Transcriptomics 2- applications and examples
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is Gene ontology?
The ‘study of being’- understanding and classifying the nature of things.
Describe what a molecular function is. Give 2 examples.
Molecular-level activities performed by gene products, e.g., catalysis, binding.
Describe what a biological process is, examples.
Larger processes accomplished by multiple molecular activities, e.g., apoptosis, DNA repair.
Describe what a cellular component is, using examples.
The locations where a gene product performs a function, e.g., cell membrane, ribosome.
What is KDM5C knock out gene?
A histone demethylase which affects DNA packaging; mutated in intellectual disability.
What does KDM5C knock out gene down-regulate? (3)
Neural differentiation, neuron-projection development, and synapse.
What is NGA1 knock out gene?
Induced under dehydration stress.
What does NGA1 knock out gene downregulate? (2)
ABA (growth hormone), reproductive structure development.
Why do we study the transcriptome?
The effect of a compound, stress, knockout on gene expression.
How different populations of a species (or dif cell lines) are affected by the environment.
How species differ in their transcriptome.
CASE STUDY 1 - The effect of potential anti-tumour Hyperoside on cervical cancer cells- drug trial.
What is hyperoside?
A plant-derived quercetin 3-d-galactoside that exhibits inhibitory activities on various tumour types (drug trial).
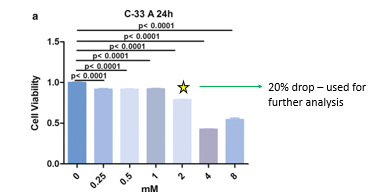
How many genes were upregulated and downregulated when treated?
754= upregulated
509= downregulated.
What did the downregulated DE genes affect? (5) What did this lead to?
Mitochondrial translational elongation
Mitochondrial elongation
Mitochondrial translational termination
Ribosomal large subunit biogenesis
rRNA processing
This leads to tumour development.
What did the upregulated DE genes effect? (4) What did this lead to?
Cell adhesion
Cell division
Mitotic cytokenesis
Homeostasis
Caused tumour cell migration or invasion.
CASE STUDY 2- Comparative response to drought and salt stress in resistant and sensetive rice.