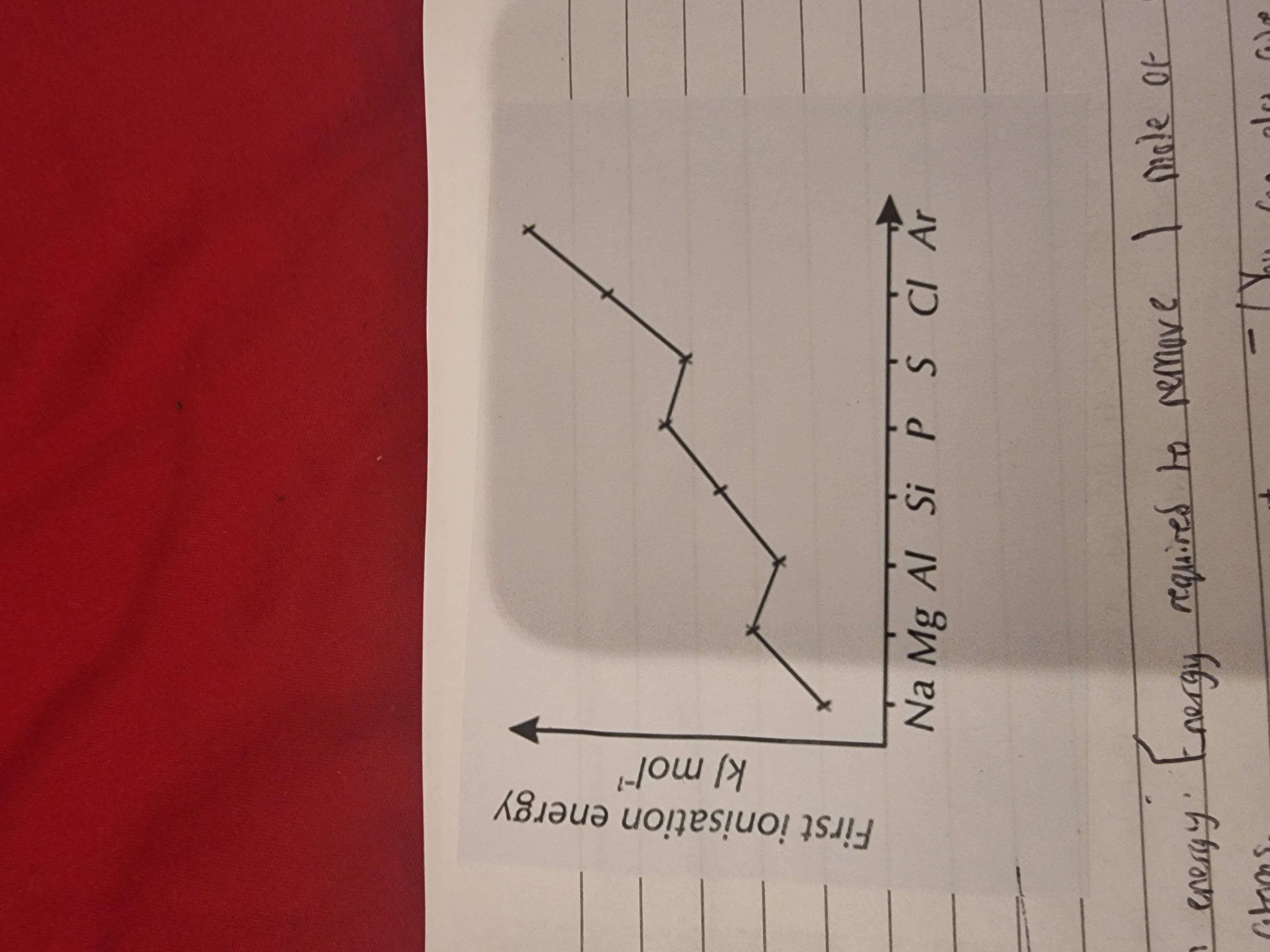
1.What is the definition of the first ionisation energy?(Simple terms:Ionization energy is the amount of energy it takes to remove an electron from an atom)
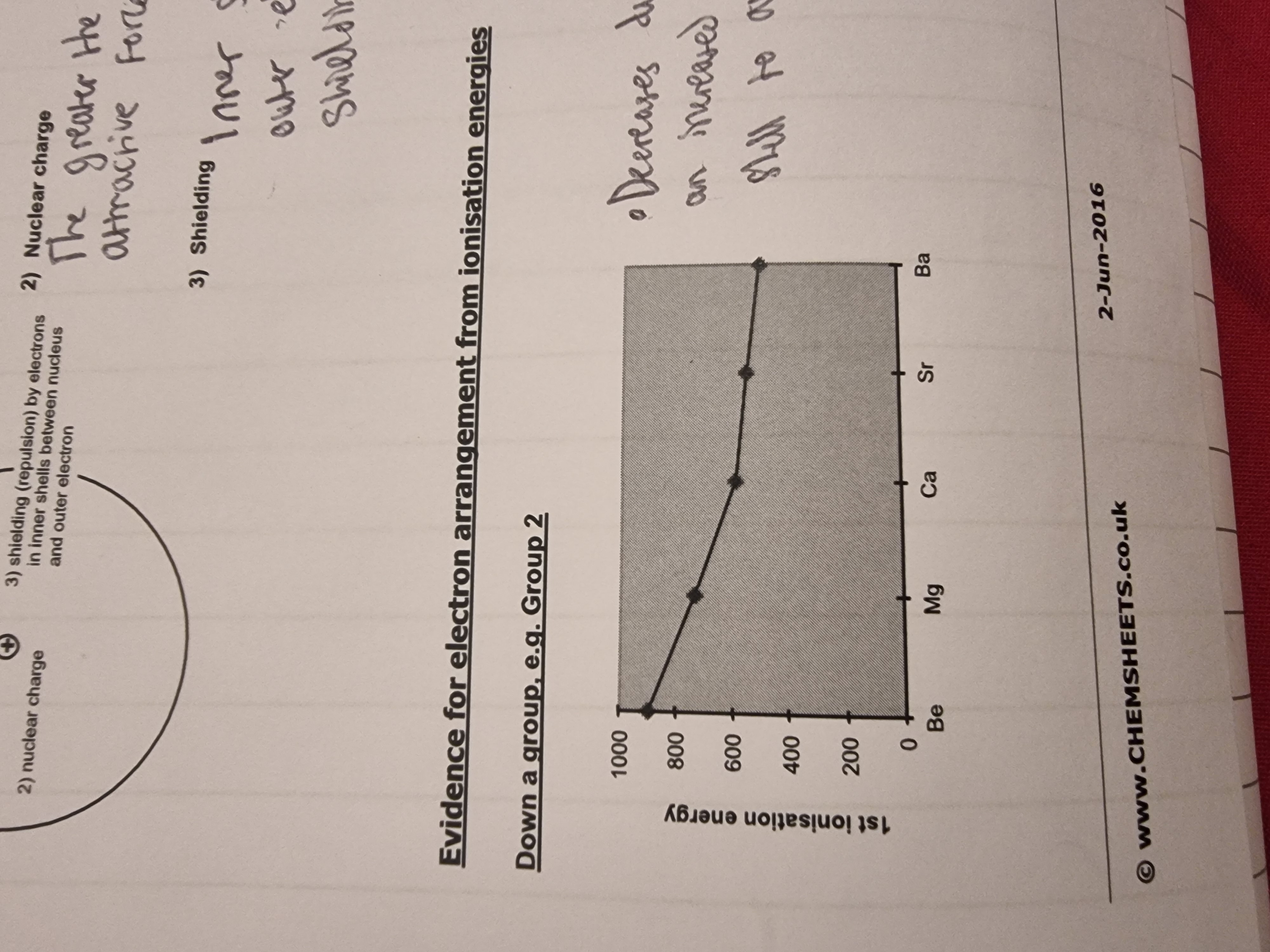
Info : Shielding is when inner electrons repel outer electrons which reduces the effectiveness of the atomic nucleus’s attraction between the outer electrons. More inner shells means more shielding.
Explain the trends in the image?
1.Energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons from a mole of gaseous atoms.→ to produce a mole of gaseous positive ions. (Mg (g) → Mg*+ (g) + e*-)(you can give the equation in an exam)
•The general trend is increasing across a period because of an increase in nuclear charge.
•But there is a fall from Mg to Al because the outer electron of Al is in a P sub-shell whereas Mg’s outer electron is in the S sub shell(orbital) and there is some shielding from the nucleus by the s-orbital.
•Sulfur is lower than Phosphorus because one of its 3p sub shells is paired and there is a degree of repulsion between paired elecrons.
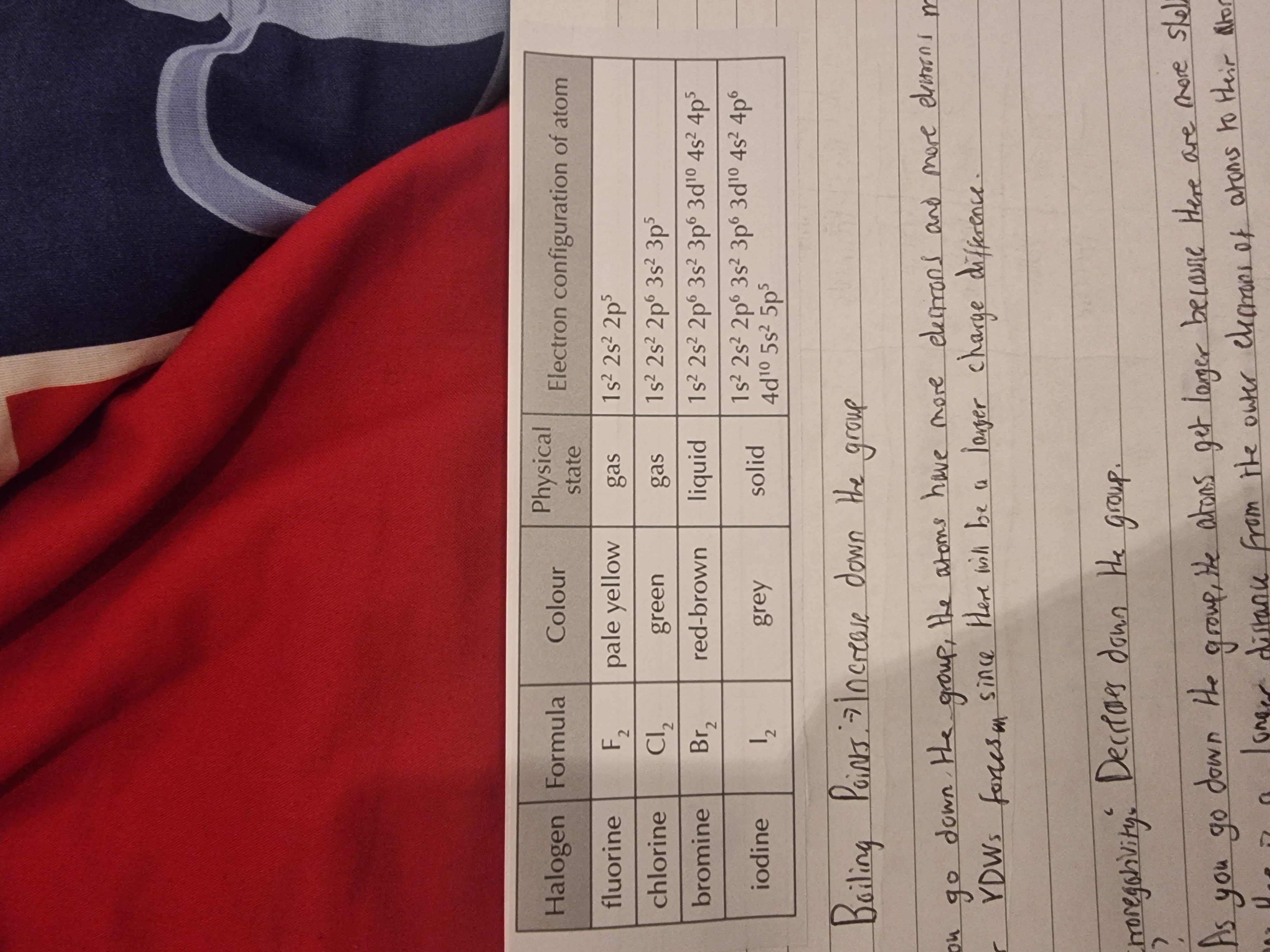
Group 7-Halogens
What is the trend of boiling points as you go down group 7?
What is the trend of electronegativity as you go down group 7?
info:Displacement reactions occur when a more reactive element replaces an element in a compound.
3.Why does bromine element change an iodine colourless solution red/brown instead of its own solutions colour which is orange?
It increases because the atoms have more electrons and so have stronger van der waal’s forces.
It decreases because the atoms get larger since there are more shells and this increases the distance from the outer electrons to the atomic nucleus. The larger distance makes attractions weaker which reduces electronegativity.
Bromine's Role: Bromine itself is orange, but the reaction's product, iodine, dominates the observed color because it's the new substance being formed. The color of the bromine is masked by the more intense color of the iodine.


Testing for halides using silver nitrate:
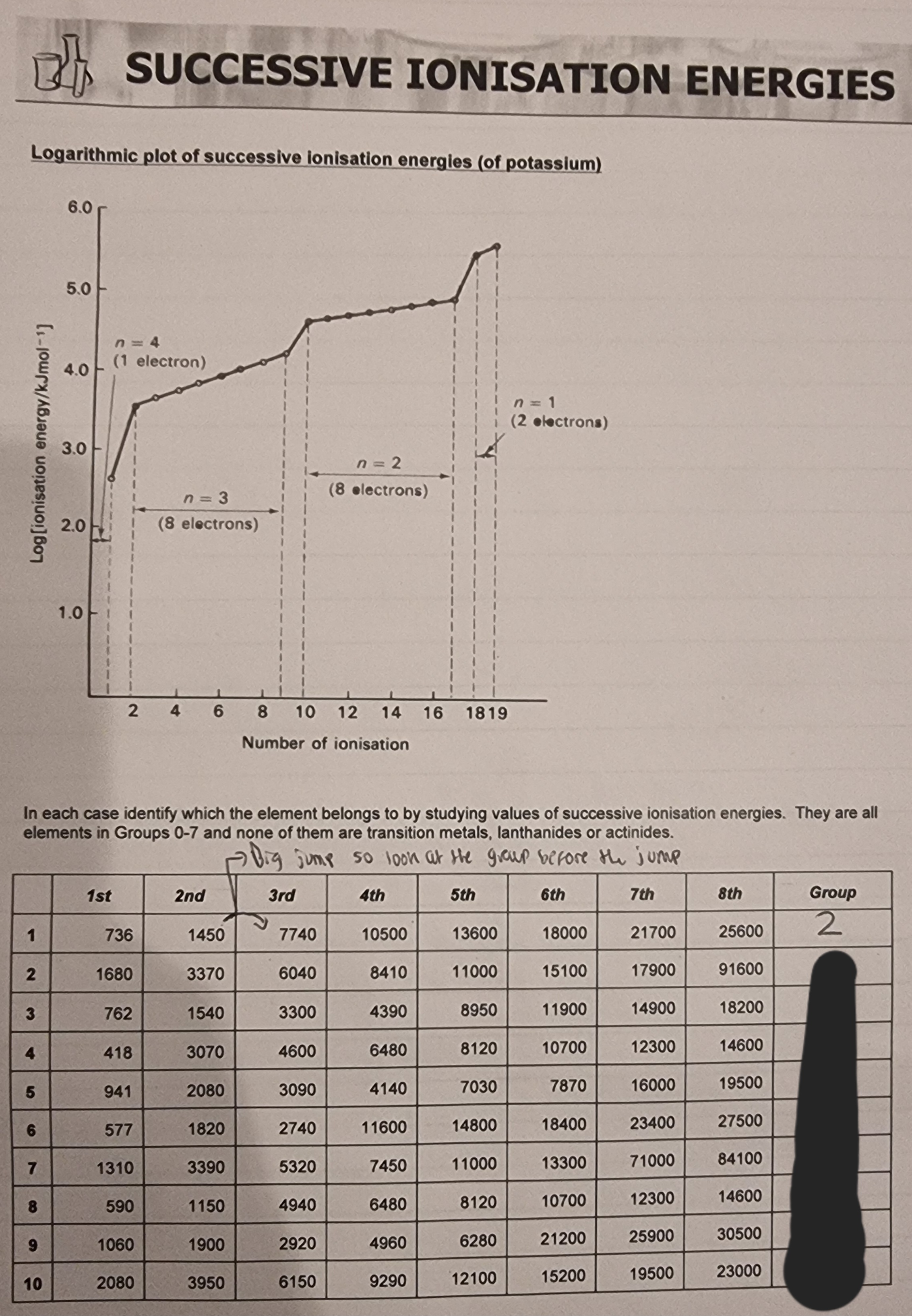
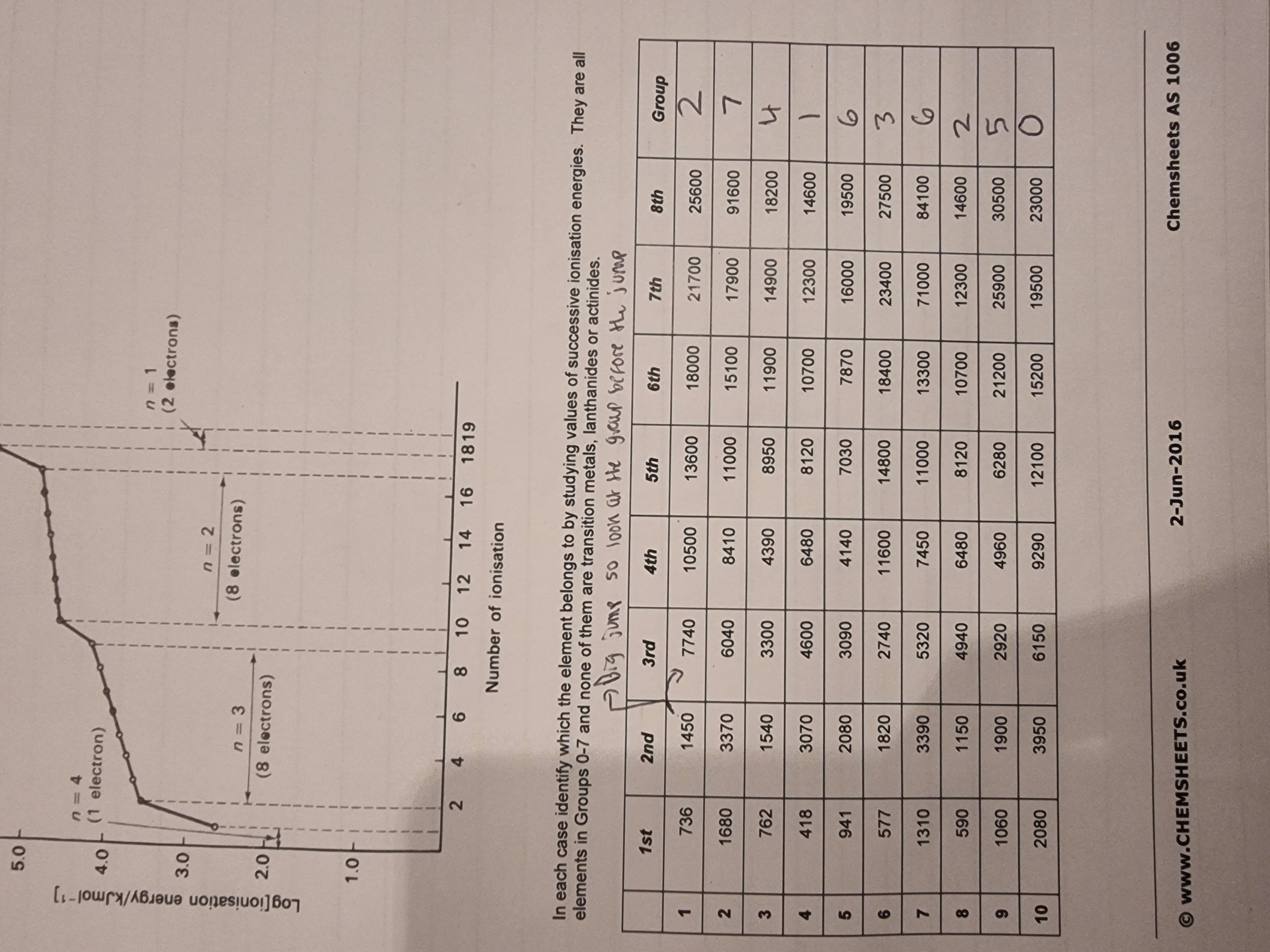
Successive Ionisation energies:
Fill in the boxes:
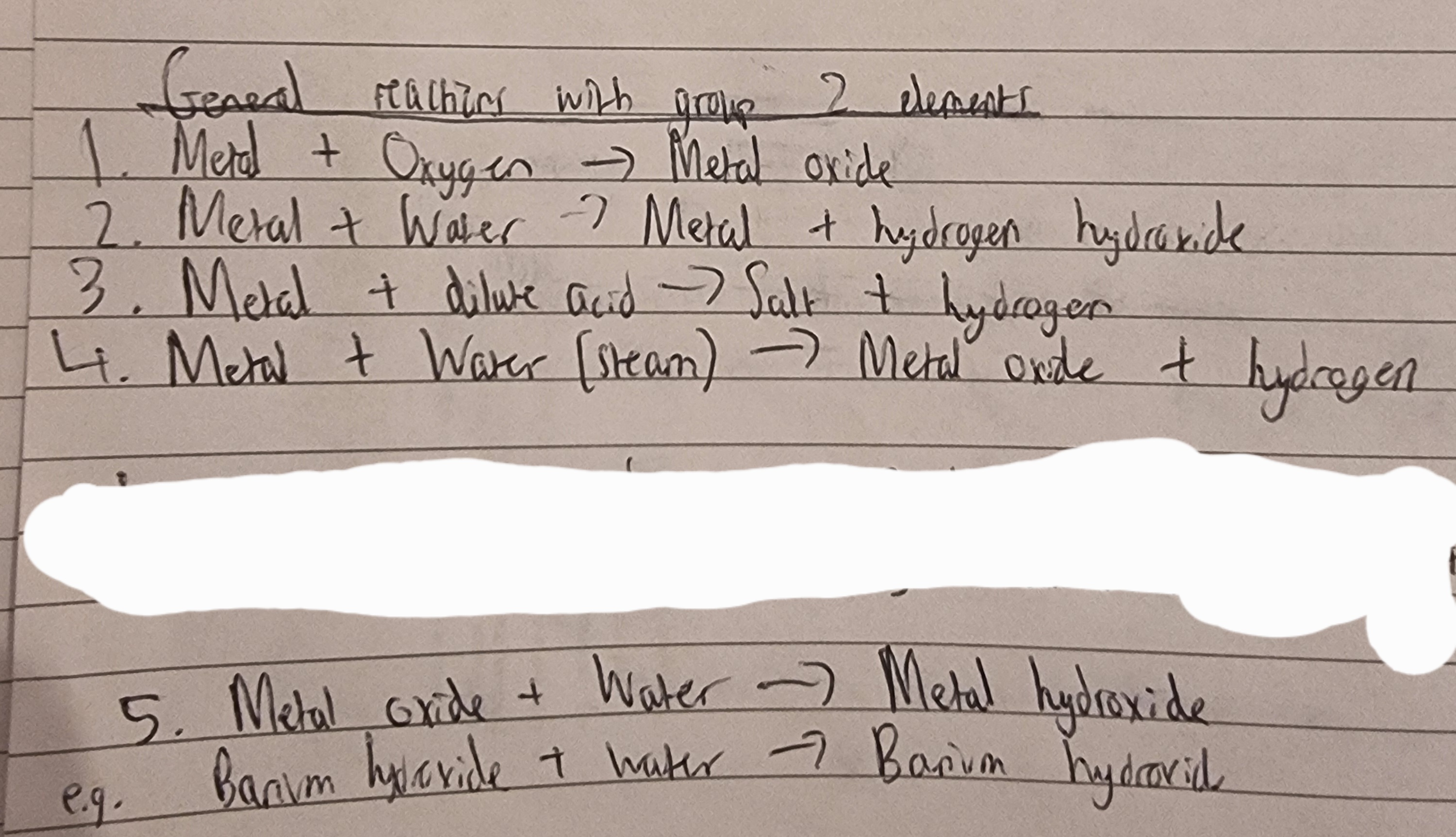
Group 2: Note- The image shows general reaction with G2 elements
1.What is a reducing agent?
•Group 2 elements are reactive metals that readily lose …2? outer shell electrons to form M*2+ ions.
•Group 2 elements can react with oxygen,water and dilute …3?.They react forming …4? ions.
•Reactivity …5? down group 2 because the 1st and 2nd ionisation energy decreases down the group making it easier to form M*2+ ions.
•Metal hydroxides increase in solubility as you go …6? group 2.
7.What is a strong acid?
• In group 2, the solubility in sulfates become less soluble going …8? the group
A substance that donates its outer electrons in order to reduce another substance.
2. 2 3.acids. 4.M2*+ 5.decreases
6.down
A substance that fully dissociates its H+ ions in solution.
8.down