OP Part A Khan Study Guide Answers
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is hydroxyapatite?
storage of calcium / skeleton form/ basically our bones
What are the normal functions of osteoblasts and osteoclasts?
osteoblasts- bone formation
osteoclasts- bone resorption
Discuss phosphate:
a) functions
b) absorption
Functions- regulate kinases, bone structure, energy
Absorption- through the intestines by passive diffusion
Discuss calcium metabolism
Absorbed in intestines, then travels to bone, filtered and reasborped in the kidney, then excereted by the kidneys
Differentiate sources of Vit D2 and Vit D3
Vit D2- PLANTS
Vit D3- ANIMALS, or by UV Light
Do Vit D2 and Vit D3 have different biological properties?
NO
What is the precursor of Vit D in the skin
7- dehydrocholesterol
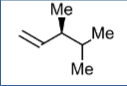
Distinguish Ergocalciferol side chain
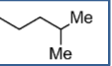
Distinguish Cholecalciferol side chain
Details of 1st hydroxylation to form calcitriol
For the 1st hydroxylation we either take Cholecalciferol or Ergocalciferol and add an -OH group on position 25 to form 25-hydroxycholecalciferol. This takes place in the liver.
Details of 2nd hydroxylation to form calcitriol
For the 2nd hydroxylation we take the 25-hydroxycholecalciferol and add an -OH group to position one to form calcitriol. This takes place in the kidneys.
Which hydroxylation is hormone dependent/independent?
1st hydroxylation- hormone INDEPENDENT
2nd hydroxylation- hormone DEPENDENT
Know effects of Vit D on:
kidney
bone secretion
intestine
kidney- increase Ca and P reabsorption
bone secretion- increase osteoclast activity
intestine- increase Ca and P absorption
Regulation of PTH secretion by Vit D
Basically Vit D turns off PTH
More specifically: Vit D binds to nuclear receptors in PTH gland and inhibits PTh synthesis and release
Receptor activation of Vit D
Vitamin D receptor is a nuclear receptor not located in the nucleus, but travels to the nucleus (if that makes sense)
How is PTH secretion regulated by Ca levels?
High Ca= Inhibit PTH secretion
Low Ca= activate PTH secretion
Discuss PTH’s effect on the kidney
increase Ca reabsorption
decrease P reabsorption
NOTE: opposite of Vit D
Discuss PTH’s catabolic effect on bone
Path: PTH—> PTH receptor (osteoblast) —> RANKL→ RANK→ Osteoclast precursor->osteoclast
we stimulate osteoclasts to resorb bone
Discuss PTH’s anabolic effect on bone
stimulate osteoblast maturation
inhibit osteoblast cell death
release growth factors from osteoblasts
Discuss PTH’s effect on the intestine
increase calcium absorption
increase phosphorus absorption
Which gland is calcitonin secreted from?
Thyroid
Is the total sequence of AA needed for calcitonin?
YES
What are triggers for calcitonin release?
increase serum Ca
What are calcitonin’s effects?
directly inhibits bone resorption
inhibits Ca and P reabsorption from kidney
decrease Ca absorption from GIT
What is FGF’s role in phosphate metabolism?
promotes urinary phosphate excretion
suppresses Vit D activation