Health assesment exam 1
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
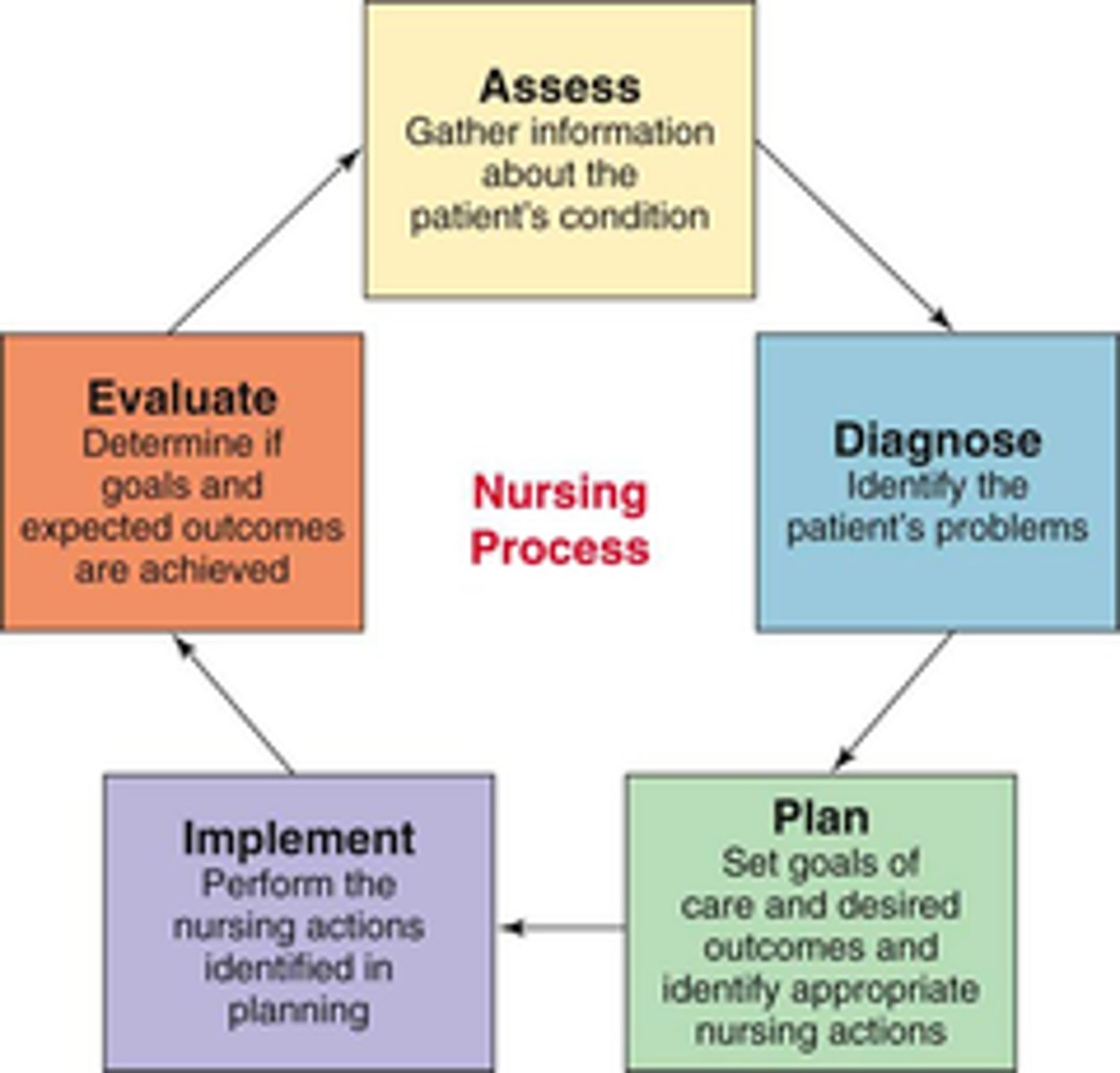
nursing process
1. assessment
2. diagnosis
3. planning
4 implementation
5. evaluation
ADPIE
first-level priority
Emergent, life threatening, and immediate

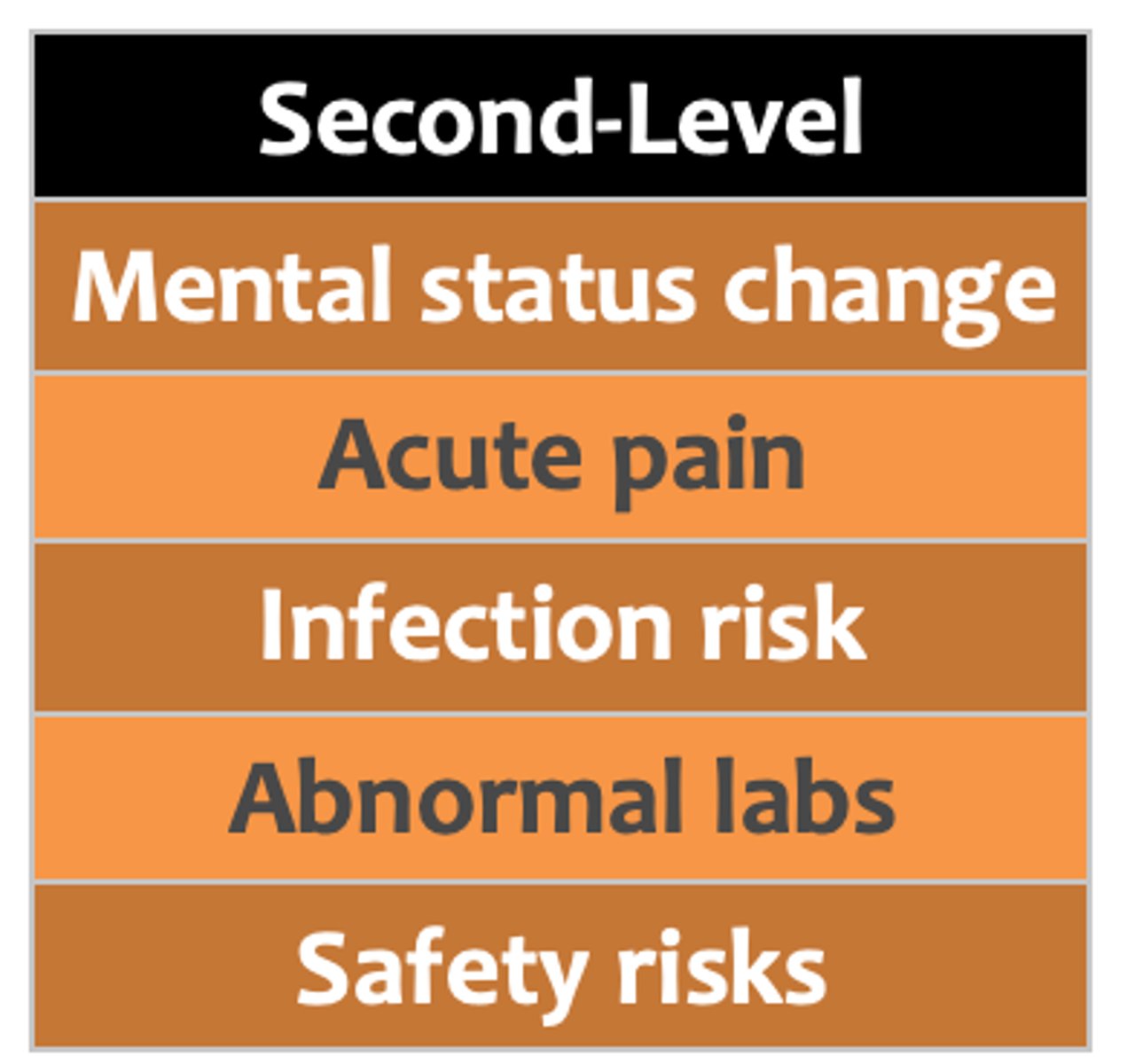
second-level priority
next in urgency, requiring attention to avoid furthur decline
subjective data
What patient says about himself or herself during history taking

objective data
observed when inspecting, percussing, palpating, and auscultating pateint during physical examination
database
formed from subjective and objective data, pateints record, and lab studies
-cluster data that is related
abductive reasoning
used with incomplete data to produce an initial diagnosis
deductive reasoning
used as you complete your assesment and apply knowledge you have about physiology and pathophysiology
inductive reasoning
used as you consider signs and symptoms of disease as a guide for decision making
clinical judgement model
structure for nursing education to improve clinical judgement skills
1. recognize cues
2. analyze cues
3. prioritize hypotheses
4. generate solutions
5. take action
6. evaluate outcomes
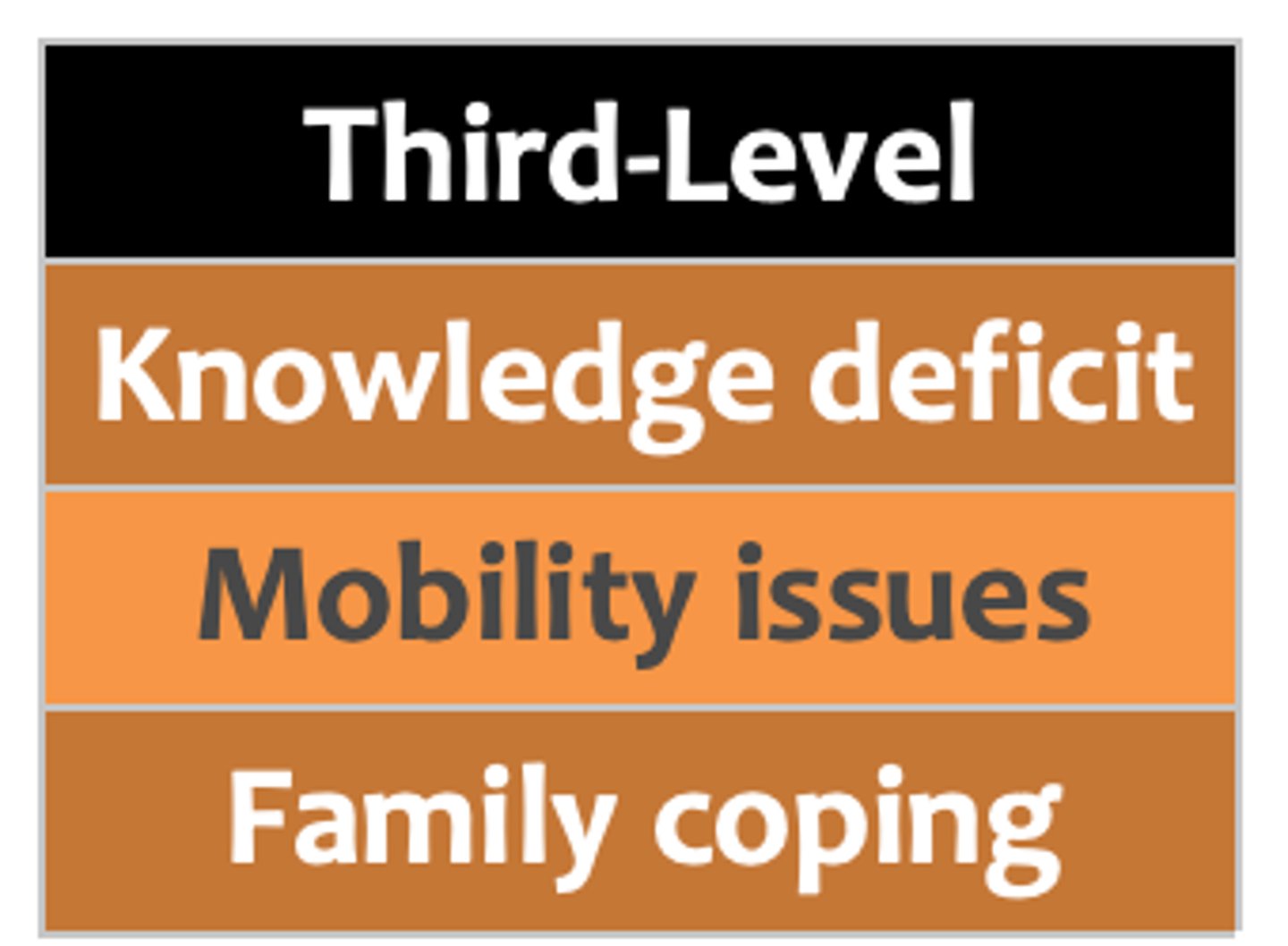
third-level priority
Important to patient's health but can be addressed after more urgent problems are addressed
collaborative problems
approach to treatment involves multiple disciplines
evidence based assesment
-current and best clinical practice based on reasearch standards focused on systematic reviews of randomized clinical trials
-utilizing EBP with provider experience leads to better patient outcomes
complete total health database
-includes health history and physical exmaination
-describes current and past health states
-provides baseline to measure all future changes
-helps from the first diagnosis
focused or problem centered database
This is for a limited or short-term problem. Here, you collect a "mini" database, smaller in scope and more targeted than the complete database. It concerns mainly one problem, one cue complex, or one body system.
follow-up database
-The status of any identified problems should be evaluated at regular and appropriate intervals
-Is it getting better or worse?
-used in all settings
emergency database
rapid collection of the database, often compiled concurrently with lifesaving measures
nurse-initiated intervention
actions performed by a nurse without a physician's order
Provider-initiated/dependent interventions
these are interventions nurses initiate as a results of a provider's rx (written, standing or verbal)
collaborative interventions
interdependent nursing actions performed jointly by nurses and other members of the health care team
holistic health
-mind, body, and spirit are interdependent
-individuals and the environment are open systems
-each person is responsible for their health state
-health promotion and disease prevention from the core fo nursing

immigration and healthcare
-some patients you come in contact with as a nurse may have been born in a foreign country.
-It is important to consider lanuage barriers
social determinants of health
The conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age, shaped by the distribution of money, power, and resources at global, national, and local levels
-EBP indicates that poverty has greatest influence on health status
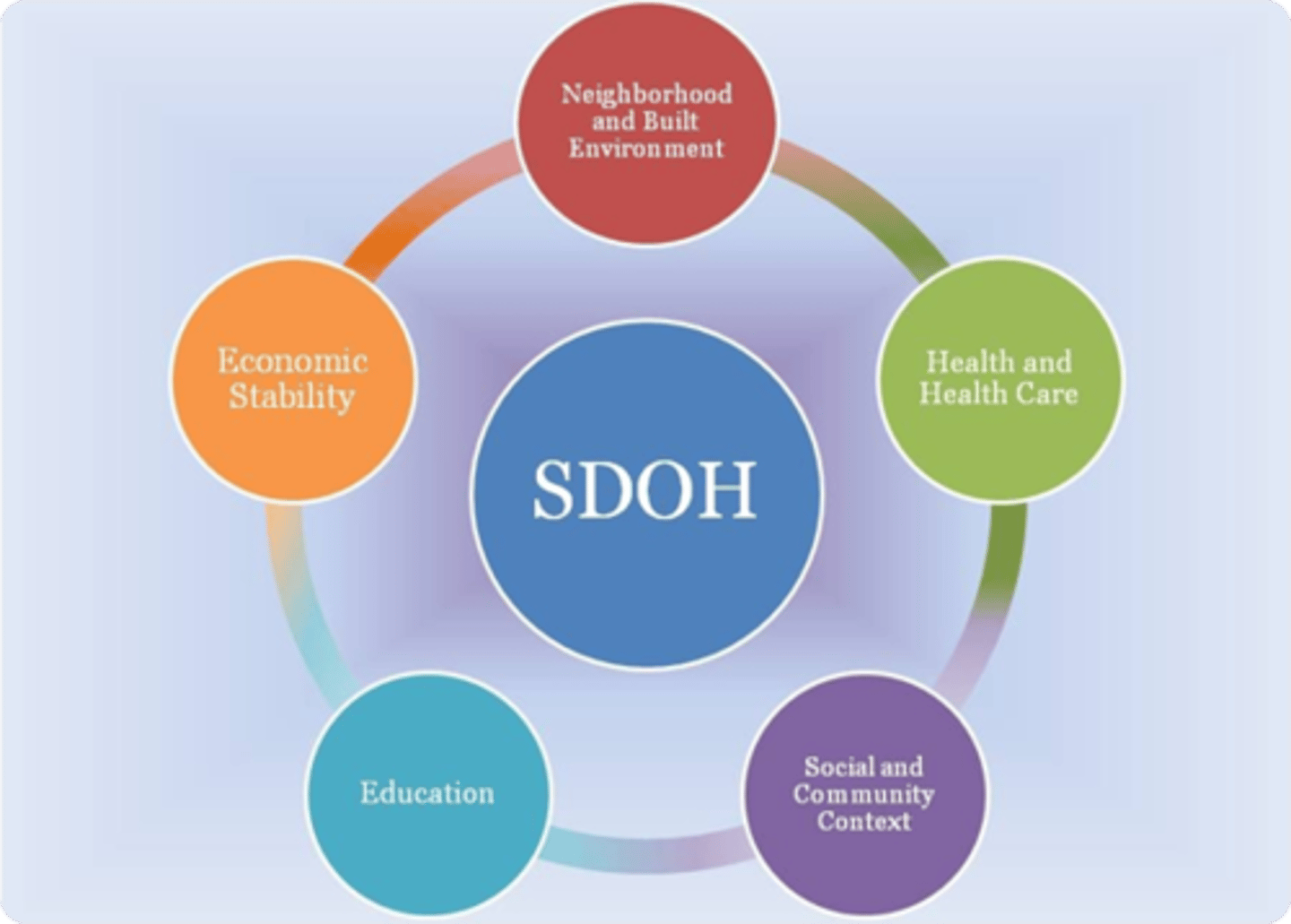
healthcare disparities
the population-specific differences in the presence of disease, health outcomes, and qualities of healthcare in different social groups
vulnerable populations
ethnic and racial minorities, people with disabilities, and the LGBT community
National Standards for Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services in Health Care
published by the office of minority health to improve quality of care and eliminate health disparities
four basic concepts of culture
1. learned
2. shared
3. adapted
4. dynamic
race
self-identification with a group who share similar and distinct physical characteristics.
ethnicity
social traits, nationality, regional culture, ancestry, and language
Acculturation
2 or more cultures encounter eachother and exchange ideas, values, and behaviors
assimilation
assuming characteristics of the dominant culture
acculturative stress
Losses and changes associated with integration of new beliefs
religion and spirituality
Organized system of beliefs versus individual's unique experience
Biomedical/scientific theory
all events in life have a cause and effect
naturalistic or holistic theory
Belief in the forces of nature that there is balance in the universe (ex: yin/yang theory)
magicoreligious perspective
illness is caused by supernatural powers and can be treated by voodoo or witchcraft
-forces of good and evil
cultural competence
-understand one's own heritage based values, beliefs, attitudes, and practices
-identify meaning of health to patient
-understand how health care systems works
-accquire knowledge about social backgrounds
-become familiar with languages, interpretive services, and community resources avaliable
becoming a culturally sensitive practitioner
1. cultural awareness: recognize your own culture before you can work with to understand a different culture
2. cultural knowledge and skills: learn about other cultures
3. cultural humility: see value in other beliefs
completing cultural assesment
- do not apply stereotypes but listen and learn
-recommended list of domains of interest: heritage, health practices, communication, etc.
spiritual assessment
FICA
-faith
-importance (how is faith or belief important in their life)
-community
-address/action: how should health care team address issues related to patient