1 - OOP
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Model, map, reuse, extend
What is the OOP model?
Model the real world problem to user’s perceive;
Use similar metaphor in computational env.
Construct reusable components;
Create new components from existing ones.
Explain OOP’s model, map, reuse, and extend
Encapsulation
Data Abstraction
Single Inheritance
Polymorphism
Persistence
Delegation
Genericity
Multiple Inheritance
Java’s Object Oriented Features
Encapsulation
It associates the code and the data it manipulates into a single unit; and keeps them safe from external interference and misuse.
Data Abstraction
The technique of creating new data types that are well suited to an application. It allows the creation of user defined data types, having the properties of built data types and a set of permitted operators.
No, Java only has partial support
Does Java have full support for Data Abstraction?
Abstract Data Type (ADT)
A structure that contains both data and the actions to be performed on that data.
Class is an implementation of an Abstract Data Type.
Example of an implemention of an ADT?
Class
a set of attributes and operations that are performed on the attributes.
Object Oriented System
A collection of interacting Objects
Object
An instance of a class
represents a template for several objects that have common properties.
A class represents what?
all the properties common to the object - attributes and methods.
A class defines what?
The object’s type
A class is sometimes called what?
Encapsulation
All information (attributes and methods) in an object oriented system are stored within the object/class.
Information can be manipulated through operations performed on the object/class – interface to the class. Implementation is hidden from the user.
Object support Information Hiding – Some attributes and methods can be hidden from the user.
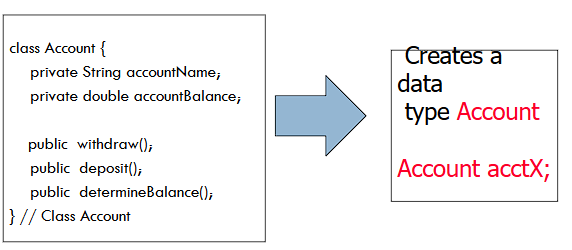
Abstraction
What is being depicted in the example?
Inheritance
New data types (classes) can be defined as extensions to previously defined types.
Super Class
Term for parent class
Sub Class
Term for the child class
If multiple classes have common attributes/methods, these methods can be moved to a common class - parent class. This allows reuse since the implementation is not repeated.
How can Inheritance be implemented in terms of reusing?
Specialization
Specialized behavior can be added to the child class. The behavior will be implemented in the child class
Ex. area() method in the child classes override the method in parent classes
Common Interface
Some methods have common implementation and others don’t.
defines a set of methods that multiple, distinct classes can implement. This allows these classes, despite their different internal implementations, to be treated polymorphically based on their shared adherence to the interface's contract.
Extension
Extend functionality of a class.
Child class adds new operations to the parent class but does not change the inherited behavior.
Multiple Inheritance
Inherit properties from more than one class.
Not supported in Java
Does Java support multiple inheritance
Polymorphism
Allow a single object, method, operator associated with different meaning depending on the type of data passed to it.
Method Overloading
Multiple methods can be defined with the same name, different input arguments.
Method 1 - initialize(int a)
Method 2 - initialize(int a, int b)
Persistence
The phenomenon where the object outlives the program execution.
Greater Reliability
Maintainability
Greater Productivity through Reuse!
Faster Design and Modelling
Why OOP?
Object Oriented Systems can be easily upgraded from small to large systems.
Message-Passing technique for communication between objects make the interface descriptions with external systems much simpler.
Software complexity can be easily managed.
Benefits of OOP