Perception-Cognition Exam #1
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Behaviorism
people are environmentally driven and shared by nature, this view dominated USA from 1900s-1940s, only measure was behavior and relied on rigorous scientific methods with no concern for internal mechanisms
Pavlov
Classical Conditioning
Stimulus Response
conditioned the dogs
Watson
Behaviorist Manifesto
Little Albert experiment
humans can be classically conditioned
thinking is subvocating
Thorndike
Connectionism
Animals and puzzle boxes
Skinner
Radical Behaviorism
Positive reinforcement in education
operant conditioning
Turn away from Behaviorism
Came from how children learned words/phrases but used them incorrectly either in turns of grammar or creating their own sentence (I hate you mommy!)
Cognitive maps
how animals can remember a layout like a maze
Bandura
learning can be modeled or socialized by watching someone else do it (like watching an adult beat the shit out of a boba doll)
Confirmation Bias
Selectively seeing results/science to see what we want to see
Probabilistic Reasoning
complex and ever-changing problems that need reasoning
Availability Heuristics
What is more available to you will be more used (Sharks may be seen as more dangerous then horses when horses are indeed more dangerous)
Post-Mortem Analysis
studying the brain after a person dies, used to be the only way to see the brain
Patient Tan
person who could only speak in words like tan and through postmortem analysis a specific part of the brain was found to be affected
Brain Scan
can look at lesions, tumors, etc..
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
can disrupt brain functions for medicinal or research purposes
Electrical Recordings
record electrical brain activity
EEG
measures electrical brain activity
MRI
looks at structure of the brain with magnets
X-Rays
look at structure of body with radiation
Computer Tomography
3-D scan of brain and used functionally
Subtraction Method
Activation during task-Activation during control=Activation involved in a task
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
injects radiation in body and then put under PET scanner to see where blood is going
Functional MRI (fMRI)
dissects magnetic property of blood and is similar to PET scan
MEG
measures the magnetic field coming off your brain
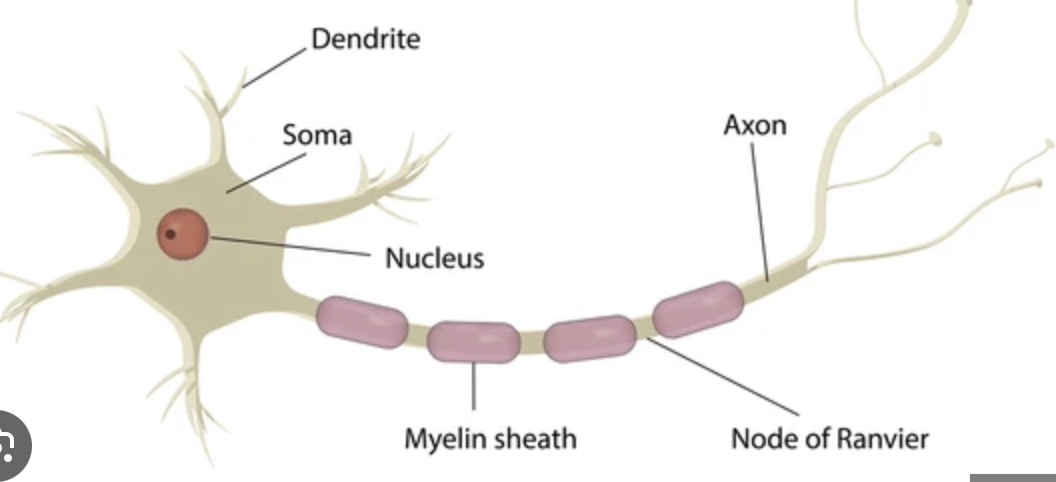
Parts of a Neuron
Soma-cell body and contains nucleus and all info
Dendrites-receive info from other sensory cell and can develop new dendrites
Axon-sends and transmits signal
Myelin Sheath-like white matter in brain
Terminal Button-where neuron stores neurotransmitters and then sends it via synaptic connection
Acetylcholine
is associated with arousal, sleep, memories, dsyregulation associated with memory loss and Alzheimers. Is the ONLY neurotransmitter to connect motor neuron to motor cells, nicotine can mimic acetylcholine
SSRI
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor, drug used for those with mental health issues
Dopamine
nuerotransmitter for behaviors, reinforces behaviors and associated with addiction because the reward circuit becomes conditioned to drink, gamble, etc.. and associated with movement and planning with lack of dopamine associated with parkinson (too little) and schizophrenia (too much)
Serotonin
Mood regulation and regulation of aggression and impulsivity, eating and driving behaviors
Midbrain
reticular activating system which monitors and regulates consciousness, heartbeat, breathing regulation (also includes the substantial nigra and colliculus)
Hindbrain
Includes Periaqueductal Grey Matter and Pons+Cerebellum, associated with fight or flight, defensiveness, startling, reflexes and coordination with body
Basil Ganglia
motor coordination and planning
Limbic System (Forebrain)
associated with emotions, reading people, memory/learning, fear reflexes, emotional stability
Hippocampus
involved in new and explicit memories
Thalamus
relay station between cortex and nest of brain, dysfunction linked to schizophrenia
Hypothalamus
controls fighting, fleeing, feeding, and fucking
Endocrine system
hormonal system in hypothalamus
Cerebral cortex
linked to speech
Parietal lobe
front area is a sensory strip, behind is involved with spatial relationships
Temporal Lobe
language comprehension, auditory processing, object recognition
Occipital Lobe
just processes visual things
Perception
how your brain processes sensory information
Top-Down Processing
Beliefs expectations impose structure on raw stimuli

Bottom-Up Processing
constructing a perceptual experience from parts of sensory
Linear Perspective
perceive depth with parallel lines
Relative size
comparative things look different depending on background
Proximity
if they look like they do go together then we group them together which is based on space
Similarity
how we group things together
Continuity
we will see connection even if there is none
Closure
our mind uses dead spaces and gaps and fills them in
Symmetry
pairing things together due to shape, size, and orientation
Size Constancy and Shape Constancy
Size Constancy: things look bigger when closer and smaller when further away
Shape Constancy: if you look at things from different angles we know its shape
Color Constancy
depending on background, colors can look different even if there the same (grey checkerboard thingy)
Sensory Adaption
our senses normalize common senses so it doesn’t alert you as much
Change Blindness
when focusing on busy scenes you may not notice other changes
Inattentional Blindness
you don’t recognize changes or even know it was there the whole time
Agnosia
problems with attention of..
Spatial Neglect
you perceive but can’t attend to certain things (like certain people with their left side of vision)
Target, Distraction, Hit
Target: what your looking for
Distraction: everything else in the environment/situation
Hit: when you find the target/s
Correct Rejection, False Alarm, Miss
Correct Rejection: looking but target was not there
False Alarm: when you think you’ve found the target but it was not the target
Miss: when you can’t find the target but it was there
Feature Search
distractors don’t matter because the target has a very specific feature (red X in a sea of blue T)
Conjunction
multiple features are needed to find a target (blue X that is sideways and has stripes, etc..)
Parallel and Serial Search
Parallel Search: searching a scene all at the same time
Serial Search: searching element by element to find a target
Feature Integration Theory
How we attend to our environment to find our targets
Step 1: Parallel Processing of Features or first seeing if the target pops out with a scan of environment
Step 2: Serial Processing of combination where if a scan does not work then you slow down and hunt for your target feature by feature
Filer Attention
Deciding which information we should or shouldn’t pay attention to
Broadbents Model of Selective Attention

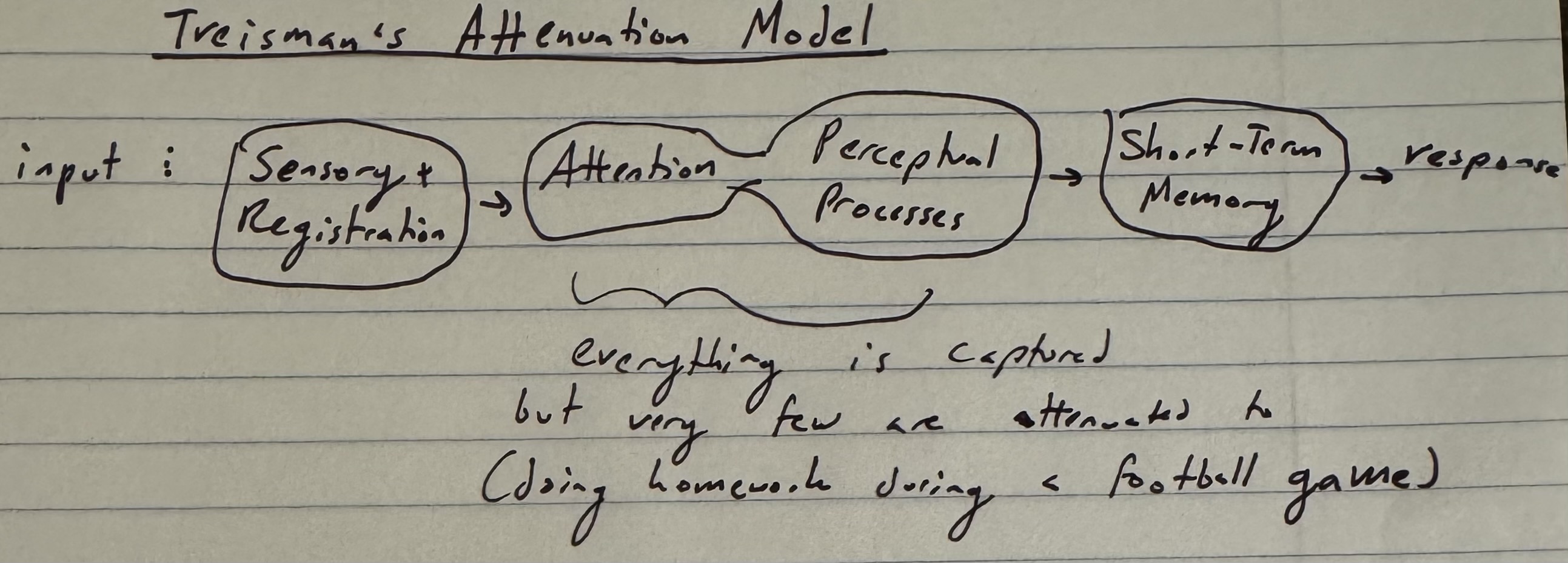
Treismans Attenuation Model
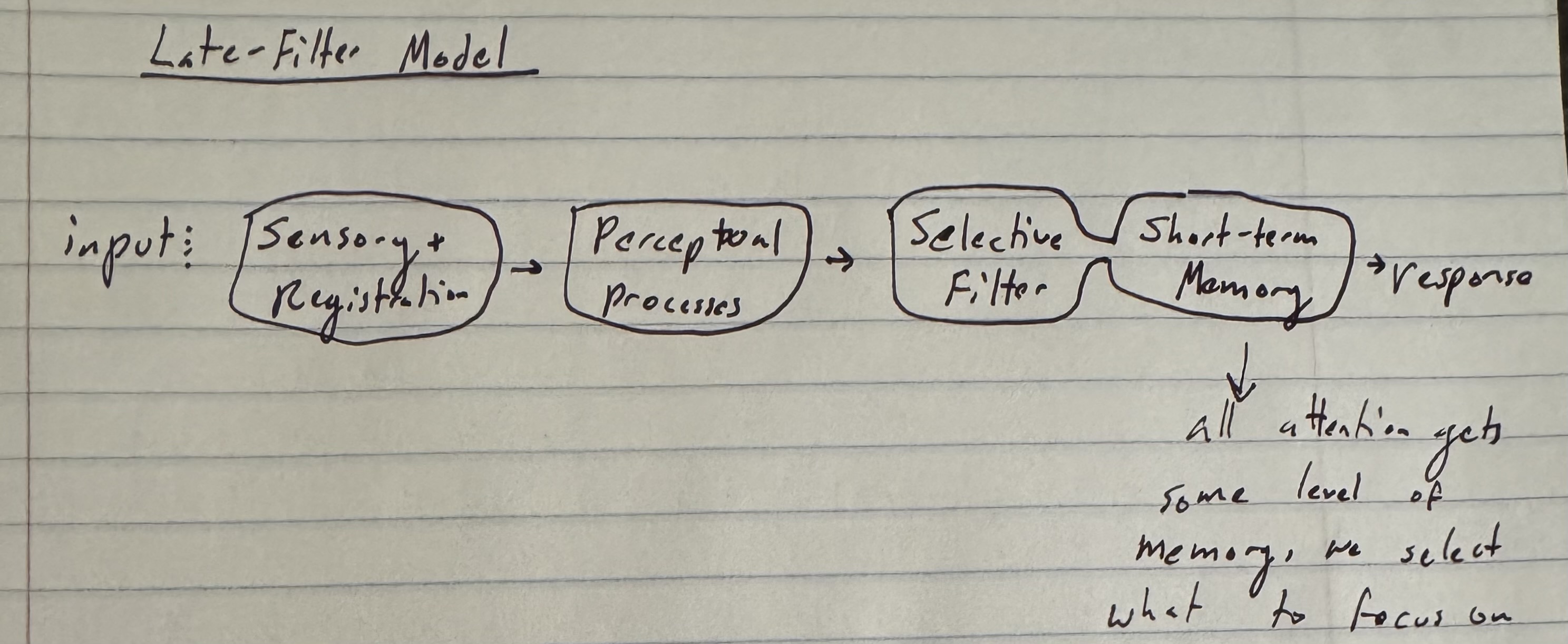
Late-Filter Model
Spotlight Attention
solely focusing on a task, helps improve mental processing, being ‘in the zone’
Binding Attention
keeping our attention locked and putting our attention and memory together to complete a task
Divided attention
trying to focus on multiple things at once, not always a bad thing like driving and reading signs on the road
Controlled Task
tasks that require/are accessible to conscious control (like when first learning something like tying your shoe)
Automaticity
ability to perform same task with little to no conscious attention
Automatic Processes
-concealed from consciousness
-unintentional
-use few attentional resources
Automatization
Process of a controlled process becoming automatic (reading)
The Stroop Effect
showing colors that match the word and then showing words with different colored ink to measure response times

Dual Task
doing two tasks at once and seeing if they interfere while single task is doing one thing
Priming
seeing images or situations that prime your subconscious which influence how you act
Tip of the Tongue Blindsight
its hard to bring something to our consciousness and we don’t have as much access to out subconscious as we think