pictures for blood cells ebola and Viral Diseases and Global Health
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
photo practise location week 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
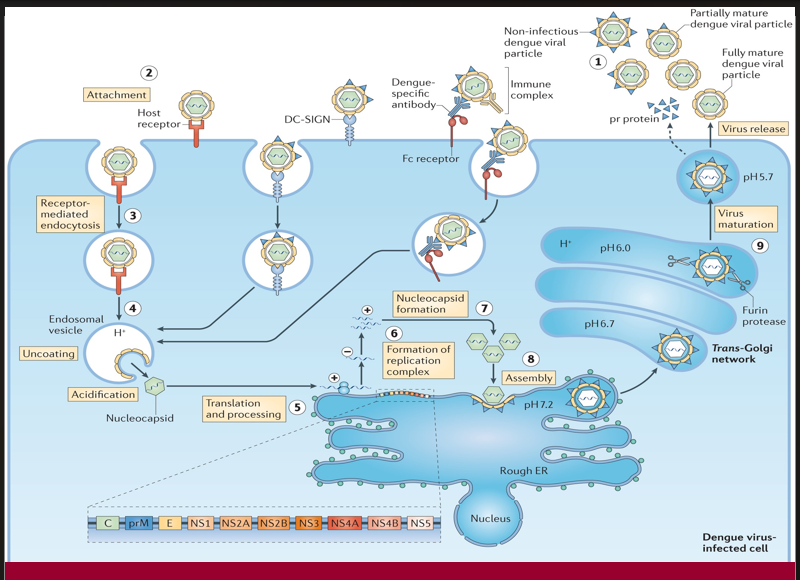
The viral particle binds to a host cell via specific receptors to initiate infection.
→ Missing Step/Component: Attachment (Step 2)
→ Location in cell: At the plasma membrane, via host receptor or DC-SIGN
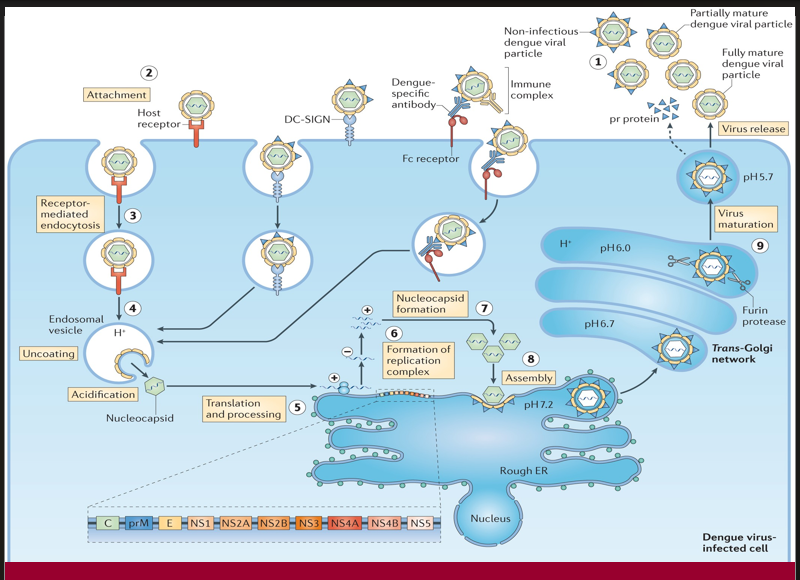
The virus enters the cell inside an endosome after engaging with the host receptor.e nucleus
→ Missing Step/Component: Receptor-mediated endocytosis (Step 3)
→ Location in cell: Plasma membrane to early endosome
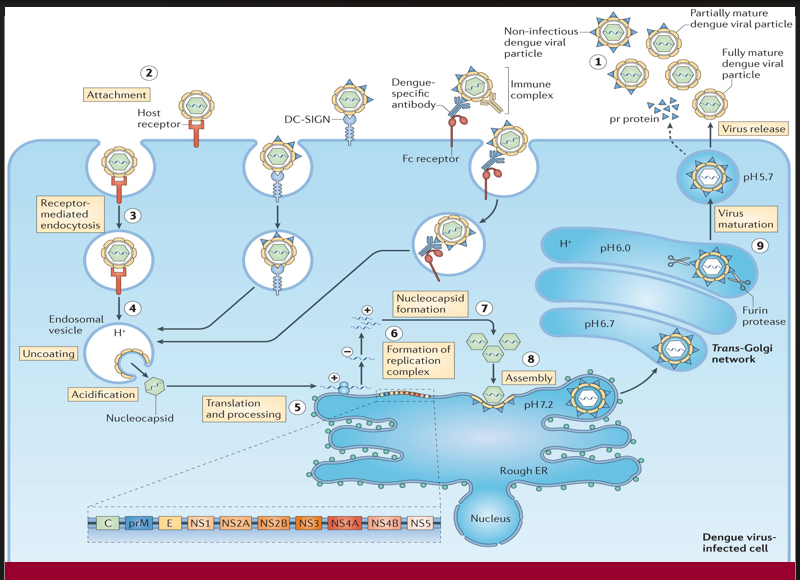
Acidification of the endosome triggers conformational changes that release the viral genome into the cytoplasm.
→ Missing Step/Component: Uncoating (Step 4)
→ Location in cell: Inside acidified endosomal vesicle
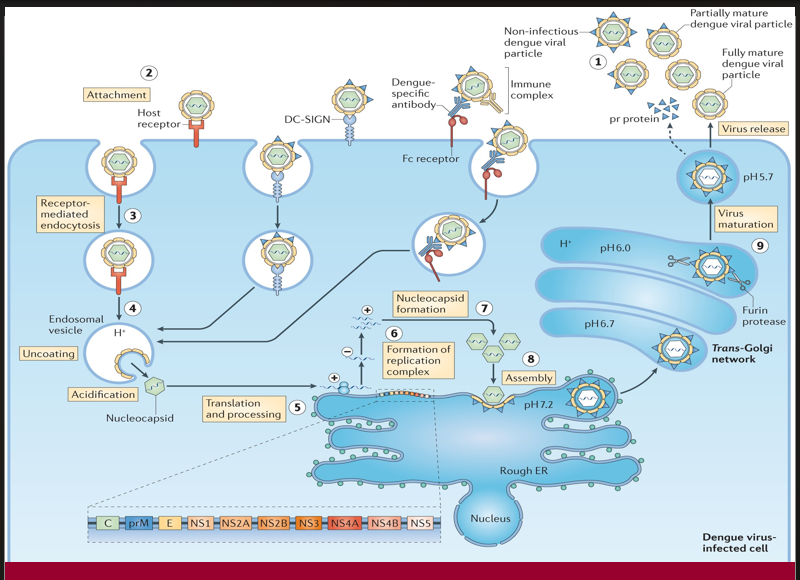
After uncoating, the viral RNA is translated into a polyprotein and processed into structural and non-structural proteins.
→ Missing Step/Component: Translation and processing (Step 5)
→ Location in cell: On ribosomes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
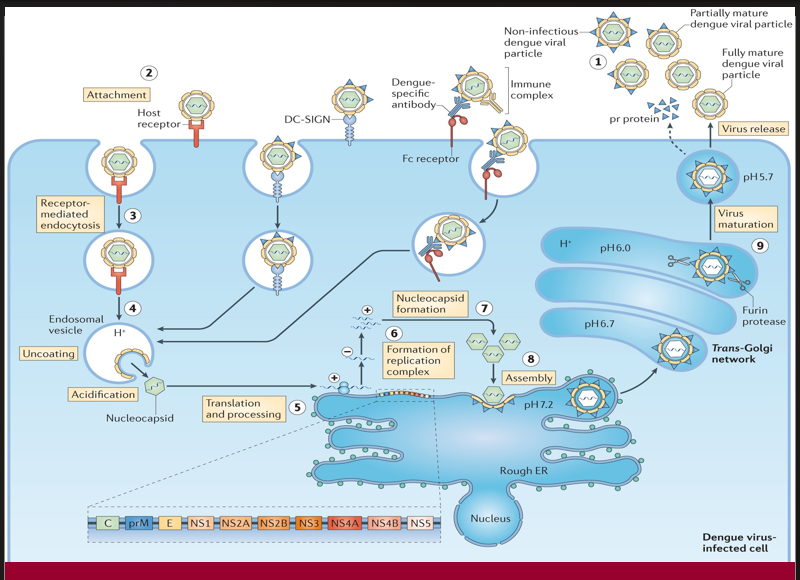
A membrane-bound platform forms for RNA replication, enabling synthesis of new viral genomes.
→ Missing Step/Component: Formation of replication complex (Step 6)
→ Location in cell: On ER membranes
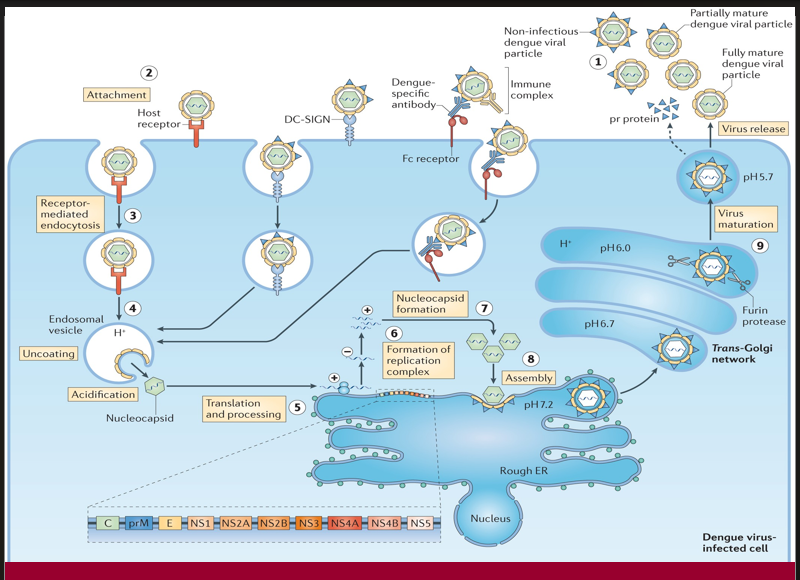
Structural proteins and newly synthesized RNA are packaged together to form immature viral particles.
→ Missing Step/Component: Assembly (Step 8)
→ Location in cell: On the luminal side of the ER
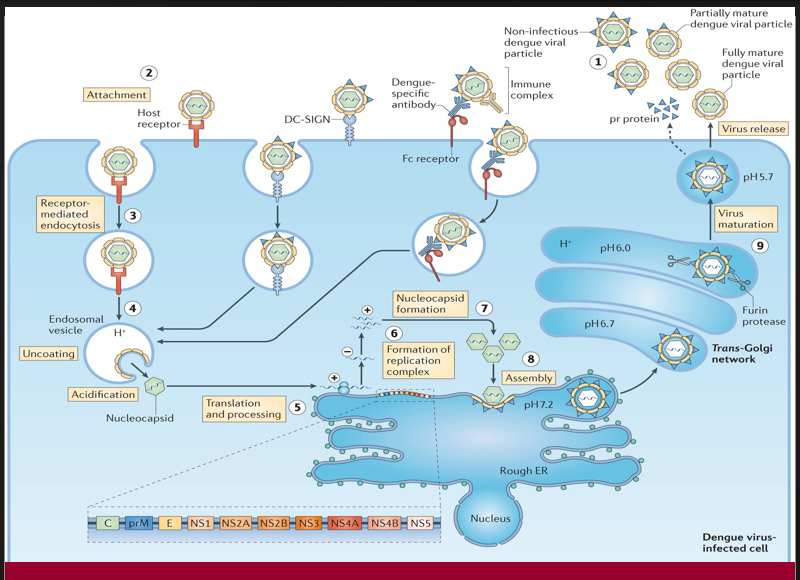
A proteolytic enzyme cleaves prM protein in the Golgi apparatus, converting the virus into its infectious form.
→ Missing Step/Component: Virus maturation (Step 9)
→ Location in cell: Trans-Golgi network (acidic pH, furin protease activity)
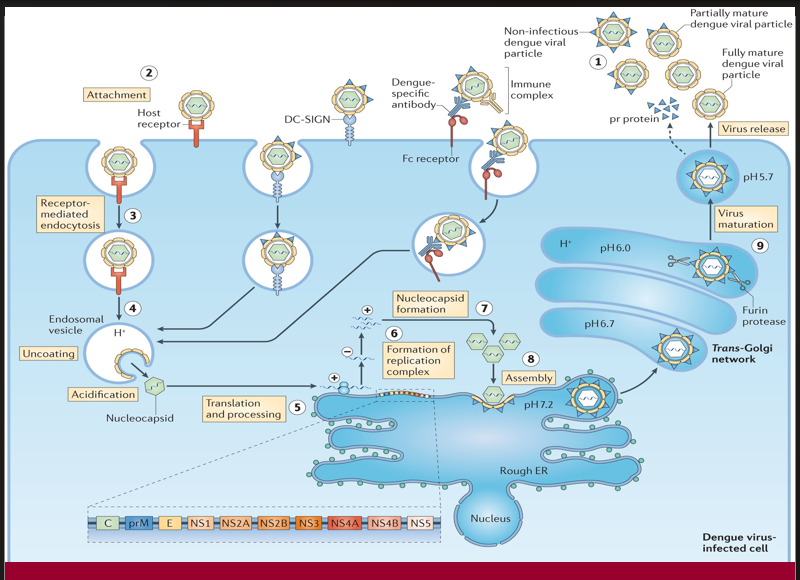
The fully infectious virion exits the host cell to spread the infection.
→ Missing Step/Component: Virus release (step 1)
→ Location in cell: Via exocytosis at the plasma membrane
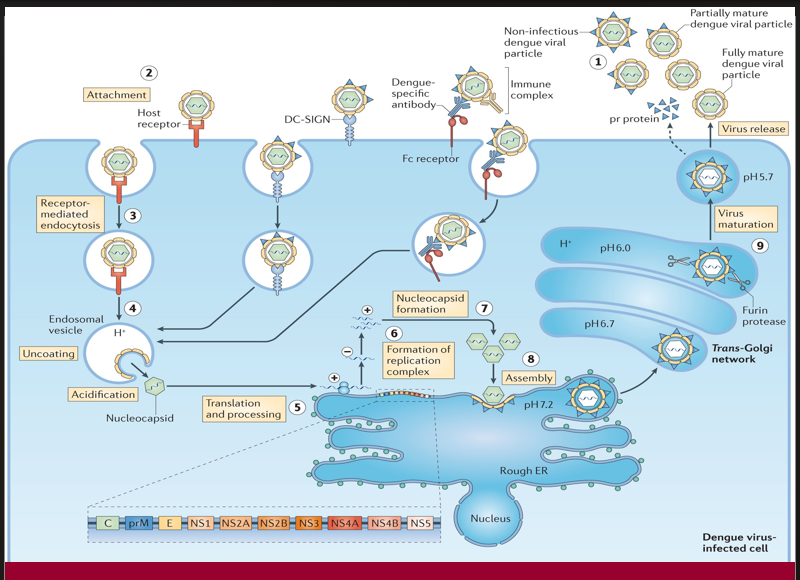
When pre-existing dengue-specific antibodies facilitate viral entry through Fc receptors instead of neutralization, this may lead to increased viral replication.
→ Missing Step/Component: Antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE)
→ Location in cell: Occurs at the cell surface and during Fc receptor-mediated endocytosis
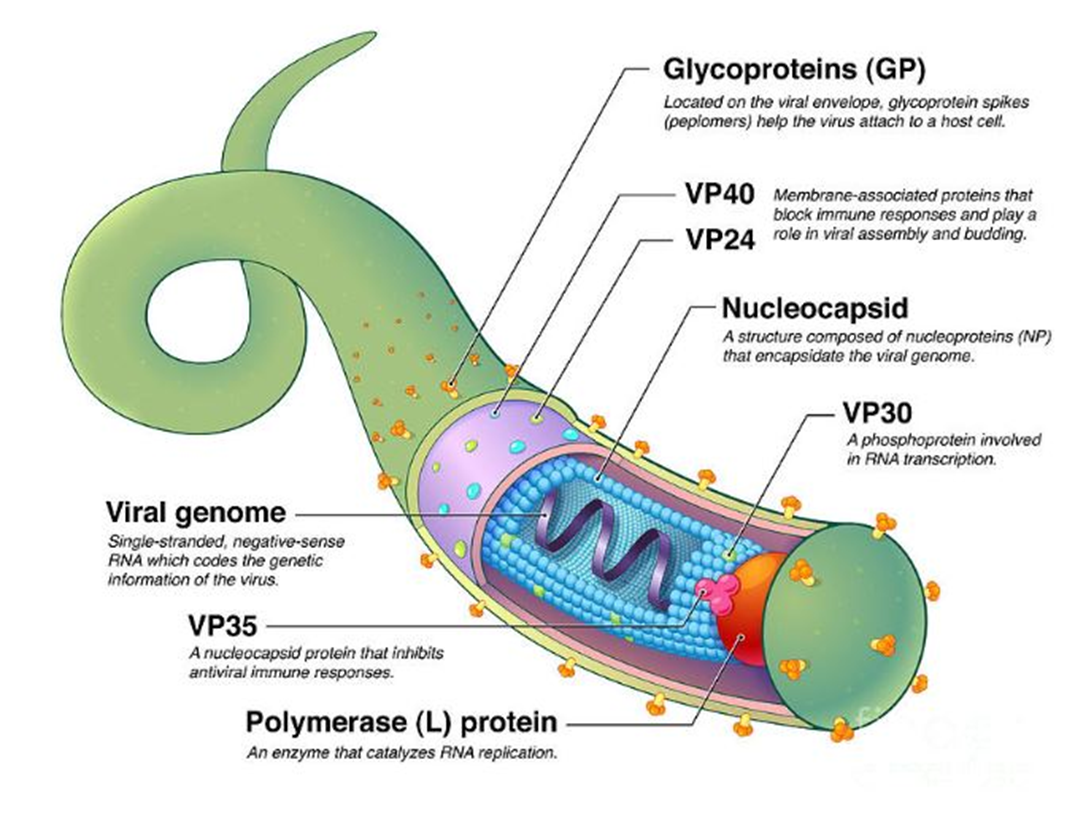
This protein is essential for initiating transcription of the negative-sense RNA genome. Without it, no mRNA can be synthesized.
Missing Component: VP30
Location in virus: Bound to the nucleocapsid complex inside the viral core
Without this structure, the viral RNA would be exposed and vulnerable to host defenses, as it is normally wrapped tightly for protection and stability.
→ Missing Component: Nucleocapsid
→ Location in virus: Encapsulating the viral RNA inside the central core of the virion
This envelope-associated protein facilitates viral entry by binding to host cell receptors and mediating membrane fusion.
→ Missing Component: Glycoproteins (GP)
→ Location in virus: Spanning the viral envelope, projecting as spikes on the outer surface
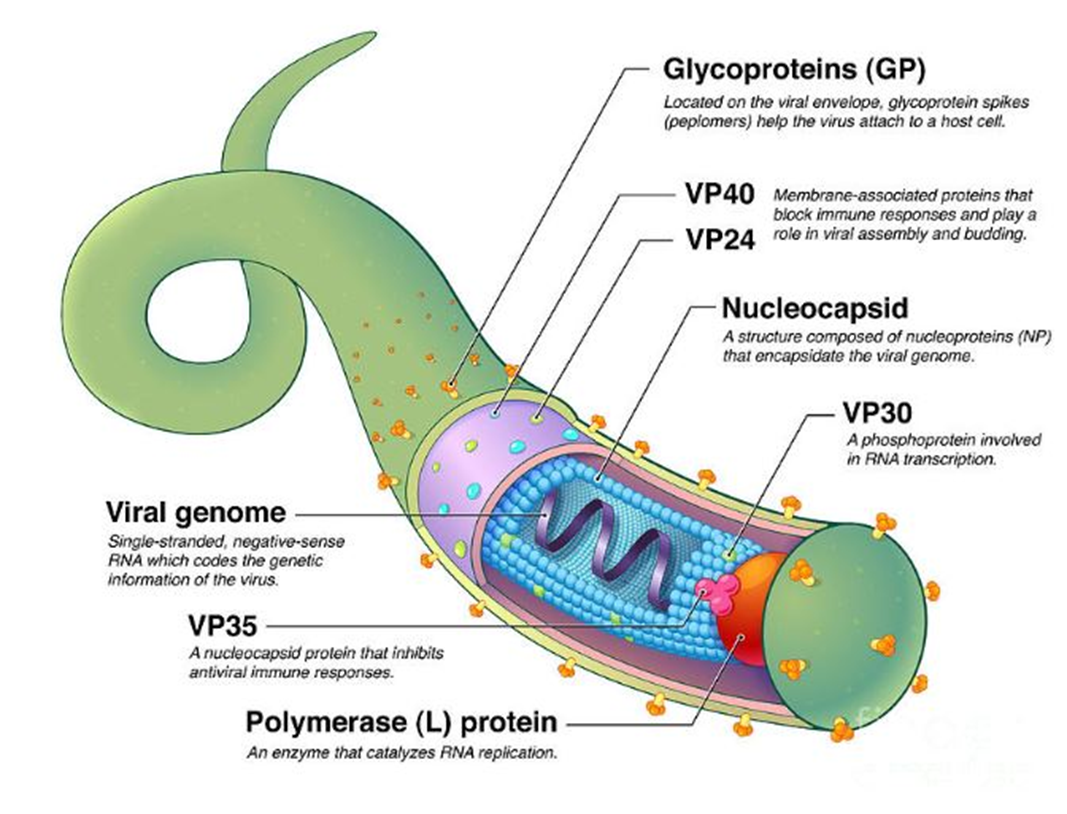
In the absence of this matrix protein, viral particles cannot assemble properly or bud from the host cell membrane.
→ Missing Component: VP40
→ Location in virus: Underneath the viral membrane, forming the inner matrix layer
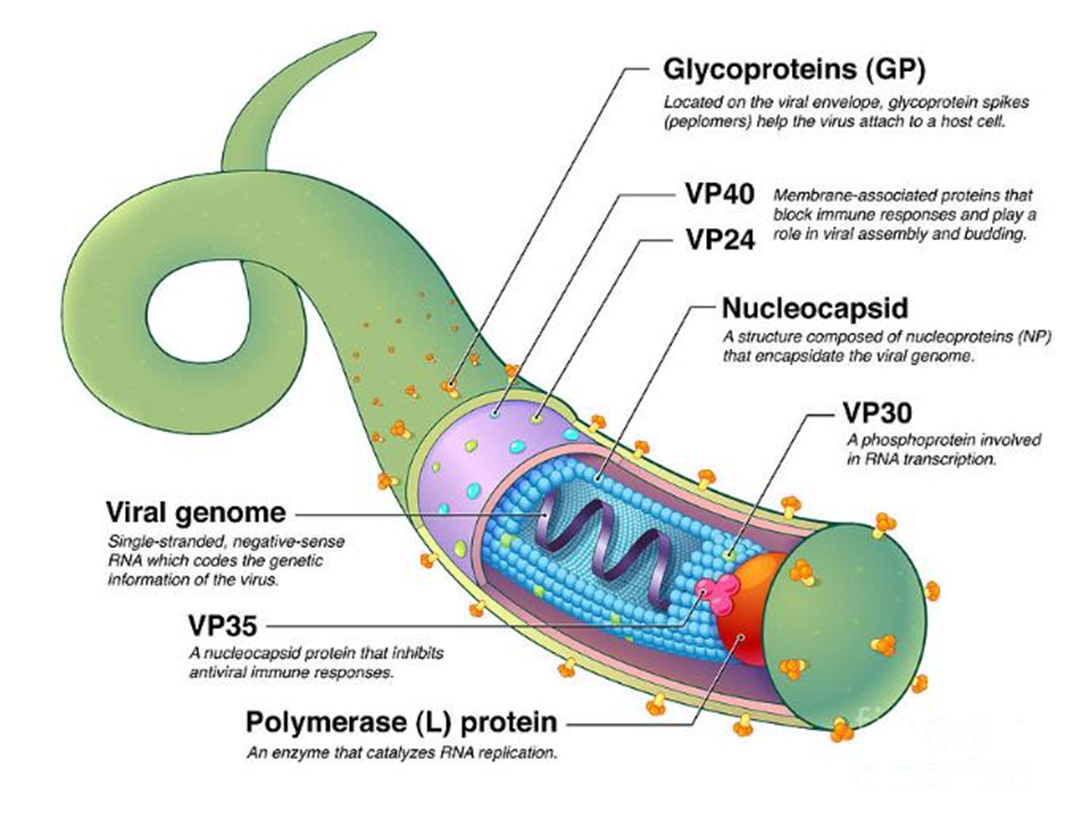
This internal enzyme is responsible for synthesizing complementary RNA strands from the viral RNA template. Its absence halts replication and transcription.
→ Missing Component: Polymerase (L) protein
→ Location in virus: Within the nucleocapsid complex, associated with the viral RNA
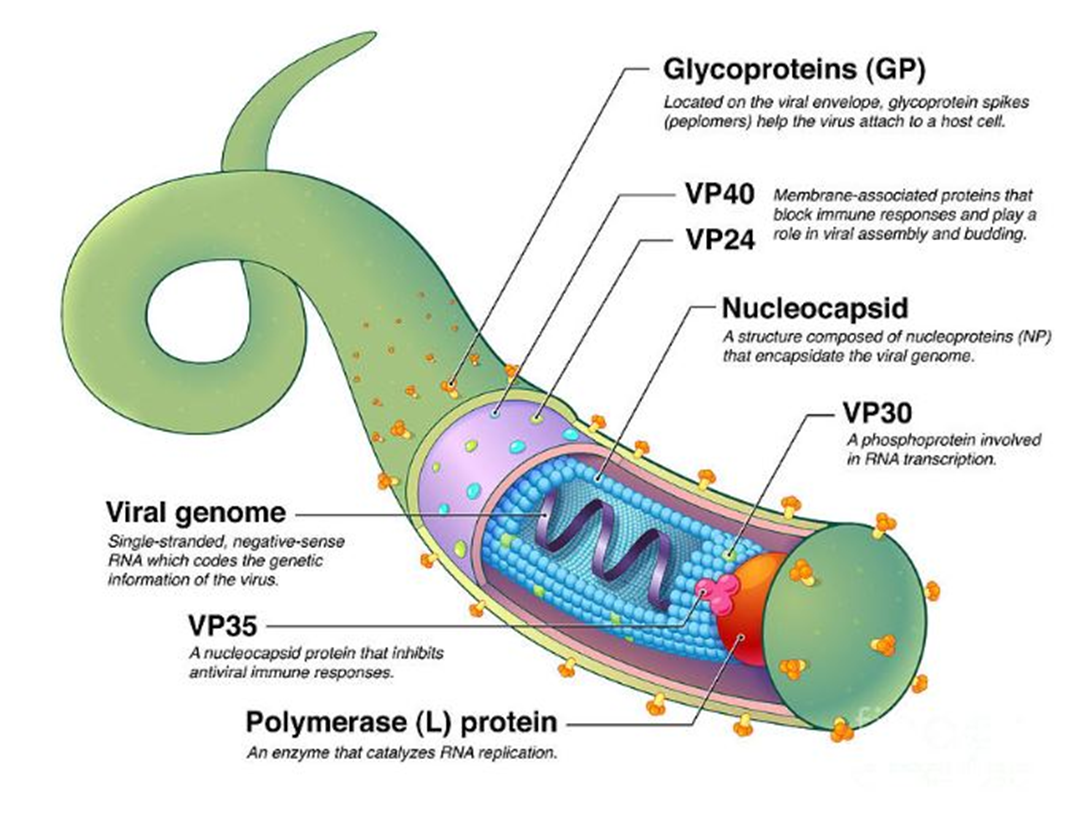
This viral genome is composed of single-stranded, negative-sense RNA and encodes all structural and non-structural proteins.
→ Missing Component: Viral Genome
→ Location in virus: Located at the center of the nucleocapsid structure
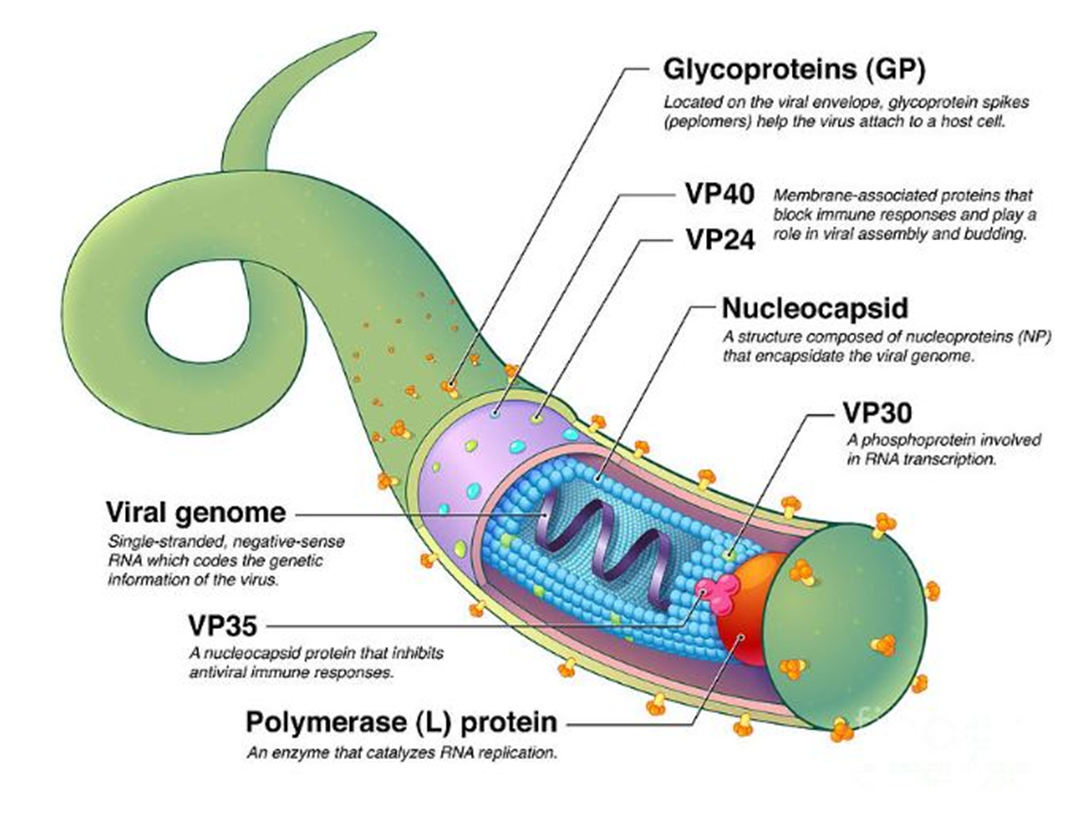
This protein is critical for suppressing interferon responses and avoiding early immune detection. Its loss would lead to strong antiviral signaling by the host.
→ Missing Component: VP35
→ Location in virus: Integrated into the nucleocapsid complex alongside VP30 and the L protein
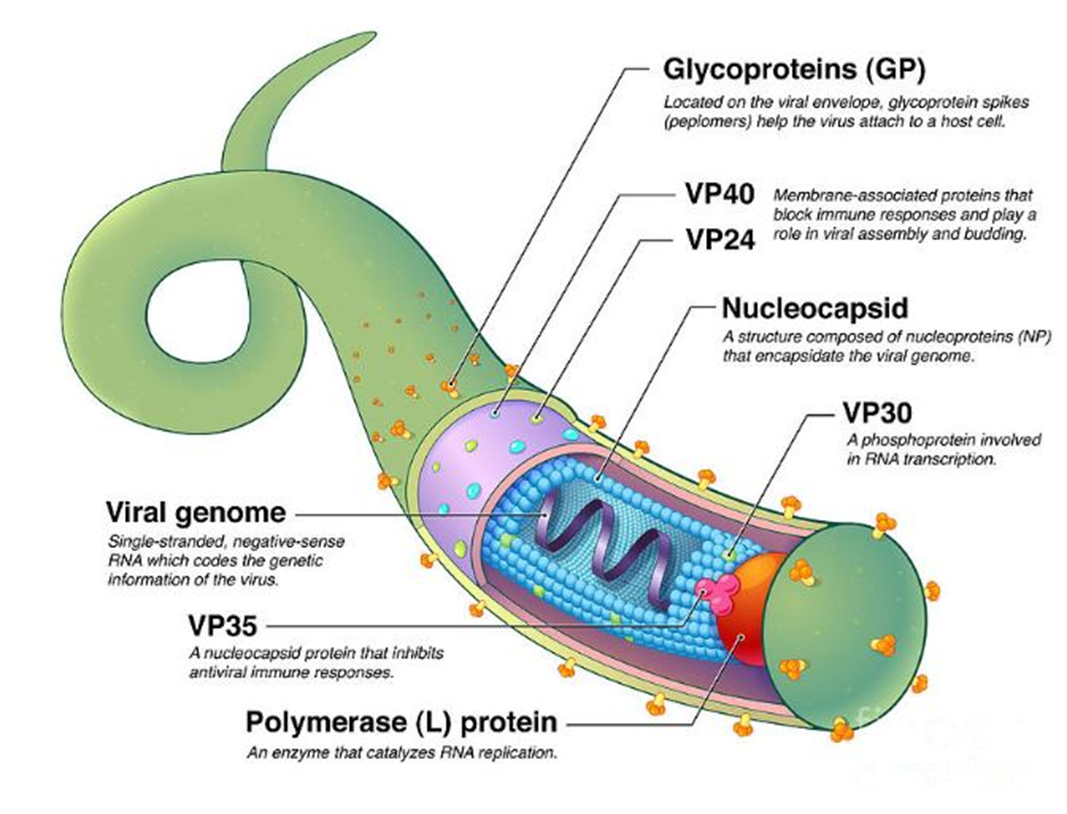
This protein contributes to immune evasion and also assists VP40 in the budding of new virions from the host cell membrane.
→ Missing Component: VP24
→ Location in virus: Membrane-associated, found just beneath the envelope
what is this cell called?
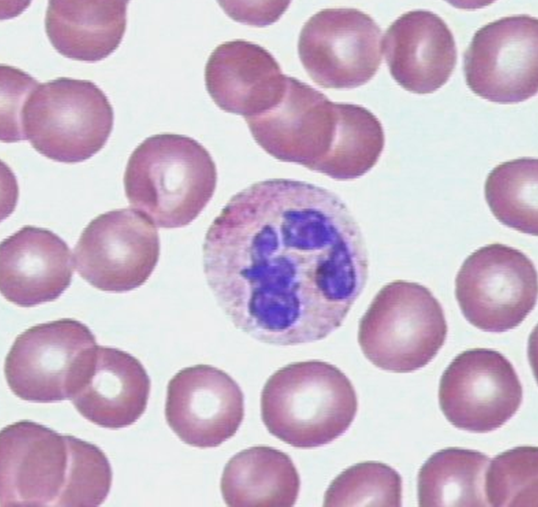
it is a neutrophils
What are these blood cells
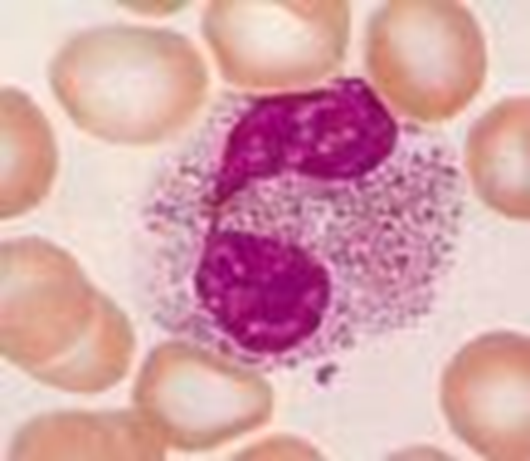
Eosinophils
what are these blood cells?
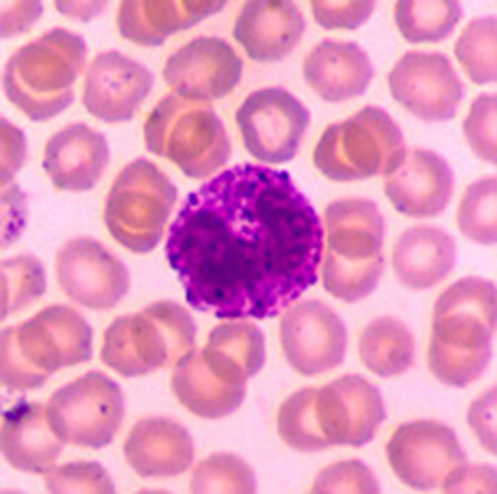
Basophils and mast cells
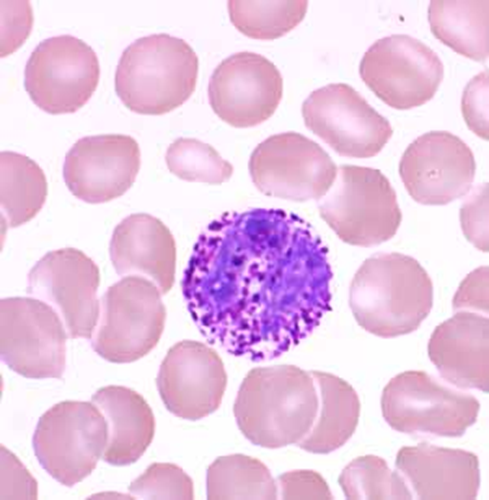
what is this blood cell
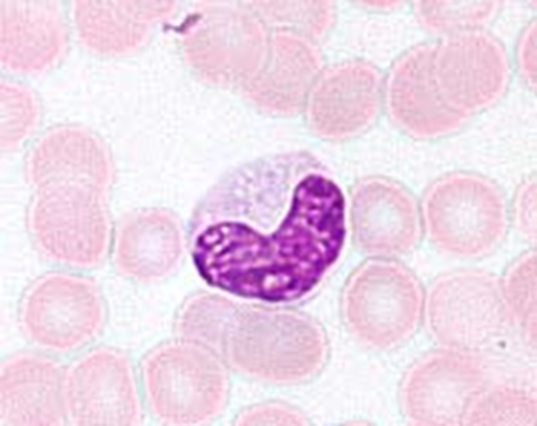
Monocytes
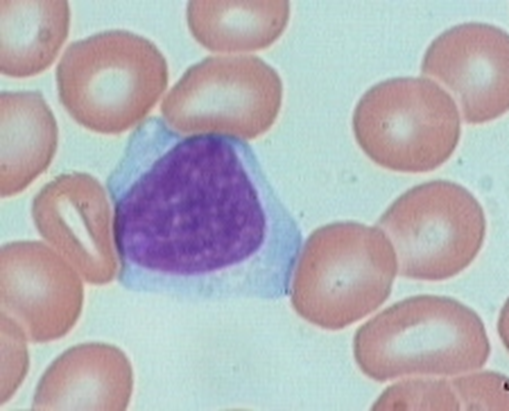
what cell is this?
Lymphocytes

what is this blood cell?

platlets
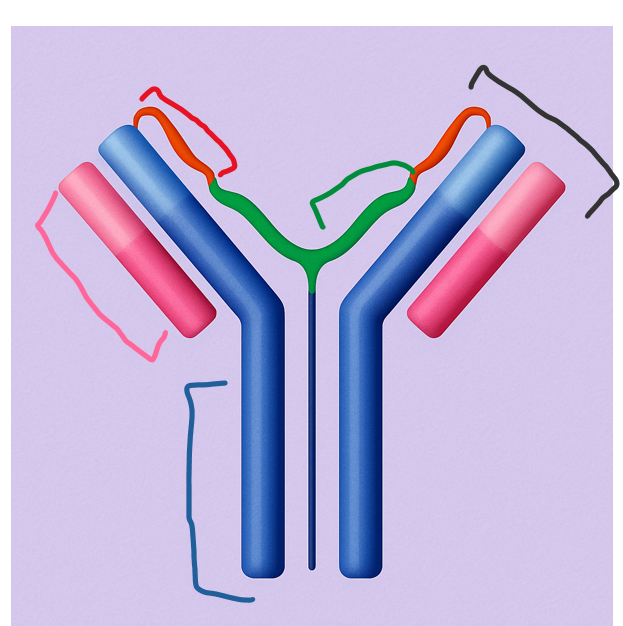
This part of the antibody remains the same among antibodies of the same isotype and determines the antibody's class and effector functions.
Which region is this?
constant region
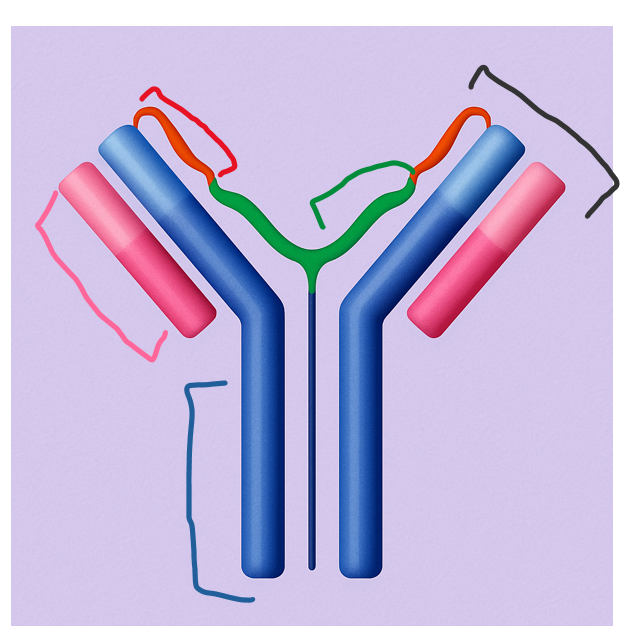
This smaller chain pairs with the heavy chain and helps form the antigen-binding site. It consists of both a variable and a constant region.
Which part of the antibody is this?
light chain
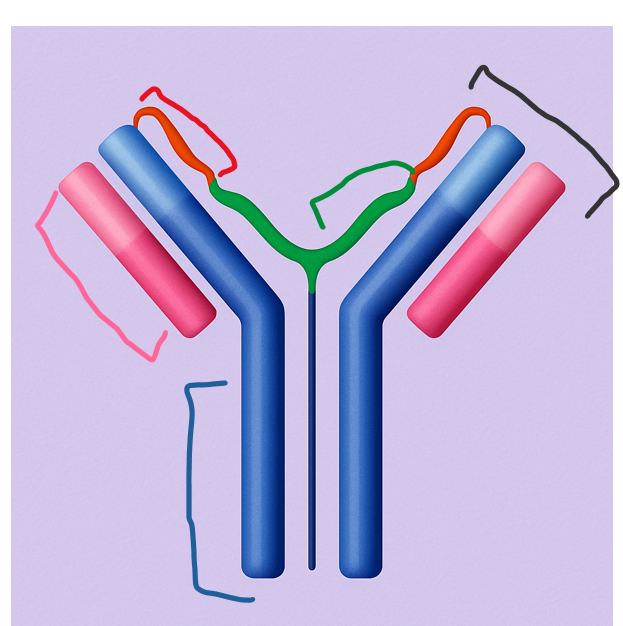
This region is formed by the variable parts of both heavy and light chains and is responsible for binding specific antigens.
Where is the antigen-binding site located?
Antigen-Binding Site
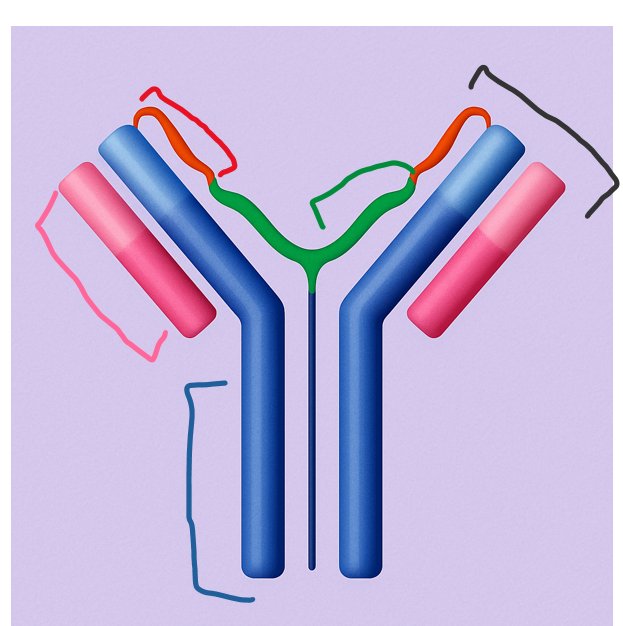
This longer chain forms the core of the antibody structure and contains both constant and variable regions. It plays a key role in immune response signaling.
Heavy chain
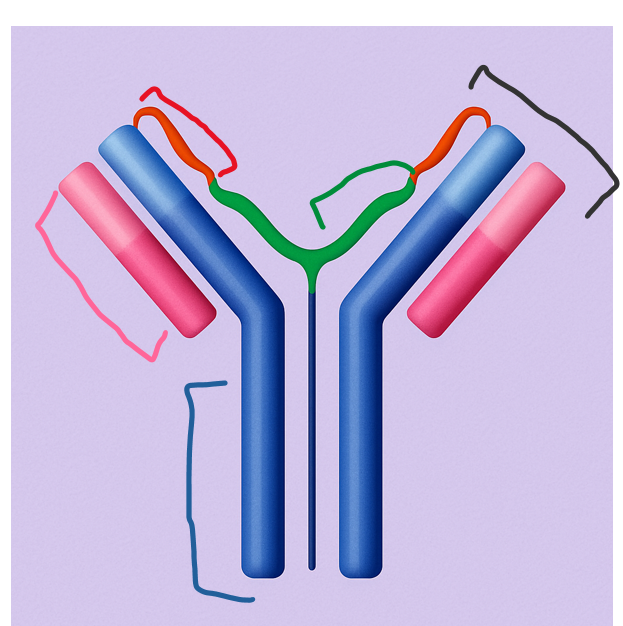
This highly diverse region gives antibodies their specificity by binding unique antigens.
Which part of the antibody is this?
variable region