Chemistry - Unit 3 Topic 1: Dissociation Constants and Acid-Base Indicators
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Acid ionisation at equilibrium equation
HA(aq)(acid) + H2O(l) -->
Ka=
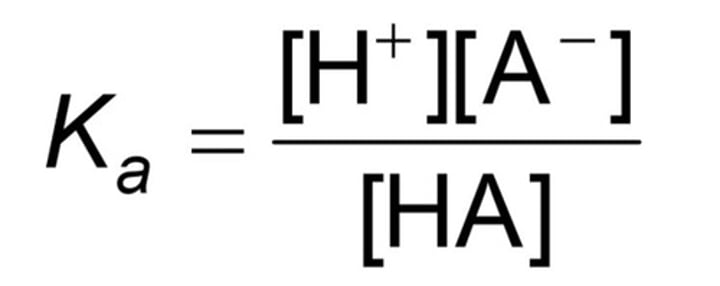
Ka > 1
strong acid
Ka < 1
weak acid
Strong acid position of ionisation equilibrium
far to the right
Weak acid position of ionisation equilibrium
far to the left
Steps to calculate Ka
1. Write out a chemical equation to visualise what is occurring
2. Write the equation for Ka
3. The first thing we can calculate is the H+ concentration from the Ph value provided
4. Use an ICE table to determine the unknown concentration
5. Substitute this value into the equation for Ka
Base ionisation at equilibrium equation
B(aq)(base) + H2O(l) -->
Kb=
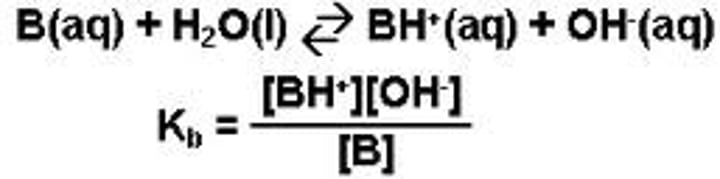
Kb > 1
strong base
Kb < 1
weak base
Steps to calculate Kb
1. Write out the chemical equation for the dissociation
2. Determine the expression for Kb
3. Use pH to calculate [OH-]
4. Calculate Kb using the molar ratio from the ionisation equation, using an ICE table
Ka x Kb
Kw
pKa=
-log10Ka
pKb=
-log10Kb
Indicators
change colour in acidic/basic solutions, so they can identify the pH of a solution
Weak acid (Hln) indicator
HIn(aq)(colour A) + H2O(l) -->
Weak base indicator
B(colour A) + H2O -->
Indicators change colours when
pKa = pH
When equilibrium lies exactly in the centre
[In-] = [HIn]