BIOL 251 Microbiology Week 13 & 14 Lecture Notes
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microbiology: An Introduction 13th Edition - Ch. 13 & Ch. 18-19
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Pathogens
Disease-causing microorganisms
Pathogenicity
Ability to cause dieases
Virulence
Degree of pathogenicity
Infection
When the body is invaded by a harmful microorganism
Disease
When the body’s health is affected by infection
Mucous membranes
Skin
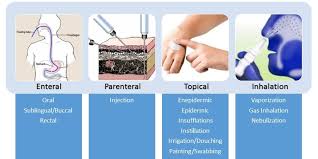
Parenteral route
What are some portals of entry for pathogens?
Parenteral
_____ Route: Direct deposition beneath the skin or membranes
ID
LD
____50: Infectious does for 50% of a sample population
Skin, inhalation, ingestion
measures microbe virulence
____50: Lethal does for 50% of a sample population
measures potentcy of toxin
ligands
glycocalyx
Mannose
Adherence of Microorganisms to Host Cells
Surface molecules on pathogens
Adhesions or _____
Located on → _____ or fimbriae or pili
Glyco- or lipoproteins
Bind to complementary surface receptors of host cell
_____ - sugar
Capsule
Cell wall components
Enzymes
Antigenic variation
Invasins
What are some ways microbes penetrate host defenses?
phagocytosis
Capsule;
Glycocalyx around cell wall
Impairs _____
M
Opa
Waxy
Cell Wall Components
__ protein resists phagocytosis
__ protein allows attachment to host cells
_____ lipid resists digestion

Coagulase
Kinases
Hyaluronidase
Collagenase
IgA
Enzymes
_____: Coagulate fibrinogen
_____: Digest fibrin clots
_____: Digests polysaccharides that holds cells together
_____: Breaks down collagen
_____ Proteases: Destroy IgA antibodies
antigens
antibodies
Antigenic Variation:
Pathogens alter surface _____
Evade destruction by host _____
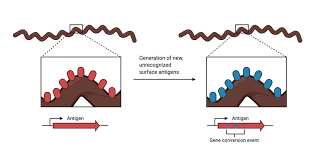
Invasins
Actin
_____: Surface proteins produced by bacteria
Rearrange _____ filaments in cytoskeleton
Cause membrane ruffling
Use actin to move from one membrane
to the next
Use host’s nutrients
Direct damage
Toxin production
What are some ways microbes damage host cells?
Siderophores
Using Host’s Nutrients;
_____: Proteins secreted by pathogens
Binds ions more tightly than host cells
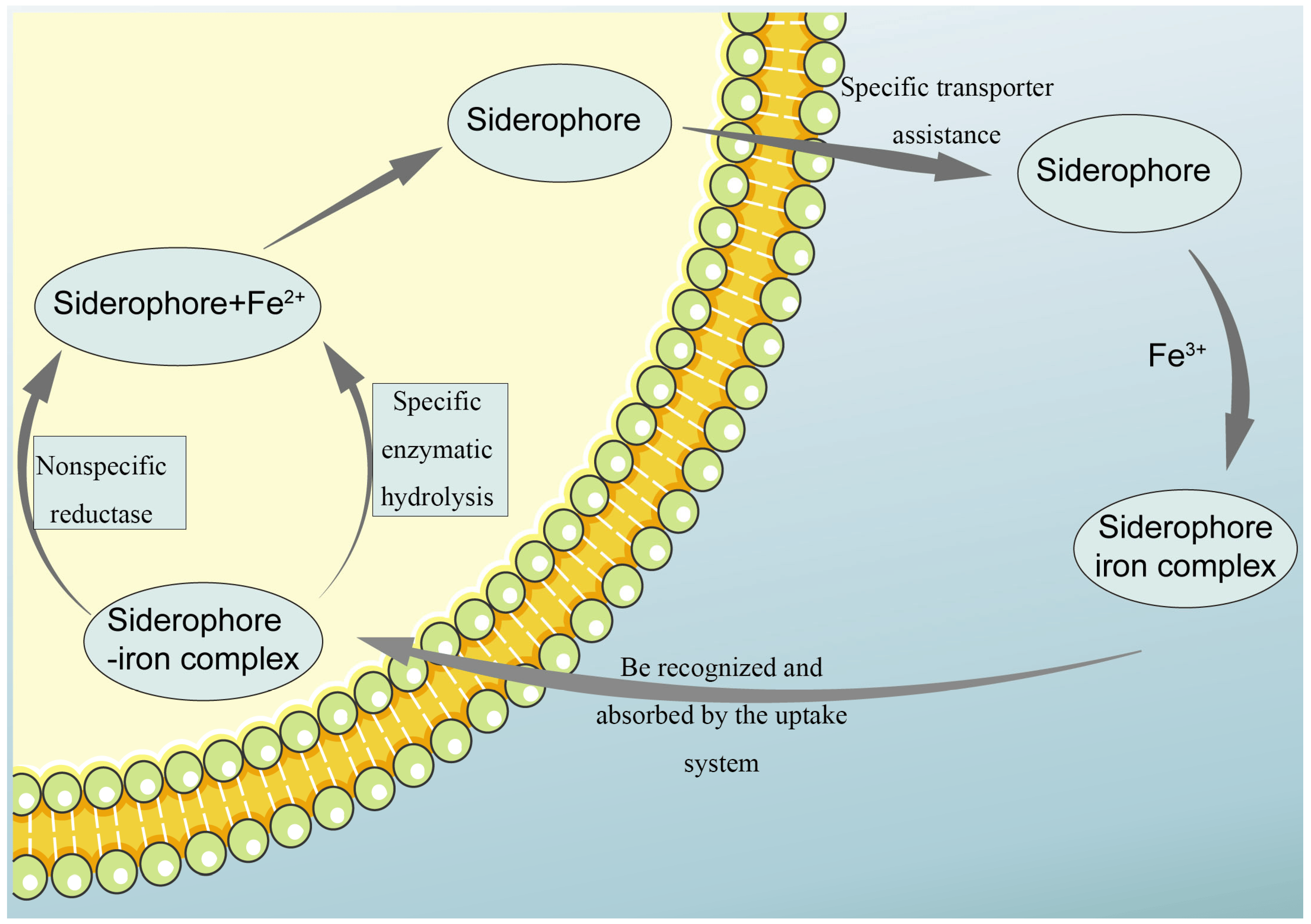
Function
waste
ruptures
Direct Damage;
Disrupts host cell _____
Uses host cell nutrients
Produces _____ products
Multiples in host cell and causes _____
Toxins
Toxigenicity
Toxemia
Toxin Production;
_____: Poisonous substances produced by microorganisms
Fever, cardiovascular problems, diarrhea, shock
_____: Ability of a microorganism to produce a toxin
_____: Presence of toxin in hosts’ blood
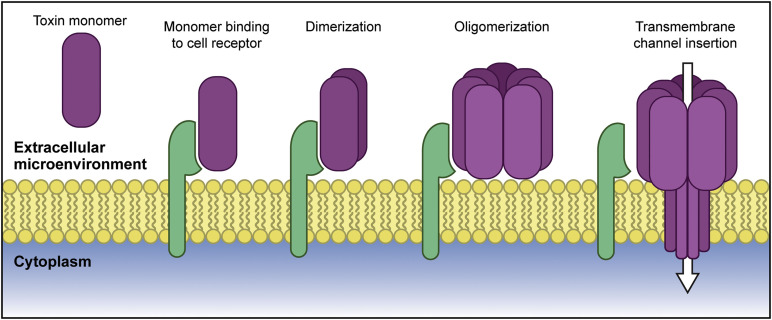
Exotoxins
_____: Proteins secreted and produced by bacteria
Soluble in body fluids; destroys host cells and inhibit metabolic functions
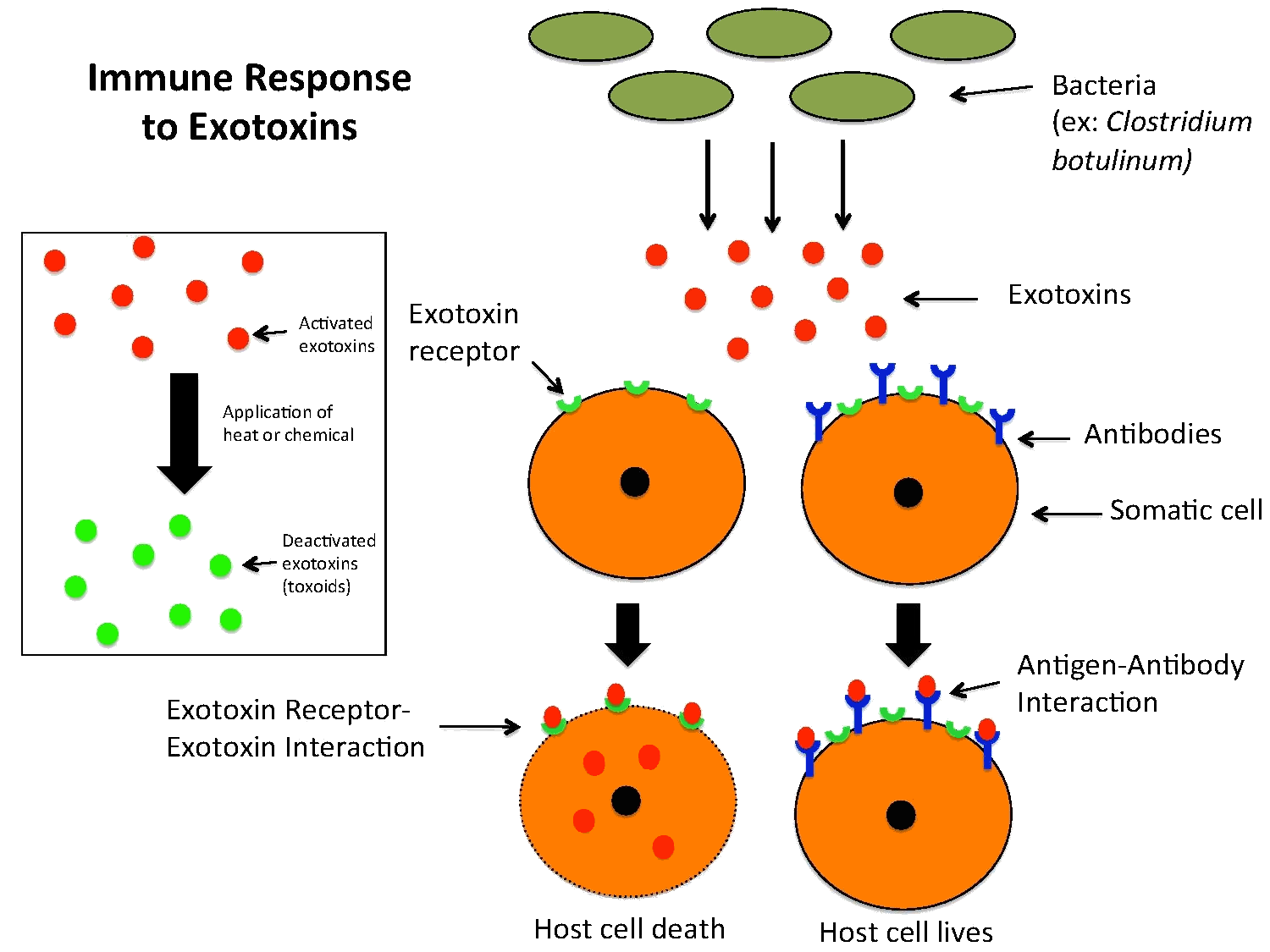
Enterotoxins
_____: Exotoxins whose activity affects the small intestine
Causes; massive fluid secretion into intestinal lumen, vomiting & diarrhea
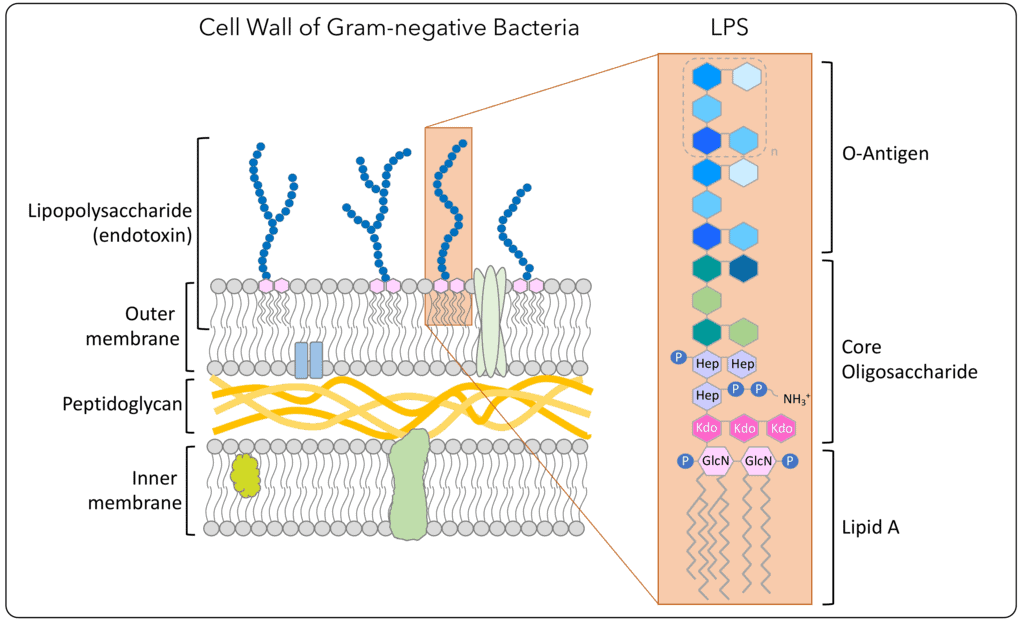
Endotoxins
_____: Present inside a bacterial cell and is released when the cell disintegrates.
Lipid A component of Gram-negative bacteria
Respiratory tract
GI tract
Genitourinary tract
Skin
Blood
What are some portals of exit?
Variolation
Obsolete medical procedure that involved intentionally infecting a healthy person with a mild form of smallpox virus to induce immunity against the disease
Vaccine
Term from Edward Jenner
Suspension of organisms or fractions of organisms that induce immunity
primary
secondary
Principles and Effects of Vaccination;
Provokes a _____ immune response
Produces a rapid, intense _____ response
Herd
_____ Immunity: Refers to immunity among most of the population
Attenuated
Live _____ Vaccines: Weakened pathogen to mimic actual infection.
Ex. MMR
Inactivated
_____ Killed Vaccines: Require repeated booster doses
Ex. rabies, influenza
Subunit
_____ Vaccines: Use antigenic fragments to stimulate an immune response
Recombinant vaccines
VLP Vaccines
Toxoids
Conjugated
_____ Vaccines: Contain bacterial capsule polysaccharides combined with proteins
Ex. H. influenzae
Nucleic
_____ Acid Vaccines: Injected naked DNA produces protein antigen encoded in the DNA
Ex. West Nile for horses
Hypersensitivity
_____ Reactions: An altered, enhanced immune reaction leading to pathological changes
Responses to antigens (allergens)
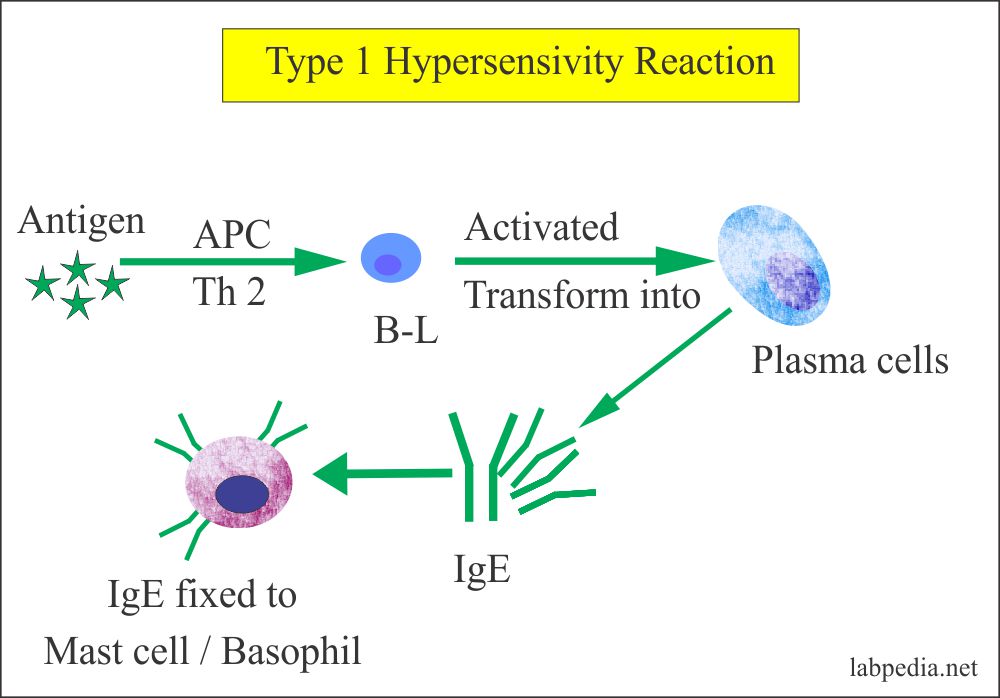
Anaphylactic
basophils
degranulation
Type 1 (_____) Reactions:
IgE attached to mast cells and _____
Antigen binds to two adjacent IgE
Mast cells and basophils undergo _____, which releases mediators;
Histamine
Leukotrienes
Prostaglandin
Systemic
Localized
Anaphylactic Reactions
_____ Anaphylaxis: May result in circulatory collapse and death
Epinephrine treatment
_____ Anaphylaxis: Hives, hay fever, asthma
Cytotoxin
Type 2 (_____) Reactions:
Involve IgG or IgM antibodies and complement
Complement activation causes cell lysis
ABO Blood system group
Antibodies form against certain carbohydrate antigens on RBC’s
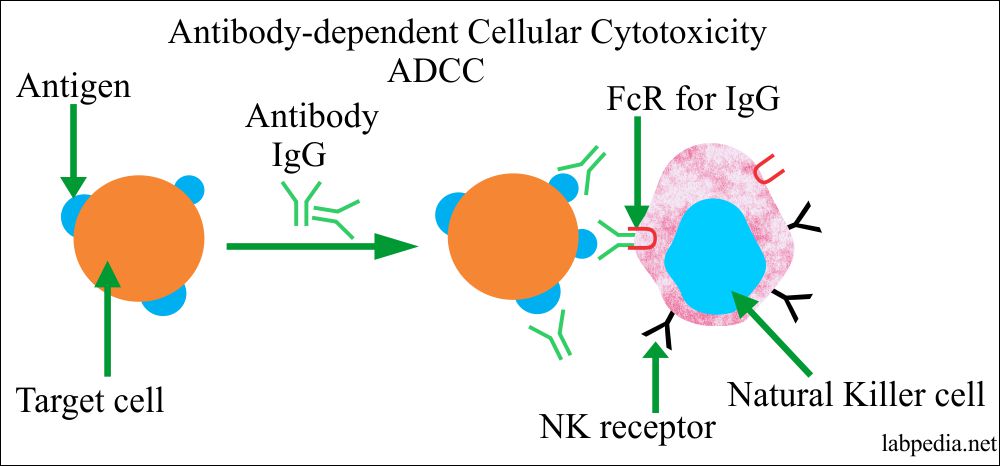
Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction
Cytotoxic Reactions
Rh blood group system: Rh+ given to Rh- recepient - stimulates anti-Rh antibodies
Immune
complexes
Type 3 (_____ Complex) Reactions:
IgG antibodies and antigens form immune _____ that lodge in basement membranes
Involves soluble antigens in serum
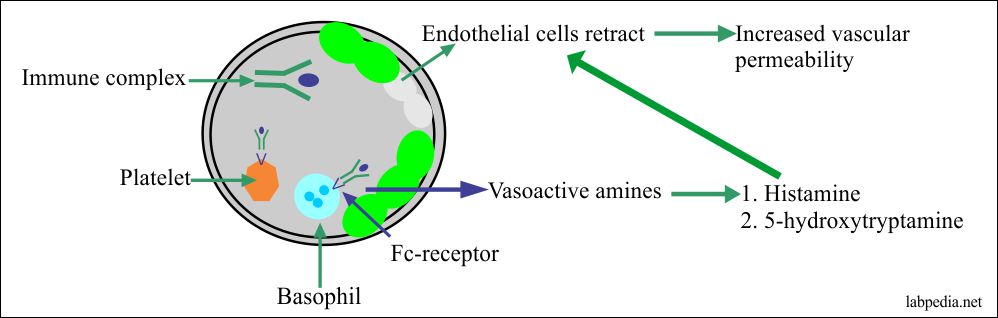
Cell
T
Type 4 (_____ Mediated) Reactions:
Delayed type sensitivities due to ___ cells
Cytokines attract macrophages and T cells
Initiate tissue damage
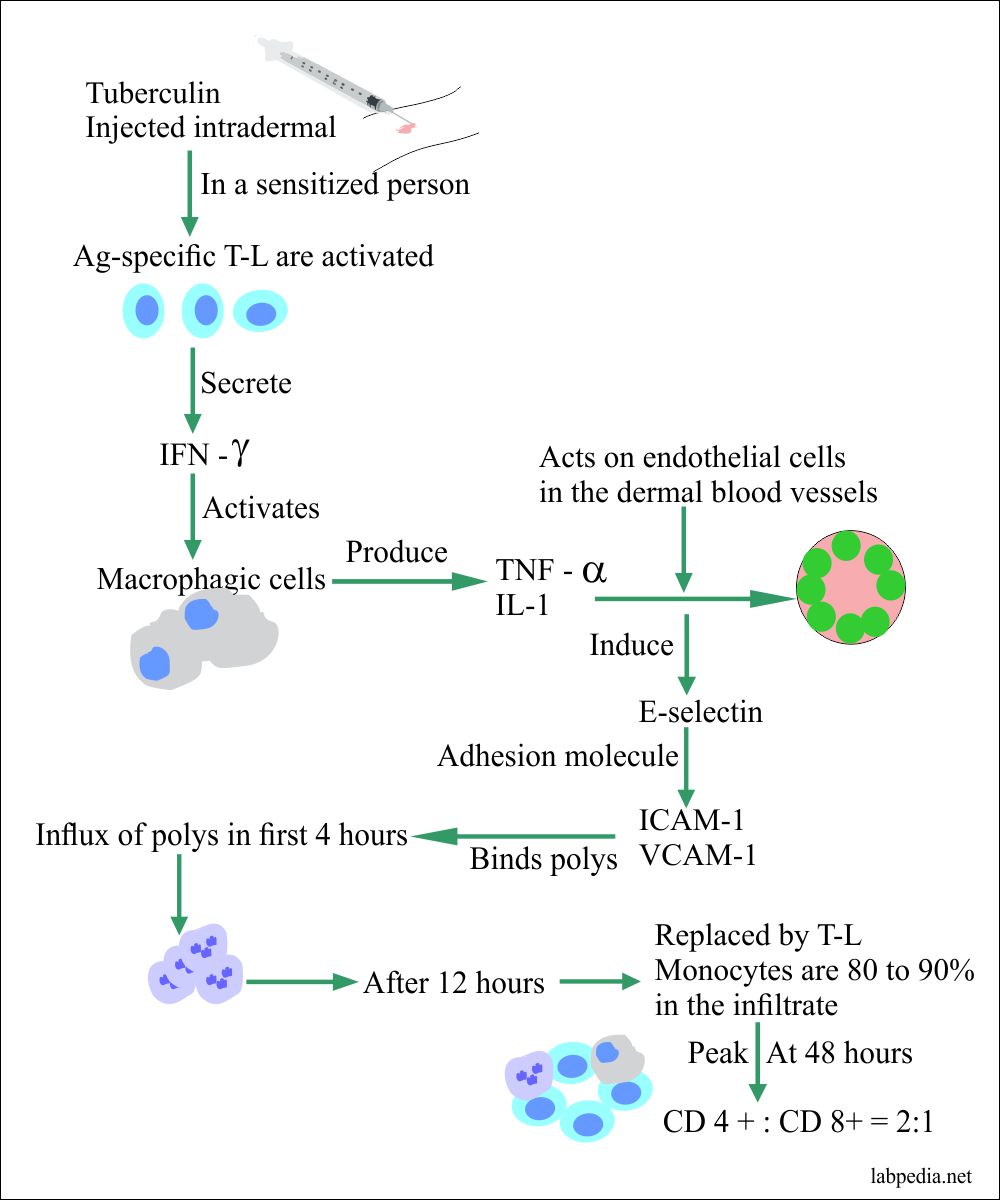
Autoimmunity
_____ is a loss of self-tolerance
leads to production of antibodies or a response by sensitized T cells against a person’s own tissues
Cytotoxic
Immune
Cell
Autoimmune Diseases
_____: Antibodies react with cell-surface antigens
Grave’s disease
_____ Complex: IgM, IgG, complement immune complexes deposit in tissues
Systemic lupus
_____-mediated: Mediated by T cells
Psoriasis, multiple sclerosis
Congenital
Acquired
Autoimmundeficiencies
_____: Due to missing or defective genes
_____: Develop during one’s life
Drugs, cancer, infections
HIV, AIDS
naked virus
What is another name for a nonenveloped virus?
Liquid medium only
Which of the followings cannot be used to culture viruses?
Tissue culture
Liquid medium only
Embryo
Animal host
HIV
Which of the following is an example of a persistent viral infection in humans?
cold sore
HIV/AIDS
shingles
influenza
oncogenic
Viruses capable of inducing tumors in animals are called
oncogenic viruses.
latent viruses.
oncolytic viruses.
lysogenic viruses.
oncolytic virus
A type of virus that selectively infects and kills cancer cells, leaving normal cells unharmed
Lysogenic virus
A type of virus that integrates its genome into the host cell's DNA, allowing for a dormant or latent infection.
respiratory tract
The easiest and MOST frequently traveled portal of entry for infectious microorganisms is the …?
parenteral route.
respiratory tract.
gastrointestinal tract.
skin.
interfere with a pathogenic bacterium's ability to adhere to and invade those cells
How would a drug that binds mannose on human cells affect a pathogenic bacterium?
breakd own fibrin
What is the action of bacterial kinases?
T coagulate fibrinogen
To hydrolyze hyaluronic acid
To break down fibrin
To break down collagen
endotoxins
The outer portion of gram-negative cell walls contain …?
exotoxins.
endotoxins.
siderophores.
exoenzymes.
secreted from bacteria
Where on bacteria are exotoxins located?